additive mixing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a
 Systems of additive color are motivated by the
Systems of additive color are motivated by the
RGB and CMYK Colour systems.
- Photos and stories from the James Clerk Maxwell Foundation. * Stanford University CS 17
comparing additive and subtractive color mixing. {{DEFAULTSORT:Additive Color Color space Color
 Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a color model
In color science, a color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components. When this model is associated with a precise description ...
that predicts the appearance of color
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though co ...
s made by coincident component light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
s, i.e. the perceived color can be predicted by summing the numeric representations of the component colors. Modern formulations of Grassmann's laws describe the additivity in the color perception of light mixtures in terms of algebraic equations. Additive color predicts perception and not any sort of change in the photons of light themselves. These predictions are only applicable in the limited scope of color matching experiments where viewers match small patches of uniform color isolated against a gray or black background.
Additive color models are applied in the design and testing of electronic displays that are used to render realistic images containing diverse sets of color using phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
s that emit light of a limited set of primary color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color prin ...
s. Examination with a sufficiently powerful magnifying lens will reveal that each pixel in CRT, LCD, and most other types of color video displays is composed of red, green, and blue light-emitting phosphors which appear as a variety of single colors when viewed from a normal distance.
Additive color, alone, does not predict the appearance of mixtures of printed color inks, dye layers in color photograph
A photograph (also known as a photo, or more generically referred to as an ''image'' or ''picture'') is an image created by light falling on a photosensitivity, photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor. Th ...
s on film
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, sinc ...
, or paint mixtures. Instead, subtractive color
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and pigments are ...
is used to model the appearance of pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s or dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
s, such as those in paint
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are ...
s and inks.
The combination of two of the common three additive primary color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color prin ...
s in equal proportions produces an additive secondary color
A secondary color is a color made by color mixing, mixing two primary colors of a given color model in even proportions. Combining two secondary colors in the same manner produces a tertiary color. Secondary colors are special in traditional co ...
—cyan
Cyan () is the color between blue and green on the visible spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength between 500 and 520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.
In the subtractive color system, or CMYK c ...
, magenta
Magenta () is a purple-red color. On color wheels of the RGB color model, RGB (additive) and subtractive color, CMY (subtractive) color models, it is located precisely midway between blue and red. It is one of the four colors of ink used in colo ...
or yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In t ...
. Additive color is also used to predict colors from overlapping projected colored lights often used in theatrical lighting for plays, concerts, circus shows, and night clubs.
The full gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. cam ...
of color available in any additive color system is defined by all the possible combinations of all the possible luminosities of each primary color in that system. In chromaticity space, a gamut is a plane convex polygon
In geometry, a convex polygon is a polygon that is the boundary of a convex set. This means that the line segment between two points of the polygon is contained in the union of the interior and the boundary of the polygon. In particular, it is ...
with corners at the primaries. For three primaries, it is a triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
.
History
 Systems of additive color are motivated by the
Systems of additive color are motivated by the Young–Helmholtz theory
The Young–Helmholtz theory (based on the work of Thomas Young and Hermann von Helmholtz in the 19th century), also known as the trichromatic theory, is a theory of trichromatic color vision – the manner in which the visual system gives rise ...
of trichromatic color vision, which was articulated around 1850 by Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (; ; 31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894; "von" since 1883) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The ...
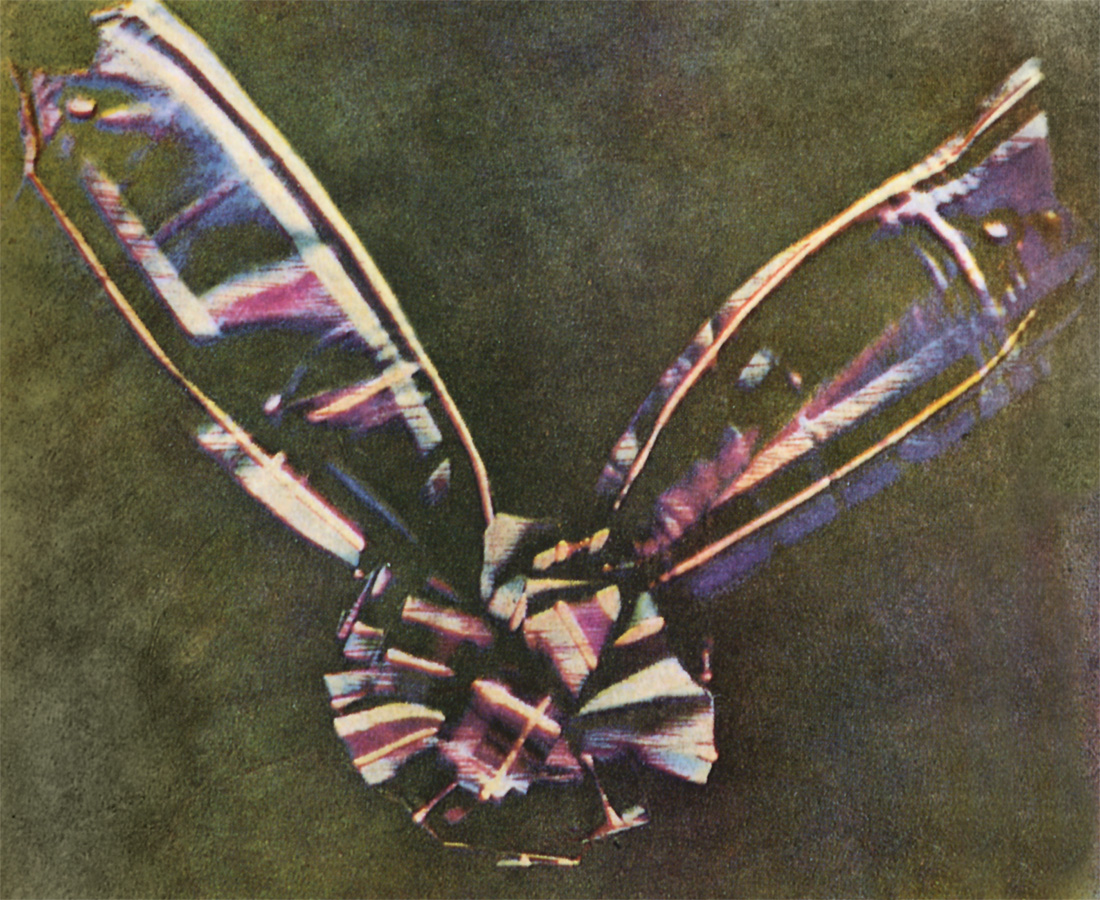
, based on earlier work by Thomas Young. For his experimental work on the subject, James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism an ...
is sometimes credited as being the father of additive color. He had the photographer Thomas Sutton photograph a tartan ribbon on black-and-white film three times, first with a red, then green, then blue color filter over the lens. The three black-and-white images were developed and then projected onto a screen with three different projectors, each equipped with the corresponding red, green, or blue color filter used to take its image. When brought into alignment, the three images (a black-and-red image, a black-and-green image and a black-and-blue image) formed a full-color image, thus demonstrating the principles of additive color.
See also
* Color mixing *Color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represe ...
* Color theory
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is a historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color th ...
* Color motion picture film
Color motion picture film refers both to unexposed color photography, color photographic film in a format suitable for use in a Movie camera, motion picture camera, and to finished motion picture film, ready for use in a projector, which bears i ...
* Kinemacolor
* Prizma Color
* RGB color model
The RGB color model is an additive color, additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials ...
* Subtractive color
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and pigments are ...
* Technicolor
Technicolor is a family of Color motion picture film, color motion picture processes. The first version, Process 1, was introduced in 1916, and improved versions followed over several decades.
Definitive Technicolor movies using three black-and ...
* William Friese-Greene
William Friese-Greene (born William Edward Green, 7 September 1855 – 5 May 1921) was a prolific English inventor and professional photographer. He was known as a pioneer in the field of motion pictures, having devised a series of cameras bet ...
References
External links
RGB and CMYK Colour systems.
- Photos and stories from the James Clerk Maxwell Foundation. * Stanford University CS 17
comparing additive and subtractive color mixing. {{DEFAULTSORT:Additive Color Color space Color