Alpha Arae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alpha Arae, is the second brightest

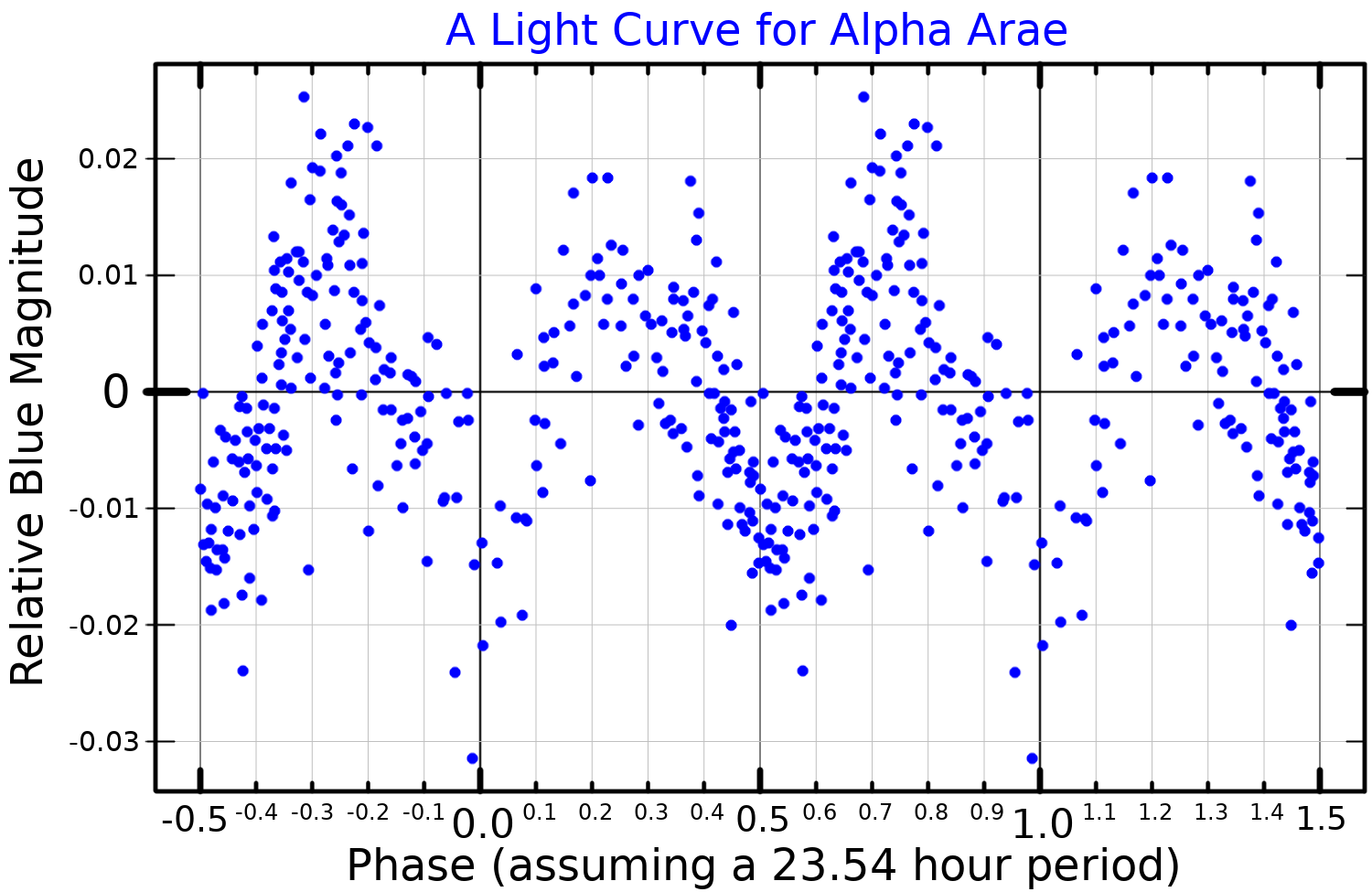 Alpha Arae has a
Alpha Arae has a
香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表
, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
Image of Alpha Arae
from Aladin {{DEFAULTSORT:Alpha Arae Be stars B-type main-sequence stars Gamma Cassiopeiae variable stars Lambda Eridani variables Ara (constellation) Arae, Alpha 6510 CD-49 11511 Arae, 62 158427 085792
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
in the southern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Ara. Its name is a Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek alphabet, Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive case, genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer design ...
that is Latinized from α Arae, and abbreviated Alpha Ara or α Ara. With an average apparent visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction of the object's light ca ...
2.93, it is readily visible to the naked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microsc ...
from the southern hemisphere. This star is close enough to the Earth that its distance can be estimated using parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
data collected during the Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions and distances of ...
mission. It is around away, with a 7% margin of error
The margin of error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in the results of a Statistical survey, survey. The larger the margin of error, the less confidence one should have that a poll result would reflect the result of ...
. The visual magnitude of the star is diminished by 0.10 magnitudes as a result of extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
from intervening gas and dust.
Properties

 Alpha Arae has a
Alpha Arae has a stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction gratin ...
of B2 Vne, indicating that it is a massive B-type main sequence star. The 'n' notation in the suffix indicates that the absorption line
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. Th ...
s in the star's spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
appear spread out and nebulous because of the Doppler effect
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described ...
from rapid rotation. The measured projected rotational velocity
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface.
The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bu ...
has been measured as high as . Meilland et al. (2007) estimate the pole of the star is inclined by 55° to the line of sight, yielding an equatorial azimuth
An azimuth (; from ) is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north, in a local or observer-centric spherical coordinate system.
Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer ( origin) to a point ...
al velocity of . This is close to the critical velocity where the star would start to break up. The rapid rotation is causing a pronounced equatorial bulge of about 2.4–2.7 times the polar radius.
It is a Be star
Be stars are a heterogeneous set of stars with B spectral types and emission lines. A narrower definition, sometimes referred to as ''classical Be stars'', is a non-supergiant B star whose spectrum has, or had at some time, one or more Balmer ...
, as indicated by the 'e' notation in the star's classification. This indicates that emission line
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used ...
s are observed in the spectrum, which is coming from a disk of material ejected from the star because of its rapid rotation. In 2003 and 2005, Alpha Arae was observed by infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important inves ...
, using the MIDI and AMBER instruments at the VLT Interferometer. The results, published in 2005 and 2007, appear to show that Alpha Arae is surrounded by a dense equatorial disk of material in Keplerian (rather than uniform) rotation, and that it is losing mass by a polar stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the stellar atmosphere, upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spheri ...
with a terminal velocity of approximately 1,000 km/s. There is also some evidence that Alpha Arae is orbited by a companion at 0.7 AU.
This star is around 9.6 times as massive as the Sun, and has an average of 4.5 times its radius. It is 5,800 times as luminous as the Sun, its energy emitted from its outer envelope at an effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
of 18,044 K. This heat gives Alpha Arae the blue-white hue that is characteristic of B-type star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
s. It is a variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
with a magnitude that varies between 2.76m and 2.90m. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars
The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) is a list of variable stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. Its first edition, containing 10,820 stars, was published in 1948 by the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, edited by and Pavel Parenago. Second a ...
classifies it only as BE, indicating that it is a variable Be star
Be stars are a heterogeneous set of stars with B spectral types and emission lines. A narrower definition, sometimes referred to as ''classical Be stars'', is a non-supergiant B star whose spectrum has, or had at some time, one or more Balmer ...
but not obviously a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable
A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae.
Variability
γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically ha ...
. The International Variable Star Index defines it as GCAS + LERI, showing both rapid periodic variation and slow irregular eruptions.
Alpha Arae has a visual companion star, ''CCDM J17318-4953B'', located approximately 50 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
s away along a position angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the Celestial pole, north celestial pole (NCP), turning pos ...
of 168°, with an apparent visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction of the object's light ca ...
of about 11. The two stars appear close to each other by coincidence and are not physically close in space.
In culture
With β and σ Ara it forms the Chinese asterism ''Choo'' (pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, officially the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. ''Hanyu'' () literally means 'Han Chinese, Han language'—that is, the Chinese language—while ''pinyin' ...
: chǔ, ), "pestle" in traditional Chinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The Ancient China, ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categori ...
. It was the second star of ''Choo'' (), but R. H. Allen used the name ''Choo'' for this star only. Patrick Moore
Sir Patrick Alfred Caldwell-Moore (; 4 March 1923 – 9 December 2012) was an English amateur astronomer who attained prominence in that field as a writer, researcher, radio commentator and television presenter.
Moore's early interest in astro ...
lists ''Choo'' as a proper name for this star in his star catalogue
A star catalogue is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the year ...
of the constellation Ara. This name is also given the French spelling ''Tchou''. There is another ''Choo'' in the constellation Pegasus
Pegasus (; ) is a winged horse in Greek mythology, usually depicted as a white stallion. He was sired by Poseidon, in his role as horse-god, and foaled by the Gorgon Medusa. Pegasus was the brother of Chrysaor, both born from Medusa's blood w ...
.
In Chinese, (), meaning ''Pestle
A mortar and pestle is a set of two simple tools used to prepare ingredients or substances by compression (physics), crushing and shear force, grinding them into a fine Paste (rheology), paste or powder in the kitchen, laboratory, and pharmacy. ...
'', refers to an asterism consisting of α Arae, σ Arae and β Arae. Consequently, the Chinese name
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethni ...
for α Arae itself is (, )., Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
See also
* Traditional Chinese star names in Ara * Traditional Chinese star names in PegasusReferences
External links
Image of Alpha Arae
from Aladin {{DEFAULTSORT:Alpha Arae Be stars B-type main-sequence stars Gamma Cassiopeiae variable stars Lambda Eridani variables Ara (constellation) Arae, Alpha 6510 CD-49 11511 Arae, 62 158427 085792