Ambient ionization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
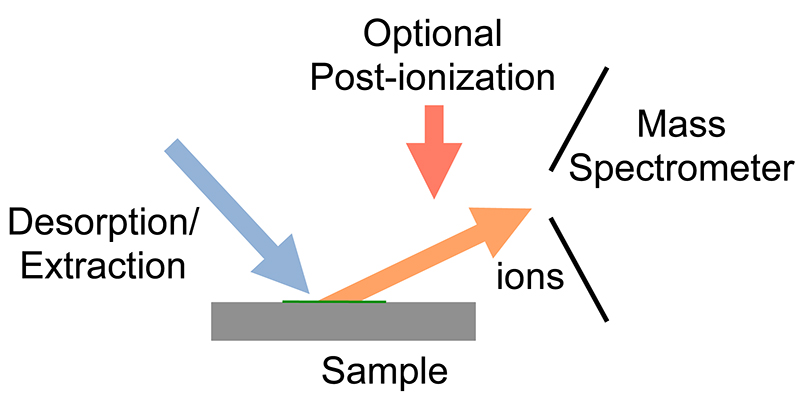 Ambient ionization is a form of
Ambient ionization is a form of
He^\ast + H2O)_\mathitH-> H2O)_H + OH^. + e^- .
The protonated water clusters can then protonate the sample molecules via
: H2O)_\mathitH + M -> + H + \mathitH2O .
For this ionization pathway, the gas-phase  One of the most used plasma-based techniques for ambient ionization is probably
One of the most used plasma-based techniques for ambient ionization is probably
 Laser-based ambient ionization is a two-step process in which a pulsed laser is used to desorb or ablate material from a sample and the plume of material interacts with an electrospray or plasma to create ions. Lasers with ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths and nanosecond to femtosecond pulse widths have been used. Although atmospheric pressure MALDI is performed under ambient conditions, it is not generally considered to be an ambient mass spectrometry technique.
Laser ablation was first coupled with mass spectrometry in the 1980s for the analysis of metals using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS). The laser ablates the sample material that is introduced into an ICP to create atomic ions.
Infrared laser desorption can be coupled with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization using laser desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (LD-APCI). For ambient ionization with a spray, the sample material is deposited on a target near the spray. The laser desorbs or ablates material from the sample that is ejected from the surface and into the spray, which can be an APCI spray with a
Laser-based ambient ionization is a two-step process in which a pulsed laser is used to desorb or ablate material from a sample and the plume of material interacts with an electrospray or plasma to create ions. Lasers with ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths and nanosecond to femtosecond pulse widths have been used. Although atmospheric pressure MALDI is performed under ambient conditions, it is not generally considered to be an ambient mass spectrometry technique.
Laser ablation was first coupled with mass spectrometry in the 1980s for the analysis of metals using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS). The laser ablates the sample material that is introduced into an ICP to create atomic ions.
Infrared laser desorption can be coupled with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization using laser desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (LD-APCI). For ambient ionization with a spray, the sample material is deposited on a target near the spray. The laser desorbs or ablates material from the sample that is ejected from the surface and into the spray, which can be an APCI spray with a
 Ambient ionization is a form of
Ambient ionization is a form of ionization
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged a ...
in which ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s are formed in an ion source
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines.
Electron ionization
Electro ...
outside the mass spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
without sample preparation or separation. Ions can be formed by extraction into charged electrospray droplets, thermally desorbed and ionized by chemical ionization
Chemical ionization (CI) is a soft ionization technique used in mass spectrometry. This was first introduced by Burnaby Munson and Frank H. Field in 1966. This technique is a branch of gaseous ion-molecule chemistry. Reagent gas molecules (often ...
, or laser desorbed
Desorption is the physical process where a previously adsorbed substance is released from a surface. This happens when a molecule gains enough energy to overcome the activation barrier of the bounding energy that keeps it in the surface.
There ...
or ablated
Ablation ( la, ablatio – removal) is removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosive processes or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, and include spacecraft material for a ...
and post-ionized before they enter the mass spectrometer.
Solid-liquid extraction
Solid-liquid extraction based ambient ionization is based on the use of a charged spray, for example electrospray to create a liquid film on the sample surface. Molecules on the surface are extracted into the solvent. The action of the primary droplets hitting the surface produces secondary droplets that are the source of ions for the mass spectrometer.Desorption electrospray ionization
Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is an ambient ionization technique that can be coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) for chemical analysis of samples at atmospheric conditions. Coupled ionization sources-MS systems are popular in chemical a ...
(DESI) is one of the original ambient ionization sources and uses an electrospray source to create charged droplets that are directed at a solid sample. The charged droplets pick up the sample through interaction with the surface and then form highly charged ions that can be sampled into a mass spectrometer.
Desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization
Desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization (DAPPI) is an ambient ionization technique for mass spectrometry that uses hot solvent vapor for desorption in conjunction with photoionization. Ambient Ionization techniques allow for direct analys ...
(DAPPI) is a solid-liquid extraction ambient ionization method that enables the direct analysis of samples deposited on surfaces by means of a jet of hot solvent vapour and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
light. The hot jet thermally desorbs the sample from a surface and the vaporized sample is ionized
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule ...
by a vacuum ultraviolet light and consequently sampled into a mass spectrometer.
Plasma-based techniques
Plasma-based ambient ionization is based on anelectrical discharge
An electric discharge is the release and transmission of electricity in an applied electric field through a medium such as a gas (ie., an outgoing flow of electric current through a non-metal medium).American Geophysical Union, National Research ...
in a flowing gas that produces metastable atoms and molecules and reactive ions. Heat is often used to assist in the desorption of volatile species from the sample. Ions are formed by chemical ionization
Chemical ionization (CI) is a soft ionization technique used in mass spectrometry. This was first introduced by Burnaby Munson and Frank H. Field in 1966. This technique is a branch of gaseous ion-molecule chemistry. Reagent gas molecules (often ...
in the gas phase.
One proposed mechanism involves Penning ionization of ambient water clusters in a helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
discharge:
:acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
of the protonated water clusters and the gas-phase basicity of the analyte molecule are of crucial importance. However, since especially smaller protonated water clusters with ''n'' = 1,2,3... exhibit very high gas-phase acidities, even compounds with a rather low gas-phase basicity are readily ionized by proton transfer, yielding +Hsup>+ quasimolecular ions.
Besides protonated water clusters, other positively charged reagent ions, such as NO+, O2+, NO2+ and CO2+, may be formed in the afterglow region. These additional reagent ions are capable of ionizing compounds via charge-transfer processes and, thus, offer alternative routes of ionization besides proton transfer, leading to a broader range of suitable analytes. Nevertheless, these ionization mechanisms may also lead to the formation of adducts and oxidation of the original analyte compounds.
Although most applications focus on the detection of positive ions, measurements in the negative mode are for most of the plasma-based ion sources also possible. In this case, reagent ions, such as O2–, can deprotonate the analyte molecules to give –Hsup>– quasimolecular ions, or form adducts with species such as NO3–, yielding +NO3sup>– ions. Measurements in the negative ion mode are especially favorable when the analyte molecules exhibit a high gas-phase acidity, as it is the case e.g. for carboxylic acids. One of the most used plasma-based techniques for ambient ionization is probably
One of the most used plasma-based techniques for ambient ionization is probably Direct analysis in real time In mass spectrometry, direct analysis in real time (DART) is an ion source that produces electronically or vibronically excited-state species from gases such as helium, argon, or nitrogen that ionize atmospheric molecules or dopant molecules. The ...
(DART), since it is commercially available. DART
Dart or DART may refer to:
* Dart, the equipment in the game of darts
Arts, entertainment and media
* Dart (comics), an Image Comics superhero
* Dart, a character from ''G.I. Joe''
* Dart, a ''Thomas & Friends'' railway engine character
* D ...
is an atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibar ...
ion source
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines.
Electron ionization
Electro ...
that operates by exposing the sample to a gas stream (typically helium or nitrogen) that contains long-lived electronically or excited neutral atoms
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
, vibronically excited molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioc ...
(or "metastables"). Excited state
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers t ...
s are formed in a glow discharge
A glow discharge is a plasma formed by the passage of electric current through a gas. It is often created by applying a voltage between two electrodes in a glass tube containing a low-pressure gas. When the voltage exceeds a value called the st ...
in a chamber through which the gas flows.
Laser assisted
 Laser-based ambient ionization is a two-step process in which a pulsed laser is used to desorb or ablate material from a sample and the plume of material interacts with an electrospray or plasma to create ions. Lasers with ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths and nanosecond to femtosecond pulse widths have been used. Although atmospheric pressure MALDI is performed under ambient conditions, it is not generally considered to be an ambient mass spectrometry technique.
Laser ablation was first coupled with mass spectrometry in the 1980s for the analysis of metals using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS). The laser ablates the sample material that is introduced into an ICP to create atomic ions.
Infrared laser desorption can be coupled with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization using laser desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (LD-APCI). For ambient ionization with a spray, the sample material is deposited on a target near the spray. The laser desorbs or ablates material from the sample that is ejected from the surface and into the spray, which can be an APCI spray with a
Laser-based ambient ionization is a two-step process in which a pulsed laser is used to desorb or ablate material from a sample and the plume of material interacts with an electrospray or plasma to create ions. Lasers with ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths and nanosecond to femtosecond pulse widths have been used. Although atmospheric pressure MALDI is performed under ambient conditions, it is not generally considered to be an ambient mass spectrometry technique.
Laser ablation was first coupled with mass spectrometry in the 1980s for the analysis of metals using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS). The laser ablates the sample material that is introduced into an ICP to create atomic ions.
Infrared laser desorption can be coupled with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization using laser desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (LD-APCI). For ambient ionization with a spray, the sample material is deposited on a target near the spray. The laser desorbs or ablates material from the sample that is ejected from the surface and into the spray, which can be an APCI spray with a corona discharge
A corona discharge is an electrical discharge caused by the ionization of a fluid such as air surrounding a conductor carrying a high voltage. It represents a local region where the air (or other fluid) has undergone electrical breakdown ...
or an electrospray. Ambient ionization by electrospray-assisted laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
desorption/ionization (ELDI) can be accomplished with ultraviolet and infrared lasers to the desorb material into the electrospray plume. Similar approaches to laser desorption/ablation into an electrospray are matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization Matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) was first introduced in 2006 as a novel ambient ionization technique which combines the benefits of electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization ( ...
(MALDESI), laser ablation electrospray ionization (LAESI), laser assisted desorption electrospray ionization (LADESI), laser desorption electrospray ionization (LDESI), laser ablation mass spectrometry (LAMS), and laser desorption spray post-ionization (LDSPI). The term laser electrospray mass spectrometry has been used to denote the use of a femtosecond laser for ablation. Laser ablation into an electrospray produces highly charged ions that are similar to those observed in direct electrospray.
An alternative ionization approach following laser desorption is a plasma. UV laser ablation can be combined with a flowing afterglow plasma for mass spectrometry imaging of small molecules. and IR desorption has been combined with a metastable ion source.
Two step non-laser
In two-step non-laser methods, the material removal from the sample and the ionization steps are separate. Probe electrospray ionization (PESI) is a modified version of conventional electrospray ionization in which the capillary for sample solution transferring is replaced by a solid needle with a sharp tip.PESI was first introduced by Kenzo Hiraoka et al. in 2007 — Compared with conventional electrospray ionization, high salt tolerance, direct sampling, and low sample consumption are found with PESI. PESI is not a continuous process; the needle for sampling and spraying is driven up and down at a frequency of 3–5 Hz.Vapor-ion, charge transfer reaction
The analytes are in the vapor phase. This includes breath, odors, VOCs, and other molecules with low volatility that, due to the constant improvements in sensitivity, are detectable in the vapor phase despite of their low vapor pressure. Analyte ions are produced via gas-phase chemical reactions, where charging agents collide with the analyte molecules and transfer their charge. In Secondary Electro-Spray Ionization (SESI), a nano-electrospray operated at high temperature produces nanodroplets that evaporate very rapidly to produce ions and protonated water clusters that ionize the vapors of interest. SESI is commonly used for the analysis of trace concentrations of vapors being able to detect low volatility species in the gas phase with molecular masses of up to 700Da.Table of techniques
In the table below, ambient ionization techniques are classified in the categories "extraction" (a solid or liquid extraction processes dynamically followed by spray or chemical ionization), "plasma" (thermal or chemical desorption with chemical ionization), "two step" (desorption or ablation followed by ionization), "laser" (laser desorption or ablation followed by ionization), "acoustic" (acoustic desorption followed by ionization), multimode (involving two of the above modes), other (techniques that do not fit into the other categories). : (*) Not an acronym.Table of commercially available ambient ionization sources
References
{{Mass spectrometry Mass spectrometry Ion source