Alcohol abuse during adolescence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
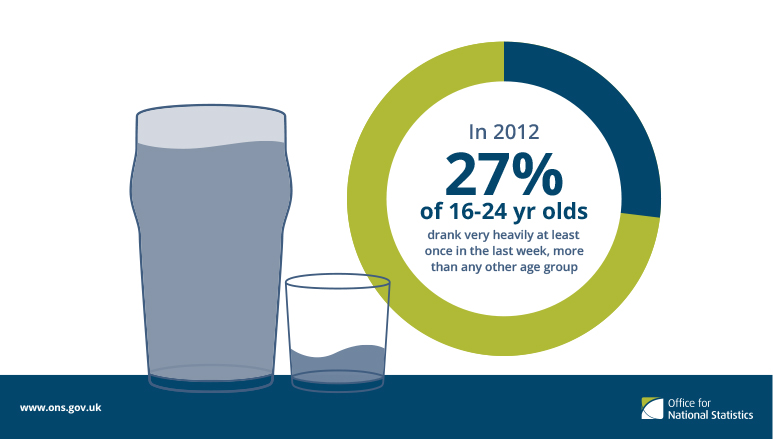 Most research is based on alcohol and the effects on people in general, essentially relating to adults. Little to no research is shown on the intake of alcohol throughout adolescents and the consequences that
Most research is based on alcohol and the effects on people in general, essentially relating to adults. Little to no research is shown on the intake of alcohol throughout adolescents and the consequences that
Marquis,
N. P. (2009). Substance Abuse Assessment, Interventions and Treatment :
Preventing and Reducing Underage Drinking. New York, NY, USA: Nova. Retrieved
from http://www.ebrary.com.ipacez.nd.edu.auhttps://ipacez.nd.edu.au/login?url=http://site.ebrary.com/lib/notredameaustralia/reader.action?docID=10661785&ppg=3 Another way in preventing underage drinking would be by reducing the cultural forces which are encouraging and supporting underage drinking will also contribute to preventing adolescents from consuming alcohol as a culture in which adolescents feel that it is acceptable, will allow them to think that it is appropriate. Another important component to preventing alcohol use disorder throughout adolescence is the responsibility of the government, to send a message to underage drinkers informing them how themselves and the rest of society strongly disapprove underage alcohol use because of the severe consequences it can cause and also informing that it will not be tolerated.
 A legal drinking age for the buying or consuming of alcohol is in place in many of the world's countries, typically with the intent to protect the young from alcohol-related harm.Callaghan, R. C., Sanches, M. and Gatley, J. M. (2013), Impacts of the minimum legal drinking age legislation on in-patient morbidity in Canada, 1997–2007: a regression-discontinuity approach. Addiction, 108: 1590–1600. This age varies between countries; for example, the legal drinking age for
A legal drinking age for the buying or consuming of alcohol is in place in many of the world's countries, typically with the intent to protect the young from alcohol-related harm.Callaghan, R. C., Sanches, M. and Gatley, J. M. (2013), Impacts of the minimum legal drinking age legislation on in-patient morbidity in Canada, 1997–2007: a regression-discontinuity approach. Addiction, 108: 1590–1600. This age varies between countries; for example, the legal drinking age for
Alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
is a liquid form substance which contains ethyl alcohol (also known formally as ethanol) that can cause harm and even damage to a person's DNA. "Alcohol consumption is recognized worldwide as a leading risk factor for disease, disability, and death" and is rated as the most used substance by adolescences. Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and psychological changes, usually a time in a person life in which they go through puberty. Combining these transitional stages and the intake of alcohol can leave a number of consequences for an adolescent.
Consequences of alcohol use disorder throughout adolescence
 Most research is based on alcohol and the effects on people in general, essentially relating to adults. Little to no research is shown on the intake of alcohol throughout adolescents and the consequences that
Most research is based on alcohol and the effects on people in general, essentially relating to adults. Little to no research is shown on the intake of alcohol throughout adolescents and the consequences that binge drinking
Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions ( see below) vary considerably.
Binge drinking ...
from a young age can create. "The rate of alcohol use increases sharply between the ages of 12 and 21 years, and adolescents frequently adopt a binge-like drinking pattern".Foltran, F., Gregori, D., Franchin, L., Verduci, E., & Giovannini, M. (2011). Effect of alcohol consumption in prenatal life, childhood, and adolescence on child development. Nutrition Reviews, 69(11), 642-659. These patterns can then lead to various consequences including automobile accidents, substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs (including alcohol) despite substantial harm and adverse consequences as a result of their use. Substance use disorders are characterized by an array of mental/emotional, physical, and ...
s, sexual activity, skipping school and failing grades. "Recent studies show that alcohol
consumption has the potential to trigger long-term biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
changes that may have detrimental effects on the developing adolescent brain, including neurocognitive impairment."
Underage drinking causes 5,000 deaths a year. 1,900 by motor vehicle, 1,600 involving homicides, 300 suicides.
Underaged drinking can cause higher risks for depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. If you're going through puberty, it can also cause changes in your hormones. It can also disrupt growth and puberty. And if you drink too much you can die from injury or alcohol poisoning. It also kills brain cells over time, which can cause behavioral changes, sleep deprivation, permanent damage to memory, and could eventually start to affect your grades. It can also lead to sexual behavior, and could also lead to sexually transmitted infections, unwanted pregnancy, and sexual assault or rape. It can also lead to these things: car accidents, falls or drowning, suicide, violence and homicide, being a victim of a violent crime, and many more accidents, that affect underage drinkers. And if a child drinks, they have a better chance of being an alcoholic when they are older. That means they might get drunk, be involved in drunken accidents, get into trouble with the law, their family, their friends, schools, and their love interest.
Reason for occurrence
Marquis states how " Adolescent alcohol use is not an acceptable rite of passage but a serious threat to adolescent development and health, as thestatistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
related to adolescent impairment, injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
, and death attest." Research shows how an adolescent makes the decision to consume alcohol because they are influenced by various factors. "These factors include normal maturational changes that all adolescents experience; genetic, psychological and social factors specific to each adolescent and the various social and cultural environments that surround adolescent, including their families, schools and communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place (geography), place, Norm (social), norms, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Identity (social science), identity. Communiti ...
". It is also shown that early onset of alcohol intake can lead to high levels of alcohol use in adulthood. Alcoholism throughout adolescents is increasing yearly for a number of different reasons. These reasons include:
* Availability of alcohol
* Peer pressure
* Role model
* Television
* Anxiety or stressK. S. Kendler, C. Gardner and D. M. Dick
(2011). Predicting alcohol consumption in adolescence from alcohol-specific and general externalizing genetic risk factors, key environmental exposures and their interaction. Psychological Medicine, 41,
pp 1507-1516. .
Prevention
There are a number of ways to preventingalcohol use disorder
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predomin ...
throughout adolescents. One of the main ways to do this is to "Promote an understanding of underage alcohol consumption in the context of human development and maturation that takes into account individual adolescent characteristics as well as environmental, ethic, cultural and gender differences".Legal drinking age
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
is 18, whereas the legal drinking age in the United States is 21.
See also
*Adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the t ...
* Short-term effects of alcohol consumption
The short-term effects of alcohol (more specifically ethanol) consumption range from a decrease in anxiety and motor skills and euphoria at lower doses to intoxication (drunkenness), to stupor, unconsciousness, anterograde amnesia (memory "black ...
* Long-term effects of alcohol consumption
The long-term heavy consumption of alcohol (alcohol use disorder) can cause severe detrimental effects. Health effects associated with alcohol intake in large amounts include an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder, malnutrition, ...
References