Alexios Komnenos (d on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alexios I Komnenos (, – 15 August 1118), Latinized as Alexius I Comnenus, was
 According to Anna Comnena's narrative in the Alexiad, Isaac and Alexios left Constantinople in mid-February 1081 to raise an army against Botaneiates. When the time was right and the army already marching to the capital, Anna Dalassene quickly and surreptitiously mobilised the remainder of the family and took sanctuary in the cathedral of
According to Anna Comnena's narrative in the Alexiad, Isaac and Alexios left Constantinople in mid-February 1081 to raise an army against Botaneiates. When the time was right and the army already marching to the capital, Anna Dalassene quickly and surreptitiously mobilised the remainder of the family and took sanctuary in the cathedral of  Nikephoros III Botaneiates was forced into a public vow that he would grant protection to the family. Straboromanos tried to give Anna his cross, but for her it was not large enough for all bystanders to witness the oath. She also demanded that the cross be personally sent by Botaneiates as a vow of his good faith. He obliged, sending a complete assurance for the family with his own cross. At the emperor's further insistence, and for their own protection, they took refuge at the convent of Petrion, where they were eventually joined by
Nikephoros III Botaneiates was forced into a public vow that he would grant protection to the family. Straboromanos tried to give Anna his cross, but for her it was not large enough for all bystanders to witness the oath. She also demanded that the cross be personally sent by Botaneiates as a vow of his good faith. He obliged, sending a complete assurance for the family with his own cross. At the emperor's further insistence, and for their own protection, they took refuge at the convent of Petrion, where they were eventually joined by
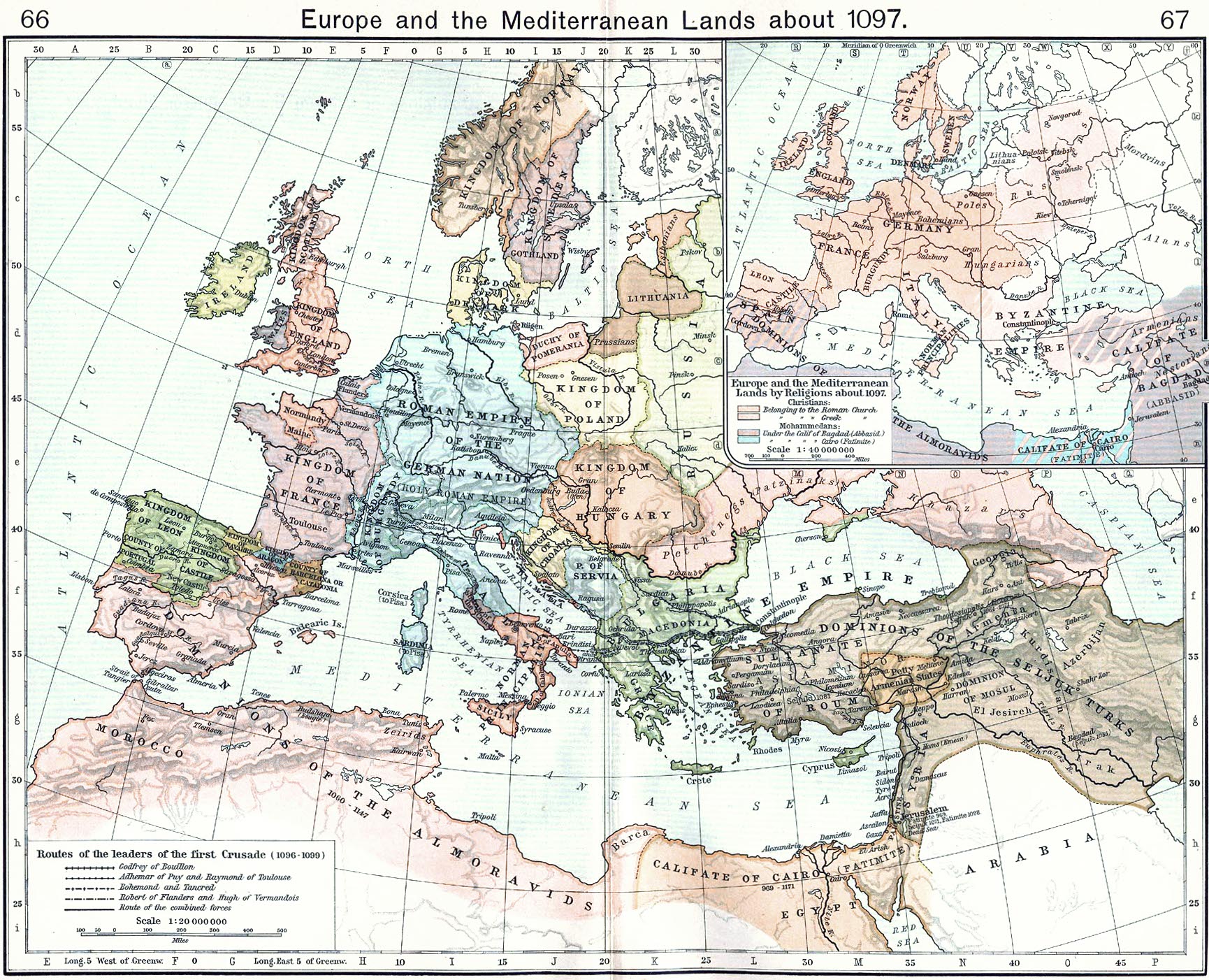 By the time Alexios ascended the throne, the Seljuqs had taken most of Asia Minor. Alexios secured much of the coastal regions by sending peasant soldiers to raid the Seljuq camps, but this did not stop the Turks altogether. He also got military support from Western rulers like
By the time Alexios ascended the throne, the Seljuqs had taken most of Asia Minor. Alexios secured much of the coastal regions by sending peasant soldiers to raid the Seljuq camps, but this did not stop the Turks altogether. He also got military support from Western rulers like
 Under Alexios the debased ''
Under Alexios the debased ''
 Alexios I had overcome dangerous crises and stabilised the Byzantine Empire, inaugurating a century of imperial prosperity and success. He had also profoundly altered the nature of the Byzantine government.Finlay 1854, p. 69 By seeking close alliances with powerful noble families, Alexios put an end to the tradition of imperial exclusivity and co-opted most of the nobility into his extended family and, through it, his government. Those who did not become part of this extended family were deprived of power and prestige. This measure, which was intended to diminish opposition, was paralleled by the introduction of new courtly dignities, like that of '' panhypersebastos'' given to Nikephoros Bryennios, or that of ''
Alexios I had overcome dangerous crises and stabilised the Byzantine Empire, inaugurating a century of imperial prosperity and success. He had also profoundly altered the nature of the Byzantine government.Finlay 1854, p. 69 By seeking close alliances with powerful noble families, Alexios put an end to the tradition of imperial exclusivity and co-opted most of the nobility into his extended family and, through it, his government. Those who did not become part of this extended family were deprived of power and prestige. This measure, which was intended to diminish opposition, was paralleled by the introduction of new courtly dignities, like that of '' panhypersebastos'' given to Nikephoros Bryennios, or that of ''
 By his marriage with
By his marriage with
Alexius coinage
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alexios 01 Komnenos * 1050s births 1118 deaths Year of birth uncertain 11th-century rebels 11th-century Byzantine emperors 1080s in the Byzantine Empire 1090s in the Byzantine Empire 1100s in the Byzantine Empire 1110s in the Byzantine Empire 12th-century Byzantine emperors Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Norman wars Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Seljuk wars Byzantine people of the Crusades Christian anti-Gnosticism Domestics of the Schools Nobilissimi Panhypersebastoi People associated with Xenophontos Monastery Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Pecheneg wars
Byzantine emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
from 1081 to 1118. After usurping the throne, he was faced with a collapsing empire and constant warfare throughout his reign, Alexios was able to curb the Byzantine decline and begin the military, financial, and territorial recovery known as the Komnenian restoration
The Komnenian restoration is the term used by historians to describe the military, financial, and territorial recovery of the Byzantine Empire under the Komnenian dynasty, from the accession of Alexios I Komnenos in 1081 to the death of Andron ...
. His appeals to Western Europe for help against the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persi ...
were the catalyst that sparked the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty
The House of Komnenos ( Komnenoi; , , ), Latinized as Comnenus ( Comneni), was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. The first reigning member, Isaac I Komnenos, ruled from 1057 to 1059. Th ...
, it was during his reign that the Komnenos family came to full power and initiated a hereditary succession to the throne.
The son of John Komnenos and a nephew of Isaac I Komnenos
Isaac I Komnenos or Comnenus (; – 1 June 1060) was Byzantine emperor from 1057 to 1059, the first reigning member of the Komnenian dynasty.
The son of the general Manuel Erotikos Komnenos, he was orphaned at an early age, and w ...
, Alexios served with distinction under three Byzantine emperors. In 1081, he led a rebellion against Emperor Nikephoros III Botaneiates
Nikephoros III Botaneiates (; 1002–1081), Romanization of Greek, Latinized as Nicephorus III Botaniates, was Byzantine Empire, Byzantine List of Byzantine Emperors, Emperor from 7 January 1078 to 1 April 1081. He became a general du ...
and took the throne for himself. He immediately faced an invasion of the western Balkans by the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
under Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard ( , ; – 17 July 1085), also referred to as Robert de Hauteville, was a Normans, Norman adventurer remembered for his Norman conquest of southern Italy, conquest of southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Robert was born ...
and his son Bohemond Bohemond or Bohemund, rarely Boamund, can refer to:
*Bohemond I of Antioch (1058–1111)
*Bohemond II of Antioch (1108–1130)
*Bohemond III of Antioch (1144–1201)
*Bohemond IV of Antioch & I of Tripoli (1172–1233)
*Bohemond V of Antioch & II o ...
. Despite initial defeats, Alexios secured an alliance with Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
Henry IV and drove back the Normans, recovering most of Byzantine losses by 1085. In 1091, he achieved a decisive victory over the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
at the Battle of Levounion in Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
with the help of Cuman
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Rus' chronicles, as " ...
allies.
Later in the 1090s, Alexios directed his attention towards Asia Minor, most of which had fallen to the Seljuk Turks. Desiring western support, he took reconciliatory measures towards the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, and in 1095 his envoys made a formal appeal to Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II (; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening the Council of Clermon ...
at the Council of Piacenza. At the subsequent Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
While the council ...
, Pope Urban formally called the First Crusade, which began a year after and concluded with much of western Anatolia restored to Byzantine rule. On Alexios' death in 1118, he was succeeded by his son John II Komnenos
John II Komnenos or Comnenus (; 13 September 1087 – 8 April 1143) was List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor from 1118 to 1143. Also known as "John the Beautiful" or "John the Good" (), he was the eldest son of Emperor Alexio ...
. Alexios' reign and campaigns were recorded by his daughter Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene (; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine Greek historian. She is the author of the '' Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. Her work constit ...
in her ''Alexiad
The ''Alexiad'' () is a medieval historical and biographical text written around the year 1148, by the Byzantine princess Anna Komnene, daughter of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. It was written in a form of artificial Attic Greek. Anna described th ...
'', a political and military history, which she named after her father.
Biography
Alexios was the son of John Komnenos andAnna Dalassene
Anna Dalassene (; ca. 1025/30 – 1 November 1100/02) was an important Byzantine noblewoman who played a significant role in the rise to power of the Komnenoi in the eleventh century. She exercised great influence over her son, the Emperor Alexi ...
,Kazhdan 1991, p. 63 and the nephew of Isaac I Komnenos
Isaac I Komnenos or Comnenus (; – 1 June 1060) was Byzantine emperor from 1057 to 1059, the first reigning member of the Komnenian dynasty.
The son of the general Manuel Erotikos Komnenos, he was orphaned at an early age, and was ...
(emperor 1057–1059). Alexios' father declined the throne on the abdication of Isaac, who was thus succeeded by Constantine X Doukas
Constantine X Doukas or Ducas (; – 23 May 1067), was Byzantine emperor from 1059 to 1067. He was the founder of the Doukid dynasty. During his reign, the Normans took over much of the remaining Byzantine territories in Italy, while in the ...
(r. 1059–1067) and died as a monk in 1067. Alexios and his elder brother, Manuel Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos (; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Latinized as Comnenus, also called Porphyrogenitus (; "born in the purple"), was a Byzantine emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history of ...
served under Romanos IV Diogenes (r. 1068–1071) with distinction against the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persi ...
.Norwich 1995, p. 4 under Michael VII Doukas ''Parapinakes'' (1071–1078) and Nikephoros III Botaneiates (1078–1081), he was militarily employed, along with his elder brother Isaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
, against rebels in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, and in Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
.Bury 1911
In 1074, western mercenaries led by Roussel de Bailleul rebelled in Asia Minor,Norwich 1995, p. 2 but Alexios successfully subdued them by 1076."Alexiad", 1.1 In 1078, he was appointed commander of the field army in the West by Nikephoros III.Norwich 1995, p. 3 In this capacity, Alexios defeated the rebellions of Nikephoros Bryennios the Elder (whose son or grandson later married Alexios' daughter Anna) and Nikephoros Basilakes, the first at the Battle of Kalavrye and the latter in a surprise night attack on his camp. Alexios was ordered to march against his brother-in-law Nikephoros Melissenos
Nikephoros Melissenos (, – 17 November 1104), Latinized as Nicephorus Melissenus, was a Byzantine general and aristocrat. Of distinguished lineage, he served as a governor and general in the Balkans and Asia Minor in the 1060s. In the turbule ...
in Asia Minor but refused to fight his kinsman. This did not, however, lead to a demotion, as Alexios was needed to counter the expected invasion of the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
of Southern Italy, led by Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard ( , ; – 17 July 1085), also referred to as Robert de Hauteville, was a Normans, Norman adventurer remembered for his Norman conquest of southern Italy, conquest of southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Robert was born ...
.
Conspiracy and revolt of the Komnenoi against Botaneiates
While Byzantine troops were assembling for the expedition, the Doukas faction at court approached Alexios and convinced him to join aconspiracy
A conspiracy, also known as a plot, ploy, or scheme, is a secret plan or agreement between people (called conspirers or conspirators) for an unlawful or harmful purpose, such as murder, treason, or corruption, especially with a political motivat ...
against Nikephoros III. The mother of Alexios, Anna Dalassene, was to play a prominent role in this coup d'état of 1081, along with the current empress, Maria of Alania
Maria of Alania (; born Martha; ka, მართა; 1053–1118) was Byzantine empress by marriages to emperors Michael VII Doukas and Nikephoros III Botaneiates. Her status as empress was considered a significant success for a newly unified ...
.Garland 2007 First married to Michael VII Doukas and secondly to Nikephoros III Botaneiates, she was preoccupied with the future of her son by Michael VII, Constantine Doukas. Nikephoros III intended to leave the throne to one of his close relatives,Finlay 1854, p. 59 and this resulted in Maria's ambivalence and alliance with the Komnenoi, though the real driving force behind this political alliance was Anna Dalassene.
The empress was already closely connected to the Komnenoi through Maria's cousin, Irene who had been married to Isaac Komnenos, thus the Komnenos brothers were able to treat her as member of the family's enlarged kinship. Furthermore, by espousing the custom of adoptive kingship, which was a social trend in the palace during the reign of empress Zoe, Maria had accepted to adopt Alexios as her son in order to aid the conspiracy.Norwich 1995, p. 5 Maria was induced to do so on advice of her own "Alans", that is her Georgian entourage, and her eunuchs, the latter being instructed by Isaac Komnenos to talk the empress into. Apparently, Anna must have been informed of the arrangement of the adoptive kingship, and her tacit agreement on the matter allowed for the final conclusion of Alexios' adoption by the empress. As a result, Alexios became the adoptive brother of Constantine Doukas's, natural son of empress Maria. The completion of the adoptive kingship entailed as part of the ritual performed from the adoptive member's behalf pledging an oath of loyalty and allegiance to the heir of the throne, a typical practice in which the prospective member since he bore no blood relation and was not of imperial lineage he had to be tied to the emperor's person by a sacred oath. Therefore, both Alexios and his brother, Isaac pledged to safeguard the heir's rights to the throne.
 According to Anna Comnena's narrative in the Alexiad, Isaac and Alexios left Constantinople in mid-February 1081 to raise an army against Botaneiates. When the time was right and the army already marching to the capital, Anna Dalassene quickly and surreptitiously mobilised the remainder of the family and took sanctuary in the cathedral of
According to Anna Comnena's narrative in the Alexiad, Isaac and Alexios left Constantinople in mid-February 1081 to raise an army against Botaneiates. When the time was right and the army already marching to the capital, Anna Dalassene quickly and surreptitiously mobilised the remainder of the family and took sanctuary in the cathedral of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia (; ; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque (; ), is a mosque and former Church (building), church serving as a major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The last of three church buildings to be successively ...
, wherefrom she negotiated with Nikephoros III Botaneiates
Nikephoros III Botaneiates (; 1002–1081), Romanization of Greek, Latinized as Nicephorus III Botaniates, was Byzantine Empire, Byzantine List of Byzantine Emperors, Emperor from 7 January 1078 to 1 April 1081. He became a general du ...
for the safety of her family, while disclaiming her two sons' hostile actions against the emperor. Anna Comnena offers in detail the course of steps her grandmother took to be able to enter the church. Under the pretence of making a vesperal visit to worship at the church, she deliberately excluded the grandson of Botaneiates and his loyal tutor and met with her sons' Alexios and Isaac and went with them to the forum of Constantine. When the tutor discovered she had gone missing, he went looking for her to eventually find her on the palace's grounds. Yet again cunningly Anna convinced him that they would leave the palace shortly. However, the rest of the female members of her family in order to be allowed to gain entrance although the church was at that time closed, pretended to be pilgrims from Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir ...
who had been penniless and wanted to prostrate the holy icons before their return trip. Straboromanos and royal guards who were caught up with them, were summoned back to the palace. Anna then went on protesting for the safety of her family, that she feared of the emperor's wrath and that her sons were nothing but loyal subjects, despite the fact that Alexios and Isaac were discovered to be missing without the emperor's consent. She even suggested that a plot had been unravelling by enemies of the family to have them blinded and for that she had fled to the capital so they may continue to be of loyal service to the emperor. She refused to go with them and demanded that they allow her to pray to the Mother of God
''Theotokos'' (Greek: ) is a title of Mary, mother of Jesus, used especially in Eastern Christianity. The usual Latin translations are or (approximately "parent (fem.) of God"). Familiar English translations are "Mother of God" or "God-bearer ...
for protection. This request was granted and Anna then manifested her true communicative and leadership capabilities:
 Nikephoros III Botaneiates was forced into a public vow that he would grant protection to the family. Straboromanos tried to give Anna his cross, but for her it was not large enough for all bystanders to witness the oath. She also demanded that the cross be personally sent by Botaneiates as a vow of his good faith. He obliged, sending a complete assurance for the family with his own cross. At the emperor's further insistence, and for their own protection, they took refuge at the convent of Petrion, where they were eventually joined by
Nikephoros III Botaneiates was forced into a public vow that he would grant protection to the family. Straboromanos tried to give Anna his cross, but for her it was not large enough for all bystanders to witness the oath. She also demanded that the cross be personally sent by Botaneiates as a vow of his good faith. He obliged, sending a complete assurance for the family with his own cross. At the emperor's further insistence, and for their own protection, they took refuge at the convent of Petrion, where they were eventually joined by Maria of Bulgaria
Maria of Bulgaria (died 21 November, after 1095), known as Maria Doukaina () in the Byzantine sources, was the wife of ''protovestiarios'' and ''domestikos ton scholon'' Andronikos Doukas (cousin of Michael VII), Andronikos Doukas and mother of E ...
, mother of Irene Doukaina. Botaneiates allowed them to be treated as refugees rather than as guests. They were allowed to have family members bring in their own food and were on good terms with the guards from whom they learned the latest news. Anna was highly successful in three important aspects of the revolt: she bought time for her sons to steal imperial horses from the stables and escape the city; she distracted the emperor, giving her sons time to gather and arm their troops; and she gave a false sense of security to Botaneiates that there was no real treasonous plot against him. After bribing the Western troops guarding the city, Isaac and Alexios Komnenos entered the capital victoriously on 1 April 1081.
During this time, Alexios was rumored to be the lover of Empress Maria, the daughter of King Bagrat IV of Georgia, who had been successively married to Michael VII Doukas and his successor Nikephoros III Botaneiates, and who was renowned for her beauty. Alexios arranged for Maria to stay on the palace grounds, and it was thought that he was considering marrying her. However, his mother consolidated the Doukas family connection by arranging the Emperor's marriage to Irene Doukaina
Irene Doukaina or Ducaena (, ''Eirēnē Doúkaina''; – 19 February 1138) was a Byzantine empress by marriage to the Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. She was the mother of Emperor John II Komnenos and the historian Anna Komnene. She w ...
, granddaughter of the Caesar John Doukas, the uncle of Michael VII, who would not have supported Alexios otherwise. As a measure intended to keep the support of the Doukai, Alexios restored Constantine Doukas, the young son of Michael VII and Maria, as co-emperor.
This situation changed drastically, however, when Alexios' first son John II Komnenos was born in 1087:Kazhdan 1991, p. 658 Anna's engagement to Constantine was dissolved, and she was moved to the main Palace to live with her mother and grandmother. Alexios became estranged from Maria, who was stripped of her imperial title and retired to a monastery, and Constantine Doukas was deprived of his status as co-emperor.
Wars against the Normans, Pechenegs, and Tzachas
The thirty-seven year reign of Alexios was full of struggle. At the outset he faced the formidable attack of the Normans, led byRobert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard ( , ; – 17 July 1085), also referred to as Robert de Hauteville, was a Normans, Norman adventurer remembered for his Norman conquest of southern Italy, conquest of southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Robert was born ...
and his son Bohemond Bohemond or Bohemund, rarely Boamund, can refer to:
*Bohemond I of Antioch (1058–1111)
*Bohemond II of Antioch (1108–1130)
*Bohemond III of Antioch (1144–1201)
*Bohemond IV of Antioch & I of Tripoli (1172–1233)
*Bohemond V of Antioch & II o ...
, who took Dyrrhachium and Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
and laid siege to Larissa
Larissa (; , , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 148,562 in the city proper, according to the 2021 census. It is also the capital of the Larissa ...
in Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
. Alexios suffered several defeats before he was able to strike back with success. He enhanced his resistance by an agreement with the German king Henry IV, who, in exchange for 360,000 gold pieces, did attack the Normans in Italy, which forced the Normans to concentrate on their defenses at home in 1083–84. He also secured the alliance of Henry, Count of Monte Sant'Angelo, who controlled the Gargano Peninsula The Apulia Carbonate Platform in Apulia, Italy, was a major palaeogeographic element of the southern margin of the Mesozoic Tethys Ocean. It is one of the so-called peri-Adriatic platforms, which are comparable to the Bahama Banks in their carbona ...
and dated his charters by Alexios' reign. Henry's allegiance would be the last example of Byzantine political control on peninsular Italy. The Norman military danger subsided with the death of Guiscard in 1085, and the Byzantines recovered most of their losses.
Alexios next had to deal with disturbances in Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, where the heretical sects of the Bogomils
Bogomilism (; ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", bogumilstvo, богумилство) was a Christian neo-Gnostic, dualist sect founded in the First Bulgarian Empire by the priest Bogomil during the reign of Tsar Peter I in the 10th century. I ...
and the Paulicians
Paulicianism (Classical Armenian: Պաւղիկեաններ, ; , "The followers of Paul"; Arab sources: ''Baylakānī'', ''al Bayāliqa'' )Nersessian, Vrej (1998). The Tondrakian Movement: Religious Movements in the Armenian Church from the 4th ...
revolted and made common cause with the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
from beyond the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
. Paulician soldiers in imperial service likewise deserted during Alexios' battles with the Normans. As soon as the Norman threat had passed, Alexios set out to punish the rebels and deserters, confiscating their lands. This led to a further revolt near Philippopolis, and the commander of the field army in the west, Gregory Pakourianos, was defeated and killed in the ensuing battle. In 1087 the Pechenegs raided into Thrace, and Alexios crossed into Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
to retaliate but failed to take Dorostolon (Silistra
Silistra ( ; ; or ) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Silistra is the administrative center of the ...
). During his retreat, the emperor was confronted and defeated by the Pechenegs, who forced him to sign a truce and to pay protection money. In 1090 the Pechenegs invaded Thrace again, while Tzachas
Chaka Bey (),"Tzachas" is the Hellenized form of a Turkish name which does not appear in any historical documents, but was likely "Chaka", "Chagha", or "Chaqan". The name "Chaka", in the modern Turkish alphabet "Çaka", prevailed especially i ...
, the brother-in-law of the Sultan of Rum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is often aged in barrels of oak. Rum originated in the Caribbean in the 17th century, but today it is produced i ...
, launched a fleet and attempted to arrange a joint siege of Constantinople with the Pechenegs. Alexios overcame this crisis by entering into an alliance with a horde of 40,000 Cumans
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cumania, Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Ru ...
, with whose help he conquered the Pechenegs at Levounion in Thrace on 29 April 1091.
This put an end to the Pecheneg threat, but in 1094 the Cumans began to raid the imperial territories in the Balkans. Led by a pretender claiming to be Constantine Diogenes
Constantine Diogenes (; died 1032) was a Byzantine general of the early 11th century, active in the Balkans. He served with distinction in the final stages of the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria under Emperor Basil II, and occupied high commands ...
, a long-dead son of the Emperor Romanos IV, the Cumans crossed the mountains and raided into eastern Thrace until their leader was eliminated at Adrianople
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
. With the Balkans more or less pacified, Alexios could now turn his attention to Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, which had been almost completely overrun by the Seljuq Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persian culture.
The founder of t ...
.
Byzantine–Seljuq Wars and the First Crusade
 By the time Alexios ascended the throne, the Seljuqs had taken most of Asia Minor. Alexios secured much of the coastal regions by sending peasant soldiers to raid the Seljuq camps, but this did not stop the Turks altogether. He also got military support from Western rulers like
By the time Alexios ascended the throne, the Seljuqs had taken most of Asia Minor. Alexios secured much of the coastal regions by sending peasant soldiers to raid the Seljuq camps, but this did not stop the Turks altogether. He also got military support from Western rulers like Robert I, Count of Flanders
Robert I ( – 13 October 1093), known as Robert the Frisian, was count of Flanders from 1071 until his death in 1093. He was a son of Baldwin V, Count of Flanders, and the younger brother of Baldwin VI, Count of Flanders. He usurped the countsh ...
(Robert the Frisian). Robert, while returning from an armed pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a travel, journey to a holy place, which can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) w ...
to Jerusalem in 1086, spent time assisting the Byzantine Emperor against the Turks. In one battle, Robert and three of his companions rode ahead of the main army, charging the forces under the command of Kerbogha
Qiwam al-Dawla Kerbogha (), known as Kerbogha or Karbughā, was the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman List of rulers of Mosul#Seljuk Atabegs, atabeg of Mosul during the First Crusade and was renowned as a soldier.
Early life
Kerbogha was a Selju ...
, whose forces were scattered completely.
As early as 1090, Alexios had taken reconciliatory measures towards the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, with the intention of seeking western support against the Seljuqs. In 1095 his ambassadors appeared before Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II (; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening the Council of Clermon ...
at the Council of Piacenza. The help he sought from the West was some mercenary forces, not the immense hosts that arrived, to his consternation and embarrassment, after the pope preached the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
at the Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
While the council ...
later that same year. This was the People's Crusade
The People's Crusade was the beginning phase of the First Crusade whose objective was to retake the Holy Land, and Jerusalem in particular, from Islamic rule. In 1095, after the head of the Roman Catholic Church Pope Urban II started to urge faith ...
: a mob of mostly unarmed poor peasants and serfs, led by the preacher Peter the Hermit
Peter the Hermit ( 1050 – 8 July 1115 or 1131), also known as Little Peter, Peter of Amiens (French language, fr. ''Pierre d'Amiens'') or Peter of Achères (French language, fr. ''Pierre d'Achères''), was a Roman Catholic priest of Amiens and ...
, fleeing from hunger in their home regions to a promised land of milk and honey. Not quite ready to supply this number of people as they traversed his territories, the emperor saw his Balkan possessions subjected to further pillage at the hands of his own allies. Eventually Alexios dealt with the People's Crusade by hustling them on to Asia Minor. There, they were massacred by the Turks of Kilij Arslan I
Kilij Arslan ibn Suleiman (; ; or ''Kılıcarslan'', "Sword Lion") (1079–1107) was the Seljuk sultan of Rûm. He reigned from 1092 until his death in 1107. He ruled the Sultanate during the time of the First Crusade and thus faced the ...
at the Battle of Civetot
The Battle of Civetot was fought between the forces of the People's Crusade and of the Seljuk Turks of Anatolia on 21 October 1096. The battle brought an end to the People's Crusade; some of the survivors joined the Princes' Crusade.
Backgrou ...
in October 1096.Kazhdan 1991, p. 1479
The "Prince's Crusade", the second and much more formidable host of Crusaders, gradually made its way to Constantinople, led in sections by Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon (; ; ; ; 1060 – 18 July 1100) was a preeminent leader of the First Crusade, and the first ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem from 1099 to 1100. Although initially reluctant to take the title of king, he agreed to rule as pri ...
, Bohemond of Taranto, Raymond IV of Toulouse
Raymond of Saint-Gilles ( 1041 – 28 February 1105), also called Raymond IV of Toulouse or Raymond I of Tripoli, was the count of Toulouse, duke of Narbonne, and margrave of Provence from 1094, and one of the leaders of the First Crusade from ...
, and other important western nobles. Alexios met the Crusader leaders separately as they arrived, extracting from them oaths of homage and the promise to turn over conquered lands to the Byzantine Empire. Transferring each contingent into Asia, Alexios promised to supply them with provisions in return for their oaths of homage. The Crusade was a notable success for Byzantium, as Alexios recovered a number of important cities and islands. The siege of Nicaea
The siege of Nicaea was the first major battle of the First Crusade, taking place from 14 May to 19 June 1097. The city was under the control of the Seljuk Turks who opted to surrender to the Byzantines in fear of the crusaders breaking into the ...
by the Crusaders forced the city to surrender to the emperor in 1097, and the subsequent Crusader victory at Dorylaion
Dorylaeum or Dorylaion (; ) was an ancient city in Anatolia. It is now an archaeological site located near the city of Eskişehir, Turkey.
Its original location was about 10 km southwest of Eskişehir, at a place now known as Karaca Hisar ...
enabled Alexios to recover much of western Asia Minor.Norwich 1995, p. 42 John Doukas re-established Byzantine rule in Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
, Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
, Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna ...
, Ephesus
Ephesus (; ; ; may ultimately derive from ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, in present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital ...
, Sardis
Sardis ( ) or Sardes ( ; Lydian language, Lydian: , romanized: ; ; ) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Lydia (satrapy) ...
, and Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
in 1097–1099. This success is ascribed by Alexios' daughter Anna to his policy and diplomacy, but by the Latin historians of the crusade to his treachery and deception. In 1099, he sent a Byzantine fleet of ten ships to assist the Crusaders in capturing Laodicea and other coastal towns as far as Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis (from , meaning "three cities") may refer to:
Places Greece
*Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in the Pelasgiotis district, Thessaly, near Larissa ...
. The Crusaders believed their oaths were made invalid when the Byzantine contingent under Tatikios
Tatikios or Taticius (, c. 1048 – died after 1110) was an Eastern Roman general of Turkish origin during the reign of Alexios I Komnenos. His name is also rendered as Tetigus, Tatizius, Tatitius, Tatic, or Tetig.
Origins and early life
The fa ...
failed to help them during the siege of Antioch
The siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusaders' way to Jerusalem through Syria (region), Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Sel ...
; Bohemund, who had set himself up as Prince of Antioch
Prince of Antioch was the title given during the Middle Ages to Normans, Norman rulers of the Principality of Antioch, a region surrounding the city of Antioch, now known as Antakya in Turkey. The Princes originally came from the County of Sicil ...
, did not return the ancient city, despite his previous agreement with Alexios. He briefly went to war with Alexios in the Balkans, but he was blockaded by the Byzantine forces and agreed to become a vassal of Alexios by the Treaty of Deabolis in 1108.
Around this time, in 1106, the twenty-fifth year of his reign, Hesychius of Miletus
Hesychius of Miletus (), Greek chronicler and biographer, surnamed Illustrius, son of an advocate, lived in Constantinople in the 6th century AD during the reign of Justinian. His writings contain more references to pagan Greek culture than Christi ...
records that the sky suddenly darkened and a "violent southern wind" blew the great statue of Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
* Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine g ...
at the Strategion from its column, killing a number of men and women nearby.
In 1116, though already terminally ill, Alexios conducted a series of defensive operations in Bithynia and Mysia to defend his Anatolian territories against the inroads of Malik Shah Malik-Shah (), also transliterated as ''Malek-Shah'', ''Malikshah'' or ''Melikshah'', may refer to:
* Malik-Shah I (1055–1092), sultan of Great Seljuq
* Malik-Shah II (), grandson of Malik Shah I, sultan of Great Seljuq
* Malik-Shah III (1152– ...
, the Seljuq Sultan of Iconium. In 1117 he moved onto the offensive and pushed his army deep into the Turkish-dominated Anatolian Plateau, where he defeated the Seljuq sultan at the Battle of Philomelion
The Battle of Philomelion ( Latinised as Philomelium - modern Akşehir) of 1116 consisted of a series of clashes over a number of days between a Byzantine expeditionary army under Emperor Alexios I Komnenos and the forces of the Sultanate of Rûm ...
.
Personal life
During the last twenty years of his life Alexios lost much of his popularity. The years were marked by persecution of the followers of the Paulician andBogomil
Bogomilism (; ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", bogumilstvo, богумилство) was a Christian neo-Gnostic, dualist sect founded in the First Bulgarian Empire by the priest Bogomil during the reign of Tsar Peter I in the 10th century. I ...
heresies—one of his last acts was publicly to burn at the stake Basil
Basil (, ; , ; ''Ocimum basilicum'' (, )), also called great basil, is a culinary herb of the family Lamiaceae (mints). It is a hardiness (plants), tender plant, and is used in cuisines worldwide. In Western cuisine, the generic term "basil" r ...
, a Bogomil leader, with whom he had engaged in a theological dispute. In spite of the success of the First Crusade, Alexios also had to repel numerous attempts on his territory by the Seljuqs in 1110–1117.
Alexios was for many years under the strong influence of an ''eminence grise'', his mother Anna Dalassene
Anna Dalassene (; ca. 1025/30 – 1 November 1100/02) was an important Byzantine noblewoman who played a significant role in the rise to power of the Komnenoi in the eleventh century. She exercised great influence over her son, the Emperor Alexi ...
, a wise and immensely able politician whom, in a uniquely irregular fashion, he had crowned as '' Augusta'' instead of the rightful claimant to the title, his wife Irene Doukaina. Anna Dalassene's ability to help him seize power and control the aristocracy, as well as her ability to understand and resolve dilemmas, assured Alexios that his mother was a capable counsel and managing partner by his side, and a sane and trusted regent in his absence. Alexios was never happier than when taking part in military exercises and he assumed personal command of his troops whenever possible. As such, Dalassene was the effective administrator of the Empire during Alexios' long absences in military campaigns: she was constantly at odds with her daughter-in-law and had assumed total responsibility for the upbringing and education of her granddaughter Anna Komnene.
Succession
Alexios' last years were also troubled by anxieties over the succession. Although he had crowned his son John II Komnenos co-emperor at the age of five in 1092, his wife Irene Doukaina wished to alter the succession in favor of their daughter Anna and Anna's husband,Nikephoros Bryennios the Younger
Nikephoros Bryennios (or Nicephorus Bryennius; Greek: Νικηφόρος Βρυέννιος, ''Nikēphoros Bryennios; ''1062/82–1137) was a Byzantine general, statesman and historian. He was born at Orestias (Adrianople) in the theme of Macedonia ...
.Norwich 1995, p. 61
Pretenders and rebels
Apart from all of his external enemies, a host of rebels also sought to overthrow Alexios from the imperial throne, thereby posing another major threat to his reign. Due to the troubled times the empire was enduring, he faced more rebellions than any other Byzantine emperor.Finlay 1854, p. 71 These included:Pre First Crusade
* Raictor, a Byzantine monk who claimed to be the emperor Michael VII. He presented himself toRobert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard ( , ; – 17 July 1085), also referred to as Robert de Hauteville, was a Normans, Norman adventurer remembered for his Norman conquest of southern Italy, conquest of southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Robert was born ...
who used him as a pretext to launch his invasion of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
.
* A conspiracy in 1084 involving several senators and officers of the army. This was uncovered before too many followers were enlisted. In order to conceal the importance of the conspiracy, Alexios merely banished the wealthiest plotters and confiscated their estates.
* Tzachas
Chaka Bey (),"Tzachas" is the Hellenized form of a Turkish name which does not appear in any historical documents, but was likely "Chaka", "Chagha", or "Chaqan". The name "Chaka", in the modern Turkish alphabet "Çaka", prevailed especially i ...
, a Seljuq Turkic emir who assumed the title of emperor in 1092.Finlay 1854, p. 72
* Constantine Humbertopoulos, who had assisted Alexios in gaining the throne in 1081 conspired against him in 1091 with an Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
called Ariebes.
* John Komnenos, Alexios' nephew, governor of Dyrrachium, accused of a conspiracy by Theophylact of Bulgaria.
* Theodore Gabras
Theodore Gabras () was a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine governor in the Pontus (region), Pontus who was involved in a minor unsuccessful rebellion against the Byzantine Emperor, Emperor Alexios I Komnenos around the year 1091. He is an Eastern Orthodo ...
, the quasi-independent governor of Trebizond and his son Gregory.
* Michael Taronites
Michael Taronites (; ) was a Byzantine aristocrat and brother-in-law of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. He was involved in a conspiracy against him and was banished in 1094.
Biography
Michael belonged to the aristocratic family of the Taronitai, a pr ...
, the brother-in-law
A sibling-in-law is the spouse of one's sibling or the sibling of one’s spouse.
More commonly, a sibling-in-law is referred to as a brother-in-law for a male sibling-in-law and a sister-in-law for a female sibling-in-law.
Sibling-in-law al ...
of Alexios.
* Nikephoros Diogenes
Nikephoros Diogenes (), Latinized as Nicephorus Diogenes, was presumably a junior Byzantine emperor around 1069–1071. He was born 1069 to Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes and Empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa. He was elevated to junior emperor in 1 ...
, the son of emperor Romanos IV.
* Pseudo-Leo Diogenes, an impostor who assumed the identity of another of Romanos' sons, Leo Diogenes.Finlay 1854, p. 73
* Karykes
Karykes (, Latinised Caryces) was the Byzantine governor of Crete who led a rebellion that began in 1090 or 1091 and lasted into 1092 or 1093 during the reign of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. The principal narrative sources for the revolt are Anna K ...
, the leader of a revolt in Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
.
* Rhapsomates
Rhapsomates (or Rapsomates) () was a Byzantine official who led a revolt in the Theme of Cyprus in the early 1090s. Nothing is known about his life prior to the revolt apart from the fact that he served as an official in the region. The motivatio ...
, who tried to create an independent kingdom in Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
.
Post First Crusade
* Salomon, asenator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or Legislative chamber, chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior ...
of great wealth who in 1106 engaged in a plot with four brothers of the Anemas
Anemas () was the name of a Byzantine aristocratic family, attested from the 9th to the 15th centuries.
The origin and etymology of the name are uncertain; it may be connected to ''anemos'', "wind", although the philologist Phaedon Koukoules sugg ...
family.Finlay 1854, p. 74
* Gregory Taronites
Gregory Taronites (; ) was an Armenian prince of Taron, who went over to Byzantine service and held senior commands and governorships under Emperor Basil II. He was killed by the Bulgarians at an ambush near Thessalonica ca. 991 or 995.
Life
G ...
, another governor of Trebizond.
* The illegitimate descendant of a Bulgarian prince named Aron formed a plot in 1107 to murder Alexios as he was encamped near Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
. The presence of the empress Irene and her attendants, however, made the execution of the plot difficult. In an attempt to have her return to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, the conspirators produced pamphlets that mocked and slandered the empress, and left them in her tent. A search for the author of the publications uncovered the whole plot, yet Aron was only banished due to his connection to the royal line of Bulgaria, whose blood also flowed in the veins of the empress Irene.
Reform of the monetary system
 Under Alexios the debased ''
Under Alexios the debased ''solidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; : ''solidi'') or ''nomisma'' () was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Later Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. It was introduced in the early ...
'' (''tetarteron
The ''tetarteron'' (, "quarter oin) was a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine term applied to two different coins, one gold circulating from the 960s to 1092 in parallel to the ''histamenon'', and one copper used from 1092 to the second half of the 13t ...
'' and ''histamenon
''Histamenon'' (, ''histámenon ómisma' ) was the name given to the gold Byzantine Empire, Byzantine ''solidus (coin), solidus'' when the slightly lighter ''tetarteron'' was introduced in the 960s. To distinguish the two, the ''histamenon'' ...
'') was discontinued and a gold coinage of higher fineness (generally .900–.950) was established in 1092, commonly called the ''hyperpyron
The ''hyperpyron'' (, ''nómisma hypérpyron'' ) was a Byzantine coin in use during the late Middle Ages, replacing the '' solidus'' as the Byzantine Empire's standard gold coinage in the 11th century. It was introduced by emperor Alexios I Komneno ...
'' at 4.45 grs. The ''hyperpyron'' was slightly smaller than the ''solidus''.
It was introduced along with the electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially and is ...
'' aspron trachy'' worth a third of a ''hyperpyron'' and about 25% gold and 75% silver, the billon ''aspron trachy'' or '' stamenon'', valued at 48 to the ''hyperpyron'' and with 7% silver wash and the copper ''tetarteron
The ''tetarteron'' (, "quarter oin) was a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine term applied to two different coins, one gold circulating from the 960s to 1092 in parallel to the ''histamenon'', and one copper used from 1092 to the second half of the 13t ...
'' and '' noummion'' worth 18 and 36 to the billon ''aspron trachy''.
Legacy
 Alexios I had overcome dangerous crises and stabilised the Byzantine Empire, inaugurating a century of imperial prosperity and success. He had also profoundly altered the nature of the Byzantine government.Finlay 1854, p. 69 By seeking close alliances with powerful noble families, Alexios put an end to the tradition of imperial exclusivity and co-opted most of the nobility into his extended family and, through it, his government. Those who did not become part of this extended family were deprived of power and prestige. This measure, which was intended to diminish opposition, was paralleled by the introduction of new courtly dignities, like that of '' panhypersebastos'' given to Nikephoros Bryennios, or that of ''
Alexios I had overcome dangerous crises and stabilised the Byzantine Empire, inaugurating a century of imperial prosperity and success. He had also profoundly altered the nature of the Byzantine government.Finlay 1854, p. 69 By seeking close alliances with powerful noble families, Alexios put an end to the tradition of imperial exclusivity and co-opted most of the nobility into his extended family and, through it, his government. Those who did not become part of this extended family were deprived of power and prestige. This measure, which was intended to diminish opposition, was paralleled by the introduction of new courtly dignities, like that of '' panhypersebastos'' given to Nikephoros Bryennios, or that of ''sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' (, ; ; ), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers whose states bordered the Empire or were within its sphere of influence (Bulgarian Empire, Serbian Empire). The word is a compound ...
'' given to the emperor's brother Isaac Komnenos. Although this policy met with initial success, it gradually undermined the relative effectiveness of imperial bureaucracy by placing family connections over merit. Alexios' policy of integration of the nobility bore the fruit of continuity: every Byzantine emperor who reigned after Alexios I Komnenos was related to him by either descent or marriage.
Family
 By his marriage with
By his marriage with Irene Doukaina
Irene Doukaina or Ducaena (, ''Eirēnē Doúkaina''; – 19 February 1138) was a Byzantine empress by marriage to the Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. She was the mother of Emperor John II Komnenos and the historian Anna Komnene. She w ...
, Alexios I had the following children:
# Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene (; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine Greek historian. She is the author of the '' Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. Her work constit ...
(1 December 1083 – 1148/55), in her infancy she was betrothed to Constantine Doukas, and with him treated as co-ruler by her father until after the birth of John II. In 1097 she married Nikephoros Bryennios the Younger
Nikephoros Bryennios (or Nicephorus Bryennius; Greek: Νικηφόρος Βρυέννιος, ''Nikēphoros Bryennios; ''1062/82–1137) was a Byzantine general, statesman and historian. He was born at Orestias (Adrianople) in the theme of Macedonia ...
, later raised to ''Caesar''. Highly ambitious, after Alexios' death she tried unsuccessfully to usurp the throne. She then withdrew to a monastery, where she wrote her history of Alexios' reign. The couple had several children, but only four survived her.
# Maria Komnene (19 September 1085 – after 1136), initially betrothed to Gregory Gabras, but married to Nikephoros Katakalon. The couple had several children, but only two sons are known by name.
# John II Komnenos (13 September 1087 – 8 April 1143), who succeeded as emperor.
# Andronikos Komnenos (18 September 1091 – 1130/31), was named ''sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' (, ; ; ), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers whose states bordered the Empire or were within its sphere of influence (Bulgarian Empire, Serbian Empire). The word is a compound ...
'' and participated in several campaigns until his death from disease. He married Irene, likely a Russian princess, and had at least two sons.
# Isaac Komnenos (16 January 1093 – after 1152), ''sebastokrator''.
# Eudokia Komnene (14 January 1094 – ), who married the son of Constantine Iasites.
# Theodora Komnene (15 January 1096) who married (1) Constantine Kourtikes and (2) Constantine Angelos
Constantine Angelos (; – after 1166) was a Byzantine aristocrat who married into the Komnenian dynasty and served as a military commander under Manuel I Komnenos, serving in the western and northern Balkans and as an admiral against the Norma ...
. By him she was the grandmother of Emperors Isaac II Angelos and Alexios III Angelos
Alexios III Angelos (; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnenos (; Aléxios Komnēnós) associating himself with the Komnenos dynasty (from whi ...
, as well as the progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus () was one of the Greek Rump state, successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claimed to be the legitimate successor of the ...
. Through Isaac II's daughter Irene Angelina
Irene Angelina (; – 27 August 1208) was a Byzantine princess and member of the Angelos dynasty and by her two marriages Queen of Sicily in 1193 and Queen of Germany from 1198 to 1208.
Life
Irene was born in Constantinople (modern-day Ista ...
's children by Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208), styled Philip II in his charters, was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of Philip's older brother Henry VI, Holy Roman E ...
, she is an ancestor of many European royal families, including all European monarchs currently reigning.
# Manuel Komnenos, born February 1097 and known only from a manuscript now in Moscow, died probably soon after his birth
# Zoe Komnene, born March 1098 and known only from a manuscript now in Moscow, died probably soon after her birth
See also
*Byzantine army (Komnenian era)
The Byzantine army of the Komnenian era or Komnenian army was a force established by Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos during the late 11th/early 12th century. It was further developed during the 12th century by his successors John II Komneno ...
*List of Byzantine emperors
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Notes
Sources
Primary sources
*Secondary sources
* * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * *External links
Alexius coinage
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alexios 01 Komnenos * 1050s births 1118 deaths Year of birth uncertain 11th-century rebels 11th-century Byzantine emperors 1080s in the Byzantine Empire 1090s in the Byzantine Empire 1100s in the Byzantine Empire 1110s in the Byzantine Empire 12th-century Byzantine emperors Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Norman wars Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Seljuk wars Byzantine people of the Crusades Christian anti-Gnosticism Domestics of the Schools Nobilissimi Panhypersebastoi People associated with Xenophontos Monastery Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Pecheneg wars