Al Midya on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
al-Midya () is a
 Excavations near Midya in the 19th century suggested that graves of the
Excavations near Midya in the 19th century suggested that graves of the
 In 1870,
In 1870,
21
/ref> increasing in the 1931 census to 286, still all-Muslim, in 59 houses.Mills, 1932,
67
/ref> In the 1945 statistics, the population of el Midya was of 320 Muslims,Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics, 1945, p
30
/ref> who owned 7,020
File:Shilta 1944.jpg, Al-Midya on 1944 1:20,000 map based on 1919 survey
File:Burj 1945.jpg, Al-Midya on 1945 1:250,000 map (upper left quadrant)
341
ff, pic.) * p. 834-5? * * * * * * * * * * (pp.
235239
* *
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 14
IAAWikimedia commons
Al Midya Village (Fact Sheet)
Al Midya Village Profile
ARIJ
Al Midya aerial photo
ARIJ {{DEFAULTSORT:Midya, Al- Villages in the West Bank Municipalities of Palestine
Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
village in the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate
The Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate () is one of 16 governorates of Palestine. It covers a large part of the central West Bank, on the northern border of the Jerusalem Governorate. Its district capital or ''muhfaza'' (seat) is the city of ...
in the western West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, located west of Ramallah
Ramallah ( , ; ) is a Palestinians, Palestinian city in the central West Bank, that serves as the administrative capital of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the Judaean Mountains, north of Jerusalem, at an average elevation of abov ...
. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ) is the official statistical institution of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures at the national and international levels. It is a state institution that provid ...
, the village had a population of over 1,533 inhabitants in 2017.
Location
Al Midya is located (horizontally) west ofRamallah
Ramallah ( , ; ) is a Palestinians, Palestinian city in the central West Bank, that serves as the administrative capital of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the Judaean Mountains, north of Jerusalem, at an average elevation of abov ...
. It is bordered by Ni'lin
Ni'lin () is a Palestinian people, Palestinian town in the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate of the State of Palestine, in the central West Bank, located west of Ramallah. Ni'lin is about east of the 1949 Armistice Line (Green Line) bordered b ...
to the east and north, the Green Line (the Armistice Line 1949)
The Green Line, or 1949 Armistice border, is the demarcation line set out in the 1949 Armistice Agreements between the armies of Israel and those of its neighbors (Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria) after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. It serve ...
to the west, and Saffa The Schweizerische Ausstellung für Frauenarbeit (SAFFA), , was an exhibition that took place in Bern in 1928 and in Zurich in 1958. SAFFA was organized by the Bund Schweizerischer Frauenvereine (BFS, the Federation of Swiss Women's Associations), t ...
to the south.
History and archaeology
Iron Age to Byzantine period
Al-Midya is one of several sites identified with ancientModi'in
Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut ( ''Mōdīʿīn-Makkabbīm-Rēʿūt'') is a city located in central Israel, about southeast of Tel Aviv and west of Jerusalem, and is connected to those two cities via Route 443 (Israel), Highway 443. In the population ...
(also Modi'im and Moditha/Mwdyʽyn/t), hometown of the Hasmonean family. The name is thought to have been preserved in its Arabicised form ''al-Midya''.
The ancient village site is located at ''Ras al-Midya'', S-E of the modern village, where pottery from the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
and later periods has been found. Additional findings include the ruins of structures, watering holes, coins from the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
and Roman periods, and an underground hiding complex where five coins, including two from the Bar Kokhba revolt (130s CE), were discovered.
According to one theory, Modi'in occupied the site of ''Khirbet er-Râs'', directly to the south-east of the modern village. Other sites in the vicinity were also suggested. Based on the archeological data, as well as the site's location, Raviv suggests that it was a Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
settlement during the Early Roman period.
Possible family tomb of the Maccabees
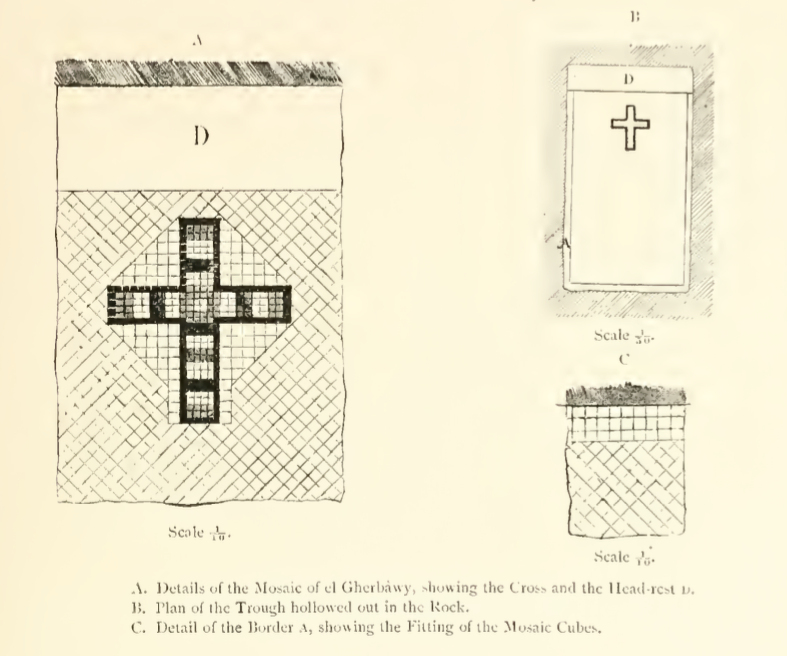
 Excavations near Midya in the 19th century suggested that graves of the
Excavations near Midya in the 19th century suggested that graves of the Maccabees
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees (, or , ; or ; , ), were a group of Jews, Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. Its leaders, the Hasmoneans, founded the Hasmonean dynasty ...
were located here. Seven triangular tombs were found, corresponding with the description of the first-century Jewish historian Josephus Flavius
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of pr ...
, who wrote that the family’s seven pyramid-shaped graves were erected in the same place. In 1870, an ancient structure near the gravesite of Sheikh al-Arabawi/Khirbet Sheikh Gharbawi (Hebrew: Horbat Ha-Gardi), adjacent to al-Midya, was identified as a Hasmonean grave, but this was rejected by another biblical archaeologist, Charles Clermont-Ganneau
Charles Simon Clermont-Ganneau (19 February 1846 – 15 February 1923) was a noted French Orientalist and archaeologist.
Biography
Clermont-Ganneau was born in Paris, the son of Simon Ganneau, a sculptor and mystic who died in 1851 when Clerm ...
. Further exploration by the Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, ; , before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of Antiquities. The IAA regulates excavation and conservatio ...
in the 21st century suggest the likelihood that Horbat Sheikh Gharbawi (Horbat Ha-Gardi) is either the original family tomb of the Maccabees, or was marking the alleged tomb in the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
period.
Mamluk period
Al-Midya was apparently mentioned during theMamluk period
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled medieval Egypt, Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military c ...
by the 14th-century Jewish doctor and geographer Ishtori Haparchi
Ishtori Haparchi (1280–1355), also Estori Haparchi and Ashtori ha-Parhi () is the pen name of the 14th-century Jewish physician, geographer, and traveller, Isaac HaKohen Ben Moses.''Encyclopedia Judaica'' Keter, Jerusalem, 1972, "Estori Ha-Parch ...
.Finkelstein and Lederman, 1997, pp. 131-134
Ottoman period
16th century
Al-Midya was incorporated into theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in 1517 with all of Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, and in the 1596 tax−records it appeared under the name of ''Midya as-Sarqiyya'' as being in the ''Nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiyeh, nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level divisi ...
'' of Ramla, part of Gaza Sanjak
Gaza Sanjak (), known in Arabic as Bilād Ghazza (the Land of Gaza), was a sanjak of the Damascus Eyalet of the Ottoman Empire centered in Gaza, and spread northwards up to the Yarkon River. In the 16th century it was divided into ''nawahi'' ...
. It had a population of 25 Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
households and paid a fixed tax rate of 25% on wheat, barley, summer crops or olives or fruit trees, and a press for olives or grapes; a total of 6,500 akçe
The ''akçe'' or ''akça'' (anglicized as ''akche'', ''akcheh'' or ''aqcha''; ; , , in Europe known as '' asper'') was a silver coin mainly known for being the chief monetary unit of the Ottoman Empire. It was also used in other states includi ...
.
19th century
 In 1870,
In 1870, Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (; 15 September 1821 – 21 September 1890) was a French people, French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included ...
visited, and thought that ruins found there were the graves of the Maccabees. However, Clermont-Ganneau
Charles Simon Clermont-Ganneau (19 February 1846 – 15 February 1923) was a noted French Orientalist and archaeologist.
Biography
Clermont-Ganneau was born in Paris, the son of Simon Ganneau, a sculptor and mystic who died in 1851 when Clerm ...
made extensive excavations later, and he found Christian crosses in the oldest part of the largest structure. He concluded the ruins were from the 5th century or later, that is, from the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
era.
An official Ottoman village list of about 1870 showed that ''el-medje'' had a total of 42 houses and a population of 159, though the population count included men only. It also noted that it was located half an hour east of Jimzu.
In 1882, PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine
The PEF Survey of Palestine was a series of surveys carried out by the Palestine Exploration Fund (PEF) between 1872 and 1877 for the completed Survey of Western Palestine (SWP) and in 1880 for the soon abandoned Survey of Eastern Palestine. The ...
'' described ''Midieh'' as being a village of a "good size", with houses either built of adobe
Adobe (from arabic: الطوب Attub ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for mudbrick. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is use ...
or stone. To the north was a small olive grove, to the south a tank. The most "peculiar feature" they found was named ''er Ras''. It was a high conical knoll, with a maqam
Maqam, makam, maqaam or maqām (plural maqāmāt) may refer to:
Musical structures
* Arabic maqam, melodic modes in traditional Arabic music
** Iraqi maqam, a genre of Arabic maqam music found in Iraq
* Persian maqam, a notion in Persian clas ...
on top, and rock-cut tombs on the side.
British Mandate
In the1922 census of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922.
The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The divis ...
conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Midya had an all-Muslim population of 245,Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Ramleh, p21
/ref> increasing in the 1931 census to 286, still all-Muslim, in 59 houses.Mills, 1932,
67
/ref> In the 1945 statistics, the population of el Midya was of 320 Muslims,Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics, 1945, p
30
/ref> who owned 7,020
dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; ; ; ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area analogous in role (but not equal) to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amo ...
s of land according to an official land and population survey. Of this, 688 dunams were plantations and irrigable land, 2,304 for cereals, while 8 dunams were built-up (urban) land.
Jordanian period
In the wake of the1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, and after the 1949 Armistice Agreements
The 1949 Armistice Agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt,rule
Rule or ruling may refer to:
Human activity
* The exercise of political or personal control by someone with authority or power
* Business rule, a rule pertaining to the structure or behavior internal to a business
* School rule, a rule th ...
.
The Jordanian census of 1961 found 570 inhabitants.
1967-present
Since theSix-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
in 1967, al-Midya has been under Israeli occupation
Israel has occupied the Golan Heights of Syria and the Palestinian territories since the Six-Day War of 1967. It has previously occupied the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt and southern Lebanon as well. Prior to 1967, control of the Palestinian terr ...
.
According to the Applied Research Institute–Jerusalem
The Applied Research Institute - Jerusalem (ARIJ; ) is a Palestinian NGO founded in 1990 with its main office in Bethlehem in the West Bank. ARIJ is actively working on research projects in the fields of management of natural resources, water m ...
, Al-Midya's total land area was 6,959 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; ; ; ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area analogous in role (but not equal) to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amo ...
s in 1942, but after 1948 most of the village's western land was expropriated, leaving 892 dunams, of which 217 were classified as built-up (urban) areas.
In 1986, when the population amounted to 570 people, largely dependent on agriculture, the villagers were woken at 3:00 a.m. by the arrival of Israeli military vehicles and were informed that a curfew would be in place until 9 pm that day. Throughout the day, roughly 1,000 Israelis, soldiers protecting the operation and workers from the Israeli Lands Administration and Nature Reserve authorities who drove bulldozers to grade a road down a steep hillside to a rough track running below it, and chainsawed an olive grove extending over 1,100 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; ; ; ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area analogous in role (but not equal) to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amo ...
s, destroying 3,000 trees. When the devastation was reported, Israel said the razing was to block Al-Midya from encroaching on Israeli state land, claiming that the olive trees were less than five years old, and planted to secure title to the area. Most cut trunks were over half a metre in diameter, suggesting centuries of growth.
After the 1995 accords, 7.4% of village land was classified as Area B, the remainder 92.6% as Area C
Area C (; ) is the fully Israeli-controlled territory in the West Bank, defined as the whole area outside the Palestinian enclaves (Areas A and B). Area C constitutes about 61 percent of the West Bank territory, containing most Israeli settle ...
. Israel has confiscated 186 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; ; ; ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area analogous in role (but not equal) to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amo ...
s of land from Al-Midya for the construction of the Israeli settlement
Israeli settlements, also called Israeli colonies, are the civilian communities built by Israel throughout the Israeli-occupied territories. They are populated by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Israeli Jews, Jewish identity or ethni ...
of Hashmonaim.
On 3 June 2022, a 17 year-old Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
by the name of Odeh Mohammed Odeh was shot dead by IDF personnel in the village.
See also
*Modi'in (ancient city)
Modi’in (, ''Mōdīʿīn''; also transliterated as Modein), also Modi’im (, ''Mōdīʿīm''), and later, Moditha (), was an ancient Jews, Jewish city located in Judea, near the modern city of Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut, Modi'in, Israel. First ment ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * (p341
ff, pic.) * p. 834-5? * * * * * * * * * * (pp.
235
* *
External links
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 14
IAA
Al Midya Village (Fact Sheet)
Applied Research Institute–Jerusalem
The Applied Research Institute - Jerusalem (ARIJ; ) is a Palestinian NGO founded in 1990 with its main office in Bethlehem in the West Bank. ARIJ is actively working on research projects in the fields of management of natural resources, water m ...
(ARIJ)Al Midya Village Profile
ARIJ
Al Midya aerial photo
ARIJ {{DEFAULTSORT:Midya, Al- Villages in the West Bank Municipalities of Palestine