African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an
American racial and ethnic group that consists of
Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
who have total or partial ancestry from any of the
Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
racial groups of
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. African Americans constitute the second largest ethno-racial group in the U.S. after
White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of
Africans enslaved in the United States.
In 2023, an estimated 48.3 million people self-identified as Black, making up 14.4% of the country’s population. This marks a 33% increase since 2000, when there were 36.2 million Black people living in the U.S.
African-American history
African-American history started with the forced transportation of List of ethnic groups of Africa, Africans to North America in the 16th and 17th centuries. The European colonization of the Americas, and the resulting Atlantic slave trade, ...
began in the 16th century, with Africans being sold to
European slave traders and
transported across the Atlantic to
the Western Hemisphere. They were
sold as slaves to European colonists and put to work on
plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
s, particularly
in the southern colonies. A few were able to achieve freedom through
manumission
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing slaves by their owners. Different approaches to manumission were developed, each specific to the time and place of a particular society. Historian Verene Shepherd states that the most wi ...
or escape, and founded independent communities before and during the
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
. After the United States was founded in 1783, most
Black people continued to be enslaved, primarily concentrated in the
American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is census regions United States Census Bureau. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the ...
, with four million enslaved people only
liberated with the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
in 1865. During
Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
, they gained
citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
and adult-males the
right to vote
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in representative democracy, public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in ...
; however, due to widespread
White supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
, they were treated as
second-class citizen
A second-class citizen is a person who is systematically and actively discriminated against within a state or other political jurisdiction, despite their nominal status as a citizen or a legal resident there. While not necessarily slaves, ou ...
s and soon
disenfranchised in the South. These circumstances changed due to participation in the
military conflicts of the United States, substantial
migration out of the South, the elimination of legal
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
, and the
civil rights movement which sought political and social freedom. However,
racism against African Americans
In the context of racism in the United States, racism against African Americans dates back to the Colonial history of the United States, colonial era, and it continues to be a persistent issue in Society of the United States, American society ...
and
racial socioeconomic disparity remain a problem into the 21st century.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, immigration has played an increasingly significant role in the African-American community. As of 2022, 10% of the U.S. Black population were immigrants, and 20% were either immigrants or the children of immigrants.
African-American culture
African-American culture, also known as Black American culture or Black culture in American English, refers to the cultural expressions of African Americans, either as part of or distinct from mainstream American culture. African-American/Bl ...
has had a significant influence on worldwide culture, making numerous contributions to
visual arts
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics (art), ceramics, photography, video, image, filmmaking, design, crafts, and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual a ...
,
literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
, the English language,
philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
, politics,
cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, List of cooking techniques, techniques and Dish (food), dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, ...
,
sports
Sport is a physical activity or game, often competitive and organized, that maintains or improves physical ability and skills. Sport may provide enjoyment to participants and entertainment to spectators. The number of participants in ...
, and
music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
. The African-American contribution to popular music is so profound that most
American music, including
jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
,
gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christianity, Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the second century Anno domino, AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message w ...
,
blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
,
rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock-n-roll, and rock 'n' roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from African ...
,
funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African-American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African-Americans in the ...
,
disco
Disco is a music genre, genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the late 1960s from the United States' urban nightclub, nightlife, particularly in African Americans, African-American, Italian-Americans, Italian-American, LGBTQ ...
,
house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air c ...
,
techno
Techno is a genre of electronic dance music (EDM) which is generally produced for use in a continuous DJ set, with tempos being in the range from 120 to 150 beats per minute (bpm). The central rhythm is typically in common time ( ) and often ...
,
hip hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip- ...
,
R&B,
trap, and
soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that ...
, has its origins either partially or entirely in the African-American community.
History
Colonial era

The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the
transatlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
were people from several
Central and
West African
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Ma ...
ethnic groups. They had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids, or sold by other West Africans, or by half-European "merchant princes" to European slave traders, who brought them to the Americas.
The first African slaves in what is now the United States arrived in the early 16th century. Africans were Among
Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León ( – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Puerto Rico in 1508 and Florida in 1513. He was born in Santervás de Campos, Valladolid, Spain, in ...
's 1513 voyage that landed in what would become
Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida () was the first major European land-claim and attempted settlement-area in northern America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and th ...
, and enslaved Africans arrived around the same time to
Spanish Puerto Rico.
Africans also came via
Santo Domingo
Santo Domingo, formerly known as Santo Domingo de Guzmán, is the capital and largest city of the Dominican Republic and the List of metropolitan areas in the Caribbean, largest metropolitan area in the Caribbean by population. the Distrito Na ...
in the
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
to the
San Miguel de Gualdape
San Miguel de Gualdape (sometimes San Miguel de Guadalupe) was a short-lived Spanish colony founded in 1526 by Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón. It was established somewhere on the coast of present-day Georgetown, South Carolina, but the exact locati ...
colony (most likely located in the
Winyah Bay
Winyah Bay is a coastal estuary that is the confluence of the Waccamaw River, the Pee Dee River, the Black River, and the Sampit River in Georgetown County, in eastern South Carolina. Its name comes from the Winyah people, who inhabited th ...
area of present-day
South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
), founded by Spanish explorer
Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón
Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón ( – 18 October 1526) was a Spanish magistrate and explorer who in 1526 established the short-lived San Miguel de Gualdape colony, one of the first European attempts at a settlement in what is now the United States. Ayl ...
in 1526.
The ill-fated colony was almost immediately disrupted by a fight over leadership, during which the slaves revolted and fled the colony to seek refuge among local
Native Americans. De Ayllón and many of the colonists died shortly afterward, due to an epidemic and the colony was abandoned. The settlers and the slaves who had not escaped returned to the Island of
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ) is an island between Geography of Cuba, Cuba and Geography of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the second-largest by List of C ...
, whence they had come.
The enslaved explorer
Esteban Esteban () is a Spanish male given name, derived from Greek Στέφανος (Stéphanos) and related to the English names Steven and Stephen. Although in its original pronunciation the accent is on the penultimate syllable, English-speakers tend ...
arrived in Florida with the
Narváez expedition
The Narváez expedition was a Spanish expedition started in 1527 that was intended to explore Florida and establish colonial settlements. The expedition was initially led by Pánfilo de Narváez, who died in 1528. Many more people died as the e ...
in 1528, a journey that first landed in Santo Domingo and later traveled into
Spanish Texas
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1519 until 1821. Spain claimed ownership of the region in 1519. Slave raids by Spaniards into what became Texas began in the 16th century and created ...
and the
Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west— ...
before ending in Mexico.
The marriage between Luisa de Abrego, a free Black domestic servant from
Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, ...
, and Miguel Rodríguez, a White
Segovia
Segovia ( , , ) is a city in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the Province of Segovia. Segovia is located in the Meseta central, Inner Pl ...
n conquistador in 1565 in
St. Augustine (Spanish Florida), is the first known and recorded Christian marriage anywhere in what is now the continental United States.

The first recorded Africans in
English America (including most of the future United States) were
"20 and odd negroes" who arrived in
Jamestown,
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
via
Cape Comfort in August 1619 as
indentured servant
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as paymen ...
s. As many Virginian settlers began to die from harsh conditions, more and more Africans were brought to work as laborers.
An indentured servant (who could be White or Black) would work for several years (usually four to seven) without wages. The status of indentured servants in early Virginia and Maryland was similar to slavery. Servants could be bought, sold, or leased, and they could be physically beaten for disobedience or attempting to running away. Unlike slaves, they were freed after their term of service expired or if their freedom was purchased. Their children did not inherit their status, and on their release from contract they received "a year's provision of corn, double apparel, tools necessary", and a small cash payment called "freedom dues". Africans could legally raise crops and cattle to purchase their freedom. They raised families, married other Africans and sometimes
intermarried with Native Americans or European
settler
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a Human settlement, settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among ...
s.

By the 1640s and 1650s, several African families owned farms around
Jamestown, and some became wealthy by colonial standards and purchased indentured servants of their own. In 1640, the Virginia General Court recorded the earliest documentation of lifetime slavery when they sentenced
John Punch, a Negro, to lifetime servitude under his master
Hugh Gwyn, for running away.
In
Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida () was the first major European land-claim and attempted settlement-area in northern America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and th ...
, some
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
married or had
unions with Pensacola
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only city in Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which ha ...
,
Creek or
African women, both enslaved and free, and their descendants created a mixed-race population of
mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturall ...
s and
mulatto
( , ) is a Race (human categorization), racial classification that refers to people of mixed Sub-Saharan African, African and Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the ...
s. The Spanish encouraged slaves from the
colony of Georgia to come to Florida as a refuge, promising freedom in exchange for conversion to
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.
King Charles II issued a royal proclamation freeing all slaves who fled to Spanish Florida and accepted conversion and baptism. Most went to the area around
St. Augustine, but escaped slaves also reached Pensacola. St. Augustine had mustered an all-Black
militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
unit defending Spanish Florida as early as 1683.

One of the Dutch African arrivals,
Anthony Johnson, would later own one of the first Black "slaves",
John Casor, resulting from the court ruling of a civil case.
[John Henderson Russell, ''The Free Negro In Virginia, 1619–1865''](_blank)
Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press, 1913, pp. 29–30, scanned text online.
The popular conception of a race-based slave system did not fully develop until the 18th century. The
Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company () was a Dutch chartered company that was founded in 1621 and went defunct in 1792. Among its founders were Reynier Pauw, Willem Usselincx (1567–1647), and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was gra ...
introduced slavery in 1625 with the importation of eleven Black slaves into
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
(present-day New York City). All the colony's slaves, however, were freed upon its surrender to the English.
Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
was the first English colony to legally recognize slavery in 1641. In 1662, Virginia passed a law that children of enslaved women would take the status of the mother, rather than that of the father, as was the case under
common law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on prece ...
. This legal principle was called ''
partus sequitur ventrum''.
[Taunya Lovell Banks, "Dangerous Woman: Elizabeth Key's Freedom Suit – Subjecthood and Racialized Identity in Seventeenth Century Colonial Virginia"](_blank)
, 41 ''Akron Law Review'' 799 (2008), Digital Commons Law, University of Maryland Law School. Retrieved April 21, 2009
By an act of 1699, Virginia ordered the deportation of all free Blacks, effectively defining all people of African descent who remained in the colony as slaves.
[William J. Wood, "The Illegal Beginning of American Slavery"](_blank)
, ''ABA Journal'', 1970, American Bar Association In 1670, the colonial assembly passed a law prohibiting free and baptized Blacks (and Native Americans) from purchasing Christians (in this act meaning White Europeans) but allowing them to buy people "of their owne nation".

In
Spanish Louisiana
Louisiana (, ), was a province of New Spain from 1762 to 1801. It was primarily located in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of the Mississippi River plus New Orleans. The area had originally been claimed and controlle ...
, although there was no movement toward abolition of the African slave trade, Spanish rule introduced a new law called
''coartación'', which allowed slaves to buy their freedom, and that of others. Although some did not have the money to do so, government measures on slavery enabled the existence of many free Blacks. This caused problems to the Spaniards with the
French creoles
The French Louisianians (), also known as Louisiana French, are French people native to the U.S., states that were established out of French Louisiana. They are commonly referred to as French Creole peoples, Creoles ().Bernard, Shane K"Creoles", ...
(French who had settled in
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
) who had also populated Spanish Louisiana. The French creoles cited that measure as one of the system's worst elements.
First established in South Carolina in 1704, groups of armed White men—
slave patrol
Slave patrols—also known as patrollers, patterrollers, pattyrollers, or paddy rollers—were organized groups of armed men who monitored and enforced discipline upon Slavery, slaves in the Antebellum South, antebellum U.S. southern states. T ...
s—were formed to monitor enslaved Black people.
Their function was to police slaves, especially fugitives. Slave owners feared that slaves might organize revolts or
slave rebellion
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by slaves, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of slaves have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedom and the dream o ...
s, so state militias were formed to provide a military command structure and discipline within the slave patrols. These patrols were used to detect, encounter, and crush any organized slave meetings which might lead to revolts or
rebellion
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
s.
The earliest African American congregations and churches were organized before 1800 in both northern and southern cities following the
Great Awakening
The Great Awakening was a series of religious revivals in American Christian history. Historians and theologians identify three, or sometimes four, waves of increased religious enthusiasm between the early 18th century and the late 20th cent ...
. By 1775, Africans made up 20% of the population in the
American colonies, which made them the second largest ethnic group after
English Americans
English Americans (also known as Anglo-Americans) are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in England. In the 2020 United States census, English Americans were the largest group in the United States with 46.6 million Ameri ...
.
From the American Revolution to the Civil War

During the 1770s, Africans, both enslaved and free, helped rebellious American colonists secure their independence by defeating the British in the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
. Blacks played a role in both sides in the American Revolution. Activists in the Patriot cause included
James Armistead,
Prince Whipple, and
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
. Around 15,000
Black Loyalist
Black Loyalists were people of African descent who sided with Loyalists during the American Revolutionary War. In particular, the term referred to men enslaved by Patriots who served on the Loyalist side because of the Crown's guarantee of fr ...
s left with the British after the war, most of them ending up as free Black people in England or its colonies, such as the
Black Nova Scotians
Black Nova Scotians (also known as African Nova Scotians, Afro-Nova Scotians, and Africadians) are Black Canadians whose ancestors primarily date back to the Colonial history of the United States, Colonial United States as Slavery in the United S ...
and the
Sierra Leone Creole people
The Sierra Leone Creole people () are an ethnic group of Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone Creole people are descendants of freed African-American, Afro-Caribbean, and Liberated African slaves who settled in the Western Area of Sierra Leone be ...
.
[ Originally published by Longman & Dalhousie University Press (1976).]
In the
Spanish Louisiana
Louisiana (, ), was a province of New Spain from 1762 to 1801. It was primarily located in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of the Mississippi River plus New Orleans. The area had originally been claimed and controlle ...
, Governor
Bernardo de Gálvez
Bernardo Vicente de Gálvez y Madrid, 1st Count of Gálvez (23 July 1746 – 30 November 1786) was a Spanish military leader and government official who served as colonial governor of Spanish Louisiana and Cuba, and later as Viceroy of New S ...
organized Spanish free Black men into two militia companies to defend
New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
during the American Revolution. They fought in the 1779 battle in which Spain captured
Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge ( ; , ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It had a population of 227,470 at the 2020 United States census, making it List of municipalities in Louisiana, Louisiana's second-m ...
from the British. Gálvez also commanded them in campaigns against the British outposts in
Mobile,
Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
, and
Pensacola
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only city in Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which ha ...
, Florida. He recruited slaves for the militia by pledging to free anyone who was seriously wounded and promised to secure a low price for ''coartación'' (buy their freedom and that of others) for those who received lesser wounds. During the 1790s, Governor
Francisco Luis Héctor, baron of Carondelet reinforced local fortifications and recruit even more free Black men for the militia. Carondelet doubled the number of free Black men who served, creating two more militia companies—one made up of Black members and the other of
pardo
In the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas, ''pardos'' (feminine ''pardas'') are triracial descendants of Europeans, Indigenous Americans and Africans.
History
In some places they were defined as neither exclusively ...
(mixed race). Serving in the militia brought free Black men one step closer to equality with Whites, allowing them, for example, the right to carry arms and boosting their earning power. However, actually these privileges distanced free Black men from enslaved Blacks and encouraged them to identify with Whites.
Slavery had been tacitly enshrined in the
US Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally including seven articles, the Constitut ...
through provisions such as Article I, Section 2, Clause 3, commonly known as the
3/5 compromise. Due to the restrictions of
Section 9, Clause 1, Congress was unable to pass an
Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves
The Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves of 1807 (, enacted March 2, 1807) is a United States federal law that prohibited the importation of slaves into the United States. It took effect on January 1, 1808, the earliest date permitted by the U ...
until 1807.
Fugitive slave laws (derived from the
Fugitive Slave Clause
The Fugitive Slave Clause in the United States Constitution, also known as either the Slave Clause or the Fugitives From Labor Clause, is Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3, which requires a "Person held to Service or Labour" (usually a slave, appr ...
of the Constitution—
Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3) were passed by Congress in both
1793
The French Republic introduced the French Revolutionary Calendar starting with the year I.
Events
January–June
* January 7 – The Ebel riot occurs in Sweden.
* January 9 – Jean-Pierre Blanchard becomes the first to ...
and
1850
Events
January–March
* January 29 – Henry Clay introduces the Compromise of 1850 to the United States Congress.
* January 31 – The University of Rochester is founded in Rochester, New York.
* January – Sacramento, Ca ...
, guaranteeing the right of a slaveholder to recover an escaped slave anywhere within the US.
Slave owners, who viewed enslaved people as property, ensured that it became a federal crime to aid or assist those who had fled slavery or to interfere with their capture.
By that time, slavery, which almost exclusively targeted Black people, had become the most critical and contentious political issue in the
Antebellum United States, repeatedly sparking crises and conflicts. Among these were the
Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise (also known as the Compromise of 1820) was federal legislation of the United States that balanced the desires of northern states to prevent the expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand ...
, the
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that temporarily defused tensions between slave and free states during the years leading up to the American Civil War. Designe ...
, the infamous
Dred Scott decision
''Dred Scott v. Sandford'', 60 U.S. (19 How.) 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, and therefore they ...
, and
John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry
John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry was an effort by abolitionist John Brown, from October 16th to 18th, 1859, to initiate a slave revolt in Southern states by taking over the United States arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia (since 1863, We ...
.
Prior to the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, eight serving presidents had owned slaves, a practice that was legally protected under the US Constitution. By 1860, the number of enslaved Black people in the US had grown to between 3.5 and 4.4 million, largely as a result of the
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
. In addition, 488,000–500,000 Black people lived free (with legislated limits)
["Background on conflict in Liberia"](_blank)
Friends Committee on National Legislation, July 30, 2003 across the country.
With legislated limits imposed upon them in addition to "unconquerable prejudice" from Whites according to
Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
. In response to these conditions, some free Black people chose to leave the US and emigrate to
Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
in West Africa.
Liberia had been established in 1821 as a settlement by the
American Colonization Society
The American Colonization Society (ACS), initially the Society for the Colonization of Free People of Color of America, was an American organization founded in 1816 by Robert Finley to encourage and support the repatriation of freeborn peop ...
(ACS), with many abolitionist members of the ACS believing Black Americans would have greater opportunities for freedom and equality in Africa than they would in the US.
Slaves not only represented a significant financial investment for their owners, but they also played a crucial role in producing the country's most valuable product and export:
cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
. Enslaved people were instrumental in the construction of several prominent structures such as, the
United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called the Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the Seat of government, seat of the United States Congress, the United States Congress, legislative branch of the Federal government of the United States, federal g ...
, the
White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
and other
Washington, D.C.–based buildings. Similar building projects existed in the
slave states
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were prohibited. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave s ...
.
By 1815, the
domestic slave trade
The internal slave trade in the United States, also known as the domestic slave trade, the Second Middle Passage and the interregional slave trade, was the mercantile trade of enslaved people within the United States. It was most significant af ...
had become a significant and major economic activity in the United States, continuing to flourish until the 1860s.
[Marcyliena H. Morgan (2002)]
''Language, Discourse and Power in African American Culture''
, p. 20. Cambridge University Press, 2002. Historians estimate that nearly one million individuals were subjected to this forced migration, which was often referred to as a new "Middle Passage". The historian
Ira Berlin described this internal forced migration of enslaved people as the "central event" in the life of a slave during the period between the American Revolution and the Civil War. Berlin emphasized that whether enslaved individuals were directly uprooted or lived in constant fear that they or their families would be involuntarily relocated, "the massive deportation traumatized Black people" throughout the US. As a result of this large-scale forced movement, countless individuals lost their connection to families and clans, and many ethnic Africans lost their knowledge of varying tribal origins in Africa.
The 1863 photograph of
Wilson Chinn, a branded slave from Louisiana, along with the famous image of
Gordon and his scarred back, served as two of the earliest and most powerful examples of how the newborn medium of photography could be used to visually document and encapsulate the brutality and cruelty of slavery.

Emigration of free Blacks to their continent of origin had been proposed since the Revolutionary war. After
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
became independent, it tried to recruit African Americans to migrate there after it re-established trade relations with the United States. The Haitian Union was a group formed to promote relations between the countries.
[Taylor, Nikki M. ''Frontiers of Freedom: Cincinnati's Black Community, 1802–1868.'' Ohio University Press, 2005, , pp. 50–79.] After riots against Blacks in
Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
, its Black community sponsored founding of the
Wilberforce Colony
Wilberforce Colony was a colony established in the year 1829 by free African Americans, African American citizens, north of present-day London, Ontario, Canada. It was an effort by African-Americans to create a place where they could live in polit ...
, an initially successful settlement of African American immigrants to Canada. The colony was one of the first such independent political entities. It lasted for a number of decades and provided a destination for about 200 Black families emigrating from a number of locations in the United States.
In 1863, during the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, President
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
signed the
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War. The Proclamation had the eff ...
. The proclamation declared that all slaves in Confederate-held territory were free. Advancing Union troops enforced the proclamation, with Texas being the last state to be emancipated, in 1865.
Slavery in a few border states continued until the ratification of the
Thirteenth Amendment in December 1865. While the
Naturalization Act of 1790
The Naturalization Act of 1790 (, enacted March 26, 1790) was a law of the United States Congress that set the first uniform rules for the granting of United States citizenship by naturalization. The law limited naturalization to "free whi ...
limited US citizenship to Whites only,
[Leland T. Saito (1998). "Race and Politics: Asian Americans, Latinos, and Whites in a Los Angeles Suburb". p. 154. University of Illinois Press] the
14th Amendment (1868) gave Black people citizenship, and the
15th Amendment (1870) gave Black men the right to vote.
Reconstruction era and Jim Crow
African Americans quickly set up congregations for themselves, as well as schools and community/civic associations, to have space away from White control or oversight. While the post-war Reconstruction era was initially a time of progress for African Americans, that period ended in 1876. By the late 1890s, Southern states enacted Jim Crow laws to enforce
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
and
disenfranchisement
Disfranchisement, also disenfranchisement (which has become more common since 1982) or voter disqualification, is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing someo ...
. Segregation was now imposed with Jim Crow laws, using signs used to show Blacks where they could legally walk, talk, drink, rest, or eat.
[Leon Litwack, ''Jim Crow Blues'', Magazine of History (OAH Publications, 2004)] For those places that were racially mixed, non-Whites had to wait until all White customers were dealt with.
Most African Americans obeyed the Jim Crow laws, to avoid
racially motivated violence. To maintain self-esteem and dignity, African Americans such as
Anthony Overton and
Mary McLeod Bethune
Mary McLeod Bethune (; July 10, 1875 – May 18, 1955) was an American educator, Philanthropy, philanthropist, Humanitarianism, humanitarian, Womanism, womanist, and civil rights activist. Bethune founded the National Council of Negro Women in ...
continued to build their own
schools
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of ...
,
churches, banks, social clubs, and other businesses.
In the last decade of the 19th century, racially discriminatory laws and racial violence aimed at African Americans began to mushroom in the United States, a period often referred to as the "
nadir of American race relations
The nadir of American race relations was the period in African-American history and the history of the United States from the end of Reconstruction in 1877 through the early 20th century, when racism in the country, and particularly anti-bl ...
". These discriminatory acts included racial segregation—upheld by the United States Supreme Court decision in ''
Plessy v. Ferguson
''Plessy v. Ferguson'', 163 U.S. 537 (1896), was a landmark U.S. Supreme Court decision ruling that racial segregation laws did not violate the U.S. Constitution as long as the facilities for each race were equal in quality, a doctrine that ...
'' in 1896—which was legally mandated by southern states and nationwide at the local level of government,
voter suppression
Voter suppression is the discouragement or prevention of specific groups of people from voting or registering to vote. It is distinguished from political campaigning in that campaigning attempts to change likely voting behavior by changing the o ...
or disenfranchisement in the southern states, denial of economic opportunity or resources nationwide, and private acts of violence and mass racial violence aimed at African Americans unhindered or encouraged by government authorities.
Great migration and civil rights movement

The desperate conditions of African Americans in the South sparked the
Great Migration during the first half of the 20th century which led to a growing African American community in
Northern and Western United States. The rapid influx of Blacks disturbed the racial balance within Northern and Western cities, exacerbating hostility between both Blacks and Whites in the two regions. The
Red Summer
The Red Summer was a period in mid-1919 during which Terrorism in the United States#White nationalism and white supremacy, white supremacist terrorism and Mass racial violence in the United States, racial riots occurred in more than three d ...
of 1919 was marked by hundreds of deaths and higher casualties across the US as a result of race riots that occurred in more than three dozen cities, such as the
Chicago race riot of 1919 and the
Omaha race riot of 1919
The Omaha Race Riot occurred in Omaha, Nebraska, September 28–29, 1919. The race riot resulted in the lynching of Will Brown, a black civilian; the death of two white rioters; the injuries of many Omaha Police Department officers and civili ...
. Overall, Blacks in Northern and Western cities experienced
systemic discrimination in a plethora of aspects of life. Within employment, economic opportunities for Blacks were routed to the lowest-status and restrictive in potential mobility. At the 1900
Hampton Negro Conference, Reverend Matthew Anderson said: "...the lines along most of the avenues of wage earning are more rigidly drawn in the North than in the South." Within the housing market, stronger discriminatory measures were used in correlation to the influx, resulting in a mix of "targeted violence,
restrictive covenants,
redlining
Redlining is a Discrimination, discriminatory practice in which financial services are withheld from neighborhoods that have significant numbers of Race (human categorization), racial and Ethnic group, ethnic minorities. Redlining has been mos ...
and
racial steering
Racial steering refers to the practice in which real estate brokers guide prospective home buyers towards or away from certain neighborhoods based on their race. The term is used in the context of ''de facto'' residential segregation in the Unit ...
". While many Whites defended their space with violence, intimidation, or legal tactics toward African Americans, many other Whites migrated to more racially homogeneous suburban or exurban regions, a process known as
White flight
The white flight, also known as white exodus, is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the Racism ...
.
Despite discrimination, drawing cards for leaving the hopelessness in the South were the growth of African American institutions and communities in Northern cities. Institutions included Black oriented organizations (e.g.,
Urban League
The National Urban League (NUL), formerly known as the National League on Urban Conditions Among Negroes, is a nonpartisan historic civil rights organization based in New York City that advocates on behalf of economic and social justice for Afri ...
,
NAACP
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is an American civil rights organization formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E. B. Du&nbs ...
), churches, businesses, and newspapers, as well as successes in the development in African American intellectual culture, music, and popular culture (e.g.,
Harlem Renaissance
The Harlem Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural revival of African-American music, dance, art, fashion, literature, theater, politics, and scholarship centered in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City, spanning the 1920s and 1930s. At the ti ...
,
Chicago Black Renaissance
The Chicago Black Renaissance (also known as the Black Chicago Renaissance) was a creative movement that blossomed out of the Chicago Black Belt on the city's South Side and spanned the 1930s and 1940s before a transformation in art and cultur ...
). The
Cotton Club
The Cotton Club was a 20th-century nightclub in New York City. It was located on 142nd Street and Lenox Avenue from 1923 to 1936, then briefly in the midtown Theater District until 1940. The club operated during the United States' era of P ...
in Harlem was a Whites-only establishment, with Blacks (such as
Duke Ellington
Edward Kennedy "Duke" Ellington (April 29, 1899 – May 24, 1974) was an American Jazz piano, jazz pianist, composer, and leader of his eponymous Big band, jazz orchestra from 1924 through the rest of his life.
Born and raised in Washington, D ...
) allowed to perform, but to a White audience. Black Americans also found a new ground for political power in Northern cities, without the enforced disabilities of
Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced racial segregation, " Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. The last of the ...
.
By the 1950s, the
civil rights movement was gaining momentum. A 1955 lynching that sparked public outrage about injustice was that of
Emmett Till
Emmett Louis Till (July 25, 1941 – August 28, 1955) was an African American youth, who was 14 years old when he was abducted and Lynching in the United States, lynched in Mississippi in 1955 after being accused of offending a white woman, ...
, a 14-year-old boy from Chicago. Spending the summer with relatives in
Money, Mississippi
Money is an unincorporated community near Greenwood in Leflore County, Mississippi, United States, in the Mississippi Delta. It has fewer than 100 residents, down from 400 in the early 1950s when a cotton mill operated there. Money is located o ...
, Till was killed for allegedly having
wolf-whistle
A wolf whistle is a distinctive two-note glissando whistled sound made to show high interest in or approval of something or someone (usually a woman), especially at someone viewed as physically or sexually attractive. A modern wolf whistle dire ...
d at a White woman. Till had been badly beaten, one of his eyes was gouged out, and he was shot in the head. The visceral response to his mother's decision to have an open-casket funeral mobilized the Black community throughout the US.
wrote "the trial of his killers became a pageant illuminating the tyranny of
White supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
".
The state of Mississippi tried two defendants, but they were speedily acquitted by an
all-White jury
Racial discrimination in jury selection is specifically prohibited by law in many jurisdictions throughout the world. In the United States, it has been defined through a series of judicial decisions. However, juries composed solely of one racial ...
. One hundred days after Emmett Till's murder,
Rosa Parks
Rosa Louise McCauley Parks (February 4, 1913 – October 24, 2005) was an American civil rights activist. She is best known for her refusal to move from her seat on a Montgomery, Alabama, bus, in defiance of Jim Crow laws, which sparke ...
refused to give up her seat on the bus in Alabama—indeed, Parks told Emmett's mother
Mamie Till that "the photograph of Emmett's disfigured face in the casket was set in her mind when she refused to give up her seat on the Montgomery bus."

The
March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom
The March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom (commonly known as the March on Washington or the Great March on Washington) was held in Washington, D.C., on August 28, 1963. The purpose of the march was to advocate for the civil and economic righ ...
and the conditions which brought it into being are credited with putting pressure on presidents
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), also known as JFK, was the 35th president of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the first Roman Catholic and youngest person elected p ...
and
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
. Johnson put his support behind passage of the
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and nationa ...
that banned discrimination in public accommodations, employment, and
labor unions
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
, and the
Voting Rights Act
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movem ...
of 1965, which expanded federal authority over states to ensure Black political participation through protection of voter registration and elections. By 1966, the emergence of the
Black Power
Black power is a list of political slogans, political slogan and a name which is given to various associated ideologies which aim to achieve self-determination for black people. It is primarily, but not exclusively, used in the United States b ...
movement, which lasted from 1966 to 1975, expanded upon the aims of the civil rights movement to include economic and political self-sufficiency, and freedom from White authority.
During the post-war period, many African Americans continued to be economically disadvantaged relative to other Americans. Average Black income stood at 54 percent of that of White workers in 1947, and 55 percent in 1962. In 1959, median family income for Whites was $5,600 (), compared with $2,900 () for non-White families. In 1965, 43 percent of all Black families fell into the poverty bracket, earning under $3,000 () a year. The 1960s saw improvements in the social and economic conditions of many Black Americans.
[''The Unfinished Journey: America Since World War II'' by William H. Chafe ]
From 1965 to 1969, Black family income rose from 54 to 60 percent of White family income. In 1968, 23 percent of Black families earned under $3,000 () a year, compared with 41 percent in 1960. In 1965, 19 percent of Black Americans had incomes equal to the national median, a proportion that rose to 27 percent by 1967. In 1960, the median level of education for Blacks had been 10.8 years, and by the late 1960s, the figure rose to 12.2 years, half a year behind the median for Whites.
Post–civil rights era
Politically and economically, African Americans have made substantial strides during the post–civil rights era. In 1967,
Thurgood Marshall
Thoroughgood "Thurgood" Marshall (July 2, 1908 – January 24, 1993) was an American civil rights lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1967 until 1991. He was the Supreme C ...
became the
first African American Supreme Court Justice. In 1968,
Shirley Chisholm
Shirley Anita Chisholm ( ; ; November 30, 1924 – January 1, 2005) was an American politician who, in 1968, became the first black woman to be elected to the United States Congress. Chisholm represented New York's 12th congressional dist ...
became the first Black woman elected to the
US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
. In 1989,
Douglas Wilder
Lawrence Douglas Wilder (born January 17, 1931) is an American lawyer and politician who served as the 66th governor of Virginia from 1990 to 1994. He was the first African American to serve as governor of a U.S. state since the Reconstruction ...
became the first African American elected governor in US history.
Clarence Thomas
Clarence Thomas (born June 23, 1948) is an American lawyer and jurist who has served since 1991 as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. President George H. W. Bush nominated him to succeed Thurgood Marshall. Afte ...
succeeded Marshall to become the second African American Supreme Court Justice in 1991. In 1992,
Carol Moseley-Braun of
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
became the first African American woman elected to the
US Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and House have the authority under Article One of the ...
. There were 8,936 Black officeholders in the United States in 2000, showing a net increase of 7,467 since 1970. In 2001, there were 484 Black mayors.
In 2005, the number of Africans immigrating to the United States, in a single year, surpassed the peak number who were involuntarily brought to the United States during the
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
. On November 4, 2008,
Democratic Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or Legislative chamber, chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior ...
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
—the son of a White American mother and a Kenyan father—
defeated Republican Senator
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American statesman and United States Navy, naval officer who represented the Arizona, state of Arizona in United States Congress, Congress for over 35 years, first as ...
to become the first African American to be elected president. At least 95 percent of African American voters voted for Obama.
He also received overwhelming support from young and educated Whites, a majority of
Asians
"Asian people" (sometimes "Asiatic people")United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purposes. is an umbrella term ...
,
and
Hispanics
The term Hispanic () are people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an ethnic or meta-ethnic term.
The term commonly appli ...
,
[ picking up a number of new states in the Democratic electoral column.][ Obama lost the overall White vote, although he won a larger proportion of White votes than any previous non-incumbent Democratic presidential candidate since ]Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
. Obama was reelected for a second and final term, by a similar margin on November 6, 2012. In 2021, Kamala Harris
Kamala Devi Harris ( ; born October 20, 1964) is an American politician and attorney who served as the 49th vice president of the United States from 2021 to 2025 under President Joe Biden. She is the first female, first African American, and ...
, the daughter of a Jamaican father and Indian mother, became the first woman, the first African American, and the first Asian American
Asian Americans are Americans with ancestry from the continent of Asia (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of those immigrants).
Although this term had historically been used fo ...
to serve as Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest ranking office in the Executive branch of the United States government, executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks f ...
. In June 2021, Juneteenth
Juneteenth is a federal holiday in the United States, federal holiday in the United States. It is celebrated annually on June 19 to commemorate the End of slavery in the United States, ending of slavery in the United States. The holiday's n ...
, a day which commemorates the end of slavery in the US, became a federal holiday.
Demographics



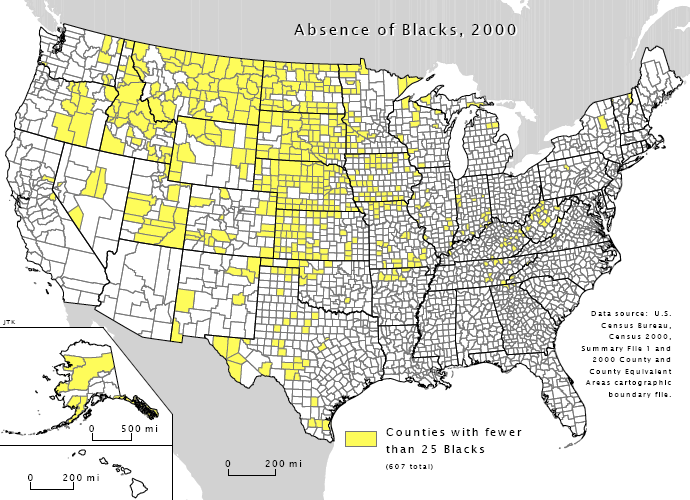
 In 1790, when the first US census was taken, Africans (including slaves and free people) numbered about 760,000—about 19.3% of the population. In 1860, at the start of the
In 1790, when the first US census was taken, Africans (including slaves and free people) numbered about 760,000—about 19.3% of the population. In 1860, at the start of the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, the African American population had increased to 4.4 million, but the percentage rate dropped to 14% of the overall population of the country. The vast majority were slaves, with only 488,000 counted as " freemen". By 1900, the Black population had doubled and reached 8.8 million.
In 1910, about 90% of African Americans lived in the South. Large numbers began migrating north looking for better job opportunities and living conditions, and to escape Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
and racial violence. The Great Migration, as it was called, spanned the 1890s to the 1970s. From 1916 through the 1960s, more than 6 million Black people
Black is a racial classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid- to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin and often additional phenotypical ...
moved north. But in the 1970s and 1980s, that trend reversed, with more African Americans moving south to the Sun Belt
The Sun Belt is a region of the United States generally considered stretching across the Southeast and Southwest. Another rough definition of the region is the area south of the Parallel 36°30′ north. Several climates can be found in the re ...
than leaving it.
The African American population in the United States declined over time as a percentage of the total population until 1930, and has been rising since then:
By 1990, the African American population reached about 30 million and represented 12% of the US population, roughly the same proportion as in 1900.
At the time of the 2000 US census, 54.8% of African Americans lived in the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
. In that year, 17.6% of African Americans lived in the Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—eac ...
and 18.7% in the Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
, while only 8.9% lived in the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
states. The west does have a sizable Black population in certain areas, however. California, the nation's most populous state, has the fifth largest African American population, only behind New York, Texas, Georgia, and Florida. According to the 2000 census, approximately 2.05% of African Americans identified as Hispanic or Latino in origin,Latin American
Latin Americans (; ) are the citizenship, citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America).
Latin American countries and their Latin American diaspora, diasporas are Metroethnicity, ...
descent. The only self-reported ''ancestral'' groups larger than African Americans are the Irish and Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
.
According to the 2010 census, nearly 3% of people who self-identified as Black had recent ancestors who immigrated from another country. Self-reported non-Hispanic Black immigrants from the Caribbean, mostly from Jamaica and Haiti, represented 0.9% of the US population, at 2.6 million.["Total Ancestry Reported"](_blank)
American FactFinder. Self-reported Black immigrants from sub-Saharan Africa also represented 0.9%, at about 2.8 million.Nigerian Americans
Nigerian Americans (; ; ) are Americans who are of Nigerian ancestry. The number of Nigerian immigrants residing in the United States is rapidly growing, expanding from a small 1980 population of 25,000. The 2022 American Community Survey (ACS) ...
and Ethiopian Americans were the most reported sub-Saharan African groups in the United States.
In the 2020 census, the African American population was undercounted at an estimated rate of 3.3%, up from 2.1% in 2010.
Proportion in each county
File:Black Americans 1790 County.png, 1790
File:Black Americans 1800 County.png, 1800
File:Black American 1810 County.png, 1810
File:Black Americans 1820 County.png, 1820
File:Black Americans 1830 County.png, 1830
File:Black Americans 1840 County.png, 1840
File:Black Americans 1850 County.png, 1850
File:Black Americans 1860 County.png, 1860
File:Black Americans 1870 County.png, 1870
File:Black Americans 1880 County.png, 1880
File:Black Americans 1890 County.png, 1890
File:Black Americans 1900 County.png, 1900
File:Black Americans 1910 County.png, 1910
File:Black Americans 1920 County.png, 1920
File:Black Americans 1930 County.png, 1930
File:Black Americans 1940 County.png, 1940
File:Black Americans 1970 County.png, 1970
File:Black Americans 1980 County.png, 1980
File:Black Americans 1990 County.png, 1990
File:Black Americans 2000 County.png, 2000
File:Black Americans 2010 County.png, 2010
File:Black Americans 2020 County.png, 2020
Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
has the largest African American population by state. Followed by Texas is Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, with 3.8 million, and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, with 3.6 million. Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
is the state with the highest African American share of the population at 39%. Followed by Mississippi is Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
at 34%, and Georgia at 32%.
US cities
After 100 years of African Americans leaving the south in large numbers seeking better opportunities and treatment in the west and north, a movement known as the Great Migration, there is now a reverse trend, called the New Great Migration
The New Great Migration is the demographic change from 1970 to the present, which is a reversal of the previous 60-year trend of black migration within the United States.
Since 1970, deindustrialization of cities in the Northeastern and Mid ...
. As with the earlier Great Migration, the New Great Migration is primarily directed toward cities and large urban areas, such as Charlotte, Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
, Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
, Fort Worth
Fort Worth is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the county seat of Tarrant County, Texas, Tarrant County, covering nearly into Denton County, Texas, Denton, Johnson County, Texas, Johnson, Parker County, Texas, Parker, and Wise County, Te ...
, Huntsville
Huntsville is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Alabama. The population of the city is estimated to be 241,114 in 2024, making it the 100th-most populous city in the U.S. The Huntsville metropolitan area had an estimated 525,465 ...
, Raleigh
Raleigh ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is the List of municipalities in North Carolina, second-most populous city in the state (after Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte) ...
, Tampa
Tampa ( ) is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and t ...
, San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
, New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, Memphis, Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
, Jacksonville
Jacksonville ( ) is the most populous city proper in the U.S. state of Florida, located on the Atlantic coast of North Florida, northeastern Florida. It is the county seat of Duval County, Florida, Duval County, with which the City of Jacksonv ...
, and so forth.[Greg Toppo and Paul Overberg]
"After nearly 100 years, Great Migration begins reversal"
, ''USA Today'', Feb 2, 2015. A growing percentage of African Americans from the west and north are migrating to the southern region of the US for economic and cultural reasons. The New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, and Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
metropolitan areas have the highest decline in African Americans, while Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
, Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
, and Houston
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
have the highest increase respectively.New York City metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also called the Tri-State area and sometimes referred to as Greater New York, is the List of cities by GDP, largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a List of U.S. metropolitan areas by GDP, gross metropo ...
still has the largest African American metropolitan population in the United States and the only to have over 3 million African Americans.
Among cities of 100,000 or more, South Fulton, Georgia
South Fulton is a city in Fulton County, Georgia, United States in the Atlanta metropolitan area. It was incorporated in 2017 from parts of southwest Fulton County and includes the communities of Red Oak, Cooks Crossing, Stonewall, Fife, Ben ...
had the highest percentage of Black residents of any large US city in 2020, with 93%. Other large cities with African American majorities include Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Mississippi, most populous city of the U.S. state of Mississippi. The city sits on the Pearl River (Mississippi–Louisiana), Pearl River and is locate ...
(80%), Detroit, Michigan
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
(80%), Birmingham, Alabama
Birmingham ( ) is a city in the north central region of Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Jefferson County, Alabama, Jefferson County. The population was 200,733 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List ...
(70%), Miami Gardens, Florida
Miami Gardens is a city in north-central Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States. It is a suburb of Miami and located north of Greater Downtown Miami, downtown Miami with city boundaries that stretch from Interstate 95 in Florida, I-95 and N ...
(67%), Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in Shelby County, Tennessee, United States, and its county seat. Situated along the Mississippi River, it had a population of 633,104 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List of municipalities in Tenne ...
(63%), Montgomery, Alabama
Montgomery is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Alabama. Named for Continental Army major general Richard Montgomery, it stands beside the Alabama River on the Gulf Coastal Plain. The population was 2 ...
(62%), Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the List of United States ...
(60%), Augusta, Georgia
Augusta is a city on the central eastern border of the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. The city lies directly across the Savannah River from North Augusta, South Carolina at the head of its navigable portion. Augusta, the third mos ...
(59%), Shreveport, Louisiana
Shreveport ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Louisiana. It is the List of municipalities in Louisiana, third-most populous city in Louisiana after New Orleans and Baton Rouge, Louisiana, Baton Rouge. The bulk of Shreveport is in Caddo Parish, Lo ...
(58%), New Orleans, Louisiana
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
(57%), Macon, Georgia
Macon ( ), officially Macon–Bibb County, is a consolidated city-county in Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, United States. Situated near the Atlantic Seaboard fall line, fall line of the Ocmulgee River, it is southeast of Atlanta and near the ...
(56%), Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Baton Rouge ( ; , ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It had a population of 227,470 at the 2020 United States census, making it List of municipalities in Louisiana, Louisiana's second-m ...
(55%), Hampton, Virginia
Hampton is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The population was 137,148 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List of cities in Virginia, seve ...
(53%), Newark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, most populous City (New Jersey), city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, the county seat of Essex County, New Jersey, Essex County, and a principal city of the New York metropolitan area. ...
(53%), Mobile, Alabama
Mobile ( , ) is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population was 187,041 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. After a successful vote to annex areas west of the city limits in July 2023, Mobil ...
(53%), Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–United States border, Canada–U.S. maritime border ...
(52%), Brockton, Massachusetts
Brockton is a city in Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States; the population was 105,643 at the 2020 United States census. Along with Plymouth, Massachusetts, Plymouth, it is one of the two county seats of Plymouth County, Massachusetts, ...
(51%), and Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Brita ...
(51%).
Claiborne County, Mississippi
Claiborne County is a county located in the U.S. state of Mississippi. As of the 2020 census, the population was 9,135. Its county seat is Port Gibson. The county is named after William Claiborne, the second governor of the Mississippi Territ ...
is the Blackest county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
in the U.S. at 87% Black in 2020. Cook County, Illinois
Cook County is the List of counties in Illinois, most populous county in the U.S. state of Illinois and the List of the most populous counties in the United States, second-most-populous county in the United States, after Los Angeles County, C ...
has the largest Black population in the U.S. with 1,185,601 Black residents in 2020.
The nation's most affluent community with an African American majority resides in View Park–Windsor Hills, California, with an annual median household income of $159,618. Other largely affluent and African American communities include Prince George's County
Prince George's County (often shortened to PG County or PG) is located in the U.S. state of Maryland bordering the eastern portion of Washington, D.C. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population was 967,201, making it the second-most populous ...
(namely Mitchellville, Woodmore, Upper Marlboro) and Charles County in Maryland, DeKalb County DeKalb County may refer to one of several counties in the United States, all of which were named for Baron Johann de Kalb:
* DeKalb County, Alabama
DeKalb County is a County (United States), county in the Northeast Alabama, northeastern part ...
(namely Stonecrest, Lithonia, Smoke Rise) and South Fulton in Georgia, Charles City County in Virginia, Baldwin Hills in California, Hillcrest and Uniondale in New York, and Cedar Hill, DeSoto, and Missouri City
Missouri City is a city in the U.S. state of Texas, within the metropolitan area. The city is mostly in Fort Bend County, with a small portion in Harris County. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 74,259, an increase ...
in Texas. Additionally, there is a significant affluent Black presence in the southern Chicago suburbs of Cook County, Illinois
Cook County is the List of counties in Illinois, most populous county in the U.S. state of Illinois and the List of the most populous counties in the United States, second-most-populous county in the United States, after Los Angeles County, C ...
. A report from the National Association of Real Estate Brokers (NAREB) indicated that 5 of the top 10 municipalities nationwide (with at least 500 Black households) registering the highest Black homeownership rates were in this area - including Olympia Fields
Olympia Fields is a village in Cook County, Illinois, United States. The population was 4,718 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is a southern suburb of Chicago. The municipality grew up around the prestigious Olympia Fields Coun ...
, South Holland
South Holland ( ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.8 million as of January 2023 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely populated areas. ...
, Flossmoor, Matteson, and Lynwood. Queens County, New York
Queens is the largest by area of the five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located near the western end of Long Island, it is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn and by Nassau County ...
is the only county with a population of 65,000 or more where African Americans have a higher median household income than White Americans.[
Seatack, Virginia is currently the oldest African American community in the United States. It survives today with a vibrant and active civic community.
]
Education
 During slavery, anti-literacy laws were enacted in the US that prohibited education for Black people. Slave owners saw literacy as a threat to the institution of slavery. As a North Carolina statute stated, "Teaching slaves to read and write, tends to excite dissatisfaction in their minds, and to produce insurrection and
During slavery, anti-literacy laws were enacted in the US that prohibited education for Black people. Slave owners saw literacy as a threat to the institution of slavery. As a North Carolina statute stated, "Teaching slaves to read and write, tends to excite dissatisfaction in their minds, and to produce insurrection and rebellion
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
."
When slavery was finally abolished in 1865, public educational systems were expanding across the country. By 1870, around seventy-four institutions in the south provided a form of advanced education for African American students. By 1900, over a hundred programs at these schools provided training for Black professionals, including teachers. Many of the students at Fisk University, including the young W. E. B. Du Bois
William Edward Burghardt Du Bois ( ; February 23, 1868 – August 27, 1963) was an American sociologist, socialist, historian, and Pan-Africanist civil rights activist.
Born in Great Barrington, Massachusetts, Du Bois grew up in a relativel ...
, taught school during the summers to support their studies.
African Americans were very concerned to provide quality education for their children, but White supremacy limited their ability to participate in educational policymaking on the political level. State governments soon moved to undermine their citizenship by restricting their right to vote. By the late 1870s, Blacks were disenfranchised and segregated across the American South. White politicians in Mississippi and other states withheld financial resources and supplies from Black schools. Nevertheless, the presence of Black teachers, and their engagement with their communities both inside and outside the classroom, ensured that Black students had access to education despite these external constraints.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, demands for unity and racial tolerance on the home front provided an opening for the first Black history curriculum in the country. For example, during the early 1940s, Madeline Morgan, a Black teacher in the Chicago public schools, created a curriculum for students in grades one through eight highlighting the contributions of Black people to the history of the United States. At the close of the war, Chicago's Board of Education downgraded the curriculum's status from mandatory to optional.
Predominantly Black schools for kindergarten through twelfth grade students were common throughout the US before the 1970s. By 1972, however, desegregation efforts meant that only 25% of Black students were in schools with more than 90% non-White students. However, since then, a trend towards re-segregation affected communities across the country: by 2011, 2.9 million African American students were in such overwhelmingly minority schools, including 53% of Black students in school districts that were formerly under desegregation orders.
As late as 1947, about one third of African Americans over 65 were considered to lack the literacy to read and write their own names. By 1969, illiteracy
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
as it had been traditionally defined, had been largely eradicated among younger African Americans.
 Between 1995 and 2009, freshmen college enrollment for African Americans increased by 73 percent and only 15 percent for Whites. Black women are enrolled in college more than any other race and gender group, leading all with 9.7% enrolled according to the 2011 US census.
The average high school graduation rate of Blacks in the United States has steadily increased to 71% in 2013. Separating this statistic into component parts shows it varies greatly depending upon the state and the school district examined. 38% of Black males graduated in the state of New York but in Maine 97% graduated and exceeded the White male graduation rate by 11 percentage points. In much of the southeastern United States and some parts of the southwestern United States the graduation rate of White males was in fact below 70% such as in Florida where 62% of White males graduated from high school. Examining specific school districts paints an even more complex picture. In the Detroit school district, the graduation rate of Black males was 20% but 7% for White males. In the New York City school district 28% of Black males graduate from high school compared to 57% of White males. In Newark County 76% of Black males graduated compared to 67% for White males. Further academic improvement has occurred in 2015. Roughly 23% of all Blacks have bachelor's degrees. In 1988, 21% of Whites had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 11% of Blacks. In 2015, 23% of Blacks had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 36% of Whites.
Between 1995 and 2009, freshmen college enrollment for African Americans increased by 73 percent and only 15 percent for Whites. Black women are enrolled in college more than any other race and gender group, leading all with 9.7% enrolled according to the 2011 US census.
The average high school graduation rate of Blacks in the United States has steadily increased to 71% in 2013. Separating this statistic into component parts shows it varies greatly depending upon the state and the school district examined. 38% of Black males graduated in the state of New York but in Maine 97% graduated and exceeded the White male graduation rate by 11 percentage points. In much of the southeastern United States and some parts of the southwestern United States the graduation rate of White males was in fact below 70% such as in Florida where 62% of White males graduated from high school. Examining specific school districts paints an even more complex picture. In the Detroit school district, the graduation rate of Black males was 20% but 7% for White males. In the New York City school district 28% of Black males graduate from high school compared to 57% of White males. In Newark County 76% of Black males graduated compared to 67% for White males. Further academic improvement has occurred in 2015. Roughly 23% of all Blacks have bachelor's degrees. In 1988, 21% of Whites had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 11% of Blacks. In 2015, 23% of Blacks had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 36% of Whites.College Board
The College Board, styled as CollegeBoard, is an American not-for-profit organization that was formed in December 1899 as the College Entrance Examination Board (CEEB) to expand access to higher education. While the College Board is not an asso ...
, which runs the official college-level advanced placement
Advanced Placement (AP) is a program in the United States and Canada created by the College Board. AP offers undergraduate university-level curricula and examinations to high school students. Colleges and universities in the US and elsewhere ...
(AP) programs in American high schools, have has received criticism in recent years that its curricula have focused too much on Euro-centric
Eurocentrism (also Eurocentricity or Western-centrism)
refers to viewing the West as the center of world events or superior to other cultures. The exact scope of Eurocentrism varies from the entire Western world to just the continent of Euro ...
history.African diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from List of ethnic groups of Africa, people from Africa. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the native West Africa, West and Central Africans who were ...
. In 2021, College Board announced it would be piloting an AP African American Studies
Advanced Placement (AP) African American Studies (also known as APAAS, APAFAM, AP African, or AP Afro) is a college-level course and examination offered to high school students in the United States through the College Board's Advanced Placement ...
course between 2022 and 2024. The course officially launched in August 2024.bachelor's degrees
A bachelor's degree (from Medieval Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Neo-Latin, Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate degree awarded by colleges and university, universities upon completion of a course of study lasting ...
owe an average of $52,726 in student loans. Nearly 70% of African Americans took out a loan to fund their undergraduate education.
Historically Black colleges and universities
Historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs), which were founded when segregated institutions of higher learning did not admit African Americans, continue to thrive and educate students of all races today. There are 101 HBCUs representing three percent of the nation's colleges and universities with the majority established in the Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, ...
. HBCUs have been largely responsible for establishing and expanding the African American middle-class by providing more career opportunities for African Americans.
Economic status
The economic disparity between the races in the US has marginally improved since the end of slavery. In 1863, two years prior to emancipation, Black people owned 0.5 percent of the national wealth, while in 2019 it is just over 1.5 percent. Racial disparity in poverty rates has narrowed since the civil rights era, with the poverty rate among African Americans decreasing from 24.7% in 2004 to 18.8% in 2020, compared to 10.5% for all Americans.mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
problems, disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, d ...
, cognitive deficit
Cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process or different areas of cognition. Cognition, also known as cognitive function, refers to the mental processes of how a person ...
s, low educational attainment, and crime. African Americans had a combined buying power of over $1.6 trillion as of 2021, a 171% increase of their buying power in 2000 but lagging significantly in growth behind American
African Americans had a combined buying power of over $1.6 trillion as of 2021, a 171% increase of their buying power in 2000 but lagging significantly in growth behind American Latinos
Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans who have a Spanish or Latin American background, culture, or family origin. This demographic group includes all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino, regardless of race. According to th ...
and Asians
"Asian people" (sometimes "Asiatic people")United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purposes. is an umbrella term ...
in the same timer period (with 288% and 383%, respectively; for reference, US growth overall was 144% in the same period); however, African American net worth had shrunk 14% in the previous year despite strong growth in property prices and the S&P 500
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 leading companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and in ...
. In 2002, African American-owned businesses accounted for 1.2 million of the US's 23 million businesses. , African American-owned businesses account for approximately 2 million US businesses.[
Twenty-five percent of Blacks had white-collar occupations (management, professional, and related fields) in 2000, compared with 33.6% of Americans overall.]public sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, pu ...
is the single most important source of employment for African Americans.Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009. , African Americans were 30% more likely than other workers to be employed in the public sector.underemployment
Underemployment is the underuse of a worker because their job does not use their skills, offers them too few hours, or leaves the worker idle. It is contrasted with unemployment, where a person lacks a job at all despite wanting one.
Examples ...
, with the Black underclass being hardest hit. The phrase "last hired and first fired" is reflected in the Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
unemployment figures. Nationwide, the October 2008 unemployment rate for African Americans was 11.1%, while the nationwide rate was 6.5%. In 2007, the average income for African Americans was approximately $34,000, compared to $55,000 for Whites. African Americans experience a higher rate of unemployment than the general population.
The income gap between Black and White families is also significant. In 2005, employed Blacks earned 65% of the wages of Whites, down from 82% in 1975.Queens
Queens is the largest by area of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located near the western end of Long Island, it is bordered by the ...
, New York, the median income among African American families exceeded that of White families, which the newspaper attributed to the growth in the number of two-parent Black families. It noted that Queens was the only county with more than 65,000 residents where that was true.
African American homeownership
 Homeownership in the US is the strongest indicator of financial stability and the primary asset most Americans use to generate wealth. African Americans continue to lag behind other racial groups in homeownership. In the first quarter of 2021, 45.1% of African Americans owned their homes, compared to 65.3% of all Americans. The African American homeownership rate has remained relatively flat since the 1970s despite an increase in anti-discrimination housing laws and protections. The African American homeownership rate peaked in 2004 at 49.7%.
The average White high school drop-out still has a slightly better chance of owning a home than the average African American college graduate usually due to unfavorable
Homeownership in the US is the strongest indicator of financial stability and the primary asset most Americans use to generate wealth. African Americans continue to lag behind other racial groups in homeownership. In the first quarter of 2021, 45.1% of African Americans owned their homes, compared to 65.3% of all Americans. The African American homeownership rate has remained relatively flat since the 1970s despite an increase in anti-discrimination housing laws and protections. The African American homeownership rate peaked in 2004 at 49.7%.
The average White high school drop-out still has a slightly better chance of owning a home than the average African American college graduate usually due to unfavorable debt-to-income ratio
In the consumer mortgage industry, debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is the percentage of a consumer's monthly gross income that goes toward paying debts. (Speaking precisely, DTIs often cover more than just debts; they can include principal, taxes, fees ...
s or credit scores
A credit score is a numerical expression based on a level analysis of a person's credit files, to represent the creditworthiness of an individual. A credit score is primarily based on a credit report, information typically sourced from credit ...
among most African American college graduates. Since 2000, fast-growing housing costs in most cities have made it even more difficult for the US African American homeownership rate to significantly grow and reach over 50% for the first time in history. From 2000 to 2022, the median home price in the US grew 160%, outpacing average annual household income growth in that same period, which only grew about 30%. South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
is the state with the most African American homeownership, with about 55% of African Americans owning their own homes.
Black people, who make up 12% of the total U.S. population, make up 32% of all people experiencing homelessness, according to the data.
Politics
Since the mid 20th century, a large majority of African Americans support the Democratic Party. In the 2024 Presidential election
This is a list of elections that were held in 2024. The National Democratic Institute also maintains a calendar of elections around the world.
*2024 United Nations Security Council election
*2024 national electoral calendar
*2024 local electoral ...
, 86% of African American voters supported Democrat Kamala Harris
Kamala Devi Harris ( ; born October 20, 1964) is an American politician and attorney who served as the 49th vice president of the United States from 2021 to 2025 under President Joe Biden. She is the first female, first African American, and ...
, while 13% supported Republican Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
. Although there is an African American lobby in foreign policy, it has not had the impact that African American organizations have had in domestic policy.
Many African Americans were excluded from electoral politics in the decades following the end of Reconstruction. For those that could participate, until the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
, African Americans were supporters of the Republican Party because it was Republican President Abraham Lincoln who helped in granting freedom to American slaves; at the time, the Republicans and Democrats represented the sectional interests of the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
, respectively, rather than any specific ideology, and both conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
and liberal were represented equally in both parties.
The African American trend of voting for Democrats can be traced back to the 1930s during the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, when Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
's New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
program provided economic relief to African Americans. Roosevelt's New Deal coalition
The New Deal coalition was an American political coalition that supported the Democratic Party beginning in 1932. The coalition is named after President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal programs, and the follow-up Democratic presidents. It was ...
turned the Democratic Party into an organization of the working class and their liberal allies, regardless of region. The African American vote became even more solidly Democratic when Democratic presidents John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), also known as JFK, was the 35th president of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the first Roman Catholic and youngest person elected p ...
and Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
pushed for civil rights legislation during the 1960s. In 1960, nearly a third of African Americans voted for Republican Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
.
Conservatism
Conservatism is a Philosophy of culture, cultural, Social philosophy, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, Convention (norm), customs, and Value (ethics and social science ...
has been steadily growing among African Americans, particularly since the 2020 Presidential election. In the 2024 election, Trump secured a larger share of the African American vote compared to his 2020 performance. Notably, Black men and younger Black voters have increasingly aligned with the Republican Party, adopting more conservative stances, such as supporting stricter crime policies, placing less emphasis on transgender rights
The legal status of transgender people varies greatly around the world. Some countries have enacted laws protecting the rights of transgender individuals, but others have criminalized their gender identity or expression. In many cases, transg ...
, and advocating for an end to illegal immigration
Illegal immigration is the migration of people into a country in violation of that country's immigration laws, or the continuous residence in a country without the legal right to do so. Illegal immigration tends to be financially upward, wi ...
, which marks a shift from the views of previous generations.
Black national anthem
"Lift Every Voice and Sing
"Lift Every Voice and Sing" is a hymn with lyrics by James Weldon Johnson (1871–1938) and set to music by his brother, J. Rosamond Johnson (1873–1954). Written from the context of African Americans in the late 19th century, the hymn is a pr ...
" is often referred to as the Black national anthem in the United States. In 1919, the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) had dubbed it the "Negro national anthem" for its power in voicing a cry for liberation and affirmation for African-American people.
Religion

 The majority of African Americans are
The majority of African Americans are Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, many of whom follow the historically Black churches.[US Religious Landscape Survey](_blank)
The Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life (February 2008). Retrieved July 20, 2009. The term Black church
The Black church (sometimes termed Black Christianity or African American Christianity) is the faith and body of Christian denominations and congregations in the United States that predominantly minister to, and are led by, African Americans, ...
refers to churches which minister to predominantly African American congregations. Black congregations were first established by freed slaves at the end of the 17th century, and later when slavery was abolished more African Americans were allowed to create a unique form of Christianity that was culturally influenced by African spiritual traditions. One of these early African American Christian cultural traditions in the Black Church is the Watchnight service
A watchnight service (also called Watchnight Mass) is a late-night Christian church service. In many different Christian traditions, such as those of Moravians, Methodists, Catholics, Lutherans, Anglicans, Baptists, Adventists and Reformed Christ ...
, also called Freedom's Eve, where African American congregations all over the nation come together on New Year's Eve through New Years morning in remembrance of the eve and New Year of their emancipation, sharing testimonies, being baptized and partaking in praise and worship.
According to a 2007 survey, more than half of the African American population are part of the historically Black churches.Baptists
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
, distributed mainly in four denominations, the largest being the National Baptist Convention, USA
The National Baptist Convention, USA, more commonly known as the National Baptist Convention (NBC USA or NBC), is a Baptist Christian denomination headquartered at the Baptist World Center in Nashville, Tennessee and affiliated with the Baptist ...
and the National Baptist Convention of America.[The NCC's 2008 Yearbook of Churches reports a wide range of health care ministries](_blank)
National Council of Churches USA. February 14, 2008. Retrieved June 22, 2009. The second largest are the Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
s,[William Henry James, Stephen Lloyd Johnson (1997). ''Doin' drugs: patterns of African American addiction''. University of Texas Press. p. 135. .] the largest denominations are the African Methodist Episcopal Church
The African Methodist Episcopal Church, usually called the AME Church or AME, is a Methodist denomination based in the United States. It adheres to Wesleyan theology, Wesleyan–Arminian theology and has a connexionalism, connexional polity. It ...
and the African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church
The African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church, or the AME Zion Church (AMEZ) is a historically African-American Christian denomination based in the United States. It was officially formed in 1821 in New York City, but operated for a number of y ...
.Pentecostals
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God through baptism with the Holy Spirit. The term ''Pentecostal'' is derived ...
are distributed among several different religious bodies, with the Church of God in Christ
The Church of God in Christ (COGIC) is an international Christian perfection#Holiness Pentecostalism, Holiness–Pentecostal Christian denomination, and a large Pentecostal denomination in the United States. Although an international and multi ...
as the largest among them by far.United Church of Christ
The United Church of Christ (UCC) is a socially liberal mainline Protestant Christian denomination based in the United States, with historical and confessional roots in the Congregational, Restorationist, Continental Reformed, and Lutheran t ...
) mostly have a 2 to 3% African American membership. There are also large numbers of Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
, constituting 5% of the African American population.Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
, 22% are Black.Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. Historically, between 15 and 30% of enslaved Africans brought to the Americas were Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s, but most of these Africans were converted to Christianity during the era of American slavery. During the twentieth century, some African Americans converted to Islam, mainly through the influence of Black nationalist
Black nationalism is a nationalist movement which seeks representation for Black people as a distinct national identity, especially in racialized, colonial and postcolonial societies. Its earliest proponents saw it as a way to advocate for ...
groups that preached with distinctive Islamic practices; including the Moorish Science Temple of America
The Moorish Science Temple of America is an American national and religious organization founded by Noble Drew Ali (born as Timothy Drew) in the early 20th century. He based it on the premise that African Americans are descendants of the Moabite ...
, and the largest organization, the Nation of Islam
The Nation of Islam (NOI) is a religious organization founded in the United States by Wallace Fard Muhammad in 1930. A centralized and hierarchical organization, the NOI is committed to black nationalism and focuses its attention on the Afr ...
, founded in the 1930s, which attracted at least 20,000 people by 1963. Prominent members included activist Malcolm X
Malcolm X (born Malcolm Little, later el-Hajj Malik el-Shabazz; May 19, 1925 – February 21, 1965) was an African American revolutionary, Islam in the United States, Muslim minister and human rights activist who was a prominent figur ...
and boxer Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and social activist. A global cultural icon, widely known by the nickname "The Greatest", he is often regarded as the gr ...
.
 Malcolm X is considered the first person to start the movement among African Americans towards mainstream Islam, after he left the Nation and made the
Malcolm X is considered the first person to start the movement among African Americans towards mainstream Islam, after he left the Nation and made the pilgrimage to Mecca
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
. In 1975, Warith Deen Mohammed
Warith Deen Mohammed (born Wallace D. Muhammad; October 30, 1933 – September 9, 2008) was an African-American Muslims, African-American Muslim leader, Theology, theologian, philosopher, Islamic revival, Muslim revivalist, and Islamic thinker. ...
, the son of Elijah Muhammad
Elijah Muhammad (born Elijah Robert Poole; October 7, 1897 – February 25, 1975) was an American religious leader, black separatist, and self-proclaimed Messenger of Allah who led the Nation of Islam (NOI) from 1933 until his death in 197 ...
took control of the Nation after his father's death and guided the majority of its members to orthodox Islam
Orthodoxy () is adherence to a purported "correct" or otherwise mainstream- or classically-accepted creed, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical co ...
.
African American Muslims constitute 20% of the total US Muslim population,Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
or orthodox Muslims, some of these identify under the community of W. Deen Mohammed. The Nation of Islam led by Louis Farrakhan
Louis Farrakhan (; born Louis Eugene Walcott; May 11, 1933) is an American religious leader who heads the Nation of Islam (NOI), a Black nationalism, black nationalist organization. Farrakhan is notable for his leadership of the 1995 Million M ...
has a membership ranging from 20,000 to 50,000 members.
There is also a small but growing group of African American Jews, making up less than 0.5% of African Americans or about 2% of the Jewish population in the United States. The majority of African-American Jews are Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that Ethnogenesis, emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium Common era, CE. They traditionally spe ...
, while smaller numbers identify as Sephardi
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
, Mizrahi
''Mizrachi'' or ''Mizrahi'' () has two meanings.
In the literal Hebrew meaning ''eastern'', it may refer to:
* Mizrahi Jews, Jews from the Middle East and North Africa
* Mizrahi (surname), a Sephardic surname, given to Jews who got to the Iberia ...
, or other.Reform
Reform refers to the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The modern usage of the word emerged in the late 18th century and is believed to have originated from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement, which ...
, Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
, Reconstructionist, or Orthodox branches of Judaism, but the majority identify as "Jews of no religion", commonly known as secular Jews. A significant number of people who identify themselves as "Black Jews" are affiliated with syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus ...
religious groups, largely the Black Hebrew Israelites
Black Hebrew Israelites (also called Hebrew Israelites, Black Hebrews, Black Israelites, and African Hebrew Israelites) are a new religious movement claiming that African Americans are descendants of the ancient Israelites. Some sub-groups ...
, whose beliefs include the claim that African Americans are descended from the Biblical Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
.atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
are less than one half of one percent, similar to numbers for Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
s.
Sexuality
According to a Gallup survey, 4.6% of Black or African Americans self-identified as LGBT
LGBTQ people are individuals who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or questioning. Many variants of the initialism are used; LGBTQIA+ people incorporates intersex, asexual, aromantic, agender, and other individuals. The gro ...
in 2016,
Health
General health
The life expectancy for Black men in 2008 was 70.8 years.European Americans
European Americans are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes both people who descend from the first European settlers in the area of the present-day United States and people who descend from more recent European arrivals. Since th ...
.obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, and hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
than the US average.alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
. Alcohol abuse is the main contributor to the top 3 causes of death among African Americans.
In December 2020, African Americans were less likely to be vaccinated
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
against COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
due to mistrust in the US medical system. From 2021 to 2022, there was an increase in African Americans who became vaccinated. Still, in 2022, COVID-19 complications became the third leading cause of death for African Americans.
Violence is a major problem within the African American community.US Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of federal laws and the administration of justice. It is equ ...
states "In 2005, homicide victimization rates for Blacks were 6 times higher than the rates for whites".[Homicide trends in the US](_blank)
, US Department of Justice The report also found that "94% of Black victims were killed by Blacks."
Sexual health
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
, African Americans have higher rates of sexually transmitted infections
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or ...
(STIs) compared to Whites, with 5 times the rates of syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The prim ...
and chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several w ...
, and 7.5 times the rate of gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
.
The disproportionately high incidence of HIV/AIDS among African Americans has been attributed to homophobic
Homophobia encompasses a range of negative attitudes and feelings toward homosexuality or people who identify or are perceived as being lesbian, Gay men, gay or bisexual. It has been defined as contempt, prejudice, aversion, hatred, or ant ...
influences and lack of proper healthcare. The prevalence of HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
among Black men is seven times higher than the prevalence for White men, and Black men are more than nine times as likely to die from HIV/AIDS-related illness than White men.
Mental health
African Americans have several barriers for accessing mental health services. Counseling
Counseling is the professional guidance of the individual by utilizing psychological methods especially in collecting case history data, using various techniques of the personal interview, and testing interests and aptitudes.
This is a list of c ...
has been frowned upon and distant in utility and proximity to many people in the African American community. In 2004, a qualitative research study explored the disconnect with African Americans and mental health. The study was conducted as a semi-structured discussion which allowed the focus group to express their opinions and life experiences. The results revealed a couple key variables that create barriers for many African American communities to seek mental health services such as the stigma, lack of four important necessities; trust, affordability, cultural understanding and impersonal services.White Americans
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person hav ...
and do not fit within the African American culture. African American families tend to resolve concerns within the family, and it is viewed by the family as a strength. On the other hand, when African Americans seek counseling, they face a social backlash and are criticized. They may be labeled "crazy", viewed as weak, and their pride is diminished.psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of Psychology, psychological methods, particularly when based on regular Conversation, personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase hap ...
'' versus counseling. In one study, psychotherapy is associated with mental illness whereas counseling approaches problem-solving, guidance and help.suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
rate trailing American Indians/Alaska Natives and White Americans. However, African Americans had the second highest increase of its suicide rate from 2011 to 2021, growing 58%. As of 2024, suicide is the second leading cause of death among African-Americans between the ages of 15 and 24, with Black men being four times more likely to kill themselves than Black women.
Genetics
Genome-wide studies
 Recent studies of African Americans using genetic testing have found ancestry to vary by region and sex of ancestors. These studies found that on average, African Americans have 73.2–82.1% Sub-Saharan African, 16.7–24% European, and 0.8–1.2% Native American genetic ancestry, with large variation between individuals.
Recent studies of African Americans using genetic testing have found ancestry to vary by region and sex of ancestors. These studies found that on average, African Americans have 73.2–82.1% Sub-Saharan African, 16.7–24% European, and 0.8–1.2% Native American genetic ancestry, with large variation between individuals.raped
Rape is a type of sexual assault involving sexual intercourse, or other forms of sexual penetration, carried out against a person without consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or against a person w ...
by White males. Consequently, the 365 African Americans in their sample have a genome-wide average of 78.1% West African ancestry and 18.5% European ancestry, with large variation among individuals (ranging from 99% to 1% West African ancestry). The West African ancestral component in African Americans is most similar to that in present-day speakers from the non- Bantu branches of the Niger-Congo family.Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
and southern Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
, reflecting the centrality of this West African region in the Atlantic slave trade. The next most frequent ancestral component found among African Americans was derived from Great Britain, in keeping with historical records. It constitutes a little over 10% of their overall ancestry and is most similar to the Northwest European ancestral component also carried by Barbadians
Barbadians, more commonly known as Bajans (pronounced ), are people who are identified with the country of Barbados, by being citizens or their descendants in the Bajan diaspora. The connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultu ...
.Guinea Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to its north and Guinea to its southeast.
Guinea-Bissau was once part of the kin ...
, Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
and Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and envi ...
in West Africa and Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
in Southern Africa.Penn State #Redirect Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with ca ...
geneticist Mark D. Shriver, around 58 percent of African Americans have at least 12.5% European ancestry (equivalent to one European great-grandparent and their forebears), 19.6 percent of African Americans have at least 25% European ancestry (equivalent to one European grandparent and their forebears), and 1 percent of African Americans have at least 50% European ancestry (equivalent to one European parent and their forebears).
Y-DNA
Africans bearing the E-V38 (E1b1a) likely traversed across the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, from east
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
to west
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
, approximately 19,000 years ago.Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the Y ...
study by Sims et al. (2007), the majority (≈60%) of African Americans belong to various subclades of the E-M2 (E1b1a1, formerly E3a) paternal haplogroup. This is the most common genetic paternal lineage found today among West/Central African males and is also a signature of the historical Bantu migration
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
* Black Association for Nationa ...
s. The next most frequent Y-DNA haplogroup observed among African Americans is the R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and across the Sahel in ...
clade, which around 15% of African Americans carry. This lineage is most common today among Northwestern European males. The remaining African Americans mainly belong to the paternal haplogroup I (≈7%), which is also frequent in Northwestern Europe.
mtDNA
According to an mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the DNA contained in ...
study by Salas et al. (2005), the maternal lineages of African Americans are most similar to haplogroups that are today especially common in West Africa (>55%), followed closely by West-Central Africa and Southwestern Africa (<41%). The characteristic West African haplogroups L1b, L2b,c,d, and L3b,d and West-Central African haplogroups L1c and L3e in particular occur at high frequencies among African Americans. As with the paternal DNA of African Americans, contributions from other parts of the continent to their maternal gene pool are insignificant.
Racism and social status
Formal political, economic and social discrimination against minorities has been present throughout American history. Leland T. Saito, Associate Professor of Sociology and American Studies & Ethnicity at the University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in ...
, writes, "Political rights have been circumscribed by race, class and gender since the founding of the United States, when the right to vote was restricted to White men of property. Throughout the history of the United States, race has been used by Whites for legitimizing and creating difference and social, economic and political exclusion."planter class
The planter class was a Racial hierarchy, racial and socioeconomic class which emerged in the Americas during European colonization of the Americas, European colonization in the early modern period. Members of the class, most of whom were settle ...
, owners of large-scale plantations where large numbers of enslaved Africans were held captive and forced to produce crops to create wealth for a White elite.London School of Economics
The London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE), established in 1895, is a public research university in London, England, and a member institution of the University of London. The school specialises in the social sciences. Founded ...
stating, "this persistence in "de facto power" in turn allowed them to block economic reforms, disenfranchise Black voters, and restrict the mobility of workers."
Although they have gained a greater degree of social equality since the civil rights movement, African Americans have remained stagnant economically, which has hindered their ability to break into the middle class and beyond. As of 2020, the racial wealth gap between Whites and Blacks remains as large as it was in 1968, with the typical net worth of a White household equivalent to that of 11.5 Black households. Despite this, African Americans have increased employment rates and gained representation in the highest levels of American government in the post–civil rights era.racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one Race (human categorization), race or ethnicity over another. It may also me ...
remains an issue that continues to undermine the development of social status.
Policing and criminal justice
In the US, which has the largest per-capita prison population in the world, African Americans are overrepresented as the second largest population of prison inmates (38%) in 2023, coming second to Whites who made up 57% of the prison population. According to the National Registry of Exonerations The National Registry of Exonerations is a project of the University of Michigan Law School, Michigan State University College of Law and the University of California Irvine Newkirk Center for Science and Society. The Registry was co-founded in 2012 ...
, Blacks are roughly 7.5 times more likely to be wrongfully convicted of murder in the US than Whites. In 2012, the New York City Police Department detained people more than 500,000 times under the city's stop-and-frisk law. Of the total detained, 55% were African-Americans, while Black people made up 20% of the city's population.Black Lives Matter
Black Lives Matter (BLM) is a Decentralization, decentralized political and social movement that aims to highlight racism, discrimination and Racial inequality in the United States, racial inequality experienced by black people, and to pro ...
movement in 2013. A historical issue in the US where women have weaponized their White privilege in the country by reporting on Black people, often instigating racial violence, difficult White women—who have been given a different name over the centuries by African Americans—calling the police on Black people became widely publicized in 2020. According to ''The Guardian'', "The specter of Karen persisted as Black Lives Matter protests and civil unrest spread around the country following Floyd’s murder and reckonings with racism began to roil institutions, toppling careers as well as statues".
In the aftermath of the peak Black Lives Matter protests and widespread police reform efforts, crime rates surged across the nation. Many cities experienced near-record or record levels of violence and other criminal activity. As a result, numerous municipalities scaled back police reform initiatives and increased funding for law enforcement.
Social issues
After over 50 years, marriage rates for all Americans began to decline while divorce rates and out-of-wedlock births have climbed.Single-parent
A single parent is a person who has a child or children but does not have a spouse or live-in partner to assist in the upbringing or support of the child. Reasons for becoming a single parent include death, divorce, break-up, abandonment, bec ...
households have become common, and according to US census figures released in January 2010, only 38 percent of Black children live with both their parents. In 2021, statistics show that over 80 percent marriages in the African American ethnic group marry within their ethnic group.
 The first ever anti-miscegenation law was passed by the
The first ever anti-miscegenation law was passed by the Maryland General Assembly
The Maryland General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland that convenes within the State House in Annapolis. It is a bicameral body: the upper chamber, the Maryland Senate, has 47 representatives, and the lower ...
in 1691, criminalizing interracial marriage
Interracial marriage is a marriage involving spouses who belong to different "Race (classification of human beings), races" or Ethnic group#Ethnicity and race, racialized ethnicities.
In the past, such marriages were outlawed in the United Sta ...
.Charleston, Illinois
Charleston is a city in and the county seat of Coles County, Illinois, United States. The population was 17,286, as of the 2020 census. The city is home to Eastern Illinois University and has close ties with its neighbor, Mattoon, Illinois, Ma ...
in 1858, Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
stated, "I am not, nor ever have been in favor of making voters or jurors of negroes, nor of qualifying them to hold office, nor to intermarry with white people". By the late 1800s, 38 US states had anti-miscegenation statutes.Sammy Davis Jr.
Samuel George Davis Jr. (December 8, 1925 – May 16, 1990) was an American singer, actor, comedian, dancer, and musician.
At age two, Davis began his career in Vaudeville with his father Sammy Davis Sr. and the Will Mastin Trio, which t ...
faced a backlash for his involvement with White actress Kim Novak
Marilyn Pauline "Kim" Novak (born February 13, 1933) is an American retired actress and painter. Her contributions to cinema have been honored with two Golden Globe Awards, an Honorary Golden Bear, a Golden Lion for Lifetime Achievement, and a s ...
.Harry Cohn
Harry Cohn (July 23, 1891 – February 27, 1958) was a co-founder, president, and production director of Columbia Pictures, Columbia Pictures Corporation.
Life and career
Cohn was born to a working-class Jewish family in New York City. His fath ...
, the president of Columbia Pictures, with whom Novak was under contract, gave in to his concerns that a racist backlash against the relationship could hurt the studio.[Lanzendorfer, Joy (August 9, 2017]
"Hollywood Loved Sammy Davis Jr. Until He Dated a White Movie Star"
, '' Smithsonian'' Retrieved February 23, 2021. In 1958, officers in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
entered the home of Mildred and Richard Loving
Mildred Delores Loving (née Jeter; July 22, 1939 – May 2, 2008) and Richard Perry Loving (October 29, 1933 – June 29, 1975) were an American married couple who were the plaintiffs in the landmark Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Su ...
and dragged them out of bed for living together as an interracial couple, on the basis that "any white person intermarry with a colored person"—or vice versa—each party "shall be guilty of a felony" and face prison terms of five years.Loving v. Virginia
''Loving v. Virginia'', 388 U.S. 1 (1967), was a landmark civil rights decision of the U.S. Supreme Court that ruled that the laws banning interracial marriage violate the Equal Protection and Due Process Clauses of the Fourteenth Amendment to ...
''.California Proposition 8
Proposition 8, known informally as Prop 8, was a California ballot proposition and a state constitutional amendment intended to ban same-sex marriage. It passed in the November 2008 California state elections and was later overturned by the ...
, African Americans voted 58% in favor of it while 42% voted against Proposition 8. On May 9, 2012, Barack Obama, the first Black president, became the first US president to support same-sex marriage. Since Obama's endorsement there has been a rapid growth in support for same-sex marriage among African Americans. As of 2012, 59% of African Americans support same-sex marriage, which is higher than support among the national average (53%) and White Americans (50%).
Polls in North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
, Florida, and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
have also shown an increase in support for same sex marriage among African Americans. On November 6, 2012, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, and Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
all voted for approve of same-sex marriage, along with Minnesota rejecting a constitutional amendment banning same-sex marriage. Exit polls in Maryland show about 50% of African Americans voted for same-sex marriage, showing a vast evolution among African Americans on the issue and was crucial in helping pass same-sex marriage in Maryland.
Black Americans hold far more conservative opinions on abortion, extramarital sex
Extramarital sex occurs when a married person engages in sexual activity with someone other than their spouse. The term may be applied to the situation of a single person having sex with a married person. It is distinguished from premarital sex ...
, and raising children out of wedlock than Democrats as a whole.progressive tax
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases. The term ''progressive'' refers to the way the tax rate progresses from low to high, with the result that a taxpayer's average tax rate is less than the ...
structure to provide more government spending on social services.
Political legacy
 African Americans have fought in every war in the
African Americans have fought in every war in the history of the United States
The history of the present-day United States began in roughly 15,000 BC with the arrival of Peopling of the Americas, the first people in the Americas. In the late 15th century, European colonization of the Americas, European colonization beg ...
.
The gains made by African Americans in the civil rights movement and in the Black Power movement not only obtained certain rights for African Americans but changed American society in far-reaching and fundamentally important ways. Prior to the 1950s, Black Americans in the South were subject to de jure discrimination, or Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
. They were often the victims of extreme cruelty and violence, sometimes resulting in deaths: by the post World War II era, African Americans became increasingly discontented with their long-standing inequality. In the words of Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil and political rights, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights move ...
, African Americans and their supporters challenged the nation to "rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed that all men are created equal..."
The civil rights movement marked an enormous change in American social, political, economic and civic life. It brought with it boycott
A boycott is an act of nonviolent resistance, nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organisation, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for Morality, moral, society, social, politics, political, or Environmenta ...
s, sit-in
A sit-in or sit-down is a form of direct action that involves one or more people occupying an area for a protest, often to promote political, social, or economic change. The protestors gather conspicuously in a space or building, refusing to mo ...
s, nonviolent
Nonviolence is the personal practice of not causing harm to others under any condition. It may come from the belief that hurting people, animals and/or the environment is unnecessary to achieve an outcome and it may refer to a general philosoph ...
demonstrations and marches, court battles, bombings and other violence; prompted worldwide media coverage and intense public debate; forged enduring civic, economic and religious alliances; and disrupted and realigned the nation's two major political parties.
Over time, it has changed in fundamental ways the manner in which Blacks and Whites interact with and relate to one another. The movement resulted in the removal of codified, ''de jure'' racial segregation and discrimination from American life and law, and heavily influenced other groups and movements in struggles for civil rights and social equality within American society, including the Free Speech Movement, the disabled
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physica ...
, the women's movement
The feminist movement, also known as the women's movement, refers to a series of social movements and political campaigns for radical and liberal reforms on women's issues created by inequality between men and women. Such issues are women's ...
, and migrant workers
A migrant worker is a person who Human migration, migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have an intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
Migrant workers ...
. It also inspired the Native American rights movement, and in King's 1964 book '' Why We Can't Wait'' he wrote the US "was born in genocide when it embraced the doctrine that the original American, the Indian, was an inferior race."
Media and coverage
Some activists and academics contend that American news media coverage of African American news, concerns, or dilemmas is inadequate, or that the news media present distorted images of African Americans.
To combat this, Robert L. Johnson founded Black Entertainment Television (BET
Black Entertainment Television (BET) is an American basic cable channel targeting Black American audiences. It is the flagship channel of the BET Media Group, a subsidiary of Paramount Global's CBS Entertainment Group. Originally launched ...
), a network that targets young African Americans and urban audiences in the United States. Over the years, the network has aired such programming as rap and R&B music videos, urban-oriented movies and television series, and some public affairs programs. On Sunday mornings, BET would broadcast Christian programming; the network would also broadcast non-affiliated Christian programs during the early morning hours daily. According to Viacom
Viacom, an abbreviation of Video and Audio Communications, may refer to:
* Viacom (1952–2005), a former American media conglomerate
* Viacom (2005–2019), a former company spun off from the original Viacom
* Viacom18, a joint venture between Pa ...
, BET is now a global network that reaches households in the United States, Caribbean, Canada, and the United Kingdom. The network has gone on to spawn several spin-off channels, including BET Her
BET Her is an American basic cable television network currently owned by the BET Media Group subsidiary of Paramount Global's CBS Entertainment Group.
The channel originally launched in 1996 as BET on Jazz, a spin-off from BET with a focus on ...
(originally launched as ''BET on Jazz'').
Another network targeting African Americans is TV One. TV One is owned by Urban One
Urban One, Inc. (formerly Radio One) is an American media conglomerate based in Silver Spring, Maryland. Founded in 1980 by Cathy Hughes, the company primarily operates media properties targeting African Americans.
It is the largest African-Ame ...
, founded and controlled by Catherine Hughes. Urban One is one of the nation's largest radio broadcasting companies and the largest African American-owned radio broadcasting company in the United States.
In June 2009, NBC News
NBC News is the news division of the American broadcast television network NBC. The division operates under NBCUniversal Media Group, a division of NBCUniversal, which is itself a subsidiary of Comcast. The news division's various operations r ...
launched a new website named TheGrio
TheGrio is a brand name owned by American media company Allen Media Group for a television network and a website aimed at African-Americans.
History
TheGrio is to "focus on news and events that have a unique interest and pronounced impact with ...
. It is the first African American video news site
An online newspaper (or electronic news or electronic news publication) is the online version of a newspaper, either as a stand-alone publication or as the online version of a printed periodical.
Going online created more opportunities for newspa ...
that focuses on underrepresented stories in existing national news.
Black-owned and oriented media outlets
* The Africa Channel
The Africa Channel is a cable and streaming channel focusing on travel, lifestyle, and culture documentaries. The channel covers the lands, people, culture, and history of Africa. Co-founded by Zimbabwean James Makawa, who had prior experience in t ...
– Dedicated to programming about African culture.
* aspireTV – a digital cable and satellite channel owned by businessman and former basketball player Magic Johnson
Earvin "Magic" Johnson Jr. (born August 14, 1959) is an American businessman and former professional basketball player. Often regarded as the greatest point guard of all time, Johnson List of NBA players who have spent their entire career w ...
.
* ATTV – an independent public affairs and educational channel.
* BET Media Group
Black Entertainment Television LLC (Trade name, doing business as the BET Media Group, and formerly known as BET Networks) is an American television company currently owned by American media conglomerate Paramount Global under its CBS Entertainmen ...
– The most prominent multimedia outlet targeting Afro-Americans.
** BET
Black Entertainment Television (BET) is an American basic cable channel targeting Black American audiences. It is the flagship channel of the BET Media Group, a subsidiary of Paramount Global's CBS Entertainment Group. Originally launched ...
** BET Her
BET Her is an American basic cable television network currently owned by the BET Media Group subsidiary of Paramount Global's CBS Entertainment Group.
The channel originally launched in 1996 as BET on Jazz, a spin-off from BET with a focus on ...
** VH1
VH1 (originally an initialism for Video Hits One) is an American basic cable television network that launched on January 1, 1985, and is currently owned by the MTV Entertainment Group unit of Paramount Global's networks division based in New Y ...
– Originally a MTV
MTV (an initialism of Music Television) is an American cable television television channel, channel and the flagship property of the MTV Entertainment Group sub-division of the Paramount Media Networks division of Paramount Global. Launched on ...
spin-off focused on light genres of music, the network's programming became slanted towards African American culture during the 2010s.
* Bounce TV
Bounce TV is an American digital terrestrial television, digital broadcast television network owned by Scripps Networks, a subsidiary of E. W. Scripps Company. It launched on September 26, 2011, and was promoted as "the first 24/7 digital multic ...
– a digital multicast network owned by the E. W. Scripps Company
The E. W. Scripps Company, also known as Scripps, is an American broadcasting company founded in 1878 as a chain of daily newspapers by Edward Willis "E. W." Scripps and his sister, Ellen Browning Scripps. It was also formerly a media conglom ...
.
* Fox Soul – a digital television and streaming network primarily airing original talk shows and syndicated programming
* Oprah Winfrey Network
The Oprah Winfrey Network (OWN, also known as the OWN Network) is an American multinational basic cable television network which launched on January 1, 2011, effectively replacing the Discovery Health Channel, which one month later merged with ...
– a cable and satellite network founded by Oprah Winfrey
Oprah Gail Winfrey (; born Orpah Gail Winfrey; January 29, 1954) is an American television presenter, talk show host, television producer, actress, author, and media proprietor. She is best known for her talk show, ''The Oprah Winfrey Show' ...
and jointly owned by Warner Bros. Discovery
Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. (WBD) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational mass media and Outline of entertainment, entertainment Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in New York City. It was formed from WarnerMedi ...
and Harpo Studios
Harpo Productions (or Harpo Studios) is an American multimedia production company founded by Oprah Winfrey and based in West Hollywood, California. The name "Harpo" is "Oprah" spelled backwards, and it was also the name of her on-screen husban ...
. While not exclusively targeting African Americans, much of its original programming is geared towards a similar demographic.
* Revolt
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
– a music channel and media company founded by Sean "Puff Daddy" Combs.
* Soul of the South Network – a regional broadcast network.
* TheGrio
TheGrio is a brand name owned by American media company Allen Media Group for a television network and a website aimed at African-Americans.
History
TheGrio is to "focus on news and events that have a unique interest and pronounced impact with ...
– a digital multicast network focused on news and opinion-based programming.
* TV One – a general entertainment network targeting adults.
** Cleo TV – a sister network targeting millennial
Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000s as ...
and Generation X
Generation X (often shortened to Gen X) is the Demography, demographic Cohort (statistics), cohort following the Baby Boomers and preceding Millennials. Researchers and popular media often use the mid-1960s as its starting birth years and the ...
women
* We TV – Owned by AMC Networks
AMC Networks Inc. is an American mass media and entertainment corporation headquartered in 11 Penn Plaza, New York City. The company owns and operates the AMC cable channel, BBC America, IFC, Sundance TV, and We TV. It also owns the art ho ...
, became slanted towards Black women during the 2010s
Culture
From their earliest presence in North America, African Americans have significantly contributed literature, art, agricultural skills, cuisine, clothing styles, music, language, and social and technological innovation to American culture. The cultivation and use of many agricultural products in the United States, such as yams, peanuts, rice, okra
Okra (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the Malvaceae, mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions aro ...
, sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
, grits
Grits (stylized as GRITS) is an American Christian hip hop group from Nashville, Tennessee. Their name is an acronym, which stands for "Grammatical Revolution In the Spirit". GRITS is made up of Stacey "Coffee" Jones and Teron "Bonafide" Carter ...
, watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
, indigo dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive indigo, blue color. Indigo is a natural dye obtained from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera#Uses, ''Indigofera'' genus, in particular ''Indigofera tinctoria''. Dye-bearing ''Indigofer ...
s, and cotton, can be traced to West African and African American influences. Notable examples include George Washington Carver
George Washington Carver ( 1864 – January 5, 1943) was an American Agricultural science, agricultural scientist and inventor who promoted alternative crops to cotton and methods to prevent soil depletion. He was one of the most prominent bla ...
, who created nearly 500 products from peanuts, sweet potatoes, and pecans. Soul food
Soul food is the ethnic cuisine of African Americans. Originating in the Southern United States, American South from the cuisines of Slavery in the United States, enslaved Africans transported from Africa through the Atlantic slave trade, sou ...
is a variety of cuisine popular among African Americans. It is closely related to the cuisine of the Southern United States
The cuisine of the Southern United States encompasses diverse food traditions of several subregions, including Indigenous cuisine of the Americas, cuisine of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern Native American tribes, ...
. The descriptive terminology may have originated in the mid-1960s, when ''soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that ...
'' was a common definer used to describe African American culture (for example, soul music
Soul music is a popular music genre that originated in African-American culture, African-American African-American neighborhood, communities throughout the United States in the late 1950s and early 1960s. Catchy rhythms, stressed by handclaps ...
). African Americans were the first peoples in the United States to make fried chicken, along with Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
immigrants to the South. Although the Scottish had been frying chicken before they emigrated, they lacked the spices and flavor that African Americans had used when preparing the meal. The Scottish American settlers therefore adopted the African American method of seasoning chicken. However, fried chicken was generally a rare meal in the African American community and was usually reserved for special events or celebrations.
Language
African-American English
African-American English (AAE) is the umbrella term for English dialects spoken predominantly by Black people in the United States and, less often, in Canada; most commonly, it refers to a dialect continuum ranging from African-American Vernacu ...
is a variety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
(dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardize ...
, ethnolect
An ethnolect is generally defined as a language variety that marks speakers as members of ethnic groups who originally used another language or distinctive variety. According to another definition, an ethnolect is any speech variety (language, dia ...
, and sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language ( non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, age group, or other social group.
Sociolects involve both passive acquisit ...
) of American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lang ...
, commonly spoken by urban working-class
The working class is a subset of employees who are compensated with wage or salary-based contracts, whose exact membership varies from definition to definition. Members of the working class rely primarily upon earnings from wage labour. Most c ...
and largely bi-dialectal middle-class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Commo ...
African Americans.
African American English evolved during the antebellum period through interaction between speakers of 16th- and 17th-century English of Great Britain and Ireland and various West African languages. As a result, the variety shares parts of its grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rul ...
and phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' 'obsolescent''1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often pre ...
with the Southern American English
Southern American English or Southern U.S. English is a regional dialect or collection of dialects of American English spoken throughout the Southern United States, primarily by White Southerners and increasingly concentrated in more rural areas ...
dialect. African American English differs from Standard American English (SAE) in certain pronunciation characteristics, tense usage, and grammatical structures, which were derived from West African languages (particularly those belonging to the Niger–Congo family).Gullah language
Gullah (also called Gullah-English, Sea Island Creole English, and Geechee) is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people (also called "Geechees" within the community), an African American population living in coastal regions of South Car ...
is an English-based creole language spoken mostly in the coastal regions of South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
by the Gullah
The Gullah () are a subgroup of the African Americans, African American ethnic group, who predominantly live in the South Carolina Lowcountry, Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida within ...
;Afro-Seminole Creole
Afro-Seminole Creole (ASC) is a dialect of Gullah spoken by Black Seminoles in scattered communities in Oklahoma, Texas, and Northern Mexico. spoken by Black Seminoles
The Black Seminoles, or Afro-Seminoles, are an ethnic group of mixed Native Americans in the United States, Native American and African American, African origin associated with the Seminole people in Florida and Oklahoma. They are mostly blood de ...
mostly now in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
and Brackettville, Texas. Louisiana Creole
Louisiana Creole is a French-based creole language spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in the U.S. state of Louisiana. Also known as Kouri-Vini, it is spoken today by people who may racially identify as white, black, mixed, and Native ...
is a French-based creole and spoken mostly in Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
.
Traditional names
African-American names
African-American names are an integral part of African-American tradition. While many Black Americans use names that are popular with wider American culture, several specific naming trends have emerged within African-American culture.
History ...
are part of the cultural traditions of African Americans, most of these cultural names having no connection to Africa but strictly an African American cultural practice that developed in the United States during enslavement.New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
.
Music
African American music
African-American music is a broad term covering a diverse range of musical genres largely developed by African Americans and their culture. Its origins are in musical forms that developed as a result of the enslavement of African Americans prio ...
is one of the most pervasive African American cultural influences in the United States today and is among the most dominant in mainstream popular music. Hip hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip- ...
, R&B, funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African-American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African-Americans in the ...
, rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock-n-roll, and rock 'n' roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from African ...
, soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that ...
, blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
, and other contemporary American musical forms originated in Black communities and evolved from other Black forms of music, including blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
, doo-wop
Doo-wop (also spelled doowop and doo wop) is a subgenre of rhythm and blues music that originated in African-American communities during the 1940s, mainly in the large cities of the United States, including New York, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, ...
, barbershop, ragtime
Ragtime, also spelled rag-time or rag time, is a musical style that had its peak from the 1890s to 1910s. Its cardinal trait is its Syncopation, syncopated or "ragged" rhythm. Ragtime was popularized during the early 20th century by composers ...
, bluegrass, jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
, and gospel music
Gospel music is a traditional genre of Christian music and a cornerstone of Christian media. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of gospel music vary according to culture and social context. Gospel music is compo ...
.
African American-derived musical forms have also influenced and been incorporated into virtually every other popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
genre in the world, including country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, ...
and techno
Techno is a genre of electronic dance music (EDM) which is generally produced for use in a continuous DJ set, with tempos being in the range from 120 to 150 beats per minute (bpm). The central rhythm is typically in common time ( ) and often ...
. African American genres are the most important ethnic vernacular tradition in America, as they have developed independent of African traditions from which they arise more so than any other immigrant groups, including Europeans; make up the broadest and longest lasting range of styles in America; and have, historically, been more influential, interculturally, geographically, and economically, than other American vernacular traditions.
Dance
African Americans have also had an important role in American dance. Bill T. Jones
William Tass Jones, known as Bill T. Jones (born February 15, 1952), is an American Choreography, choreographer, director, author and dancer. He is the co-founder of the Bill T. Jones/Arnie Zane Dance Company. The company's home in Manhattan. J ...
, a prominent modern choreographer and dancer, has included historical African American themes in his work, particularly in the piece "Last Supper at Uncle Tom's Cabin/The Promised Land". Likewise, Alvin Ailey
Alvin Ailey Jr. (January 5, 1931 – December 1, 1989) was an American dancer, director, choreographer, and activist who founded the Alvin Ailey American Dance Theater (AAADT). He created AAADT and its affiliated Alvin Ailey American Dance Cent ...
's artistic work, including his "Revelations" based on his experience growing up as an African American in the South during the 1930s, has had a significant influence on modern dance. Another form of dance, stepping, is an African American tradition whose performance and competition has been formalized through the traditionally Black fraternities and sororities at universities.
Sports
Literature and academics
Many African American authors have written stories, poems, and essays influenced by their experiences as African Americans. African American literature is a major genre in American literature. Famous examples include Langston Hughes
James Mercer Langston Hughes (February 1, 1901 – May 22, 1967) was an American poet, social activist, novelist, playwright, and columnist from Joplin, Missouri. An early innovator of jazz poetry, Hughes is best known as a leader of the Harl ...
, James Baldwin
James Arthur Baldwin (né Jones; August 2, 1924 – December 1, 1987) was an American writer and civil rights activist who garnered acclaim for his essays, novels, plays, and poems. His 1953 novel '' Go Tell It on the Mountain'' has been ranked ...
, Richard Wright, Zora Neale Hurston
Zora Neale Hurston (January 7, 1891 – January 28, 1960) was an American writer, anthropologist, folklorist, and documentary filmmaker. She portrayed racial struggles in the early-20th-century American South and published research on Hoodoo ...
, Ralph Ellison
Ralph Waldo Ellison (March 1, 1913 – April 16, 1994) was an American writer, literary critic, and scholar best known for his novel '' Invisible Man'', which won the National Book Award in 1953.
Ellison wrote '' Shadow and Act'' (1964), a co ...
, Nobel Prize winner Toni Morrison
Chloe Anthony Wofford Morrison (born Chloe Ardelia Wofford; February 18, 1931 – August 5, 2019), known as Toni Morrison, was an American novelist and editor. Her first novel, ''The Bluest Eye'', was published in 1970. The critically accl ...
, and Maya Angelou
Maya Angelou ( ; born Marguerite Annie Johnson; April 4, 1928 – May 28, 2014) was an American memoirist, poet, and civil rights activist. She published seven autobiographies, three books of essays, several books of poetry, and is credi ...
.
African American inventors have created many widely used devices in the world and have contributed to international innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a n ...
. Norbert Rillieux
Norbert Rillieux (March 17, 1806 – October 8, 1894) was a Louisiana Creole inventor who was widely considered one of the earliest chemical engineers and noted for his pioneering invention of the multiple-effect evaporator. This invention w ...
created the technique for converting sugar cane juice into white sugar crystals. Moreover, Rillieux left Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
in 1854 and went to France, where he spent ten years working with the Champollions deciphering Egyptian hieroglyphics
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters.I ...
from the Rosetta Stone
The Rosetta Stone is a stele of granodiorite inscribed with three versions of a Rosetta Stone decree, decree issued in 196 BC during the Ptolemaic dynasty of ancient Egypt, Egypt, on behalf of King Ptolemy V Epiphanes. The top and middle texts ...
. Most slave inventors were nameless, such as the slave owned by the Confederate
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
President Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the only President of the Confederate States of America, president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the Unite ...
who designed the ship propeller used by the Confederate navy.
By 1913, over 1,000 inventions were patented by Black Americans. Among the most notable inventors were Jan Matzeliger, who developed the first machine to mass-produce shoes, and Elijah McCoy
Elijah J. McCoy (May 2, 1844 – October 10, 1929) was a Canadian-American engineer of African Americans, African-American descent who invented lubrication systems for steam engines. Born free on the Ontario shore of Lake Erie to parents ...
, who invented automatic lubrication devices for steam engines. Granville Woods
Granville Tailer Woods (April 23, 1856 – January 30, 1910) was an American inventor who held more than 60 patents in the United States. He was the first African American mechanical and electrical engineer after the Civil War. Self-taught, ...
had 35 patents to improve electric railway systems, including the first system to allow moving trains to communicate. Garrett A. Morgan developed the first automatic traffic signal and gas mask.
Lewis Howard Latimer invented an improvement for the incandescent light bulb. More recent inventors include Frederick McKinley Jones, who invented the movable refrigeration unit for food transport in trucks and trains.Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
) and helped develop the first nuclear reactor.
As part of the preservation of their culture, African Americans have continuously launched their own publications and publishing houses, such as Robert Sengstacke Abbott
Robert Sengstacke Abbott (December 24, 1870 – February 29, 1940) was an American lawyer, newspaper publisher and editor. Abbott founded ''The Chicago Defender'' in 1905, which grew to have the highest circulation of any black-owned newspaper in ...
, founder of the Chicago Defender newspaper, and Carter G. Woodson, the founder of Black History Month
Black History Month is an annually observed commemorative month originating in the United States, where it is also known as African-American History Month. It began as a way of remembering important people and events in the history of the Af ...
who spent over thirty years documenting and publishing African American history in journals and books. The Johnson Publishing Company
Johnson Publishing Company, Inc. (JPC) was an American publishing company founded in November 1942 by African-American businessman John H. Johnson. It was headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. JPC was privately held and run by Johnson until his de ...
, founded by John H. Johnson in 1942, is a National Historic Landmark.
Terminology
General
The term ''African American'' was popularized by Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (Birth name#Maiden and married names, né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American Civil rights movements, civil rights activist, Politics of the United States, politician, and ordained Baptist minister. Beginning as a ...
in the 1980s,colored
''Colored'' (or ''coloured'') is a racial descriptor historically used in the United States during the Jim Crow era to refer to an African American. In many places, it may be considered a slur.
Dictionary definitions
The word ''colored'' wa ...
'', ''person of color
The term "person of color" (: people of color or persons of color; abbreviated POC) is used to describe any person who is not considered "white". In its current meaning, the term originated in, and is associated with, the United States. From th ...
'', or ''negro
In the English language, the term ''negro'' (or sometimes ''negress'' for a female) is a term historically used to refer to people of Black people, Black African heritage. The term ''negro'' means the color black in Spanish and Portuguese (from ...
'') were included in the wording of various laws and legal decisions which some thought were being used as tools of White supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
and oppression
Oppression is malicious or unjust treatment of, or exercise of power over, a group of individuals, often in the form of governmental authority. Oppression may be overt or covert, depending on how it is practiced.
No universally accepted model ...
. A 16-page pamphlet entitled "A Sermon on the Capture of Lord Cornwallis" is notable for the attribution of its authorship to "An ''African American''". Published in 1782, the book's use of this phrase predates any other yet identified by more than 50 years.
In the 1980s, the term ''African American'' was advanced on the model of, for example,
A 16-page pamphlet entitled "A Sermon on the Capture of Lord Cornwallis" is notable for the attribution of its authorship to "An ''African American''". Published in 1782, the book's use of this phrase predates any other yet identified by more than 50 years.
In the 1980s, the term ''African American'' was advanced on the model of, for example, German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
or Irish American
Irish Americans () are Irish ethnics who live within in the United States, whether immigrants from Ireland or Americans with full or partial Irish ancestry.
Irish immigration to the United States
From the 17th century to the mid-19th c ...
, to give descendants of American slaves, and other American Blacks who lived through the slavery era, a heritage
Heritage may refer to:
History and society
* A heritage asset A heritage asset is an item which has value because of its contribution to a nation's society, knowledge and/or culture. Such items are usually physical assets, but some countries also ...
and a cultural base.word of mouth
Word of mouth is the passing of information from person to person using oral communication, which could be as simple as telling someone the time of day. Storytelling is a common form of word-of-mouth communication where one person tells others a ...
and ultimately received mainstream use after Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (Birth name#Maiden and married names, né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American Civil rights movements, civil rights activist, Politics of the United States, politician, and ordained Baptist minister. Beginning as a ...
publicly used the term in front of a national audience in 1988. Subsequently, major media outlets adopted its use.Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
updated its AP Stylebook
''The Associated Press Stylebook'' (generally called the ''AP Stylebook''), alternatively titled ''The Associated Press Stylebook and Briefing on Media Law'', is a style and usage guide for American English grammar created by American journali ...
to direct its writers to capitalize the first letter of ''Black'' when it is used "in a racial, ethnic or cultural sense, conveying an essential and shared sense of history, identity and community among people who identify as Black, including those in the African diaspora and within Africa." ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' and other outlets made similar changes at the same time, to put "Black" on the same footing as other racial and ethnic terms, such as Latino, Asian, and African-American.
In 2023, the government released a new more detailed breakdown due to the rise in racially Black immigration into the US, listing African American as a compound termed ethnicity, distinguished from other racially Black ethnicities such as Nigerian, Jamaican etc.
The term ''African American'' embraces pan-Africanism
Pan-Africanism is a nationalist movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atla ...
as earlier enunciated by prominent African thinkers such as Marcus Garvey
Marcus Mosiah Garvey Jr. (17 August 188710 June 1940) was a Jamaican political activist. He was the founder and first President-General of the Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League (UNIA-ACL) (commonly known a ...
, W. E. B. Du Bois
William Edward Burghardt Du Bois ( ; February 23, 1868 – August 27, 1963) was an American sociologist, socialist, historian, and Pan-Africanist civil rights activist.
Born in Great Barrington, Massachusetts, Du Bois grew up in a relativel ...
, and George Padmore
George Padmore (28 June 1903 – 23 September 1959), born Malcolm Ivan Meredith Nurse, was a leading Pan-Africanist, journalist, and author. He left his native Trinidad in 1924 to study medicine in the United States, where he also joined the C ...
. The term ''Afro-Usonia
Usonia () is a term that was used by the American architect Frank Lloyd Wright to refer to the United States in general (in preference over ''America''), and more specifically to his vision for the landscape of the country, including the planni ...
n'', and variations of such, are more rarely used.
Official identity
Since 1977, in an attempt to keep up with changing social opinion, the United States government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct ...
has officially classified Black people (revised to ''Black'' or ''African American'' in 1997) as "having origins in any of the Black racial groups of Africa."Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). The office's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, while it also examines agency pro ...
standards on race in their data collection and tabulation efforts.Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
of the US Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of federal laws and the administration of justice. It is equ ...
categorizes Black or African American people as " person having origins in any of the Black racial groups of Africa" through racial categories used in the UCR Program adopted from the Statistical Policy Handbook (1978) and published by the Office of Federal Statistical Policy and Standards, US Department of Commerce
The United States Department of Commerce (DOC) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for gathering data for business and governmental decision making, establishing industrial standards, catalyzing econo ...
, derived from the 1977 Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). The office's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, while it also examines agency pro ...
classification.
Admixture
Historically, " race mixing" between Black and White people was taboo
A taboo is a social group's ban, prohibition or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, offensive, sacred or allowed only for certain people.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
in the United States. So-called anti-miscegenation laws
Anti-miscegenation laws are laws that enforce racial segregation at the level of marriage and intimate relationships by criminalizing interracial marriage sometimes, also criminalizing sex between members of different races.
In the United Stat ...
, barring Blacks and Whites from marrying or having sex, were established in colonial America
The colonial history of the United States covers the period of European colonization of North America from the late 15th century until the unifying of the Thirteen British Colonies and creation of the United States in 1776, during the Re ...
as early as 1691, and endured in many Southern states until the Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled them unconstitutional in ''Loving v. Virginia
''Loving v. Virginia'', 388 U.S. 1 (1967), was a landmark civil rights decision of the U.S. Supreme Court that ruled that the laws banning interracial marriage violate the Equal Protection and Due Process Clauses of the Fourteenth Amendment to ...
'' (1967). The taboo among American Whites surrounding White-Black relations is a historical consequence of the oppression and racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
of African Americans. Historian David Brion Davis
David Brion Davis (February 16, 1927 – April 14, 2019) was an American intellectual and cultural historian, and a leading authority on slavery and abolition in the Western world. He was a Sterling Professor of History at Yale University, ...
notes the racial mixing that occurred during slavery was frequently attributed by the planter class
The planter class was a Racial hierarchy, racial and socioeconomic class which emerged in the Americas during European colonization of the Americas, European colonization in the early modern period. Members of the class, most of whom were settle ...
to the "lower-class white males" but Davis concludes that "there is abundant evidence that many slaveowners, sons of slaveowners, and overseers took Black mistresses or in effect raped the wives and daughters of slave families." A famous example was Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
's mistress, Sally Hemings
Sarah "Sally" Hemings ( 1773 – 1835) was a Black people, black woman Slavery in the United States, enslaved to the third President of the United States Thomas Jefferson, inherited among many others from his father-in-law, John Wayles.
Hemi ...
. Although publicly opposed to race mixing, Jefferson, in his ''Notes on the State of Virginia
''Notes on the State of Virginia'' (1785) is a book written by the American statesman, philosopher, and planter Thomas Jefferson. He completed the first version in 1781 and updated and enlarged the book in 1782 and 1783. It originated in Jeffers ...
'' published in 1785, wrote: "The improvement of the Blacks in body and mind, in the first instance of their mixture with the whites, has been observed by every one, and proves that their inferiority is not the effect merely of their condition of life".
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
historian Henry Louis Gates Jr.
Henry Louis Gates Jr. (born September 16, 1950), popularly known by his childhood nickname "Skip", is an American literary critic, professor, historian, and filmmaker who serves as the Alphonse Fletcher University Professor and the director of t ...
wrote in 2009 that "African Americans...are a racially mixed or mulatto
( , ) is a Race (human categorization), racial classification that refers to people of mixed Sub-Saharan African, African and Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the ...
people—deeply and overwhelmingly so". After the Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War. The Proclamation had the eff ...
, Chinese American
Chinese Americans are Americans of Chinese ancestry. Chinese Americans constitute a subgroup of East Asian Americans which also constitute a subgroup of Asian Americans. Many Chinese Americans have ancestors from mainland China, Hong Kong ...
men married African American women in high proportions to their total marriage numbers due to few Chinese American women being in the United States.Puerto Ricans
Puerto Ricans (), most commonly known as Puerto Rico#Etymology, Boricuas, but also occasionally referred to as '':es:Anexo:Gentilicios de Puerto Rico#Lista general, Borinqueños'', '':es:Anexo:Gentilicios de Puerto Rico#Lista general, Borincan ...
and African Americans.
Racially mixed marriages have become increasingly accepted in the United States since the civil rights movement and up to the present day.Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
impregnated local non-Black women, resulting in the birth of thousands of mixed-race children. Many of these families later immigrated to the United States.
Terminology dispute
Author Debra Dickerson has argued that the term ''Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
'' should refer strictly to the descendants of Africans who were brought to America as slaves, and not to the sons and daughters of Black immigrants who lack that ancestry. Thus, under her definition, President Barack Obama, who is the son of a Kenyan, is not Black.Stanley Crouch
Stanley Lawrence Crouch (December 14, 1945 – September 16, 2020) was an American cultural critic, poet, playwright, novelist, biographer, and syndicated columnist. He was known for his jazz criticism and his 2000 novel ''Don't the Moon Lo ...
in a ''New York Daily News
The ''Daily News'' is an American newspaper based in Jersey City, New Jersey. It was founded in 1919 by Joseph Medill Patterson in New York City as the ''Illustrated Daily News''. It was the first U.S. daily printed in Tabloid (newspaper format ...
'' piece, Charles Steele Jr. of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference
The Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) is an African Americans, African-American civil rights organization based in Atlanta, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. SCLC is closely associated with its first president, Martin Luther King Jr., ...
and African American columnist David Ehrenstein of the ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' is an American Newspaper#Daily, daily newspaper that began publishing in Los Angeles, California, in 1881. Based in the Greater Los Angeles city of El Segundo, California, El Segundo since 2018, it is the List of new ...
'', who accused White liberals of flocking to Blacks who were '' Magic Negros'', a term that refers to a Black person with no past who simply appears to assist the mainstream White (as cultural protagonists/drivers) agenda.American Descendants of Slavery
American Descendants of Slavery (ADOS) is a term referring to descendants of enslaved Africans in the area that would become the United States (from its colonial period onward), and to the political movement of the same name. Both the term and th ...
(ADOS) movement coalesces around this view, arguing that Black descendants of American slavery deserve a separate ethnic category that distinguishes them from other Black groups in the United States.Pan-African
Pan-Africanism is a nationalist movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all indigenous peoples and diasporas of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the Trans-Sa ...
movements and organizations that are ideologically Black nationalist
Black nationalism is a nationalist movement which seeks representation for Black people as a distinct national identity, especially in racialized, colonial and postcolonial societies. Its earliest proponents saw it as a way to advocate for ...
, anti-imperialist
Anti-imperialism in political science and international relations is opposition to imperialism or neocolonialism. Anti-imperialist sentiment typically manifests as a political principle in independence struggles against intervention or influenc ...
, anti-Zionist
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the State of Israel in 1948, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the Palestine (region) ...
, and Scientific socialist like The All-African People's Revolutionary Party (A-APRP), have argued that African (relating to the diaspora) or New Afrikan should be used instead of African American. Most notably, Malcolm X
Malcolm X (born Malcolm Little, later el-Hajj Malik el-Shabazz; May 19, 1925 – February 21, 1965) was an African American revolutionary, Islam in the United States, Muslim minister and human rights activist who was a prominent figur ...
and Kwame Ture
Kwame Ture (; born Stokely Standiford Churchill Carmichael; June 29, 1941November 15, 1998) was an American activist who played a major role in the civil rights movement in the United States and the global pan-African movement. Born in Trinid ...
expressed similar views that African Americans are Africans who "happen to be in America", and should not claim or identify as being American if they are fighting for Black (New Afrikan) liberation. Historically, this is due to the enslavement of Africans during the transatlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
, ongoing anti-Black violence, and structural racism in countries like the United States.
Terms no longer in common use
Before the independence of the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
until the abolition of slavery in 1865, an African American slave was commonly known as a ''negro
In the English language, the term ''negro'' (or sometimes ''negress'' for a female) is a term historically used to refer to people of Black people, Black African heritage. The term ''negro'' means the color black in Spanish and Portuguese (from ...
''. '' Free negro'' was the legal status in the territory of an African American person who was not enslaved. In response to the project of the American Colonization Society
The American Colonization Society (ACS), initially the Society for the Colonization of Free People of Color of America, was an American organization founded in 1816 by Robert Finley to encourage and support the repatriation of freeborn peop ...
to transport free Blacks to the future Liberia, a project most Blacks strongly rejected, the Blacks at the time said they were no more African than White Americans were European, and referred to themselves with what they considered a more acceptable term, "colored
''Colored'' (or ''coloured'') is a racial descriptor historically used in the United States during the Jim Crow era to refer to an African American. In many places, it may be considered a slur.
Dictionary definitions
The word ''colored'' wa ...
Americans". The term was used until the second quarter of the 20th century, when it was considered outmoded and generally gave way again to the exclusive use of ''negro''. By the 1940s, the term was commonly capitalized (''Negro''); but by the mid-1960s, it was considered disparaging. By the end of the 20th century, ''negro'' had come to be considered inappropriate and was rarely used and perceived as a pejorative
A pejorative word, phrase, slur, or derogatory term is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hosti ...
. The term is rarely used by younger Black people, but remained in use by many older African Americans who had grown up with the term, particularly in the Southern US. The term remains in use in some contexts, such as the United Negro College Fund
UNCF, the United Negro College Fund, also known as the United Fund, is an American philanthropic organization that funds scholarships for black students and general scholarship funds for 37 private historically black colleges and universities. ...
, an American philanthropic organization.
There are many other deliberately insulting terms, many of which were in common use (e.g., ''nigger
In the English language, ''nigger'' is a racial slur directed at black people. Starting in the 1990s, references to ''nigger'' have been increasingly replaced by the euphemistic contraction , notably in cases where ''nigger'' is Use–menti ...
''), but had become unacceptable in normal discourse before the end of the 20th century. One exception is the use, among the Black community, of the slur ''nigger'' rendered as ''nigga
''Nigga'' (), also known as "''the N-word''", is a colloquial term in African-American Vernacular English that is considered as a vulgar word in most contexts of its use. It began as a dialect form of the word ''nigger'', an ethnic slur agai ...
'', representing the pronunciation of the word in African American English
African-American English (AAE) is the umbrella term for English dialects spoken predominantly by Black people in the United States and, less often, in Canada; most commonly, it refers to a dialect continuum ranging from African-American Vern ...
. This usage has been popularized by American rap and hip-hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hi ...
music cultures and is used as part of an in-group
In social psychology and sociology, an in-group is a social group to which a person psychologically identifies as being a member. By contrast, an out-group is a social group with which an individual does not identify. People may for example ...
lexicon
A lexicon (plural: lexicons, rarely lexica) is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Greek word () ...
and speech. It is not necessarily derogatory
A pejorative word, phrase, slur, or derogatory term is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility ...
and, when used among Black people, the word is often used to mean " homie" or "friend".NAACP
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is an American civil rights organization formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E. B. Du&nbs ...
denounces the use of both ''nigga'' and ''nigger''.
See also
* African-American art
African-American art is known as a broad term describing visual art created by African Americans. The range of art they have created, and are continuing to create, over more than two centuries is as varied as the artists themselves. Some have dr ...
* African American cinema
* African-American middle class
The African-American middle class consists of African-Americans who have middle-class status within the American class structure. It is a societal level within the African-American community that primarily began to develop in the early 1960s, ...
* African-American neighborhood
African-American neighborhoods or black neighborhoods are types of ethnic enclaves found in many cities in the United States. Generally, an African American neighborhood is one where the majority of the people who live there are African American ...
* African-American politics:
:*African-American leftism
African-American leftism refers to Left-wing politics, left-wing political currents that have developed among various African-American communities in the United States. These currents are active around social issues, and often call for an Afr ...
:*African-American socialism
African-American socialism is a political current that emerged in the nineteenth century, specifically referring to the origins and proliferation of Marxist ideologies among African-Americans for whom socialism represents a potential for equal c ...
:* Black anarchism
:*Black conservatism in the United States
In the United States, black conservatism is a political and social movement rooted in African-American communities that aligns largely with the American conservative movement, including the Christian right. Black conservatism emphasizes social c ...
:* Black liberalism
:* Black populism
:*Black women in American politics
Black women have been involved in American Political sociology, socio-political issues and advocating for the community since the American Civil War era through Nonprofit organization, organizations, clubs, community-based social services, and adv ...
* African-American upper class
The African-American upper class, sometimes referred to as the black upper class, the black upper middle class or black elite, is a social class that consists of African-American individuals who have high disposable incomes and high net wor ...
* African diaspora in the Americas
The African diaspora in the Americas refers to the people born in the Americas with partial, predominant, or complete sub-Saharan African ancestry. Many are descendants of persons enslaved in Africa and transferred to the Americas by Europeans, ...
* Afrophobia
Anti-African sentiment, Afroscepticism, or Afrophobia is prejudice, discrimination, or racism towards people and cultures of Africa and of the African diaspora.
Prejudice against Africans and people of African descent has a long history, dati ...
* AP African American Studies
Advanced Placement (AP) African American Studies (also known as APAAS, APAFAM, AP African, or AP Afro) is a college-level course and examination offered to high school students in the United States through the College Board's Advanced Placement ...
* Black Belt in the American South
The Black Belt in the American South refers to the social history, especially concerning slavery and black workers, of the geological region known as the Black Belt. The geology emphasizes the highly fertile black soil. Historically, the bla ...
* Black Hispanic and Latino Americans
Black Hispanic and Latino Americans, also called Afro-Hispanics, Afro-Latinos, Black Hispanics, or Black Latinos, are classified by the United States Census Bureau, Office of Management and Budget, and other U.S. government agencies as Black ...
* Black mecca
A black mecca, in the United States, is a city to which African Americans, particularly singles, professionals, and middle-class families, are drawn to live, due to some or all of the following factors:
* superior economic opportunities for bla ...
* Black Ozarkers
* Black Southerners
Black Southerners are African Americans living in the Southern United States, the United States region with the largest black population.
Despite a total of 6 million Blacks migrating from the South to cities in the North and West from 1916 ...
* Brown Babies
* Civil rights movement (1865–1896)
The civil rights movement (1865–1896) aimed to eliminate racial discrimination against African Americans, improve their educational and employment opportunities, and establish their electoral power, just after the abolition of slavery in the U ...
* Civil rights movement (1896–1954)
The civil rights movement (1896–1954) was a long, primarily nonviolent action to bring full civil rights and equality under the law to all Americans. The era has had a lasting impact on American society – in its tactics, the increased social ...
* Juneteenth
Juneteenth is a federal holiday in the United States, federal holiday in the United States. It is celebrated annually on June 19 to commemorate the End of slavery in the United States, ending of slavery in the United States. The holiday's n ...
* National Museum of African American History and Culture
The National Museum of African American History and Culture (NMAAHC), colloquially known as the Blacksonian, is a Smithsonian Institution museum located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., in the United States. It was established in 2003 an ...
* North Africans in the United States
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' ...
* Society and Black people in the Spanish Colonial Americas
* South African Americans
* Stereotypes of African Americans
Stereotypes of African Americans are misleading beliefs about the African-American culture, culture of people with partial or total ancestry from any Black people, black racial groups of Africa whose ancestors resided in the United States sin ...
* Timeline of the civil rights movement
* African immigration to the United States
African immigration to the United States refers to immigrants to the United States who are or were nationals of modern African countries. The term ''African'' in the scope of this article refers to geographical or national origins rather than rac ...
* West Indian Americans
* African American–Jewish relations
* African American–Korean American relations
Diaspora
* African Americans in Africa
** African Americans in Ghana
** Americo-Liberian people
** Sierra Leone Creole people
The Sierra Leone Creole people () are an ethnic group of Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone Creole people are descendants of freed African-American, Afro-Caribbean, and Liberated African slaves who settled in the Western Area of Sierra Leone be ...
* African Americans in Canada
* African Americans in France
* African Americans in Israel
* Black Nova Scotians
Black Nova Scotians (also known as African Nova Scotians, Afro-Nova Scotians, and Africadians) are Black Canadians whose ancestors primarily date back to the Colonial history of the United States, Colonial United States as Slavery in the United S ...
* Samaná Americans
* Haitian emigration
* Merikins
Lists
* Index of articles related to African Americans
* List of African-American neighborhoods
* List of majority-Black counties in the United States
* List of African-American newspapers and media outlets
* List of historically black colleges and universities
* List of African-American astronauts
* List of African-American inventors and scientists
* List of African-American LGBT people
* List of African American poets
* List of African-American visual artists
* List of monuments to African Americans
* List of populated places in the United States with African-American plurality populations
* List of topics related to the African diaspora
* List of African-American holidays
* Lists of African Americans
Notes
References
Further reading
*
* Finkelman, Paul, ed. ''Encyclopedia of African American History, 1619–1895: From the Colonial Period to the Age of Frederick Douglass'' (3 vol Oxford University Press, 2006).
** Finkelman, Paul, ed. ''Encyclopedia of African American History, 1896 to the Present: From the Age of Segregation to the Twenty-first Century'' (5 vol. Oxford University Press, US, 2009).
* John Hope Franklin, Alfred Moss, ''From Slavery to Freedom. A History of African Americans'', McGraw-Hill Education 2001, standard work, first edition in 1947.
* Gates, Henry L. and Evelyn Brooks Higginbotham (eds), ''African American Lives'', Oxford University Press, 2004 – more than 600 biographies.
* Darlene Clark Hine, Hine, Darlene Clark, Rosalyn Terborg-Penn, Elsa Barkley Brown (eds), ''Black Women in America: An Historical Encyclopedia'', (Indiana University Press 2005).
*
* Horton, James Oliver, and Lois E. Horton. ''Hard Road to Freedom: The Story of African America, African Roots Through the Civil War. Vol. 1'' (Rutgers University Press, 2002); ''Hard Road to Freedom: The Story of African America: Volume 2: From the Civil War to the Millennium'' (2002)
online
* Kranz, Rachel. ''African-American Business Leaders and Entrepreneurs'' (Infobase Publishing, 2004).
* Salzman, Jack, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Afro-American culture and history'', New York City: Macmillan Library Reference US, 1996.
*
*
External links
* Richard Thompson For
Name Games
''Slate'', September 16, 2004. Article discussing the problems of defining ''African American''
''Scientific American'' Magazine (June 2006) Trace Elements
Reconnecting African Americans to an ancestral past
Black History related original documents and photos
* Frank Newport
"Black or African American?"
, Gallup, September 28, 2007
"The Long Journey of Black Americans"
nbsp;– slideshow by ''The First Post''
{{Authority control
African-American society,
Ethnic groups in the United States
History of civil rights in the United States
African-American culture,
Ethnonyms of African Americans
 The first recorded Africans in English America (including most of the future United States) were "20 and odd negroes" who arrived in Jamestown,
The first recorded Africans in English America (including most of the future United States) were "20 and odd negroes" who arrived in Jamestown,  By the 1640s and 1650s, several African families owned farms around Jamestown, and some became wealthy by colonial standards and purchased indentured servants of their own. In 1640, the Virginia General Court recorded the earliest documentation of lifetime slavery when they sentenced John Punch, a Negro, to lifetime servitude under his master Hugh Gwyn, for running away.
In
By the 1640s and 1650s, several African families owned farms around Jamestown, and some became wealthy by colonial standards and purchased indentured servants of their own. In 1640, the Virginia General Court recorded the earliest documentation of lifetime slavery when they sentenced John Punch, a Negro, to lifetime servitude under his master Hugh Gwyn, for running away.
In  One of the Dutch African arrivals, Anthony Johnson, would later own one of the first Black "slaves", John Casor, resulting from the court ruling of a civil case.John Henderson Russell, ''The Free Negro In Virginia, 1619–1865''
One of the Dutch African arrivals, Anthony Johnson, would later own one of the first Black "slaves", John Casor, resulting from the court ruling of a civil case.John Henderson Russell, ''The Free Negro In Virginia, 1619–1865'' In
In  During the 1770s, Africans, both enslaved and free, helped rebellious American colonists secure their independence by defeating the British in the
During the 1770s, Africans, both enslaved and free, helped rebellious American colonists secure their independence by defeating the British in the  Emigration of free Blacks to their continent of origin had been proposed since the Revolutionary war. After
Emigration of free Blacks to their continent of origin had been proposed since the Revolutionary war. After  The desperate conditions of African Americans in the South sparked the Great Migration during the first half of the 20th century which led to a growing African American community in Northern and Western United States. The rapid influx of Blacks disturbed the racial balance within Northern and Western cities, exacerbating hostility between both Blacks and Whites in the two regions. The
The desperate conditions of African Americans in the South sparked the Great Migration during the first half of the 20th century which led to a growing African American community in Northern and Western United States. The rapid influx of Blacks disturbed the racial balance within Northern and Western cities, exacerbating hostility between both Blacks and Whites in the two regions. The  The
The 

 In 1790, when the first US census was taken, Africans (including slaves and free people) numbered about 760,000—about 19.3% of the population. In 1860, at the start of the
In 1790, when the first US census was taken, Africans (including slaves and free people) numbered about 760,000—about 19.3% of the population. In 1860, at the start of the  During slavery, anti-literacy laws were enacted in the US that prohibited education for Black people. Slave owners saw literacy as a threat to the institution of slavery. As a North Carolina statute stated, "Teaching slaves to read and write, tends to excite dissatisfaction in their minds, and to produce insurrection and
During slavery, anti-literacy laws were enacted in the US that prohibited education for Black people. Slave owners saw literacy as a threat to the institution of slavery. As a North Carolina statute stated, "Teaching slaves to read and write, tends to excite dissatisfaction in their minds, and to produce insurrection and  Between 1995 and 2009, freshmen college enrollment for African Americans increased by 73 percent and only 15 percent for Whites. Black women are enrolled in college more than any other race and gender group, leading all with 9.7% enrolled according to the 2011 US census.
The average high school graduation rate of Blacks in the United States has steadily increased to 71% in 2013. Separating this statistic into component parts shows it varies greatly depending upon the state and the school district examined. 38% of Black males graduated in the state of New York but in Maine 97% graduated and exceeded the White male graduation rate by 11 percentage points. In much of the southeastern United States and some parts of the southwestern United States the graduation rate of White males was in fact below 70% such as in Florida where 62% of White males graduated from high school. Examining specific school districts paints an even more complex picture. In the Detroit school district, the graduation rate of Black males was 20% but 7% for White males. In the New York City school district 28% of Black males graduate from high school compared to 57% of White males. In Newark County 76% of Black males graduated compared to 67% for White males. Further academic improvement has occurred in 2015. Roughly 23% of all Blacks have bachelor's degrees. In 1988, 21% of Whites had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 11% of Blacks. In 2015, 23% of Blacks had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 36% of Whites. Foreign born Blacks, 9% of the Black population, made even greater strides. They exceed native born Blacks by 10 percentage points.
Between 1995 and 2009, freshmen college enrollment for African Americans increased by 73 percent and only 15 percent for Whites. Black women are enrolled in college more than any other race and gender group, leading all with 9.7% enrolled according to the 2011 US census.
The average high school graduation rate of Blacks in the United States has steadily increased to 71% in 2013. Separating this statistic into component parts shows it varies greatly depending upon the state and the school district examined. 38% of Black males graduated in the state of New York but in Maine 97% graduated and exceeded the White male graduation rate by 11 percentage points. In much of the southeastern United States and some parts of the southwestern United States the graduation rate of White males was in fact below 70% such as in Florida where 62% of White males graduated from high school. Examining specific school districts paints an even more complex picture. In the Detroit school district, the graduation rate of Black males was 20% but 7% for White males. In the New York City school district 28% of Black males graduate from high school compared to 57% of White males. In Newark County 76% of Black males graduated compared to 67% for White males. Further academic improvement has occurred in 2015. Roughly 23% of all Blacks have bachelor's degrees. In 1988, 21% of Whites had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 11% of Blacks. In 2015, 23% of Blacks had obtained a bachelor's degree versus 36% of Whites. Foreign born Blacks, 9% of the Black population, made even greater strides. They exceed native born Blacks by 10 percentage points.
 Homeownership in the US is the strongest indicator of financial stability and the primary asset most Americans use to generate wealth. African Americans continue to lag behind other racial groups in homeownership. In the first quarter of 2021, 45.1% of African Americans owned their homes, compared to 65.3% of all Americans. The African American homeownership rate has remained relatively flat since the 1970s despite an increase in anti-discrimination housing laws and protections. The African American homeownership rate peaked in 2004 at 49.7%.
The average White high school drop-out still has a slightly better chance of owning a home than the average African American college graduate usually due to unfavorable
Homeownership in the US is the strongest indicator of financial stability and the primary asset most Americans use to generate wealth. African Americans continue to lag behind other racial groups in homeownership. In the first quarter of 2021, 45.1% of African Americans owned their homes, compared to 65.3% of all Americans. The African American homeownership rate has remained relatively flat since the 1970s despite an increase in anti-discrimination housing laws and protections. The African American homeownership rate peaked in 2004 at 49.7%.
The average White high school drop-out still has a slightly better chance of owning a home than the average African American college graduate usually due to unfavorable  The majority of African Americans are
The majority of African Americans are  Malcolm X is considered the first person to start the movement among African Americans towards mainstream Islam, after he left the Nation and made the
Malcolm X is considered the first person to start the movement among African Americans towards mainstream Islam, after he left the Nation and made the  Recent studies of African Americans using genetic testing have found ancestry to vary by region and sex of ancestors. These studies found that on average, African Americans have 73.2–82.1% Sub-Saharan African, 16.7–24% European, and 0.8–1.2% Native American genetic ancestry, with large variation between individuals. Commercial testing services have reported similar variation, with ranges from 0.6 to 2 percent Native American, 19 to 29 percent European, and 65 to 80 percent Sub-Saharan African ancestry.
According to a genome-wide study by Bryc et al. (2009), the mixed ancestry of African Americans in varying ratios came about as the result of sexual contact between West/Central Africans (more frequently females) and Europeans (more frequently males). This can be understood as being the result of enslaved African American females being
Recent studies of African Americans using genetic testing have found ancestry to vary by region and sex of ancestors. These studies found that on average, African Americans have 73.2–82.1% Sub-Saharan African, 16.7–24% European, and 0.8–1.2% Native American genetic ancestry, with large variation between individuals. Commercial testing services have reported similar variation, with ranges from 0.6 to 2 percent Native American, 19 to 29 percent European, and 65 to 80 percent Sub-Saharan African ancestry.
According to a genome-wide study by Bryc et al. (2009), the mixed ancestry of African Americans in varying ratios came about as the result of sexual contact between West/Central Africans (more frequently females) and Europeans (more frequently males). This can be understood as being the result of enslaved African American females being  The first ever anti-miscegenation law was passed by the
The first ever anti-miscegenation law was passed by the  African Americans have fought in every war in the
African Americans have fought in every war in the  A 16-page pamphlet entitled "A Sermon on the Capture of Lord Cornwallis" is notable for the attribution of its authorship to "An ''African American''". Published in 1782, the book's use of this phrase predates any other yet identified by more than 50 years.
In the 1980s, the term ''African American'' was advanced on the model of, for example,
A 16-page pamphlet entitled "A Sermon on the Capture of Lord Cornwallis" is notable for the attribution of its authorship to "An ''African American''". Published in 1782, the book's use of this phrase predates any other yet identified by more than 50 years.
In the 1980s, the term ''African American'' was advanced on the model of, for example,