Altsek on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alcek or Alzeco was allegedly a son of Kubrat and led the Bulgars to Ravenna that later settled in the villages of Gallo Matese, 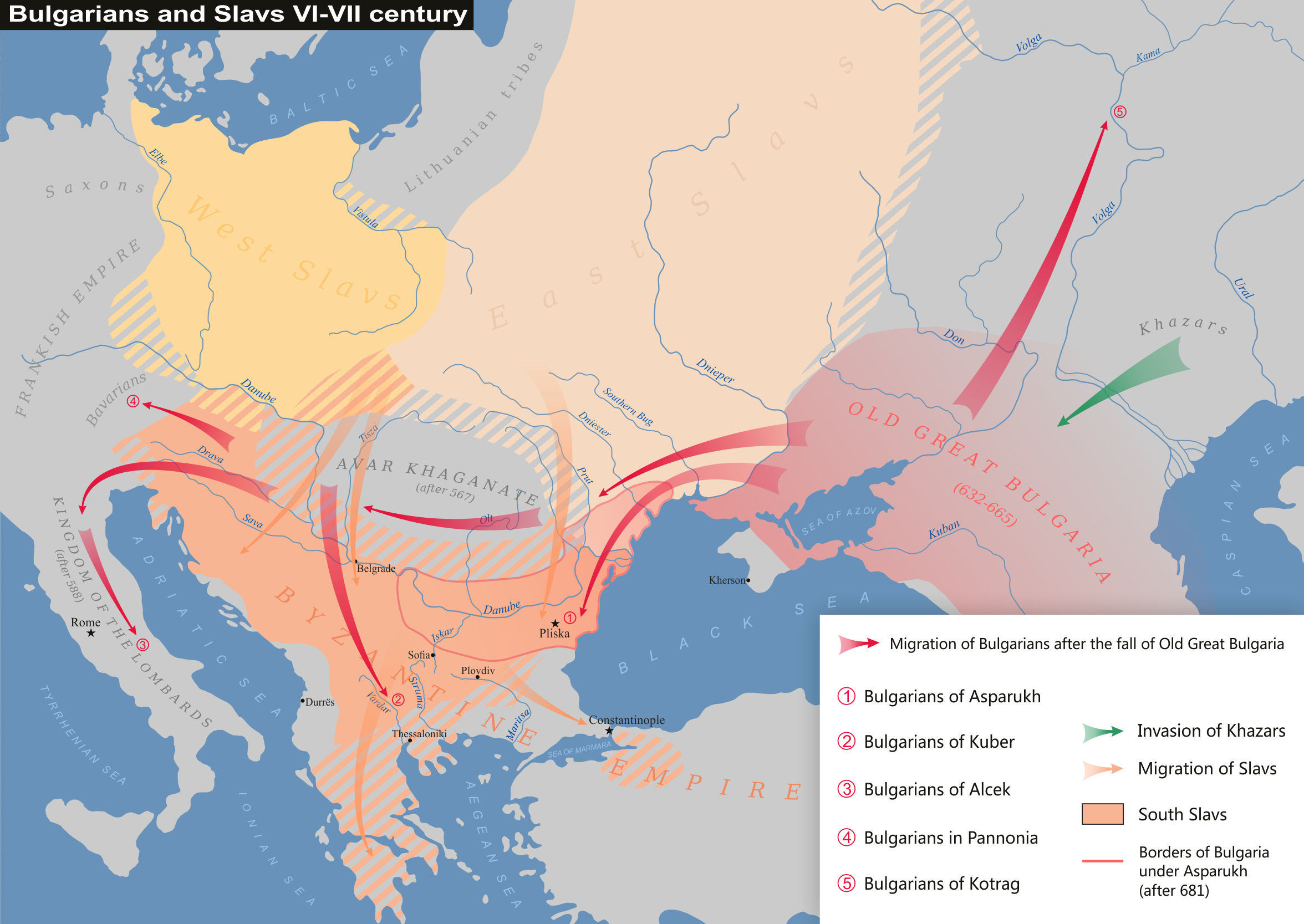 After the collapse of
After the collapse of
I Bulgari stanziati nelle terre d'Italia nell'Alto Medio Evo
by Vincenzo D'Amico {{Authority control Dulo clan 7th-century Bulgarian people
Sepino
Sepino is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Campobasso in the Italian region Molise, located about south of Campobasso. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages of Italy").
The archaeological site of ...
, Boiano and Isernia
Isernia () is a town and ''comune'' in the southern Italian region of Molise, and the capital of the province of Isernia.
Geography
Situated on a rocky crest rising from between the Carpino and the Sordo rivers, the plan of Isernia still refl ...
in the Matese mountains of southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
.
 After the collapse of
After the collapse of Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria (Medieval Greek: Παλαιά Μεγάλη Βουλγαρία, ''Palaiá Megálē Voulgaría''), also often known by the Latin names ''Magna Bulgaria'' and ''Patria Onoguria'' (" Onogur land"), was a 7th-century Turkic noma ...
, some of the Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
, led by Alzeco, thought to be a son of Kubrat, settled in the lands of the Longobard Kingdom. Paul the Deacon
Paul the Deacon ( 720s 13 April in 796, 797, 798, or 799 AD), also known as ''Paulus Diaconus'', ''Warnefridus'', ''Barnefridus'', or ''Winfridus'', and sometimes suffixed ''Cassinensis'' (''i.e.'' "of Monte Cassino"), was a Benedictine monk, sc ...
places a settlement in his history of the migration of the Bulgars in the area of the Duchy of Benevento
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
. Under the leadership of Alzeco, the Bulgars (called "Vulgars" by Paul) came to Italy in Benevento, where they settled in the Molise region.
Alciocus
The earlierKhagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im ...
called Alciocus who was the leader of Bulgar hordes of the Avar Khanganate, is also known. The main source for these events is the medieval chronicle of Fredegar
The ''Chronicle of Fredegar'' is the conventional title used for a 7th-century Frankish chronicle that was probably written in Burgundy. The author is unknown and the attribution to Fredegar dates only from the 16th century.
The chronicle begi ...
. In 623 Samo
Samo (–) was the founder and sole ruler of the first recorded political union of Slavs, Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire ("realm", "kingdom", or "tribal union"), ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to Fredegarius, the only ...
led a rebellion against the Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empi ...
. Alciocus fled with 9,000 Bulgars to Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
where he asked the Frankish king
The Franks, Germanic peoples that invaded the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, were first led by individuals called dux, dukes and monarch, reguli. The earliest group of Franks that rose to prominence was the Salian Franks, Salian Mero ...
Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the ...
for a piece of land to settle in. The king at first allowed them some land, but one night he ordered his army to slaughter the Bulgars. Only 700 out of 9,000 survived the slaughter and fled for protection to Valuk king of the Wends
Wends is a historical name for Slavs who inhabited present-day northeast Germany. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying ...
.
After the departure of Alciocus, Kubrat established peace between the Avars and Byzantium in 632.
Alzeco
Although only three of Kubrat's sons are mentioned by name it has been suggested that Kubrat gave the name Alzeco to one of his other two sons. After Kubrat's death over 40 years later, his empire was divided by his five sons in the 670s. Alzeco gained permission from theKing of the Lombards
The kings of the Lombards or ''reges Langobardorum'' (singular ''rex Langobardorum'') were the monarchs of the Lombard people from the early 6th century until the Lombardic identity became lost in the 9th and 10th centuries. After 774, the kings ...
, Grimoald, to settle in the area of Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
. Eventually they were sent south into the Duchy of Benevento
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
, where Alzeco was granted the rule of their settlements with the Longobard (Italian) title of gastald.
Italian archaeology
Human graves of a steppe-nomadic character as well as horse burials datable to the second half of the eighth century attest to the presence of Pannonian peoples in theMolise
Molise ( , ; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. Until 1963, it formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Ital ...
and Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
. In the lifetime of Paul the Deacon
Paul the Deacon ( 720s 13 April in 796, 797, 798, or 799 AD), also known as ''Paulus Diaconus'', ''Warnefridus'', ''Barnefridus'', or ''Winfridus'', and sometimes suffixed ''Cassinensis'' (''i.e.'' "of Monte Cassino"), was a Benedictine monk, sc ...
, he recorded that the descendants of these "Vulgars" still spoke their original language, as well as Latin.
Alzeco as Alciocus
Researchers have, in the past, claimed one identification of both historical figures. They have suggested that Alzeco might be identified with the Bulgar leader Alciocus of the Fredegar chronicle. This notion, however, must surmount a significant chronological contradiction, and it is possible that this was a title rather than a personal name. In any case, it seems more likely that the "Vulgares" that settled in the Molise are more likely to refer to the men of Alciocus, as most of the tombs excavated at Campochiaro can be dated around the middle of the 7th century, with some being certainly earlier or later. This would indicate a settlement in the area some time before the reign of Romuald as Duke in Benevento and Grimoald as king in Pavia. Furthermore, this is supported by the fact that the Longobards had no control of the Ravennate lands until the second half of the 8th century, meaning that Grimoald would have been unable to settle them in this area without Byzantine approval, which would be strange as Costans II was in the midst of a disastrous Italian campaign against the Southern Longobards. It is very probable that Paul the Deacon confused the settlement of Alzeco/Alciocus in the Molise after his flight from Dagobert I with another event about 50 years later, specifically the settlement of one of Kubrat's/Kurt's unnamed sons around Ravenna, most likely as a form of protection against the Longobards for the nominally Byzantine Exarchate. The name of the leader of this group is completely unknown, although the settlement may have been known thanks to Byzantine records in the Exarchate.Gli Àvari. Un popolo d'oriente nell'Europa dell'Alto Medioevo Bóna, István. (2000) - In: L'oro degli Avari. Popolo delle steppe in Europa S. 10Sources
*Dillon, John B. "Bulgars". ''Medieval Italy: An Encyclopedia'', ed. Christopher Kleinhenz. London: Routledge, 2004. * D'Amico, Vincenzo. ''I Bulgari trasmigrati in Italia nei secoli VI e VII dell’era volgare e loro speciale diffusione nel Sannio''. Campobasso, 1933.. * Paulus Diaconus, Historia Langobardorum, Book IV * Bòna, Istvàn, (2000) Gli Àvari. Un popolo d'oriente nell'Europa dell'Alto Medioevo - In: L'oro degli Avari. Popolo delle steppe in Europa S. 10Notes
External links
I Bulgari stanziati nelle terre d'Italia nell'Alto Medio Evo
by Vincenzo D'Amico {{Authority control Dulo clan 7th-century Bulgarian people