All humanity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In world demographics, the world population is the total number of
In world demographics, the world population is the total number of
 Estimates of world population by their nature are an aspect of
Estimates of world population by their nature are an aspect of
 During the European
During the European
 As of 2020, the global
As of 2020, the global


 In fact, during the 2010s, Japan and some countries in Europe began to reduce in population, due to
In fact, during the 2010s, Japan and some countries in Europe began to reduce in population, due to
File:Population curve.svg, Estimated world population figures, 10,000 BC – AD 2000
File:World population growth (lin-log scale).png, Estimated world population figures, 10,000 BC – AD 2000 (in log y scale)
File:World population history.svg, World population figures, 1950–2017
Download Files
where it states that the figures are for 1 July of the given year. Using the above figures, the change in population from 2010 to 2015 was: * World: +420 million * Africa: +142 million * Asia: +223 million * Europe: +3 million * Latin America and Caribbean: +35 million * Northern America: +14 million * Oceania: +2.9 million
BBC News, 13 October 2012
Worldometer) predicts a population of 5,986,622,074 for the beginning of the year 1997: : The actual figure was 5,924,787,816. The doomsday equation is called so because it predicts that the number of people living on the planet Earth will become maximally ''positive'' by 13 November 2026, and on the next moment will become ''negative''. Said otherwise, the equation predicts that on 13 November 2026 all humans will instantaneously disappear.

Human Population Numbers as a Function of Food Supply
, ''Environment, Development and Sustainability'', vol. 3, no. 1, March 2001, pp. 1–15 behavioral scientist Russell Hopfenberg (the former two publishing a study on the topic in 2001), anthropologist and activist Virginia Abernethy, ecologist Garrett Hardin, science writer and anthropologist Peter Farb, journalist Richard Manning, environmental biologist Alan D. Thornhill, cultural critic and writer Daniel Quinn, and anarcho-primitivist John Zerzan. Scientists generally acknowledge that at least one significant factor contributing to population growth (or overpopulation) is that as agriculture advances in creating more food, the population consequently increases—the
. ''National Geographic''. 2022. Furthermore, certain scientific studies do lend evidence to food availability in particular being the dominant factor within a more recent timeframe. Other studies take it as a basic model from which to make broad population conjectures. The idea became
"World Population Prospects, the 2010 Revision"
"World Population Prospects, the 2012 Revision"
"World Population History Graph"
World population graph 10,000 BC – AD 1950. *
World
. ''
"The World in Balance"
(transcript). Two-part PBS ''Nova'' episode on world population. 20 April 2004. Retrieved 19 July 2013.
"Global population: Faces of the future"
''The Economist''. 22 June 2013. Retrieved 25 June 2013. *Hopfenberg, Russell, and David Pimentel.
Human population numbers as a function of food supply
" Environment, development and sustainability 3 (2001): 1–15.
The Day of 6 Billion
an
7 Billion
– Official homepages maintained by UNFPA
Population Reference Bureau
– News and issues related to population
Berlin Institute for Population and Development
Statistics and maps
HiveGroup.com – World population statistics presented in a treemap interface
Population clocks
U.S. and World Population Clock (US Census Bureau)
World Population Clock – Worldometer
{{DEFAULTSORT:World Population Cultural globalization Human overpopulation
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of human prehistory
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
and history
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
for the human population to reach a billion and only 218 more years to reach 8 billion.
The human population has experienced continuous growth following the Great Famine of 1315–1317
The Great Famine of 1315–1317 (occasionally dated 1315–1322) was the first of a series of large-scale crises that struck parts of Europe early in the 14th century. Most of Europe (extending east to Poland and south to the Alps) was affected ...
and the end of the Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
in 1350, when it was nearly 370,000,000. The highest global population growth rates, with increases of over 1.8% per year, occurred between 1955 and 1975, peaking at 2.1% between 1965 and 1970. The growth rate declined to 1.1% between 2015 and 2020 and is projected to decline further in the 21st century. The global population is still increasing, but there is significant uncertainty about its long-term trajectory due to changing fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
and mortality rates. The UN Department of Economics and Social Affairs projects between 9 and 10 billion people by 2050 and gives an 80% confidence interval of 10–12 billion by the end of the 21st century, with a growth rate by then of zero. Other demographers predict that the human population will begin to decline in the second half of the 21st century.
The total number of births globally is currently (2015–2020) 140 million/year, which is projected to peak during the period 2040–2045 at 141 million/year and then decline slowly to 126 million/year by 2100. The total number of deaths is currently 57 million/year and is projected to grow steadily to 121 million/year by 2100.
The median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ...
age
Age or AGE may refer to:
Time and its effects
* Age, the amount of time someone has been alive or something has existed
** East Asian age reckoning, an Asian system of marking age starting at 1
* Ageing or aging, the process of becoming older
...
of human beings is 31 years.
History
 Estimates of world population by their nature are an aspect of
Estimates of world population by their nature are an aspect of modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular Society, socio-Culture, cultural Norm (social), norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the ...
, possible only since the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
. Early estimates for the population of the world date to the 17th century: William Petty
Sir William Petty (26 May 1623 – 16 December 1687) was an English economist, physician, scientist and philosopher. He first became prominent serving Oliver Cromwell and the Commonwealth of England, Commonwealth in Cromwellian conquest of I ...
, in 1682, estimated the world population at 320 million (current estimates ranging close to twice this number); by the late 18th century, estimates ranged close to one billion (consistent with current estimates). More refined estimates, broken down by continents, were published in the first half of the 19th century, at 600 million to 1 billion in the early 1800s and 800 million to 1 billion in the 1840s.
It is difficult for estimates to be better than rough approximations, as even current population estimates are fraught with uncertainties from 3% to 5%.
Ancient and post-classical history
Estimates of the population of the world at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Even earlier, genetic evidence suggests humans may have gone through a population bottleneck of between 1,000 and 10,000 people about 70,000 BC, according to the now largely discredited Toba catastrophe theory. By contrast, it is estimated that around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and westernRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in the 4th century AD.
The Plague of Justinian
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (AD 541–549) was an epidemic of Plague (disease), plague that afflicted the entire Mediterranean basin, Mediterranean Basin, Europe, and the Near East, especially the Sasanian Empire and the Byza ...
caused Europe's population to drop by around 50% between the 6th and 8th centuries AD. The population of Europe was more than 70 million in 1340. From 1340 to 1400, the world's population fell from an estimated 443 million to 350–375 million, with the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
suffering the most tremendous loss and Europe suffering the Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
; it took 200 years for European population figures to recover. The population of China decreased from 123 million in 1200 to 65 million in 1393, presumably from a combination of Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
invasions, famine, and plague.
Starting in AD 2, the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
of ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
kept consistent family registers to properly assess the poll taxes and labor service duties of each household.Nishijima, Sadao (1986), "The economic and social history of Former Han", in Twitchett, Denis; Loewe, Michael, ''Cambridge History of China: Volume I: the Ch'in and Han Empires, 221 B.C. – A.D. 220'', Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp 595–96. In that year, the population of Western Han
The Han dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring int ...
was recorded as 57,671,400 individuals in 12,366,470 households, decreasing to 47,566,772 individuals in 9,348,227 households by AD 146, towards the end of the Han dynasty
The end of the (Eastern) Han dynasty was the period of History of China, Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian. It was followed by the ...
. From 200 to 400, the world population fell from an estimated 257 million to 206 million, with China suffering the greatest loss. At the founding of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
in 1368, China's population was reported to be close to 60 million; toward the end of the dynasty in 1644, it may have approached 150 million. England's population reached an estimated 5.6 million in 1650, up from an estimated 2.6 million in 1500. New crops that were brought to Asia and Europe from the Americas by Portuguese and Spanish colonists in the 16th century are believed to have contributed to population growth. Since their introduction to Africa by Portuguese traders in the 16th century, maize and cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
have similarly replaced traditional African crops as the most important staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs an ...
crops grown on the continent.
The pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European col ...
population of the Americas is uncertain; historian David Henige called it "the most unanswerable question in the world." By the end of the 20th century, scholarly consensus favored an estimate of roughly 55 million people, but numbers from various sources have ranged from 10 million to 100 million. Encounters between European explorers and populations in the rest of the world often introduced local epidemics
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of Host (biology), hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example ...
of extraordinary virulence. According to the most extreme scholarly claims, as many as 90% of the Native American population of the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
died of Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
diseases such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
, measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, and influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
. Over the centuries, the Europeans had developed high degrees of immunity to these diseases, while the indigenous peoples had no such immunity.
Modern history
 During the European
During the European Agricultural
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created f ...
and Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
s, the life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
of children increased dramatically. The percentage of the children born in London who died before the age of five decreased from 74.5% in 1730–1749 to 31.8% in 1810–1829. Between 1700 and 1900, Europe's population increased from about 100 million to over 400 million. Altogether, the areas populated by people of European descent comprised 36% of the world's population in 1900.
Population growth in the Western world became more rapid after the introduction of vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
and other improvements in medicine and sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
. Improved material conditions led to the population of Britain increasing from 10 million to 40 million in the 19th century. The population of the United Kingdom reached 60 million in 2006. The United States saw its population grow from around 5.3 million in 1800 to 106 million in 1920, exceeding 307 million in 2010.
The first half of the 20th century in Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
was marked by a succession of major wars, famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
s and other disasters which caused large-scale population losses (approximately 60 million excess deaths). After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia's population declined significantly – from 150 million in 1991 to 143 million in 2012 – but by 2013 this decline appeared to have halted.
Many countries in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
have experienced extremely rapid population growth since the early 20th century, due to economic development and improvements in public health. China's population rose from approximately 430 million in 1850 to 580 million in 1953, and now stands at over 1.3 billion. The population of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, which was about 125 million in 1750, increased to 389 million in 1941; today, India, Pakistan and Bangladesh are collectively home to about billion people. Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, an island in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, had about 5 million inhabitants in 1815; it had a population of over 139 million in 2020. In just one hundred years, the population of Brazil decupled (x10), from about 17 million in 1900, or about 1% of the world population in that year, to about 176 million in 2000, or almost 3% of the global population in the very early 21st century. Mexico's population grew from 13.6 million in 1900 to about 112 million in 2010. Between the 1920s and 2000s, Kenya's population grew from 2.9 million to 37 million.
Milestones by the billions
The UN estimated that the world population reached one billion for the first time in 1804. It was another 123 years before it reached two billion in 1927, but it took only 33 years to reach three billion in 1960. Thereafter, it took 14 years for the global population to reach four billion in 1974, 13 years to reach five billion in 1987, 12 years to reach six billion in 1999 and, according to the United States Census Bureau, 13 years to reach seven billion in March 2012. The number on this page is automatically updated daily. The United Nations, however, estimated that the world population reached seven billion in October 2011. According to the UN, the global population reached eight billion in November 2022, but because the growth rate is slowing, it will take another 15 years to reach around 9 billion by 2037 and 20 years to reach 10 billion by 2057. Alternative scenarios for 2050 range from a low of 7.4 billion to a high of more than 10.6 billion.* * * * * Projected figures vary depending on underlying statistical assumptions and the variables used in projection calculations, especially thefertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
and mortality variables. Long-range predictions to 2150 range from a population decline to 3.2 billion in the "low scenario", to "high scenarios" of 24.8 billion. One extreme scenario predicted a massive increase to 256 billion by 2150, assuming the global fertility rate remained at its 1995 level of 3.04 children per woman; however, by 2010 the global fertility rate had declined to 2.52.
There is no estimation for the exact day or month the world's population surpassed one or two billion. The points at which it reached three and four billion were not officially noted, but the International Database of the United States Census Bureau placed them in July 1959 and April 1974 respectively. The United Nations did determine, and commemorate, the "Day of 5 Billion" on 11 July 1987, and the "Day of 6 Billion" on 12 October 1999. The Population Division of the United Nations declared the " Day of Seven Billion" to be 31 October 2011. The United Nations marked the birth of the eight billionth person on 15 November 2022.
Global demographics
sex ratio
A sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. However, many species deviate from an even sex ratio, ei ...
is approximately 1.01 males to 1 female. Approximately 24.7% of the global population is aged under 15, while 65.2% is aged 15–64 and 10.1% is aged 65 or over. The median age of the world's population is estimated to be 31 years in 2020, and is expected to rise to 37.9 years by 2050.
According to the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, the global average life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
is 73.3 years as of 2020, with women living an average of 75.9 years and men approximately 70.8 years. In 2010, the global fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
was estimated at 2.44 children per woman. In June 2012, British researchers calculated the total weight of Earth's human population as approximately , with the average person weighing around .
The IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of la ...
estimated nominal 2021 gross world product
The gross world product (GWP), also known as gross world income (GWI), is the combined gross national income (previously, the "gross national product") of all the countries in the world. Because imports and exports balance exactly when consider ...
at US$94.94 trillion, giving an annual global per capita figure of around US$12,290. Around 9.3% of the world population live in extreme poverty
Extreme poverty is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, including food, safe drinking water, sanitation facilities, health, shelter, ...
, subsisting on less than US$1.9 per day; around 8.9% are malnourished
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. 87% of the world's over-15s are considered literate
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
. As of January 2024, there were about 5 billion global Internet users, constituting 66% of the world population.
The Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's la ...
are the world's largest single ethnic group, constituting over 19% of the global population in 2011. The world's most-spoken languages are English (1.132B), Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretch ...
(1.117B), Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
(615M), Spanish (534M) and French (280M). More than three billion people speak an Indo-European language, which is the largest language family by number of speakers. Standard Arabic is a language with no native speakers, but the total number of speakers is estimated at 274 million people.
The largest religious categories in the world as of 2020 are estimated as follows: Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
(31%), Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(25%), Unaffiliated (16%) and Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
(15%).
Population by region
Six of the Earth's sevencontinent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
s are permanently inhabited on a large scale. Asia is the most populous continent, with its 4.64 billion inhabitants accounting for 60% of the world population. The world's two most populated countries, India and China, together constitute about 36% of the world's population. Africa is the second most populated continent, with around 1.34 billion people, or 17% of the world's population. Europe's 747 million people make up 10% of the world's population as of 2020,while the Latin American
Latin Americans (; ) are the citizenship, citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America).
Latin American countries and their Latin American diaspora, diasporas are Metroethnicity, ...
and Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
regions are home to around 653 million (8%). Northern America, primarily consisting of the United States and Canada, has a population of around 368 million (5%), and Oceania, the least populated region, has about 42 million inhabitants (0.5%). Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
only has a very small, fluctuating population of about 1200 people based mainly in polar science stations.
Largest populations by country

Ten most populous countries
Approximately 4.6 billion people live in these ten countries, representing around 57% of the world's population as of July 2023.Most densely populated countries
The tables below list the world's most densely populated countries, both in absolute terms and in comparison to their total populations, as of November 2022. All areas and populations are from ''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
'', unless otherwise noted.
Fluctuation
Population size fluctuates at differing rates in differing regions. Nonetheless, population growth has been the long-standing trend on all inhabited continents, as well as in most individual states. During the 20th century, the global population saw its greatest increase in known history, rising from about 1.6 billion in 1900 to over 6 billion in 2000 as the whole world entered the early phases of what has come to be called the "demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory in the Social science, social sciences referring to the historical shift from high birth rates and high Mortality rate, death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as societi ...
". Some of the key factors contributing to this increase included the lessening of the mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
in many countries by improved sanitation and medical advances, and a massive increase in agricultural productivity attributed to the Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
. By 2000, there were approximately ten times as many people on Earth as there had been in 1700.
However, this rapid growth did not last. During the period 2000–2005, the United Nations estimates that the world's population was growing at an annual rate of 1.3% (equivalent to around 80 million people), down from a peak of 2.1% during the period 1965–1970. Globally, although the population growth rate has been steadily declining from its peak in 1968, growth still remains high in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
.
sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
rates.
In 2019, the United Nations reported that the rate of population growth continues to decline due to the ongoing global demographic transition. If this trend continues, the rate of growth may diminish to zero by 2100, concurrent with a world population plateau of 10.9 billion. However, this is only one of many estimates published by the UN; in 2009, UN population projections for 2050 ranged between around 8 billion and 10.5 billion. An alternative scenario is given by the statistician Jorgen Randers, who argues that traditional projections insufficiently take into account the downward impact of global urbanization on fertility. Randers' "most likely scenario" reveals a peak in the world population in the early 2040s at about 8.1 billion people, followed by decline. Adrian Raftery, a University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW and informally U-Dub or U Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington, United States. Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast of the Uni ...
professor of statistics and of sociology, states that "there's a 70 percent probability the world population will not stabilize this century. Population, which had sort of fallen off the world's agenda, remains a very important issue."
Annual population growth
Population growth by region
The table below shows historical and predicted regional population figures in millions. The availability of historical population figures varies by region.Past population
The following table gives estimates, in millions, of population in the past. The data for 1750 to 1900 are from the UN report "The World at Six Billion" whereas the data from 1950 to 2015 are from a UN data sheet.. Linked to aDownload Files
where it states that the figures are for 1 July of the given year. Using the above figures, the change in population from 2010 to 2015 was: * World: +420 million * Africa: +142 million * Asia: +223 million * Europe: +3 million * Latin America and Caribbean: +35 million * Northern America: +14 million * Oceania: +2.9 million
Projections
Long-term global population growth is difficult to predict. The United Nations and the US Census Bureau both give different estimates – according to the UN, the world population reached seven billion in late 2011, while the USCB asserted that this occurred in March 2012. Since 1951, the UN has issued multiple projections of future world population, based on different assumptions. From 2000 to 2005, the UN consistently revised these projections downward, until the 2006 revision, issued on 14 March 2007, revised the 2050 mid-range estimate upwards by 273 million. Complicating the UN's and others' attempts to project future populations is the fact that average globalbirth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
s, as well as mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
s, are declining rapidly, as the nations of the world progress through the stages of the demographic transition, but both vary greatly between developed countries (where birth rates and mortality rates are often low) and developing countries (where birth and mortality rates typically remain high). Different ethnicities also display varying birth rates. Birth rate and mortality rates can change rapidly due to disease epidemics, wars
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
and other mass catastrophes, or advances in medicine and public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the de ...
.
The UN's first report in 1951 showed that during the period 1950–55 the crude birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration syste ...
was 36.9/1,000 population and the crude death rate was 19.1/1,000. By the period 2015–20, both numbers had dropped significantly to 18.5/1,000 for the crude birth rate and 7.5/1,000 for the crude death rate. UN projections for 2100 show a further decline in the crude birth rate to 11.6/1,000 and an increase in the crude death rate to 11.2/1,000.
The total number of births globally is currently (2015–20) 140 million/year, is projected to peak during the period 2040–45 at 141 million/year and thereafter decline slowly to 126 million/year by 2100. The total number of deaths is currently 57 million/year and is projected to grow steadily to 121 million/year by 2100.
2012 United Nations projections show a continued increase in population in the near future with a steady decline in population growth rate; the global population is expected to reach between 8.3 and 10.9 billion by 2050. 2003 UN Population Division population projections for the year 2150 range between 3.2 and 24.8 billion. One of many independent mathematical models supports the lower estimate, while a 2014 estimate forecasts between 9.3 and 12.6 billion in 2100, and continued growth thereafter. The 2019 Revision of the UN estimates gives the "medium variant" population as; nearly 8.6 billion in 2030, about 9.7 billion in 2050 and about 10.9 billion in 2100. In December 2019, the German Foundation for World Population projected that the global population will reach 8 billion by 2023 as it increases by 156 every minute. In a modeled future projection by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) is a public health research institute of the University of Washington in Seattle. Its research fields are global health statistics and impact evaluation.
IHME is headed by Christopher J.L. ...
, the global population was projected to peak in 2064 at 9.73 billion people and decline to 8.79 billion in 2100. Some analysts have questioned the sustainability of further world population growth, highlighting the growing pressures on the environment, global food supplies, and energy resources.
Some scholars have argued that a form of "cultural selection" may be occurring due to significant differences in fertility rates between cultures, and it can therefore be expected that fertility rates and rates of population growth may rise again in the future. An example is certain religious groups that have a higher birth rate that is not accounted for by differences in income. In his book ''Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth?'', Eric Kaufmann
Eric Peter Kaufmann (born 11 May 1970) is a Canadians, Canadian professor of politics at the University of Buckingham. He was appointed in October 2023, following his resignation from his post at Birkbeck, University of London, after two decades ...
argues that demographic trends point to religious fundamentalists greatly increasing as a share of the population over the next century. From the perspective of evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is a theoretical approach in psychology that examines cognition and behavior from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify human psychological adaptations with regard to the ancestral problems they evolved ...
, it is expected that selection pressure should occur for whatever psychological or cultural traits maximize fertility.Can we be sure the world's population will stop rising?BBC News, 13 October 2012
Mathematical models
The doomsday equation
A 1960 issue of ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'' magazine included an article by Heinz von Foerster and his colleagues, P. M. Mora and L. W. Amiot, proposing an equation representing the best fit to the historical data on the Earth's population available in 1958:
Fifty years ago, ''Science'' published a study with the provocative title �In 1975, von Hoerner suggested that von Foerster's doomsday equation can be written, without a significant loss of accuracy, in a simplified
Doomsday: Friday, 13 November, A.D. 2026
��. It fitted world population during the previous two millennia with ''P'' = 179 × 109/(2026.9 − ''t'')0.99. This “quasi-hyperbolic” equation (hyperbolic having exponent 1.00 in the denominator) projected to infinite population in 2026—and to an imaginary one thereafter. :—Taagepera, Rein
A world population growth model: Interaction with Earth's carrying capacity and technology in limited space
''Technological Forecasting and Social Change'', vol. 82, February 2014, pp. 34–41
hyperbolic
Hyperbolic may refer to:
* of or pertaining to a hyperbola, a type of smooth curve lying in a plane in mathematics
** Hyperbolic geometry, a non-Euclidean geometry
** Hyperbolic functions, analogues of ordinary trigonometric functions, defined u ...
form (''i.e.'' with the exponent in the denominator assumed to be 1.00):
:
where
* 2026.9 is 13 November 2026 AD—the date of the so-called "demographic singularity" and von Foerster's 115th anniversary;
* ''t'' is the number of a year of the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in October 1582 following the papal bull issued by Pope Gregory XIII, which introduced it as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian cale ...
.
Despite its simplicity, von Foerster's equation is very accurate in the range from 4,000,000 BP to 1997 AD. For example, the doomsday equation (developed in 1958, when the Earth's population was 2,911,249,671World Population by YearWorldometer) predicts a population of 5,986,622,074 for the beginning of the year 1997: : The actual figure was 5,924,787,816. The doomsday equation is called so because it predicts that the number of people living on the planet Earth will become maximally ''positive'' by 13 November 2026, and on the next moment will become ''negative''. Said otherwise, the equation predicts that on 13 November 2026 all humans will instantaneously disappear.
Years for world population to double
According to linear interpolation and extrapolation of UNDESA population estimates, the world population has doubled, or will double, in the years listed in the tables below (with two different starting points). During the2nd millennium
File:2nd millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: in 1492, Christopher Columbus reaches the New World, opening the European colonization of the Americas; the American Revolution, one of the late 1700s Enlightenment-inspired Atlantic Rev ...
, each doubling took roughly half as long as the previous doubling, fitting the hyperbolic growth model described above. However, after 2024, it is unlikely that there will be another doubling of the global population in the 21st century.
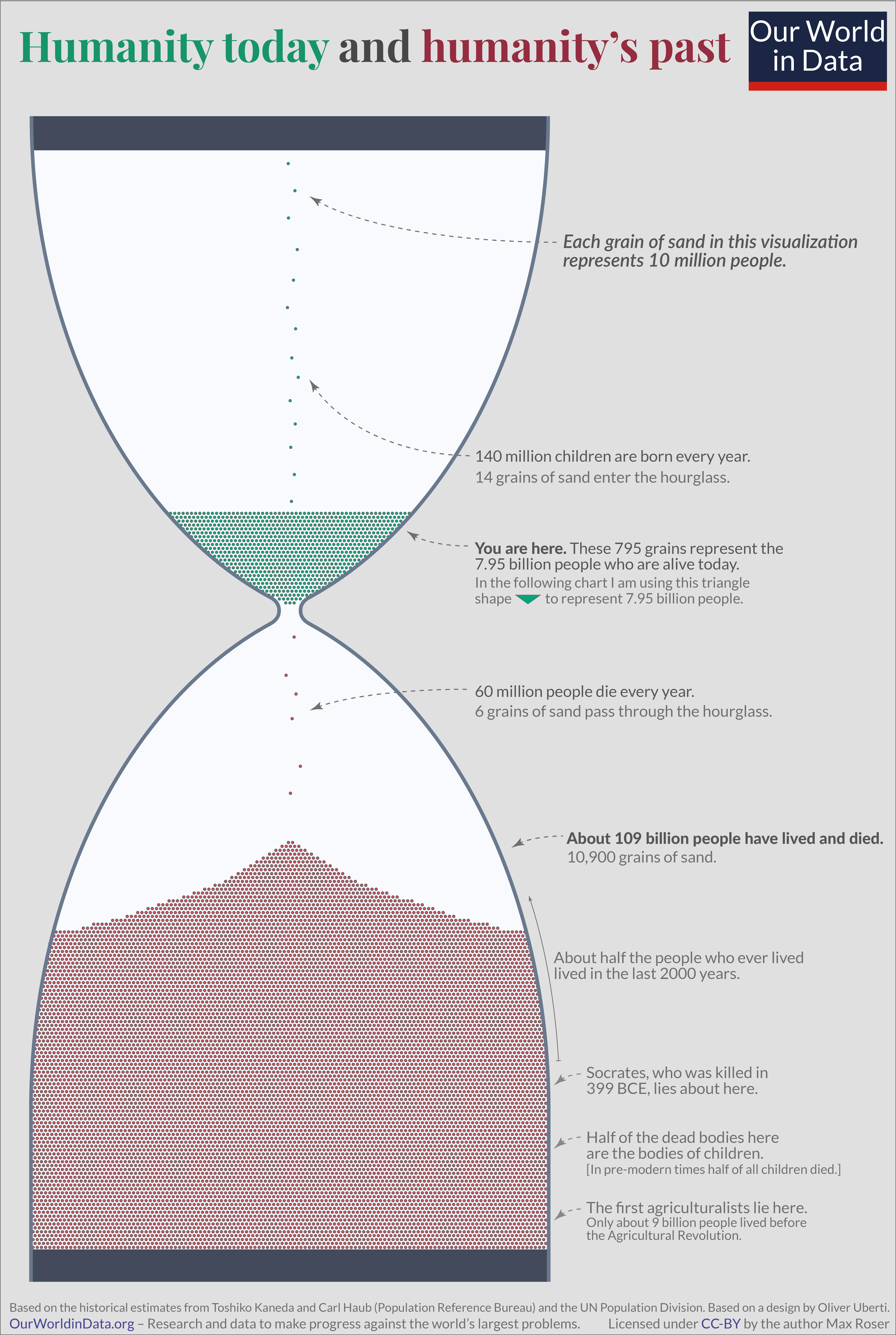
Number of humans who have ever lived
The total number of humans who have ever lived is estimated to be approximately 100 billion. Such estimates can only be rough approximations, as even modern population estimates are subject to uncertainty of around 3% to 5%." en recent demographic data is accurate only from 3 to 5%, although in demography traditionally more digits are indicated than those having a meaning. This is partially due to the ethical difficulty in rounding off numbers that supposedly represent real people, officially counted during a census". Sergei P. Kapitza, "The phenomenological theory of world population growth", ''Physics-Uspekhi'' 39(1) 57–71 (1996). Kapitsa (1996) cites estimates ranging between 80 and 150 billion. The PRB puts the figure at 117 billion as of 2020, estimating that the current world population is 6.7% of all the humans who have lived since 190,000 BCE. Haub (1995) prepared another figure, updated in 2002 and 2011; the 2011 figure was approximately 107 billion. ''Note: text of paper publication slightly different from text of on-line publication''. Haub characterized this figure as an estimate that required "selecting population sizes for different points from antiquity to the present and applying assumed birth rates to each period". Robust population data only exist for the last two or three centuries. Until the late 18th century, few governments had ever performed an accurate census. In many early attempts, such as inAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
and the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
, the focus was on counting merely a subset of the population for purposes of taxation or military service. Thus, there is a significant margin of error when estimating ancient global populations.
Pre-modern infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
rates are another critical factor for such an estimate; these rates are very difficult to estimate for ancient times due to a lack of accurate records. Haub (1995) estimates that around 40% of those who have ever lived did not survive beyond their first birthday. Haub also stated that "life expectancy at birth
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, organisation, metabolism, growth, adaptation, respons ...
probably averaged only about ten years for most of human history", which is not to be mistaken for the life expectancy after reaching adulthood. The latter equally depended on period, location and social standing, but calculations
A calculation is a deliberate mathematical process that transforms a plurality of inputs into a singular or plurality of outputs, known also as a result or results. The term is used in a variety of senses, from the very definite arithmetical ...
identify averages from roughly 30 years upward.
The National Institute of Corrections estimates that the number of people who have ever lived will rise to 121 billion by 2050, 4 billion more than their 2021 estimate.
Human population as a function of food availability
Individuals from a wide range of academic fields and political backgrounds have proposed that, like all other animal populations, anyhuman population
In world demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of human prehistory and histor ...
(and, by extension, the world population) predictably grows and shrinks according to available food supply, growing during an abundance of food and shrinking in times of scarcity. This idea may run counter to the popular thinking that, as population grows, food supply must also be increased to support the growing population; instead, the claim here is that growing population is the ''result'' of a growing food supply. Notable proponents of this notion include: agronomist
An agriculturist, agriculturalist, agrologist, or agronomist (abbreviated as agr.) is a professional in the science, practice, and management of agriculture and agribusiness. It is a regulated profession in Canada, India, the Philippines, the Uni ...
and insect ecologist David Pimentel,Hopfenberg, Russell and Pimentel, David,Human Population Numbers as a Function of Food Supply
, ''Environment, Development and Sustainability'', vol. 3, no. 1, March 2001, pp. 1–15 behavioral scientist Russell Hopfenberg (the former two publishing a study on the topic in 2001), anthropologist and activist Virginia Abernethy, ecologist Garrett Hardin, science writer and anthropologist Peter Farb, journalist Richard Manning, environmental biologist Alan D. Thornhill, cultural critic and writer Daniel Quinn, and anarcho-primitivist John Zerzan. Scientists generally acknowledge that at least one significant factor contributing to population growth (or overpopulation) is that as agriculture advances in creating more food, the population consequently increases—the
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
and Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
often specifically provided as examples of such agricultural breakthroughs.Gilland, Bernard (2006). "Population, nutrition and agriculture". ''Population and Environment'', 28(1), 1.The Development of Agriculture. ''National Geographic''. 2022. Furthermore, certain scientific studies do lend evidence to food availability in particular being the dominant factor within a more recent timeframe. Other studies take it as a basic model from which to make broad population conjectures. The idea became
taboo
A taboo is a social group's ban, prohibition or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, offensive, sacred or allowed only for certain people.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
following the United Nations' 1994 International Conference on Population and Development, where framing human population growth as negatively impacting the natural environment became regarded as "anti-human".
Most human populations throughout history validate this theory, as does the overall current global population. Populations of hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s fluctuate in accordance with the amount of available food. The world human population began consistently and sharply to rise, and continues to do so, after sedentary agricultural lifestyles became common due to the Neolithic Revolution and its increased food supply. This was, subsequent to the Green Revolution starting in the 1940s, followed by even more severely accelerated population growth. Often, wealthier countries send their surplus food resources to the aid of starving communities; however, some proponents of this theory argue that this seemingly beneficial strategy only results in further harm to those communities in the long run. Anthropologist Peter Farb, for example, has commented on the paradox that "intensification of production to feed an increased population leads to a still greater increase in population." Environmental writer Daniel Quinn has also focused on this phenomenon, which he calls the "food race", coining a term he felt was comparable, in terms of both escalation and potential catastrophe, to the nuclear arms race
The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War. During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuc ...
.
Criticism of this theory can come from multiple angles, for example by demonstrating that human population is not solely an effect of food availability, but that the situation is more complex. For instance, other relevant factors that can increase or limit human population include access to birth control, fresh water availability, arable land availability, energy consumed per person, heat removal, forest products, and various nonrenewable resources like fertilizers. Another criticism is that, in the modern era, birth rates are lowest in the developed nation
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
s, which also have the highest access to food. In fact, some developed countries have both a diminishing population and an abundant food supply. The United Nations projects that the population of 51 countries or areas, including Germany, Italy, Japan, and most of the states of the former Soviet Union, is expected to be lower in 2050 than in 2005. This shows that, limited to the scope of the population living within a single given political boundary, particular human populations do not always grow to match the available food supply. However, the global population as a whole still grows in accordance with the total food supply and many of these wealthier countries are major ''exporters'' of food to poorer populations, so that, according to Hopfenberg and Pimentel's 2001 research, "it is through exports from food-rich to food-poor areas... that the population growth in these food-poor areas is further fueled. Their study thus suggests that human population growth is an exacerbating feedback loop in which food availability creates a growing population, which then causes the misimpression that food production must be consequently expanded even further.
Regardless of criticisms against the theory that population is a function of food availability, the human population is, on the global scale, undeniably increasing, as is the net quantity of human food produced—a pattern that has been true for roughly 10,000 years, since the human development of agriculture. The fact that some affluent countries demonstrate negative population growth fails to discredit the theory as a whole, since the world has become a globalized system with food moving across national borders from areas of abundance to areas of scarcity. Hopfenberg and Pimentel's 2001 findings support both this and Daniel Quinn's direct accusation, in the early 2010s, that "First World farmers are fueling the Third World population explosion".Quinn, Daniel: "The Question (ID Number 122)". Retrieved October 2014 from .
See also
Explanatory notes
References
Citations
General and cited sources
*Further reading
* * Guinnane, Timothy W. (2023). " We Do Not Know the Population of Every Country in the World for the Past Two Thousand Years". ''The Journal of Economic History'' 83(3): 912–938. ."World Population Prospects, the 2010 Revision"
United Nations Population Division
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Eco ...
. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
"World Population Prospects, the 2012 Revision"
United Nations Population Division
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Eco ...
. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
"World Population History Graph"
World population graph 10,000 BC – AD 1950. *
World
. ''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
''. US Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
(CIA). Retrieved 6 November 2012.
"The World in Balance"
(transcript). Two-part PBS ''Nova'' episode on world population. 20 April 2004. Retrieved 19 July 2013.
"Global population: Faces of the future"
''The Economist''. 22 June 2013. Retrieved 25 June 2013. *Hopfenberg, Russell, and David Pimentel.
Human population numbers as a function of food supply
" Environment, development and sustainability 3 (2001): 1–15.
External links
OrganizationsThe Day of 6 Billion
an
7 Billion
– Official homepages maintained by UNFPA
Population Reference Bureau
– News and issues related to population
Berlin Institute for Population and Development
Statistics and maps
HiveGroup.com – World population statistics presented in a treemap interface
Population clocks
U.S. and World Population Clock (US Census Bureau)
World Population Clock – Worldometer
{{DEFAULTSORT:World Population Cultural globalization Human overpopulation