Aecial on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
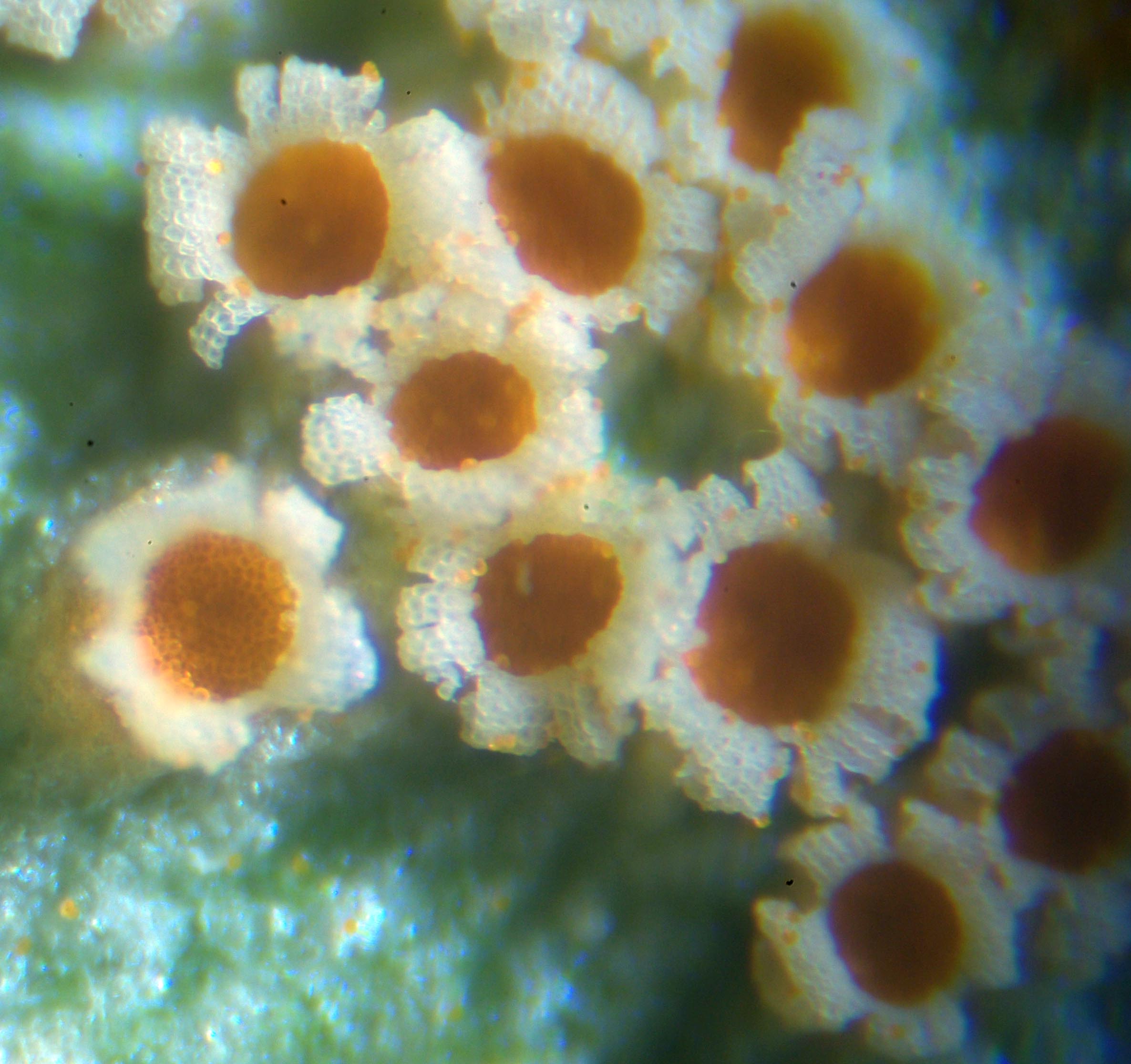 An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic
An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic  In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species.
In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species.
 An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic
An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH) ...
fungi that produce aeciospores. Aecia may also be referred to as "cluster cups". The term aecidium (plural aecidia) is used interchangeably but is not preferred.
In some rust fungi such as '' Phragmidium'', aecia lack an outer wall structure (a peridium
The peridium is the protective layer that encloses a mass of spores in fungi. This outer covering is a distinctive feature of gasteroid fungi.
Description
Depending on the species, the peridium may vary from being paper-thin to thick and rubb ...
) but instead produce a diffuse aecium called a caeoma.''Fungi''. Lilian E Hawker, 1966, Hutchinson University Library
 In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species.
In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species.
References
Fungal morphology and anatomy Reproductive system {{mycology-stub