Alpha² Canum Venaticorum variable on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of
 Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of magnetic
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, m ...
variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
. These are chemically peculiar star
In astrophysics, chemically peculiar stars (CP stars) are stars with distinctly unusual Metallicity, metal abundances, at least in their surface layers.
Classification
Chemically peculiar stars are common among hot main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) ...
s of the CP2 type that are photometrically variable. That is, they are upper main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s of spectral class
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
B8p to A7p, with strong magnetic fields and strong silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
, strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
, or chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
spectral lines
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used ...
. Their brightness typically varies by 0.01 to 0.1 magnitudes over the course of 0.5 to 160 days.
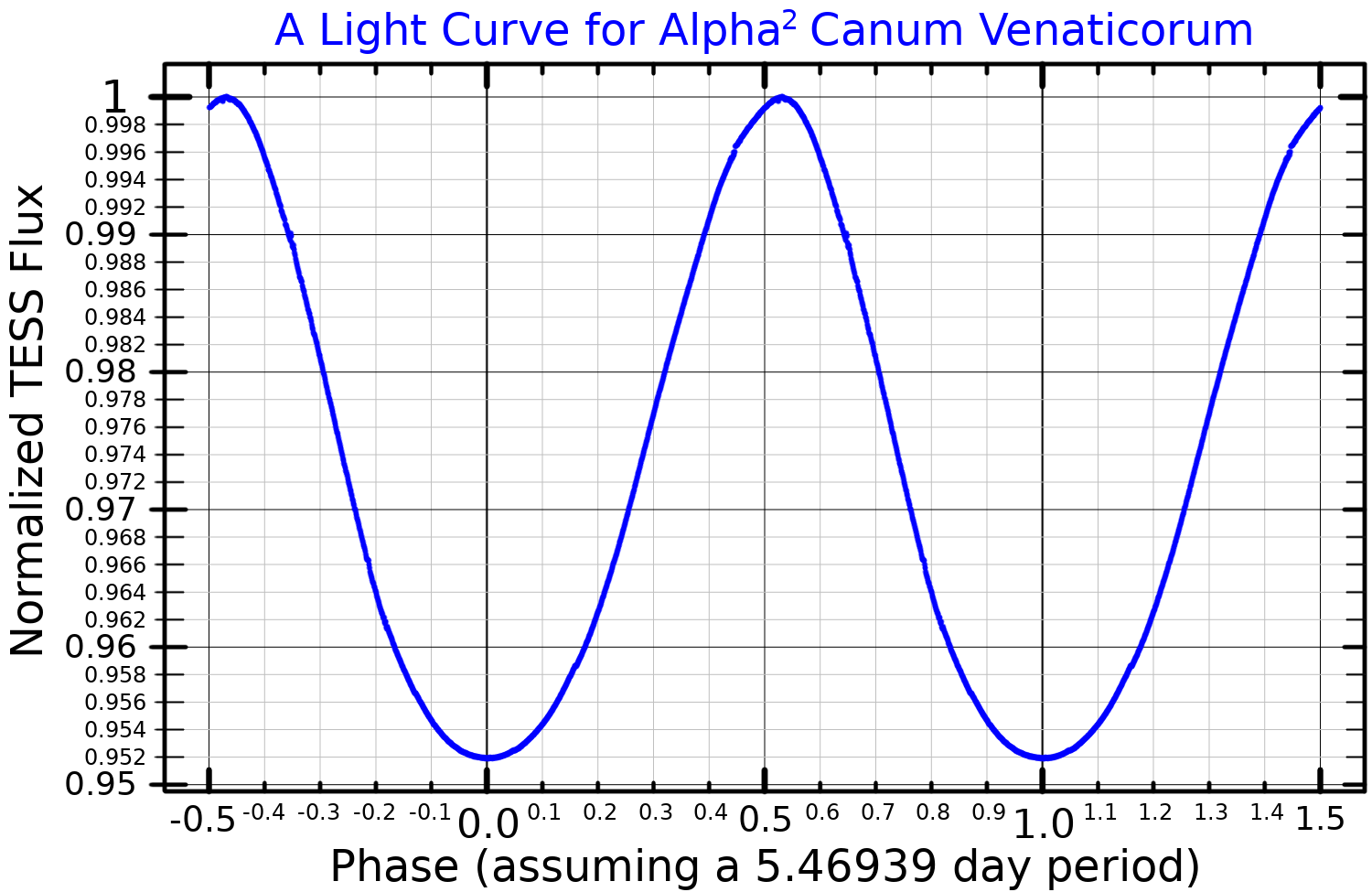
The first CP2 variable to be discovered was α2 Canum Venaticorum, a star in the binary system of Cor Caroli, which lies in the northern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Canes Venatici
Canes Venatici ( ) is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and ...
. Its brightness fluctuates by 0.14 magnitudes with a period of 5.47 days. This is now the prototype of the α2 CVn class of variables.
In addition to their brightness, the intensities and profiles of the spectral lines
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used ...
of α2 CVn variables vary, as do their magnetic fields. The periods of these variations are all equal and are believed to equal the period of rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
of the star. It is thought that they are caused by an inhomogeneous distribution of chemical elements in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
s of these stars. These result in spots and enhanced element abundances, which produce localized variations in surface flux. The oblique rotator model explains how these variations are carried across the field of view, resulting in the stellar variability. Several factors are thought responsible for the spots, including a weak stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the stellar atmosphere, upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spheri ...
, the properties of the magnetic field, a weak convection zone
A convection zone, convective zone or convective region of a star is a layer which is unstable due to convection. Energy is primarily or partially transported by convection in such a region. In a radiation zone, energy is transported by radiation ...
, and a slow rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
rate.
Naked eye examples
This list shows selected variables of this class that are visible to thenaked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microsc ...
. That is, their typical brightness is magnitude 6.5 or brighter.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable