Alaska Native Corporation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Alaska Native Regional Corporations were established in 1971 when the
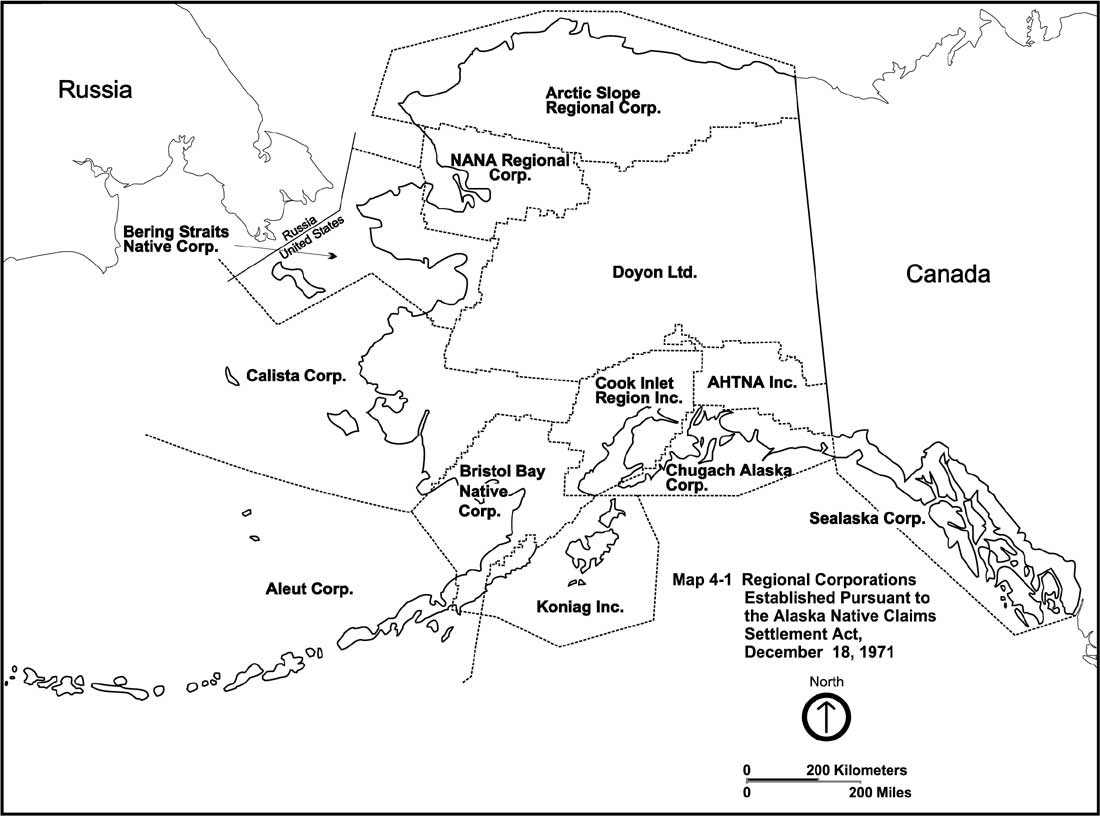 The thirteen regional corporations created under ANCSA are:
The thirteen regional corporations created under ANCSA are:
www.nativeco.com
The place to go for Alaska Native Corporation business, run b
www.morganhowardproductions.com
from the Justice Center, University of Alaska Anchorage.
The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act Resource Center
run b
Landye Bennett Blumstein LLP
www.ancsa.net
a portal dedicated to ANCSA run b
Karabelnikoff & Associates
{{USCensus Geography 1971 establishments in Alaska
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
passed the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) was signed into law by U.S. President, President Richard Nixon on December 18, 1971, constituting what is still the largest land claims settlement in United States history. ANCSA was intended to reso ...
(ANCSA) which settled land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of Earth not submerged by the ocean or another body of water. It makes up 29.2% of Earth's surface and includes all continents and islands. Earth's land sur ...
and financial claims made by the Alaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tli ...
and provided for the establishment of 13 regional corporations to administer those claims.
Associations, regional and village corporations
Under ANCSA the state was originally divided into twelve regions, each represented by a "Native association" responsible for the enrollment of past and present residents of the region. IndividualAlaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tli ...
enrolled in these associations, and their village level equivalents, were made shareholder in the Regional and Village Corporations created by the Act. The twelve for-profit regional corporations, and a thirteenth region representing those Alaska Natives who were no longer residents of Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
in 1971, were awarded the monetary and property compensation created by ANCSA. Village corporations and their shareholders received compensation through the regional corporations. The fact that many ostensibly Alaska Native villages throughout the state were not empowered by the ANCSA to form village corporations later led to a number of lawsuits.
The regional and village corporations are now owned by Alaska Native people through privately owned shares of corporation stock. Alaska Natives alive at ANCSA's enactment on December 17, 1971, who enrolled in a Native association (at the regional and/or village level) received 100 shares of stock in the respective corporation. In 2006, the 109th Congress passed S.449 which amended ANCSA, and allowed for shares to be more easily issued to those who had missed the enrollment, or were born after the enrollment period by reducing the requirement for voting from a majority of shareholders to a majority of attending shareholders at corporation meetings.
During the 1970s, ANCSA regional and village corporations selected land in and around native villages in the state in proportion to their enrolled populations. Village corporations own the surface rights to the lands they selected, but regional corporations own the subsurface rights of both their own selections and of those of the village corporations.
Text of the act
The Act lays out the specifics of the corporations' status. Here is an excerpt of the relevant portion: :43 U.S.C. § 1606 ::(a) Division of Alaska into twelve geographic regions; common heritage and common interest of region; area of region commensurate with operations of Native association; boundary disputes, arbitration. For purposes of this chapter, the State of Alaska shall be divided by the Secretary within one year after December 18, 1971, into twelve geographic regions, with each region composed as far as practicable of Natives having a common heritage and sharing common interests. In the absence of good cause shown to the contrary, such regions shall approximate the areas covered by the operations of the following existing Native associations: :::(1) Arctic Slope Native Association (Utqiaġvik
Utqiagvik ( ; , ), formerly known as Barrow ( ), is the borough seat and largest city of the North Slope Borough, Alaska, North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located north of the Arctic Circle, it is one of the List of northernmost ...
, Point Hope, Point Lay, Wainwright, Atqasuk, Nuiqsut, Kaktovik, Anaktuvuk Pass);
:::(2) Bering Straits Association (Seward Peninsula
The Seward Peninsula is a large peninsula on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska whose westernmost point is Cape Prince of Wales. The peninsula projects about into the Bering Sea between Norton Sound, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi ...
, Unalakleet, Saint Lawrence Island);
:::(3) Northwest Alaska Native Association ( Kotzebue);
:::(4) Association of Village Council Presidents (southwest coast, all villages in the Bethel
Bethel (, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; ; ) was an ancient Israelite city and sacred space that is frequently mentioned in the Hebrew Bible.
Bet ...
area, including all villages on the Lower Yukon River
The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon (itself named after the river). The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S ...
and the Lower Kuskokwim River);
:::(5) Tanana Chiefs' Conference ( Koyukuk, Middle and Upper Yukon River
The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon (itself named after the river). The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S ...
s, Upper Kuskokwim, Tanana River);
:::(6) Cook Inlet Association ( Kenai, Tyonek, Eklutna, Iliamna);
:::(7) Bristol Bay Native Association ( Dillingham, Upper Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq language, Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. T ...
);
:::(8) Aleutian Pribilof Islands Association, Inc., formerly the Aleut League (Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; , "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before Alaska Purchase, 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain ...
, Pribilof Islands and that part of the Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq language, Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. T ...
which is in the Aleut League);
:::(9) Chugach Native Association ( Cordova, Tatitlek, Port Graham, English Bay, Valdez, and Seward);
:::(10) Tlingit-Haida Central Council (southeastern Alaska, including Metlakatla);
:::(11) Kodiak Area Native Association (all villages on and around Kodiak Island
Kodiak Island (, ) is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the Un ...
); and
:::(12) Copper River Native Association ( Copper Center, Glennallen, Chitina, Mentasta).
: ..
::(c) Establishment of thirteenth region for nonresident Natives; majority vote; Regional Corporation for thirteenth region. ..
::(d) Incorporation; business for profit; eligibility for benefits; provisions in articles for carrying out chapter. Five incorporators within each region, named by the Native association in the region, shall incorporate under the laws of Alaska a Regional Corporation to conduct business for profit, which shall be eligible for the benefits of this chapter so long as it is organized and functions in accordance with this chapter. The articles of incorporation shall include provisions necessary to carry out the terms of this chapter.
 The thirteen regional corporations created under ANCSA are:
The thirteen regional corporations created under ANCSA are:
Alaska Native village corporations
There are over 200 village corporations, corresponding to the list of villages published in the text of ANCSA. Most corporations serve a single village, although some smaller villages have consolidated their corporations over the years. Afognak Native Corporation The Afognak Native Corporation was organized in 1977 through the merger of two ANCSA village corporations: Port Lions Native Corporation and Natives of Afognak, Inc. It is governed by a nine-member board of directors. Afognak Native Corporation has many business interests. For 18 years it participated in and profited from timber development ventures on Afogank Island. It operates a number of successful subsidiaries including leasing, bioenergy operations and oil field services. In the late 1990s, the Afognak Native Corporation launched a government contracting business. The Afognak Native Corporation is a wealthy corporation and was listed in the Top 100 Contractors of the Federal Government in 2010. Coming in at No. 79, The Afognak Native Corporation's contracts were $749,557,576.49. Afognak Native Corporation entities also received NASA Small Business Contractor of the Year Award in 2013. The Corporation's profile is listed as "Construction and Engineering" services. The Afognak Native Corporation has approximately 900 shareholders and pays over $12 million in dividends annually. The Afognak Native Corporation controls over 160,000 acres of land in the Kodiak Archipelago and the lands form the core of financial success of the corporation.Subsequent legislation and litigation
The federalIndian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975
The Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975 (Public Law 93-638) authorized the Secretary of the Interior, the Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare, and some other government agencies to enter into contracts with, ...
(ISDA) gave self-autonomy to both Native Indian tribal governments and to ANCs.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, the CARES Act
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2trillion Stimulus (economics), economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March ...
set aside about in funds for federally-recognized "tribal governments". The U.S. Treasury Department earmarked about of those funds for ANCs. While the federal government had generally recognized that ANCs fell under "tribal governments" since the passage of the ISDA, three Native Indian tribes from the lower 48 states sued the Treasury, asserting that the ANCs were not federally-recognized "tribal governments" under a statutory interpretation
Statutory interpretation is the process by which courts interpret and apply legislation. Some amount of interpretation is often necessary when a case involves a statute. Sometimes the words of a statute have a plain and a straightforward meani ...
of the law. That led to the United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that turn on question ...
case, '' Yellen v. Confederated Tribes of the Chehalis Reservation'', which was decided in June 2021 that under ISDA, the ANCs were federally-recognized "tribal governments" and thus qualified for CARES funds.
Financial performance
See also
Compare: * Makivik Corporation, an Inuit-owned company inNunavik
Nunavik (; ; ) is an area in Canada which comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homelan ...
, Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
created by a land claims agreement
* Nunatsiavut
Nunatsiavut (; ) is an autonomous area claimed by the Inuit in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement area includes territory in Labrador extending to the Quebec border. In 2002, the Labrador Inuit Association submitted a proposal for ...
, an autonomous Inuit Land Claims Area in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
* Emil Notti, key developer of ANCSA
Notes
References
*Gavin Kentch, ''A Corporate Culture? The Environmental Justice Challenges of the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act'', 81 813 (2012). * *External links
www.nativeco.com
The place to go for Alaska Native Corporation business, run b
www.morganhowardproductions.com
from the Justice Center, University of Alaska Anchorage.
The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act Resource Center
run b
Landye Bennett Blumstein LLP
www.ancsa.net
a portal dedicated to ANCSA run b
Karabelnikoff & Associates
{{USCensus Geography 1971 establishments in Alaska
Corporation
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the State (polity), state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as ...