Amazigh language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight, are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related but mostly mutually unintelligible languages spoken by
 Berber languages are primarily oral languages without a major written component. Historically, they were written with the Libyco-Berber script. Early uses of the script have been found on
Berber languages are primarily oral languages without a major written component. Historically, they were written with the Libyco-Berber script. Early uses of the script have been found on
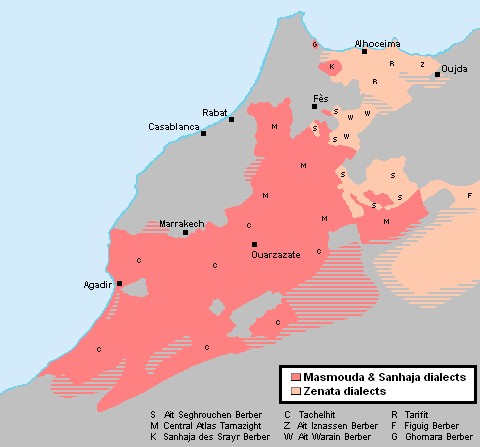 Morocco is the country with the greatest number of speakers of Berber languages. As of 2022, Ethnologue estimates there to be 13.8 million speakers of Berber languages in Morocco, based on figures from 2016 and 2017.
In 1960, the first census after Moroccan independence was held. It claimed that 32 percent of Moroccans spoke a Berber language, including bi-, tri- and quadrilingual people. The 2004 census found that 3,894,805 Moroccans over five years of age spoke Tashelhit, 2,343,937 spoke Central Atlas Tamazight, and 1,270,986 spoke Tarifit, representing 14.6%, 8.8%, and 4.8% respectively of the surveyed population, or roughly 28.2% of the surveyed population combined. The 2014 census found that 14.1% of the population spoke Tashelhit, 7.9% spoke Central Atlas Tamazight, and 4% spoke Tarifit, or about 26% of the population combined.
The 2024 census found that 14.2% of the population spoke Tashelhit, 7.4% spoke Central Atlas Tamazight, and 3.2% spoke Tarifit, which represents 24.8% of the population.
These estimates, as well as the estimates from various academic sources, are summarized as follows:
Morocco is the country with the greatest number of speakers of Berber languages. As of 2022, Ethnologue estimates there to be 13.8 million speakers of Berber languages in Morocco, based on figures from 2016 and 2017.
In 1960, the first census after Moroccan independence was held. It claimed that 32 percent of Moroccans spoke a Berber language, including bi-, tri- and quadrilingual people. The 2004 census found that 3,894,805 Moroccans over five years of age spoke Tashelhit, 2,343,937 spoke Central Atlas Tamazight, and 1,270,986 spoke Tarifit, representing 14.6%, 8.8%, and 4.8% respectively of the surveyed population, or roughly 28.2% of the surveyed population combined. The 2014 census found that 14.1% of the population spoke Tashelhit, 7.9% spoke Central Atlas Tamazight, and 4% spoke Tarifit, or about 26% of the population combined.
The 2024 census found that 14.2% of the population spoke Tashelhit, 7.4% spoke Central Atlas Tamazight, and 3.2% spoke Tarifit, which represents 24.8% of the population.
These estimates, as well as the estimates from various academic sources, are summarized as follows:
Population estimates are summarized as follows:
Tamazight-English Dictionary
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110624061513/http://www.llmap.org/languages/tzm.html Map of Berber language from the LL-Map Project(archived 24 June 2011)
The Berber Language Profile
(archived 2 October 2010)
Etymology of "Berber"
Etymology of "Amazigh"
Early Christian history of Berbers
(archived 26 August 2017)
Imyura Kabyle site about literature
(archived 12 August 2013)
Amawal: The online open source Berber dictionary
{{DEFAULTSORT:Berber Languages Afroasiatic languages Maghreb Languages of Algeria Languages of Morocco Languages of Mali Languages of Niger Languages of Mauritania Languages of Tunisia Languages of Gibraltar Languages of Sicily Languages of Western Sahara
Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
communities, who are indigenous to North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
.Hayward, Richard J., chapter ''Afroasiatic'' in Heine, Bernd & Nurse, Derek, editors, ''African Languages: An Introduction'' Cambridge 2000. . The languages are primarily spoken and not typically written. Historically, they have been written with the ancient Libyco-Berber script, which now exists in the form of Tifinagh. Today, they may also be written in the Berber Latin alphabet
The Berber Latin alphabet () is the version of the Latin alphabet used to write the Berber languages. It was adopted in the 19th century, using a variety of letters.
History
The Berber languages were originally written using the ancient ''Libyco- ...
or the Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widel ...
, with Latin being the most pervasive.
The Berber languages have a similar level of variety to the Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, although they are sometimes referred to as a single collective language, often as "Berber", "Tamazight", or "Amazigh". The languages, with a few exceptions, form a dialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of Variety (linguistics), language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulat ...
. There is a debate as to how to best sub-categorize languages within the Berber branch. Berber languages typically follow verb–subject–object word order
In linguistic typology, a verb–subject–object (VSO) language has its most typical sentences arrange their elements in that order, as in ''Ate Sam apples'' (Sam ate apples). VSO is the third-most common word order among the world's languages, ...
. Their phonological inventories are diverse.
Millions of people in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
and Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
natively speak a Berber language, as do smaller populations of Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
, Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, northern Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, western and northern Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, northern Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 ...
and Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
and the Siwa Oasis
The Siwa Oasis ( ) is an urban oasis in Egypt. It is situated between the Qattara Depression and the Great Sand Sea in the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert, east of the Egypt–Libya border and from the Egyptian capital city of Cairo. I ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. There are also probably a few million speakers of Berber languages in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
. Tashlhiyt, Kabyle, Central Atlas Tamazight, Tarifit, and Shawiya are some of the most commonly spoken Berber languages. Exact numbers are impossible to ascertain as there are few modern North African censuses that include questions on language use, and what censuses do exist have known flaws.
Following independence in the 20th century, the Berber languages have been suppressed and suffered from low prestige
Prestige may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Films
*Prestige (film), ''Prestige'' (film), a 1932 American film directed by Tay Garnett: woman travels to French Indochina to meet up with husband
*The Prestige (film), ''The Prestige'' (fi ...
in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
. Recognition of the Berber languages has been growing in the 21st century, with Morocco and Algeria adding Tamazight as an official language to their constitutions in 2011 and 2016 respectively.
Most Berber languages have a high percentage of borrowing and influence from the Arabic language
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, as well as from other languages. For example, Arabic loanwords represent 35% to 46% of the total vocabulary of the Kabyle language and represent 44.9% of the total vocabulary of Tarifit. Almost all Berber languages took from Arabic the pharyngeal fricatives /ʕ/ and /ħ/, the (nongeminated) uvular stop /q/, and the voiceless pharyngealized consonant /ṣ/. Unlike the Chadic,
Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2 ...
, and Omotic
The Omotic languages are a group of languages spoken in southwestern Ethiopia, in the Omo River region and southeastern Sudan in Blue Nile State. The Geʽez script is used to write some of the Omotic languages, the Latin script for some others. T ...
languages of the Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of th ...
phylum, Berber languages are not tonal languages.
Terminology
"Tamazight" and "Berber languages" are often used interchangeably. However, "Tamazight" is sometimes used to refer to a specific subset of Berber languages, such as Central Tashlhiyt. "Tamazight" can also be used to refer to Standard Moroccan Tamazight or Standard Algerian Tamazight, as in the Moroccan and Algerian constitutions respectively. In Morocco, besides referring to all Berber languages or to Standard Moroccan Tamazight, "Tamazight" is often used in contrast to Tashelhit and Tarifit to refer to Central Atlas Tamazight. The use of ''Berber'' has been the subject of debate due to its historical background as anexonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
and present equivalence with the Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
word for "barbarian." One group, the Linguasphere Observatory
The Linguasphere Observatory (or the Observatoire, based on its original French and legal title: ''Observatoire Linguistique'') is a non-profit transnational research network, devoted (alongside related programs) to the gathering, study, classifica ...
, has attempted to introduce the neologism
In linguistics, a neologism (; also known as a coinage) is any newly formed word, term, or phrase that has achieved popular or institutional recognition and is becoming accepted into mainstream language. Most definitively, a word can be considered ...
"Tamazic languages" to refer to the Berber languages. Amazigh people typically use "Tamazight" when speaking English. Historically, Berbers did not refer to themselves as Berbers/Amazigh but had their own terms to refer to themselves. For example, the Kabyles use the term "Leqbayel" to refer to their own people, while the Chaouis identified themselves as "Ishawiyen" instead of Berber/Amazigh.
Origin
Since modern Berber languages are relatively homogeneous, the date of the Proto-Berber language from which the modern group is derived was probably comparatively recent, comparable to the age of the Germanic or Romance subfamilies of the Indo-European family. In contrast, the split of the group from the other Afroasiatic sub-phyla is much earlier, and is therefore sometimes associated with the localMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
Capsian culture. A number of extinct populations are believed to have spoken Afroasiatic languages of the Berber branch. According to Peter Behrens and Marianne Bechaus-Gerst, linguistic evidence suggests that the peoples of the C-Group culture in present-day southern Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and northern Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
spoke Berber languages. The Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributari ...
Nobiin language today contains a number of key loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
s related to pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The anim ...
that are of Berber origin, including the terms for sheep and water/Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
. This in turn suggests that the C-Group population—which, along with the Kerma culture
The Kingdom of Kerma or the Kerma culture was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BC to 1500 BC in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based in the southern part of Nubia, or "Upper Nubia" (in parts of ...
, inhabited the Nile valley immediately before the arrival of the first Nubian speakers—spoke Afroasiatic languages.
Orthography
 Berber languages are primarily oral languages without a major written component. Historically, they were written with the Libyco-Berber script. Early uses of the script have been found on
Berber languages are primarily oral languages without a major written component. Historically, they were written with the Libyco-Berber script. Early uses of the script have been found on rock art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type al ...
and in various sepulchres; the oldest known variations of the script dates to inscriptions in Dugga from 600 BC. Usage of this script, in the form of Tifinagh, has continued into the present day among the Tuareg people
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; Endonym and exonym, endonym, depending on Tuareg languages#Subclassification, variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berbers, Berber ethnic group, ...
. Following the spread of Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, some Berber scholars also utilized the Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widel ...
. The Berber Latin alphabet
The Berber Latin alphabet () is the version of the Latin alphabet used to write the Berber languages. It was adopted in the 19th century, using a variety of letters.
History
The Berber languages were originally written using the ancient ''Libyco- ...
was developed following the introduction of the Latin script in the nineteenth century by the West. The nineteenth century also saw the development of Neo-Tifinagh, an adaptation of Tuareg Tifinagh for use with other Berber languages.
There are now three writing systems in use for Berber languages: Tifinagh, the Arabic script, and the Berber Latin alphabet
The Berber Latin alphabet () is the version of the Latin alphabet used to write the Berber languages. It was adopted in the 19th century, using a variety of letters.
History
The Berber languages were originally written using the ancient ''Libyco- ...
, with the Latin alphabet being the most widely used today.
Subclassification
With the exception of Zenaga, Tetserret, and Tuareg, the Berber languages form adialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of Variety (linguistics), language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulat ...
. Different linguists take different approaches towards drawing boundaries between languages in this continuum. Maarten Kossmann notes that it is difficult to apply the classic tree model
In historical linguistics, the tree model (also Stammbaum, genetic, or cladistic model) is a model of the evolution of languages analogous to the concept of a family tree, particularly a phylogenetic tree in the biological evolution of species. ...
of historical linguistics towards the Berber languages:he Berber language familys continuous history of convergence and differentiation along new lines makes any definition of branches arbitrary. Moreover, mutual intelligibility and mutual influence render notions such as "split" or "branching" rather difficult to apply except, maybe, in the case of Zenaga and Tuareg.Kossmann roughly groups the Berber languages into seven blocks: * Berber **
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
(Zenaga, Tetserret)
** Tuareg
** Western Moroccan
*** southwestern and central Moroccan languages (Tashelhiyt, most of Central Atlas Tamazight)
*** northwestern Moroccan languages (Ghomara, Senhadja de Sraïr)
** Zenatic (a dialect continuum stretching from eastern Morocco to the Siwa Oasis
The Siwa Oasis ( ) is an urban oasis in Egypt. It is situated between the Qattara Depression and the Great Sand Sea in the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert, east of the Egypt–Libya border and from the Egyptian capital city of Cairo. I ...
)
** Kabyle
** Ghadames
** Awjila
The Zenatic block is typically divided into the Zenati and Eastern Berber branches, due to the marked difference in features at each end of the continuum. Otherwise, subclassifications by different linguists typically combine various blocks into different branches. Western Moroccan languages, Zenati languages, Kabyle, and Ghadames may be grouped under Northern Berber; Awjila is often included as an Eastern Berber language alongside Siwa, Sokna, and El Foqaha. These approaches divide the Berber languages into Northern, Southern (Tuareg), Eastern, and Western varieties.
Population
The vast majority of speakers of Berber languages are concentrated in Morocco and Algeria. The exact population of speakers has been historically difficult to ascertain due to lack of official recognition.Morocco
Algeria
Algeria is the country with the second greatest number of speakers of Berber languages. In 1906, the total population speaking Berber languages in Algeria, excluding the thinly populated Sahara region, was estimated at 1,305,730 out of 4,447,149, or 29%. Secondary sources disagree on the percentage of self-declared native Berber speakers in the 1966 census, the last Algerian census containing a question about the mother tongue. Some give 17.9% while other report 19%. Kabyle speakers account for the vast majority of speakers of Berber languages in Algeria. Shawiya is the second most commonly spoken Berber language in Algeria. Other Berber languages spoken in Algeria include: Shenwa, with 76,300 speakers; Tashelhit, with 6,000 speakers; Ouargli, with 20,000 speakers; Tamahaq, with 71,400 speakers; Tugurt, with 8,100 speakers; Tidikelt, with 1,000 speakers; Gurara, with 11,000 speakers; and Mozabite, with 150,000 speakers.Population estimates are summarized as follows:
Other countries
As of 1998, there were an estimated 450,000 Tawellemmet speakers, 250,000 Air Tamajeq speakers, and 20,000 Tamahaq speakers inNiger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
.
As of 2018 and 2014 respectively, there were an estimated 420,000 speakers of Tawellemmet and 378,000 of Tamasheq in Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
.
As of 2022, based on figures from 2020, Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
estimates there to be 285,890 speakers of Berber languages in Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
: 247,000 speakers of Nafusi, 22,800 speakers of Tamahaq, 13,400 speakers of Ghadamés, and 2,690 speakers of Awjila. The number of Siwi speakers in Libya is listed as negligible, and the last Sokna speaker is thought to have died in the 1950s.
There are an estimated 50,000 Djerbi speakers in Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, based on figures from 2004. Sened is likely extinct, with the last speaker having died in the 1970s. Ghadamés, though not indigenous to Tunisia, is estimated to have 3,100 speakers throughout the country. Chenini is one of the rare remaining Berber-speaking villages in Tunisia.
There are an estimated 20,000 Siwi speakers in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, based on figures from 2013.
As of 2018 and 2017 respectively, there were an estimated 200 speakers of Zenaga and 117,000 of Tamasheq in Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
.
As of 2009, there were an estimated 122,000 Tamasheq speakers in Burkina Faso.
There are an estimated 1.5 million speakers of various Berber languages in France. A small number of Tawellemmet speakers live in Nigeria.
In total, there are an estimated 3.6 million speakers of Berber languages in countries outside of Morocco and Algeria, summarized as follows:
Status
After independence, all theMaghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
countries to varying degrees pursued a policy of Arabisation, aimed partly at displacing French from its colonial position as the dominant language of education and literacy. Under this policy the use of the Berber languages was suppressed or even banned. This state of affairs has been contested by Berbers in Morocco and Algeria—especially Kabylie
Kabylia or Kabylie (; in Kabyle language, Kabyle: Tamurt n leqbayel; in Tifinagh: ⵜⴰⵎⵓⵔⵜ ⵏ ⵍⴻⵇⴱⴰⵢⴻⵍ; ), meaning "Land of the Tribes" is a mountainous coastal region in northern Algeria and the homeland of the Kaby ...
—and was addressed in both countries by affording the language official status and introducing it in some schools.
Morocco
After gaining independence from France in 1956, Morocco began a period of Arabisation through 1981, with primary and secondary school education gradually being changed to Arabic instruction, and with the aim of having administration done in Arabic, rather than French. During this time, there were riots amongst the Amazigh population, which called for the inclusion of Tamazight as an official language. The 2000 Charter for Education Reform marked a change in policy, with its statement of "openness to Tamazight." Planning for a public Tamazight-language TV network began in 2006; in 2010, the Moroccan government launched Tamazight TV. On July 29, 2011, Tamazight was added as an official language to the Moroccan constitution.Algeria
After gaining independence from France in 1962, Algeria committed to a policy of Arabisation, which, after the imposition of the Circular of July 1976, encompassed the spheres of education, public administration, public signage, print publication, and the judiciary. While primarily directed towards the erasure of French in Algerian society, these policies also targeted Berber languages, leading to dissatisfaction and unrest amongst speakers of Berber languages, who made up about one quarter of the population. After the 1994-1995 general school boycott in Kabylia, Tamazight was recognized for the first time as a national language. In 2002, following the riots of the Black Spring, Tamazight was recognized for the second time as anational language
'' ''
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection— de facto or de jure—with a nation. The term is applied quite differently in various contexts. One or more languages spoken as first languag ...
, though not as an official
An official is someone who holds an office (function or Mandate (politics), mandate, regardless of whether it carries an actual Office, working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority (eithe ...
one. This was done on April 8, 2003.
Tamazight has been taught for three hours a week through the first three years of Algerian middle schools since 2005.
On January 5, 2016, it was announced that Tamazight had been added as a national and official language in a draft amendment to the Algerian constitution; it was added to the constitution as a national and official language on February 7, 2016.
Libya
Although regional councils in Libya's Nafusa Mountains affiliated with theNational Transitional Council
The National Transitional Council (NTC) was a transitional government established in the 2011 Libyan civil war. After rebel forces overthrew the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya of Muammar Gaddafi in August 2011, the NTC governed Libya for a further ...
reportedly use the Berber language of Nafusi and have called for it to be granted co-official status with Arabic in a prospective new constitution, it does not have official status in Libya as in Morocco and Algeria. As areas of Libya south and west of Tripoli such as the Nafusa Mountains were taken from the control of Gaddafi government forces in early summer 2011, Berber workshops and exhibitions sprang up to share and spread the Berber culture and language.
Other countries
In Mali and Niger, someTuareg languages
Tuareg (), also known as ''Tamasheq'' (), ''Tamajaq'' or ''Tamahaq'' (Tifinagh: ), is a group of closely related Berber languages, Berber Linguistic variety, varieties. They are spoken by the Tuareg people, Tuareg Berbers in large parts of Mali, ...
have been recognized as national languages and have been part of school curriculums since the 1960s.
Phonology
Notation
In linguistics, the phonology of Berber languages is written with theInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ...
, with the following exceptions:
Consonants
The influence of Arabic, the process of spirantization, and the absence of labialization have caused the consonant systems of Berber languages to differ significantly by region. Berber languages found north of, and in the northern half of, the Sahara have greater influence from Arabic, including that of loaned phonemes, than those in more southern regions, like Tuareg. Most Berber languages in northern regions have additionally undergone spirantization, in which historical short stops have changed into fricatives. Northern Berber languages (which is a subset of but not identical to Berber languages in geographically northern regions) commonly have labialized velars and uvulars, unlike other Berber languages.Two languages that illustrate the resulting range in consonant inventory across Berber languages are Ahaggar Tuareg and Kabyle; Kabyle has two more places of articulation and three more manners of articulation than Ahaggar Tuareg. There is still, however, common consonant features observed across Berber languages. Almost all Berber languages have bilabial, dental, palatal, velar, uvular, pharyngeal, and laryngeal consonants, and almost all consonants have a long counterpart. All Berber languages, as is common in Afroasiatic languages, have pharyngealized consonants and phonemicgemination
In phonetics and phonology, gemination (; from Latin 'doubling', itself from '' gemini'' 'twins'), or consonant lengthening, is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from ...
. The consonants which may undergo gemination, and the positions in a word where gemination may occur, differ by language. They have also been observed to have tense and lax consonants, although the status of tense consonants has been the subject of "considerable discussion" by linguists. Three (Kabyle, Tarifit and Shawiya) of the most spoken five Tamazight languages have the interdental consonants and which are considered rare cross-linguistically.
Vowels
The vowel systems of Berber languages also vary widely, with inventories ranging from three phonemic vowels in most Northern Berber languages, to seven in some Eastern Berber and Tuareg languages. For example, Taselhiyt has the vowels /i/, /a/, and /u/, while Ayer Tuareg has the vowels /i/, / ə/, /u/, /e/, / ɐ/, /o/, and /a/. Contrastivevowel length
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived or actual length (phonetics), duration of a vowel sound when pronounced. Vowels perceived as shorter are often called short vowels and those perceived as longer called long vowels.
On one hand, many ...
is rare in Berber languages. Tuareg languages had previously been reported to have contrastive vowel length, but this is no longer the leading analysis. A complex feature of Berber vowel systems is the role of central vowel
A central vowel, formerly also known as a mixed vowel, is any in a class of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a central vowel is that the tongue is positioned approximately halfway between a front vowel ...
s, which vary in occurrence and function across languages; there is a debate as to whether schwa is a proper phoneme of Northern Berber languages.
Suprasegmentals
Most Berber languages: * allow for any combination of CC consonant clusters. * have no lexical tones. * either have no lexical stress (Northern Berber languages) or have grammatically significant lexical stress.Phonetic correspondences
Phonetic correspondences between Berber languages are fairly regular. Some examples, of varying importance and regularity, include 'g/ž/y'' 'k/š'' 'l/ř/r'' 'l/ž, ll/ddž'' rill/ vocalized r 'šš/ttš'' 'ss/ttš'' 'w/g/b'' 'q''/''ɣ'' 'h''/Ø and 's-š-ž/h'' Words in various Berber languages are shown to demonstrate these phonetic correspondences as follows:Grammar
Berber languages characteristically make frequent use of apophony in the form of ablaut. Berber apophony has been historically analyzed as functioning similarly to theSemitic root
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or " radicals" (hence the term consonantal root). Such abstract consonantal roots are used in the formation of actual words by adding the vowel ...
, but this analysis has fallen out of favor due to the lexical significance of vowels in Berber languages, as opposed to their primarily grammatical significance in Semitic languages.
The lexical categories of all Berber languages are noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
s, verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic f ...
s, pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but so ...
s, adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by ...
s, and prepositions. With the exception of a handful of Arabic loanwords in most languages, Berber languages do not have proper adjectives. In Northern and Eastern Berber languages, adjectives are a subcategory of nouns; in Tuareg, relative clauses and stative verb forms are used to modify nouns instead.
The gender, number, and case of nouns, as well as the gender, number, and person of verbs, are typically distinguished through affixes. Arguments are described with word order and clitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic ( , backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a ...
s. When sentences have a verb, they essentially follow verb–subject–object word order
In linguistic typology, a verb–subject–object (VSO) language has its most typical sentences arrange their elements in that order, as in ''Ate Sam apples'' (Sam ate apples). VSO is the third-most common word order among the world's languages, ...
, although some linguists believe alternate descriptors would better categorize certain languages, such as Taqbaylit.
Pronouns
Berber languages have both independent and dependent pronouns, both of which distinguish between person and number. Gender is also typically distinguished in the second and third person, and sometimes in first person plural. Linguist Maarten Kossmann divides pronouns in Berber languages into three morphological groups: # Independent pronouns # Direct object clitics # Indirect object clitics; prepositional suffixes; adnominal suffixes When clitics precede or follow a verb, they are almost always ordered with the indirect object first, direct object second, and andative-venitive deictic clitic last. An example in Tarifit is shown as follows: The allowed positioning of different kinds of clitics varies by language.Nouns
Nouns are distinguished bygender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
, number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
, and case in most Berber languages, with gender being feminine or masculine, number being singular or plural, and case being in the construct or free state. Some Arabic borrowings in Northern and Eastern Berber languages do not accept these affixes; they instead retain the Arabic article regardless of case, and follow Arabic patterns to express number and gender.
Gender can be feminine or masculine, and can be lexically determined, or can be used to distinguish qualities of the noun. For humans and "higher" animals (such as mammals and large birds), gender distinguishes sex, whereas for objects and "lesser" animals (such as insects and lizards), it distinguishes size. For some nouns, often fruits and vegetables, gender can also distinguish the specificity of the noun. The ways in which gender is used to distinguish nouns is shown in as follows, with examples from Figuig:
An example of nouns with lexically determined gender are the feminine ''t-lussi'' ("butter") and masculine ''a-ɣi'' ("buttermilk") in Figuig. Mass nouns have lexically determined gender across Berber languages.
Most Berber languages have two cases, which distinguish the construct state from the free state. The construct state is also called the "construct case, "relative case," "annexed state" (''état d'annexion'')'','' or the "nominative case"; the free state (''état libre'') is also called the "direct case" or "accusative case." When present, case is always expressed through nominal prefixes and initial-vowel reduction. The use of the marked nominative system and constructions similar to Split-S alignment varies by language. Eastern Berber languages do not have case.
Number can be singular or plural, which is marked with prefixation, suffixation, and sometimes apophony. Nouns usually are made plural by one of either suffixation or apophony, with prefixation applied independently. Specifics vary by language, but prefixation typically changes singular ''a-'' and ''ta-'' to plural ''i-'' and ''ti-'' respectively. The number of mass nouns are lexically determined. For example, in multiple Berber languages, such as Figuig, ''a-ɣi'' ("buttermilk") is singular while ''am-an'' ("water") is plural.
Nouns or pronouns—optionally extended with genitival pronominal affixes, demonstrative clitics, or pre-nominal elements, and then further modified by numerals, adjectives, possessive phrases, or relative clauses—can be built into noun phrases. Possessive phrases in noun phrases must have a genitive proposition.
There are a limited number of pre-nominal elements, which function similarly to pronoun syntactic heads of the noun phrase, and which can be categorized into three types as follows:
* The pluralizer ''id-''
* The four pre-nominal elements roughly meaning "son(s) of" and "daughter(s) of", which commonly denote group identity and origin
* Pre-nominal elements which expand on the meaning of the noun
Verbs
Verb bases are formed by stems that are optionally extended by prefixes, with mood, aspect, and negation applied with a vocalic scheme. This form can then be conjugated with affixes to agree with person, number, and gender, which produces a word. Different linguists analyze and label aspects in the Berber languages vary differently. Kossman roughly summarizes the basic stems which denote aspect as follows: *Aorist
Aorist ( ; abbreviated ) verb forms usually express perfective aspect and refer to past events, similar to a preterite. Ancient Greek grammar had the aorist form, and the grammars of other Indo-European languages and languages influenced by the ...
, also called aoriste, without a preceding particle:
** imperative
** unmarked (taking aspect from preceding verb)
* Aorist, with the preceding article ''ad:''
** irrealis (adhortative, future)
* Preterite, or accompli:
** past tense, in dynamic use
** states (such as "to want, to know"), in stative use
* Intensive Aorist, also called habitative or inaccompli:
** dynamic present
** habitative and iterative
** habitative imperative
** negation of any imperative
Different languages may have more stems and aspects, or may distinguish within the above categories. Stem formation can be very complex, with Tuareg by some measures having over two hundred identified conjugation subtypes.
The aspectual stems of some classes of verbs in various Berber languages are shown as follows:
Verb phrases are built with verb morphology, pronominal and deictic clitics, pre-verbal particles, and auxiliary elements. The pre-verbal particles are ''ad'', ''wər,'' and their variants, which correspond to the meanings of "non-realized" and "negative" respectively.
Numerals
Many Berber languages have lost use of their original numerals from three onwards due to the influence of Arabic; Tarifit has lost all except one. Languages that may retain all their original numerals include Tashelhiyt, Tuareg, Ghadames, Ouargla, and Zenaga. Original Berber numerals agree in gender with the noun they describe, whereas the borrowed Arabic forms do not. The numerals 1–10 in Tashelhiyt and Mali Tuareg are as follows:Sentence structure
Sentences in Berber languages can be divided into verbal and non-verbal sentences. The topic, which has a unique intonation in the sentence, precedes all other arguments in both types. Verbal sentences have a finite verb, and are commonly understood to followverb–subject–object word order
In linguistic typology, a verb–subject–object (VSO) language has its most typical sentences arrange their elements in that order, as in ''Ate Sam apples'' (Sam ate apples). VSO is the third-most common word order among the world's languages, ...
(VSO). Some linguists have proposed opposing analyses of the word order patterns in Berber languages, and there has been some support for characterizing Taqbaylit as discourse-configurational.
Existential, attributive, and locational sentences in most Berber languages are expressed with non-verbal sentences, which have no finite verb. In these sentences, the predicate follows the noun, with the predicative particle ''d'' sometimes in between. Two examples, one without and one with a subject, are given from Kabyle as follows:
Non-verbal sentences may use the verb meaning "to be," which exists in all Berber languages. An example from Tarifit is given as follows:
Lexicon
Above all in the area of basic lexicon, the Berber languages are very similar. However, the household-related vocabulary in sedentary tribes is especially different from the one found in nomadic ones: whereas Tahaggart has only two or three designations for species of palm tree, other languages may have as many as 200 similar words. In contrast, Tahaggart has a rich vocabulary for the description of camels. Some loanwords in the Berber languages can be traced to pre-Roman times. The Berber words ''te-ḇăyne'' "date" and ''a-sḇan'' "loose woody tissue around the palm tree stem" originate fromAncient Egyptian
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, likely due to the introduction of date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
cultivation into North Africa from Egypt. Around a dozen Berber words are probable Phoenician-Punic loanwords, although the overall influence of Phoenician-Punic on Berber languages is negligible. A number of loanwords could be attributed to Phoenician-Punic, Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
, or Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
. The similar vocabulary between these Semitic languages, as well as Arabic, is a complicating factor in tracing the etymology of certain words.
Words of Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
origin have been introduced into Berber languages over time. Maarten Kossman separates Latin loanwords in Berber languages into those from during the Roman empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
("Latin loans"), from after the fall of the Roman empire ("African Romance
African Romance, African Latin or Afroromance is an extinct Romance languages, Romance language that was spoken in the various provinces of Africa (Roman province), Roman Africa by the African Romans under the later Roman Empire and its various ...
loans"), precolonial non-African Romance loans, and colonial and post-colonial Romance loans. It can be difficult to distinguish Latin from African Romance loans. There are about 40 likely Latin or African Romance loanwords in Berber languages, which tend to be agricultural terms, religious terms, terms related to learning, or words for plants or useful objects. Use of these terms varies by language. For example, Tuareg does not retain the Latin agricultural terms, which relate to a form of agriculture not practiced by the Tuareg people. There are some Latin loans that are only known to be used in Shawiya.
The Berber calendar uses month names derived from the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts ...
. Not every language uses every month. For example, Figuig appears to use only eight of the months. These names may be precolonial non-African Romance loans, adopted into Berber languages through Arabic, rather than from Latin directly.
The most influential external language on the lexicon of Berber languages is Arabic. Maarten Kossmann calculates that 0-5% of Ghadames and Awdjila's core vocabularies, and over 15% of Ghomara, Siwa, and Senhadja de Sraïr's core vocabularies, are loans from Arabic. Most other Berber languages loan from 6–15% of their core vocabulary from Arabic. Salem Chaker estimates that Arabic loanwords represent 38% of Kabyle vocabulary, 25% of Tashelhiyt vocabulary, and 5% of Tuareg vocabulary, including non-core words.
On the one hand, the words and expressions connected to Islam were borrowed, e.g. Tashlhiyt ''bismillah'' "in the name of Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
" < Classical Arabic ''bi-smi-llāhi'', Tuareg ''ta-mejjīda'' "mosque" (Arabic ''masjid''); on the other, Berber adopted cultural concepts such as Kabyle ''ssuq'' "market" from Arabic ''as-sūq'', ''tamdint'' "town" < Arabic ''madīna''. Even expressions such as the Arabic greeting ''as-salāmu ʿalaikum'' "Peace be upon you!" were adopted (Tuareg ''salāmu ɣlīkum'').
Influence on other languages
The Berber languages have influenced localArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
dialects in the Maghreb. Although Maghrebi Arabic
Maghrebi Arabic, often known as ''ad-Dārija'' to differentiate it from Literary Arabic, is a vernacular Arabic dialect continuum spoken in the Maghreb. It includes the Moroccan, Algerian, Tunisian, Libyan, Hassaniya and Saharan Arabic di ...
has a predominantly Semitic and Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
vocabulary, it contains a few Berber loanwords which represent 2–3% of the vocabulary of Libyan Arabic, 8–9% of Algerian Arabic
Algerian Arabic (, romanized: ), natively known as , or , is a variety of Arabic spoken in Algeria. It belongs to the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and is mostly intelligible with the Tunisian and Moroccan dialects. Darja () means "eve ...
and Tunisian Arabic
Tunisian Arabic, or simply Tunisian (), is a Varieties of Arabic, variety of Arabic spoken in Tunisia. It is known among its 13 million speakers as ''Tūnsi'', "Tunisian" or ''Maghrebi Arabic, Derja'' (; meaning "common or everyday dialect") t ...
, and 10–15% of Moroccan Arabic
Moroccan Arabic ( ), also known as Darija ( or ), is the dialectal, vernacular form or forms of Arabic spoken in Morocco. It is part of the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and as such is mutually intelligible to some extent with Algerian ...
. Their influence is also seen in some languages in West Africa. F. W. H. Migeod pointed to strong resemblances between Berber and Hausa in such words and phrases as these:
In addition he notes that the genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can ...
in both languages is formed with n = "of" (though likely a common inheritance from Proto-Afro-Asiatic; cf. A.Eg genitive ''n'').Migeod, F. W. H., ''The Languages of West Africa''. Kegan, Paul, Trench & Trübner, London 1913. pages 232, 233.
Extinct languages
A number of extinct populations are believed to have spoken Afro-Asiatic languages of the Berber branch. According to Peter Behrens (1981) and Marianne Bechaus-Gerst (2000), linguistic evidence suggests that the peoples of the C-Group culture in present-day southernEgypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and northern Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
spoke Berber languages. The Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributari ...
Nobiin language today contains a number of key pastoralism related loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
s that are of Berber origin, including the terms for sheep and water/Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
. This in turn suggests that the C-Group population—which, along with the Kerma culture
The Kingdom of Kerma or the Kerma culture was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BC to 1500 BC in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based in the southern part of Nubia, or "Upper Nubia" (in parts of ...
, inhabited the Nile valley immediately before the arrival of the first Nubian speakers—spoke Afro-Asiatic languages.
Additionally, historical linguistics indicate that the Guanche language
Guanche is an extinct language or dialect continuum that was spoken by the Guanches of the Canary Islands until the 16th or 17th century. It died out after the conquest of the Canary Islands as the Guanche ethnic group was assimilated into the d ...
, which was spoken on the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
by the ancient Guanches
The Guanche were the Indigenous peoples, indigenous inhabitants of the Spain, Spanish Canary Islands, located in the Atlantic Ocean some to the west of modern Morocco and the North African coast. The islanders spoke the Guanche language, which i ...
, likely belonged to the Berber branch of the Afro-Asiatic family.Richard Hayward, 2000, "Afroasiatic", in Heine & Nurse eds, ''African Languages,'' Cambridge University Press
See also
* List of Berber-language television channels * Amazigh Cultural Association in America * Shilha literatureNotes
References
External links
Tamazight-English Dictionary
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110624061513/http://www.llmap.org/languages/tzm.html Map of Berber language from the LL-Map Project(archived 24 June 2011)
The Berber Language Profile
(archived 2 October 2010)
Etymology of "Berber"
Etymology of "Amazigh"
Early Christian history of Berbers
(archived 26 August 2017)
Imyura Kabyle site about literature
(archived 12 August 2013)
Amawal: The online open source Berber dictionary
{{DEFAULTSORT:Berber Languages Afroasiatic languages Maghreb Languages of Algeria Languages of Morocco Languages of Mali Languages of Niger Languages of Mauritania Languages of Tunisia Languages of Gibraltar Languages of Sicily Languages of Western Sahara