Alamans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the
ELIOHS
This etymology has remained the standard derivation of the name. An alternative suggestion proposes derivation from '' *alah'' "sanctuary".
 Early Roman writers did not mention the Alemanni, and it is likely that they had not yet come to exist. In his ''
Early Roman writers did not mention the Alemanni, and it is likely that they had not yet come to exist. In his '' The Alemanni were first mentioned by
The Alemanni were first mentioned by
xvii.1.11
that much later the Emperor Julian undertook a
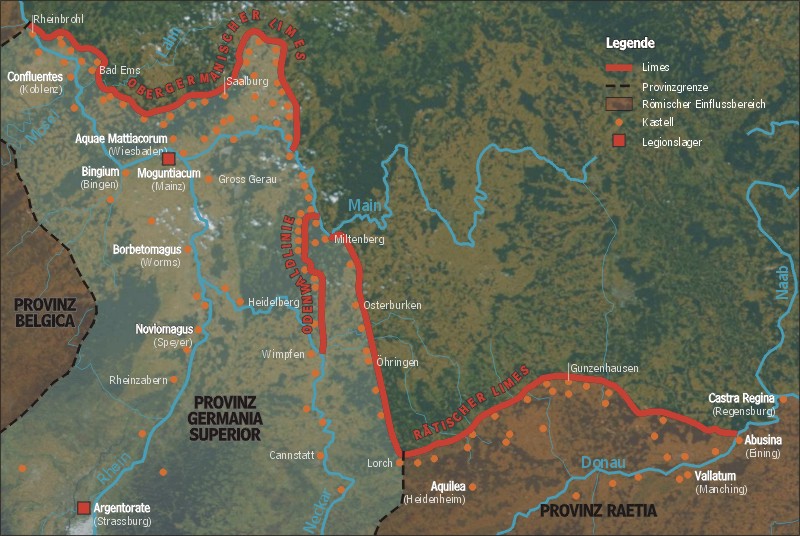 The Alemanni were continually engaged in conflicts with the
The Alemanni were continually engaged in conflicts with the
''Historia Francorum'' Book I.32–34
. Thus sixth-century Gallo-Romans of Gregory's class, surrounded by the ruins of
 * 259, Battle of Mediolanum Emperor Gallienus defeats the Alemanni to rescue Rome
* 268, Battle of Lake BenacusRomans under Emperor
* 259, Battle of Mediolanum Emperor Gallienus defeats the Alemanni to rescue Rome
* 268, Battle of Lake BenacusRomans under Emperor
 The kingdom of Alamannia between Strasbourg and Augsburg lasted until 496, when the Alemanni were conquered by
The kingdom of Alamannia between Strasbourg and Augsburg lasted until 496, when the Alemanni were conquered by
Book II.31
After their defeat in 496, the Alemanni bucked the Frankish yoke and put themselves under the protection of
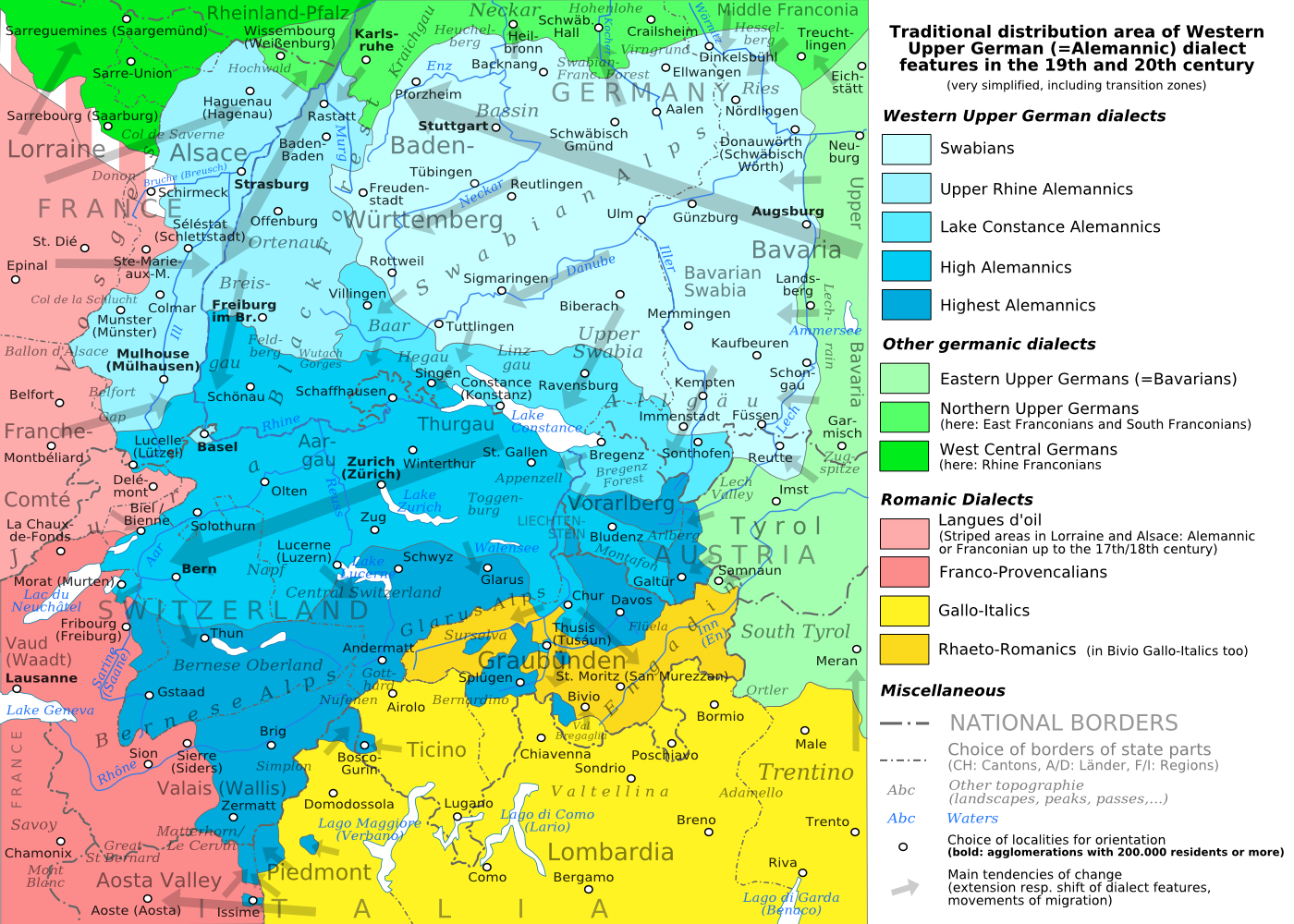 The German spoken today over the range of the former Alemanni is termed
The German spoken today over the range of the former Alemanni is termed
 The
The
The Agri Decumates
(archived)
(archived) * ttps://www.alemannische-seiten.de/bilder/schwaebisch-alemannische-fasnet/ Brauchtum und Masken Alemannic Fastnacht {{Authority control Early Germanic peoples Germanic tribal confederacies History of Swabia History of Alsace Medieval history of Switzerland
 The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine
Upper Rhine ( ; ; kilometres 167 to 529 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between the Middle Bridge, Basel, Middle Bridge in Basel, Switzerland, and the Rhine knee in Bingen am Rhein, Bingen, Germany. It is surrounded by the Upper Rhine P ...
River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname Caracalla (; ), was Roman emperor from 198 to 217 AD, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father and then r ...
of 213 CE, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
language in those regions, which by the eighth century were collectively referred to as ''Alamannia
Alamannia, or Alemania, was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic tribal confederation that had broken through the Roman '' limes'' in 213.
The Alemanni expanded from the Main River basin during the 3rd century and ...
''.
In 496, the Alemanni were conquered
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or legal prohibitions against conquest ...
by the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the ...
allies of the Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">st ...
over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia
Theudebald or Theutbald was the Duke of Alamannia from 730 until his deposition. He was a son of Gotfrid and brother and co-ruler with Lantfrid from 709.
In 727, Theudebald expelled Pirmin, the founder of Reichenau Abbey, out of a hatred for ...
, however, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish dukes.
During the later and weaker years of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
, the Alemannic counts became almost independent, and a struggle for supremacy took place between them and the Bishopric of Constance
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance () was a small Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its German Mediatisation, secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dual capacity as prince and as bisho ...
. The chief family in Alamannia was that of the counts of , who were sometimes called margraves, and one of whom, Burchard II, established the Duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (; ) was one of the five stem duchy, stem duchies of the medieval Kingdom of Germany, German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While th ...
, which was recognized by Henry the Fowler
Henry the Fowler ( or '; ; – 2 July 936) was the duke of Saxony from 912 and the king of East Francia from 919 until his death in 936. As the first non- Frankish king of East Francia, he established the Ottonian dynasty of kings and emper ...
in 919 and became a stem duchy
A stem duchy (, from '':wikt:Stamm, Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Baiuvarii, Bavarians and Alemanni, Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dyna ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
.
The area settled by the Alemanni corresponds roughly to the area where Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alemanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxi ...
dialects remain spoken, including German Swabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
and Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
, French Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
, German-speaking Switzerland
The German-speaking part of Switzerland ( ; ; ; ) comprises about 65 percent of Switzerland (North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switzerland, most of the Swiss Plateau and the greater part of the Swiss Alps).
The variety ...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
and Austrian Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
. The French-language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in ...
name of Germany
There are many widely varying names of Germany in different languages, more so than for any other European nation. For example:
* the German language endonym is , from the Old High German , meaning "of the people";
* the French exonym is , ...
, , is derived from their name, from Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th [2-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...
''aleman(t)'', and from French was loaned into a number of other languages, including Middle English, which commonly used the term ''Almains'' for Germans. Likewise, the Arabic name for Germany is (''Almanya''), the Turkish is ''Almanya'', the Spanish is ''Alemania'', the Portuguese is ''Alemanha'', the Welsh is ''Yr Almaen'' and the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
is (''Alman'').
Name
According to Gaius Asinius Quadratus (quoted in the mid-sixth century by Byzantine historianAgathias
Agathias Scholasticus (; Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 23–25582/594) was a Greek poet and the principal historian of part of the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian I between 552 and 558.
Biography
Agathias was a native of Myrina ( ...
), the name ''Alamanni'' (Ἀλαμανοι) means "all men". It indicates that they were a conglomeration drawn from various Germanic tribes. The Romans and the Greeks called them as such (Alamanni, all men, in the sense of a group composed of men of all groups in the region). This derivation was accepted by Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English essayist, historian, and politician. His most important work, ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1789, is known for ...
, in his ''Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'' and by the anonymous contributor of notes assembled from the papers of Nicolas Fréret, published in 1753.''Histoire de l'Académie Royale des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, avec les Mémoires de Littérature tirés des Registres de cette Académie, depuis l'année MDCCXLIV jusques et compris l'année MDCCXLVI'', vol. XVIII, (Paris 1753) pp. 49–71. Excerpts are on-line aELIOHS
This etymology has remained the standard derivation of the name. An alternative suggestion proposes derivation from '' *alah'' "sanctuary".
Walafrid Strabo
Walafrid, alternatively spelt Walahfrid, nicknamed Strabo (or Strabus, i.e. " squint-eyed") (c. 80818 August 849), was an Alemannic Benedictine monk and theological writer who lived on Reichenau Island in southern Germany.
Life
Walafrid Strab ...
in the ninth century remarked, in discussing the people of Switzerland and the surrounding regions, that only foreigners called them the Alemanni, but that they gave themselves the name of ''Suebi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
''.
The Suebi are given the alternative name of ''Ziuwari'' (as ''Cyuuari'') in an Old High German gloss, interpreted by Jacob Grimm
Jacob Ludwig Karl Grimm (4 January 1785 – 20 September 1863), also known as Ludwig Karl, was a German author, linguist, philologist, jurist, and folklorist. He formulated Grimm's law of linguistics, and was the co-author of the ''Deutsch ...
as ''Martem colentes'' ("worshippers of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
"). Annio da Viterbo a scholar and historian of the 15th century claimed the Alemanni had their name from the Hebrew language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language unti ...
, as in Hebrew the river Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
was translated into ''Mannum'' and the people who live at its shores were called ''Alemannus''. This was refuted by Beatus Rhenanus, a humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential, and agency of human beings, whom it considers the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humanism" ha ...
of the 16th century. Rhenanus argued the term Alemanni was meant for the whole Germanic people only in late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
and before it was only meant to designate the population of an island in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
.
First appearance in historical record
 Early Roman writers did not mention the Alemanni, and it is likely that they had not yet come to exist. In his ''
Early Roman writers did not mention the Alemanni, and it is likely that they had not yet come to exist. In his ''Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
'' Tacitus (AD 90) does not mention the Alemanni. He uses the term Agri Decumates to describe the region between the Rhine, Main and Danube rivers. He says that it had once been the home of the Helvetians, who had moved westwards into Gaul in the time of Julius Caesar. The people living there in Caesar's time are not Germanic. Instead, "Reckless adventurers from Gaul, emboldened by want, occupied this land of questionable ownership. After a while, our frontier having been advanced, and our military positions pushed forward, it was regarded as a remote nook of our empire and a part of a Roman province."
 The Alemanni were first mentioned by
The Alemanni were first mentioned by Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
describing the campaign of Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname Caracalla (; ), was Roman emperor from 198 to 217 AD, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father and then r ...
in 213. At that time, they apparently dwelt in the basin of the Main, to the south of the Chatti.
Cassius Dio portrays the Alemanni as victims of this treacherous emperor. They had asked for his help, according to Dio, but instead he colonized their country, changed their place names, and executed their warriors under a pretext of coming to their aid. When he became ill, the Alemanni claimed to have put a hex on him. Caracalla, it was claimed, tried to counter this influence by invoking his ancestral spirits.
In retribution, Caracalla then led the Legio II ''Traiana Fortis'' against the Alemanni, who lost and were pacified for a time. The legion was as a result honoured with the name ''Germanica.'' The fourth-century fictional Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, Caesar (title), designated heirs and Roman usurper, usurpers from 117 to 284. S ...
, ''Life of Antoninus Caracalla'', relates (10.5) that Caracalla then assumed the name ''Alemannicus,'' at which Helvius Pertinax
Publius Helvius Pertinax ( ; 1 August 126 – 28 March 193) was Roman emperor for the first three months of 193. He succeeded Commodus to become the first emperor during the tumultuous Year of the Five Emperors.
Born to the son of a freed sl ...
jested that he should really be called ''Geticus Maximus,'' because in the year before he had murdered his brother, Geta
Geta may refer to:
Places
*Geta (woreda), a woreda in Ethiopia's Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region
*Geta, Åland, a municipality in Finland
*Geta, Nepal, a town in Attariya Municipality, Kailali District, Seti Zone, Nepal
*Get� ...
.
Through much of his short reign, Caracalla was known for unpredictable and arbitrary operations launched by surprise after a pretext of peace negotiations. If he had any reasons of state for such actions, they remained unknown to his contemporaries. Whether or not the Alemanni had been previously neutral, they were certainly further influenced by Caracalla to become thereafter notoriously implacable enemies of Rome.
This mutually antagonistic relationship is perhaps the reason why the Roman writers persisted in calling the Alemanni "barbari," meaning "savages." The archaeology, however, shows that they were largely Romanized, lived in Roman-style houses and used Roman artefacts, the Alemannic women having adopted the Roman fashion of the ''tunic
A tunic is a garment for the torso, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the ankles. It might have arm-sleeves, either short or full-length. Most forms have no fastenings. The name deri ...
a'' even earlier than the men.
Most of the Alemanni were probably at the time, in fact, resident in or close to the borders of Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesont ...
. Although Dio is the earliest writer to mention them, Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquit ...
used the name to refer to Germans on the Limes Germanicus
The (Latin for ''Germanic frontier''), or 'Germanic Limes', is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier () fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman ...
in the time of Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
's governorship of the province shortly after it was formed, around 98–99 AD. At that time, the entire frontier was being fortified for the first time. Trees from the earliest fortifications found in Germania Inferior
''Germania Inferior'' ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed ''Germania Secunda'' in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Cl ...
are dated by dendrochronology
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of chronological dating, dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed in a tree. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, ...
to 99–100 AD.
Ammianus relatesxvii.1.11
that much later the Emperor Julian undertook a
punitive expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beha ...
against the Alemanni, who by then were in Alsace, and crossed the Main (Latin ''Menus''), entering the forest, where the trails were blocked by felled trees. As winter was upon them, they reoccupied a
"fortification which was founded on the soil of the Alemanni that Trajan wished to be called with his own name".
In this context, the use of Alemanni is possibly an anachronism, but it reveals that Ammianus believed they were the same people, which is consistent with the location of the Alemanni of Caracalla's campaigns.
Conflicts with the Roman Empire
 The Alemanni were continually engaged in conflicts with the
The Alemanni were continually engaged in conflicts with the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in the third and fourth centuries. They launched a major invasion of Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
and northern Italy in 268 when the Romans were forced to denude much of their German frontier of troops in response to a massive invasion of the Goths
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is ...
from the east. Their raids throughout the three parts of Gaul were traumatic: Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
(died ca 594) mentions their destructive force at the time of Valerian and Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empire. He ...
(253–260), when the Alemanni assembled under their "king", whom he calls Chrocus
Chrocus or Crocus (fl. 260–306 AD) was a leader of the Alamanni in the late 3rd to early 4th centuries. In 260, he led an uprising of the Alamanni against the Roman Empire, traversing the Upper Germanic Limes and advancing as far as Clermont-Fe ...
, who acted "by the advice, it is said, of his wicked mother, and overran the whole of the Gauls, and destroyed from their foundations all the temples which had been built in ancient times. And coming to Clermont he set on fire, overthrew and destroyed that shrine which they call ''Vasso Galatae'' in the Gallic tongue," martyring many Christians''Historia Francorum'' Book I.32–34
. Thus sixth-century Gallo-Romans of Gregory's class, surrounded by the ruins of
Roman temple
Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in culture of ancient Rome, Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Architecture of ancient Rome, Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete ...
s and public buildings, attributed the destruction they saw to the plundering raids of the Alemanni.
In the early summer of 268, the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empire. He ...
halted their advance into Italy but then had to deal with the Goths. When the Gothic campaign ended in Roman victory at the Battle of Naissus
The Battle of Naissus in 268 or 269 was the defeat of a Gothic coalition by the Roman Empire under Emperor Gallienus (or Emperor Claudius II Gothicus) and the future Emperor Aurelian near Naissus (Niš). The events around the invasion and the ...
in September, Gallienus' successor Claudius Gothicus
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – August/September 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Batt ...
turned north to deal with the Alemanni, who were swarming over all Italy north of the Po River
The Po ( , ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy, starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is , or if the Maira (river), Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. The headwaters of the Po are forme ...
.
After efforts to secure a peaceful withdrawal failed, Claudius forced the Alemanni to battle at the Battle of Lake Benacus in November. The Alemanni were routed, forced back into Germany, and did not threaten Roman territory for many years afterwards.
Their most famous battle against Rome took place in Argentoratum
Argentoratum or Argentorate was the ancient name of the city of Strasbourg. The name was first mentioned in 12 BC, when it was a Roman military outpost established by Nero Claudius Drusus. From 90 AD the Legio VIII Augusta was permanently statio ...
(Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
), in 357, where they were defeated by Julian, later Emperor of Rome, and their king Chnodomarius was taken prisoner to Rome.
On January 2, 366, the Alemanni yet again crossed the frozen Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
in large numbers, to invade the Gallic provinces, this time being defeated by Valentinian (see Battle of Solicinium). In the great mixed invasion of 406, the Alemanni appear to have crossed the Rhine river
The Rhine ( ) is one of the major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Cons ...
a final time, conquering and then settling what is today Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
and a large part of the Swiss Plateau. The crossing is described in Wallace Breem's historical novel '' Eagle in the Snow''. The Chronicle of Fredegar
The ''Chronicle of Fredegar'' is the conventional title used for a 7th-century Frankish chronicle that was probably written in Burgundy. The author is unknown and the attribution to Fredegar dates only from the 16th century.
The chronicle begi ...
gives the account. At ''Alba Augusta'' ( Alba-la-Romaine) the devastation was so complete, that the Christian bishop retired to Viviers, but in Gregory's account at Mende in Lozère
Lozère (; ) is a landlocked Departments of France, department in the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie in Southern France, located near the Massif Central, bounded to the northeast by Haute-Loire, to the ...
, also deep in the heart of Gaul, bishop Privatus was forced to sacrifice to idols in the very cave where he was later venerated. It is thought this detail may be a generic literary ploy to epitomize the horrors of barbarian violence.
List of battles between Romans and Alemanni
 * 259, Battle of Mediolanum Emperor Gallienus defeats the Alemanni to rescue Rome
* 268, Battle of Lake BenacusRomans under Emperor
* 259, Battle of Mediolanum Emperor Gallienus defeats the Alemanni to rescue Rome
* 268, Battle of Lake BenacusRomans under Emperor Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – August/September 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Batt ...
defeat the Alemanni.
* 271
** Battle of PlacentiaEmperor Aurelian
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disinte ...
is defeated by the Alemanni forces invading Italy
** Battle of Fano The Battle of Fano also known as the Battle of Fanum FortunaeMichael Grant, The History of Rome, p. 285 was fought in 271 between the Roman and the Juthungian armies. The Romans led by Emperor Aurelian, were victorious.
Background
Aurelian ...
Aurelian defeats the Alemanni, who begin to retreat from Italy
** Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, Holy Roman Empero ...
Aurelian destroys the retreating Alemanni army.
* 298
** Battle of LingonesCaesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war. He ...
Constantius Chlorus
Flavius Valerius Constantius ( – 25 July 306), also called Constantius I, was a Roman emperor from 305 to 306. He was one of the four original members of the Tetrarchy established by Diocletian, first serving as Caesar (title), ''caesar'' ...
defeats the Alemanni
** Battle of VindonissaConstantius defeats the Alemanni.
* 356, Battle of ReimsCaesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war. He ...
Julian is defeated by the Alemanni
* 357, Battle of StrasbourgJulian expels the Alemanni from the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
* 368, Battle of SoliciniumRomans under Emperor Valentinian I
Valentinian I (; 32117 November 375), also known as Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. He ruled the Western Roman Empire, Western half of the empire, while his brother Valens ruled the Byzantine Empire, East. During his re ...
defeat an Alemanni incursion.
* 378, Battle of ArgentovariaWestern Emperor Gratianus is victorious over the Alemanni.
* 451, Battle of the Catalaunian FieldsRoman General Aetius and his army of Romans and barbarian allies defeat Attila's army of Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
and other Germanic allies, including the Alemanni.
* 457, Battle of Campi CanniniAlemanni invade Italy and are defeated near Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore (, ; ; ; ; literally 'greater lake') or Verbano (; ) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest lake in Italy and the largest in southern Switzerland. The lake and its shoreline are divided be ...
by Majorian
Majorian (; 7 August 461) was Western Roman emperor from 457 to 461. A prominent commander in the Late Roman army, Western military, Majorian deposed Avitus in 457 with the aid of his ally Ricimer at the Battle of Placentia (456), Battle of Place ...
* 554, Battle of the VolturnusByzantine General Narses
Narses (also spelled Nerses; ; ; ; c. 478–573) was a distinguished Byzantine general and statesman of Armenian heritage, renowned for his critical role in Emperor Justinian I’s military campaigns. Alongside the famed Belisarius, Narses was ...
defeats a combined force of Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
and Alemanni in southern Italy.
Subjugation by the Franks
 The kingdom of Alamannia between Strasbourg and Augsburg lasted until 496, when the Alemanni were conquered by
The kingdom of Alamannia between Strasbourg and Augsburg lasted until 496, when the Alemanni were conquered by Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
at the Battle of Tolbiac
The Battle of Tolbiac was fought between the Franks, who were fighting under Clovis I, and the Alamanni, whose leader is not known. The date of the battle has traditionally been given as 496, though other accounts suggest it may either have been ...
. The war of Clovis with the Alemanni forms the setting for the conversion of Clovis, briefly treated by Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
.Book II.31
After their defeat in 496, the Alemanni bucked the Frankish yoke and put themselves under the protection of
Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526 ...
of the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populatio ...
but after his death they were again subjugated by the Franks under Theudebert I in 536. Subsequently, the Alemanni formed part of the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
dominions and were governed by a Frankish duke.
In 746, Carloman ended an uprising by summarily executing all Alemannic nobility at the blood court at Cannstatt, and for the following century, Alemannia was ruled by Frankish dukes. Following the treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (; ), agreed to on 10 August 843, ended the Carolingian civil war and divided the Carolingian Empire between Lothair I, Louis the German, Louis II and Charles the Bald, Charles II, the surviving sons of the emperor Louis the ...
of 843, Alemannia became a province of the eastern kingdom of Louis the German
Louis the German (German language, German: ''Ludwig der Deutsche''; c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany (German language, German: ''Ludwig II. von Deutschland''), was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 8 ...
, the precursor of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. The duchy persisted until 1268.
Culture
Language
 The German spoken today over the range of the former Alemanni is termed
The German spoken today over the range of the former Alemanni is termed Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alemanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxi ...
, and is recognised among the subgroups of the High German languages
The High German languages (, i.e. ''High German dialects''), or simply High German ( ) – not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called "High German" – comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Ben ...
. Alemannic runic inscriptions such as those on the Pforzen buckle are among the earliest testimonies of Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
. The High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development (sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic languages, West Germanic dialect continuum. The ...
is thought to have originated around the fifth century either in Alemannia or among the Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
; before that, the dialect spoken by Alemannic tribes was little different from that of other West Germanic peoples.
''Alemannia'' lost its distinct jurisdictional identity when Charles Martel
Charles Martel (; – 22 October 741), ''Martel'' being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Franks, Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of ...
absorbed it into the Frankish empire, early in the eighth century. Today, ''Alemannic'' is a linguistic term, referring to Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alemanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxi ...
, encompassing the dialects of the southern two-thirds of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
(German State), in western Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
(German State), in Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
(Austrian State), Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , ,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no #Conventions, defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others; ) is any of the Alemannic German, Alemannic ...
in Switzerland and the Alsatian language
Alsatian ( or "Alsatian German"; Lorraine Franconian: ''Elsässerdeitsch''; ; or ) is the group of Alemannic German dialects spoken in most of Alsace, a formerly disputed region in eastern France that has passed between French and German cont ...
of the Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
(France).
Political organization
The Alemanni established a series of territorially defined ''pagi'' (cantons) on the east bank of the Rhine. The exact number and extent of these ''pagi'' is unclear and probably changed over time. ''Pagi'', usually pairs of ''pagi'' combined, formed kingdoms (''regna'') which, it is generally believed, were permanent and hereditary. Ammianus describes Alemanni rulers with various terms: ''reges excelsiores ante alios'' ("paramount kings"), ''reges proximi'' ("neighbouring kings"), ''reguli'' ("petty kings") and ''regales'' ("princes"). This may be a formal hierarchy, or they may be vague, overlapping terms, or a combination of both. In 357, there appear to have been two paramount kings (Chnodomar and Westralp) who probably acted as presidents of the confederation and seven other kings (''reges''). Their territories were small and mostly strung along the Rhine (although a few were in the hinterland). It is possible that the ''reguli'' were the rulers of the two ''pagi'' in each kingdom. Underneath the royal class were the nobles (called ''optimates'' by the Romans) and warriors (called ''armati'' by the Romans). The warriors consisted of professional warbands and levies of free men. Each nobleman could raise an average of c. 50 warriors.Religion
 The
The Christianization
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individu ...
of the Alemanni took place during Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
times (sixth to eighth centuries). We know that in the sixth century, the Alemanni were predominantly pagan, and in the eighth century, they were predominantly Christian. The intervening seventh century was a period of genuine syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the ...
during which Christian symbolism and doctrine gradually grew in influence.
Some scholars have speculated that members of the Alemannic elite such as king Gibuld due to Visigothic
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the comman ...
influence may have been converted to Arianism
Arianism (, ) is a Christology, Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is co ...
even in the later fifth century.
In the mid-6th century, the Byzantine historian Agathias
Agathias Scholasticus (; Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 23–25582/594) was a Greek poet and the principal historian of part of the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian I between 552 and 558.
Biography
Agathias was a native of Myrina ( ...
records, in the context of the wars of the Goths and Franks against Byzantium, that the Alemanni fighting among the troops of Frankish king Theudebald
Theudebald (in modern English, ''Theobald''; in French, ''Thibaut'' or ''Théodebald''; in German, ''Theudowald'') (534 – 555), son of Theudebert I and Deuteria, was the king of Metz, Rheims, or Austrasia—as it is variously called ...
were like the Franks in all respects except religion, since
He also spoke of the particular ruthlessness of the Alemanni in destroying Christian sanctuaries and plundering churches while the genuine Franks were respectful towards those sanctuaries. Agathias expresses his hope that the Alemanni would assume better manners through prolonged contact with the Franks, which is by all appearances, in a manner of speaking, what eventually happened.
Apostles of the Alemanni were Columbanus
Saint Columbanus (; 543 – 23 November 615) was an Irish missionary notable for founding a number of monasteries after 590 in the Frankish and Lombard kingdoms, most notably Luxeuil Abbey in present-day France and Bobbio Abbey in presen ...
and his disciple Saint Gall
Gall (; 550 645) according to hagiographic tradition was a disciple and one of the traditional twelve companions of Columbanus on his mission from Ireland to the continent. However, he may have originally come from the border region betwe ...
. Jonas of Bobbio
Jonas of Bobbio (also known as Jonas of Susa) (Sigusia, now Susa, Italy, 600 – after 659 AD) was a Columbanian monk and a major Latin monastic author of hagiography. His ''Life of Saint Columbanus'' is "one of the most influential works of ...
records that Columbanus was active in Bregenz
Bregenz (; ) is the capital of Vorarlberg, the westernmost states of Austria, state of Austria. The city lies on the east and southeast shores of Lake Constance, the third-largest freshwater lake in Central Europe, between Switzerland in the wes ...
, where he disrupted a beer sacrifice to Wodan
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Emp ...
. Despite these activities, for some time, the Alemanni seem to have continued their pagan cult activities, with only superficial or syncretistic Christian elements. In particular, there was no change in burial practice, and tumulus warrior graves continued to be erected throughout Merovingian times. Syncretism of traditional Germanic animal style with Christian symbolism is also present in artwork, but Christian symbolism became more and more prevalent during the seventh century. Unlike the later Christianization of the Saxons and of the Slavs, the Alemanni seem to have adopted Christianity gradually, and voluntarily, spread in emulation of the Merovingian elite.
From c. the 520s to the 620s, there was a surge of Alemannic Elder Futhark inscriptions. About 70 specimens have survived, roughly half of them on fibulae, others on belt buckles (see Pforzen buckle, Bülach fibula) and other jewellery and weapon parts. The use of runes subsides with the advance of Christianity.
The Nordendorf fibula (early seventh century) clearly records pagan theonyms, ''logaþorewodanwigiþonar '' read as "Wodan and Donar are magicians/sorcerers", but this may be interpreted as either a pagan invocation of the powers of these deities, or a Christian protective charm against them.
A runic inscription on a fibula found at Bad Ems reflects Christian pious sentiment (and is also explicitly marked with a Christian cross), reading ''god fura dih deofile ᛭'' ("God for/before you, Theophilus!", or alternatively "God before you, Devil!"). Dated to between AD 660 and 690, it marks the end of the native Alemannic tradition of runic literacy. Bad Ems is in Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are ...
, on the northwestern boundary of Alemannic settlement, where Frankish influence would have been strongest.Wolfgang Jungandreas, 'God fura dih, deofile †' in: Zeitschrift für deutsches Altertum und deutsche Literatur, 101, 1972, pp. 84–85.
The establishment of the bishopric of Konstanz
Konstanz ( , , , ), traditionally known as Constance in English, is a college town, university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the Baden-Württemberg state of south Germany. The city ho ...
cannot be dated exactly and was possibly undertaken by Columbanus himself (before 612). In any case, it existed by 635, when Gunzo
:''The article is about the historical figure. For the Japanese magazine, see Gunzo''.
Gunzo (also ''Cunzo'') was a 7th-century duke of the Alamanni under Frankish sovereignty. His residence was at ''villa Iburninga'' (today's Überlingen) at L ...
appointed John of Grab bishop. Constance was a missionary bishopric in newly converted lands, and did not look back on late Roman church history unlike the Raetian bishopric of Chur
''
Chur (locally) or ; ; ; ; ; ; or ; , and . is the capital and largest List of towns in Switzerland, town of the Switzerland, Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of the Grisons and lies in the Alpine Rhine, Grisonian Rhine Valley, where ...
(established 451) and Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
(an episcopal seat from 740, and which continued the line of Bishops of Augusta Raurica, see Bishop of Basel
The Diocese of Basel (; ) is a Latin Church, Latin Catholic diocese in Switzerland.
Historically, the bishops of Basel were also secular rulers of the Prince-Bishopric of Basel (). Today the diocese of Basel includes the Swiss Cantons of Switze ...
). The establishment of the church as an institution recognized by worldly rulers is also visible in legal history. In the early seventh century '' Pactus Alamannorum'' hardly ever mentions the special privileges of the church, while Lantfrid
Lanfredus (Latinisation of names, Latinised from ''Lantfrid'' or ''Lanfred'') (died 730) was duke of Alamannia under Franks, Frankish sovereignty from 709 until his death. He was the son of duke Cotefredus. Lanfredus's brother was Theudebald (Ala ...
's ''Lex Alamannorum The Lex Alamannorum and Pactus Alamannorum were two early medieval law codes of the Alamanni. They were first edited in parts in 1530 by Johannes Sichard in Basel.
Pactus Alamannorum
The ''Pactus Alamannorum'' or ''Pactus legis Alamannorum'' is t ...
'' of 720 has an entire chapter reserved for ecclesial matters alone.
Genetics
A genetic study published in ''Science Advances
''Science Advances'' is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary open-access scientific journal established in early 2015 and published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. The journal's scope includes all areas of science.
Hist ...
'' in September 2018 examined the remains of eight individuals buried at a seventh-century Alemannic graveyard in Niederstotzingen, Germany. This is the richest and most complete Alemannic graveyard ever found. The highest-ranking individual at the graveyard was a male with Frankish grave goods. Four males were found to be closely related to him. They were all carriers of types of the paternal haplogroup R1b1a2a1a1c2b2b. A sixth male was a carrier of the paternal haplogroup R1b1a2a1a1c2b2b1a1 and the maternal haplogroup U5a1a1. Along with the five closely related individuals, he displayed close genetic links to northern and eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
, particularly Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
and Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
. Two individuals buried at the cemetery were found to be genetically different from both the others and each other, displaying genetic links to Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, C ...
, particularly northern Italy and Spain. Along with the sixth male, they might have been adoptees or slaves.
See also
*Annales Alamannici
The ''Annales Alamannici'' provide one of the earliest records of Medieval Europe available. The core text of the ''Annales Alamannici'' covers the years 709 through to 799. Spread over several Swabian monasteries, the annals were continued indep ...
* List of rulers of Alamannia
* List of confederations of Germanic tribes
* Armalausi
* Varisci
* Helvetii
The Helvetii (, , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. According to Ju ...
* Charietto
References
Sources
*Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquit ...
, ''passim''
* O. Bremer in H. Paul, ''Grundriss der germanischen Philologie'' (2nd ed., Strassburg, 1900), vol. iii. pp. 930 ff.
* Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
lxvii. ff.
*
* Ian Wood (ed.), ''Franks and Alamanni in the Merovingian Period: An Ethnographic Perspective (Studies in Historical Archaeoethnology)'', Boydell & Brewer Ltd, 2003, .
* Melchior Goldast, ''Rerum Alamannicarum scriptores'' (1606, 2nd ed. Senckenburg 1730)
* Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (born ; 30 November – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history". He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encom ...
, ''Historia Francorum'', book ii.
*
* C. Zeuss, ''Die Deutschen und die Nachbarstämme'' (Munich, 1837), pp. 303 ff.
External links
The Agri Decumates
(archived)
(archived) * ttps://www.alemannische-seiten.de/bilder/schwaebisch-alemannische-fasnet/ Brauchtum und Masken Alemannic Fastnacht {{Authority control Early Germanic peoples Germanic tribal confederacies History of Swabia History of Alsace Medieval history of Switzerland