Absorption Nebula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of 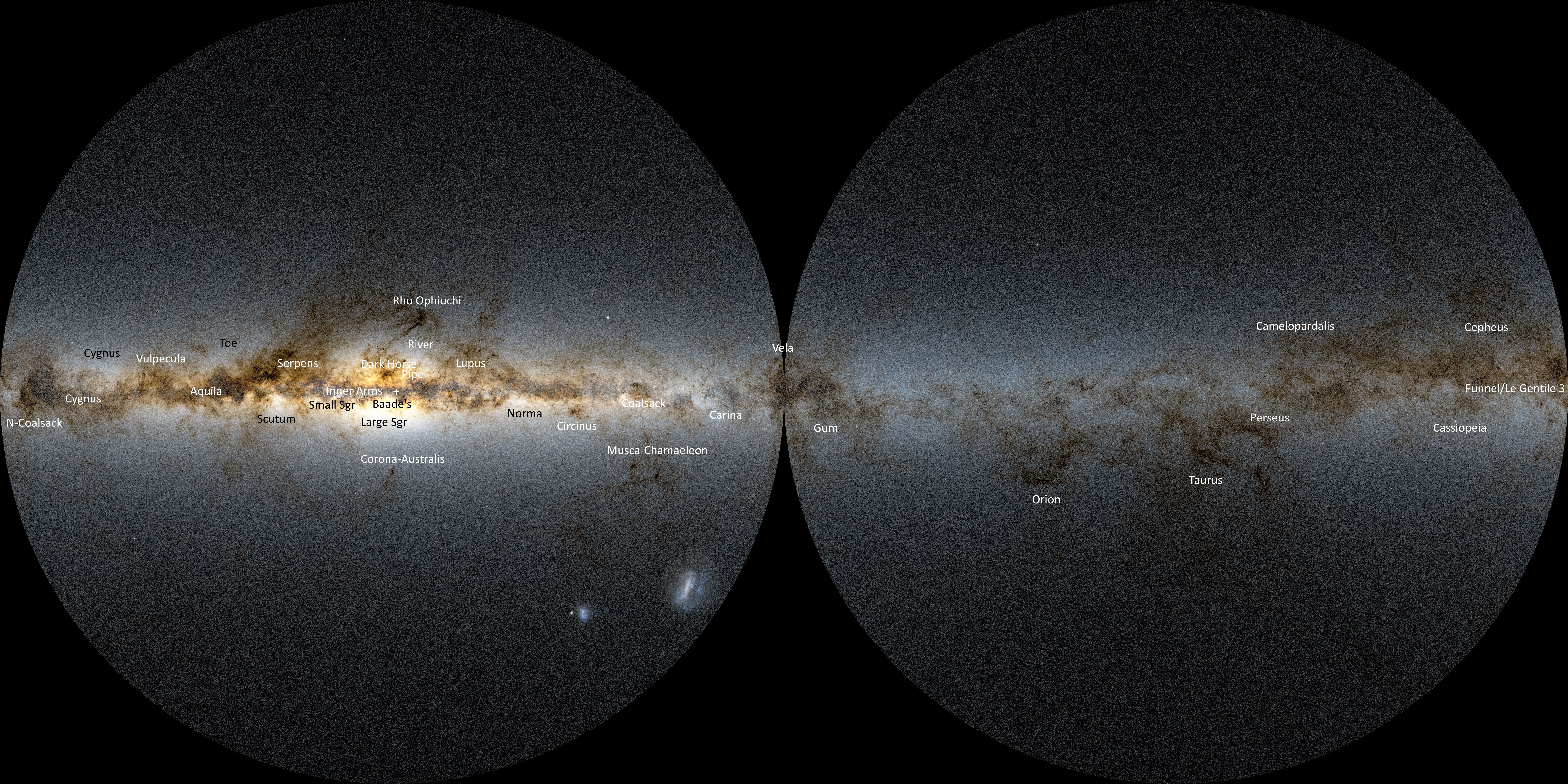


File:All Quiet in the Nursery?.jpg, Dark nebula
interstellar cloud
An interstellar cloud is generally an accumulation of gas, plasma, and dust in our and other galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium, the matter and radiation that exists in ...
, particularly molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
s, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection nebulae. The extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds ( taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed ...
of the light is caused by interstellar dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
grains located in the coldest, densest parts of molecular clouds. Clusters and large complexes of dark nebulae are associated with Giant Molecular Clouds. Isolated small dark nebulae are called Bok globule
In astronomy, Bok globules are isolated and relatively small dark nebulae, containing dense cosmic dust and gas from which star formation may take place. Bok globules are found within H II regions, and typically have a mass of about 2 to 50 so ...
s. Like other interstellar dust or material, things it obscures are only visible using radio waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (s ...
in radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation comi ...
or infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from aroun ...
in infrared astronomy
Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers, and falls in betwee ...
.
Dark clouds appear so because of sub-micrometre-sized dust particles, coated with frozen carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
and nitrogen, which effectively block the passage of light at visible wavelengths. Also present are molecular hydrogen, atomic helium, C18O (CO with oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
as the 18O isotope), CS, NH3 (ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogeno ...
), H2CO (formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) ( systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
), c-C3H2 (cyclopropenylidene
Cyclopropenylidene, or ''c''-C3H2, is a partially aromatic molecule belonging to a highly reactive class of organic molecules known as carbenes. On Earth, cyclopropenylidene is only seen in the laboratory due to its reactivity. However, cyclopr ...
) and a molecular ion N2H+ (diazenylium frameless, right
Diazenylium is the chemical N2H+, an inorganic cation that was one of the first ions to be observed in interstellar clouds. Since then, it has been observed for in several different types of interstellar environments, observatio ...
), all of which are relatively transparent. These clouds are the spawning grounds of stars and planets, and understanding their development is essential to understanding star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions", collapse and form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includ ...
.
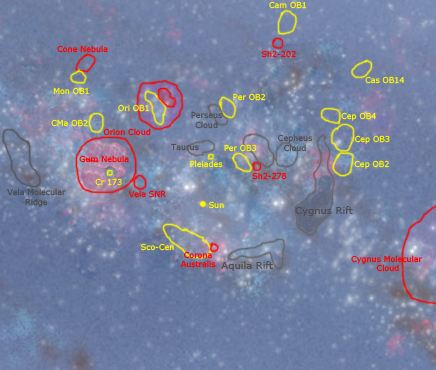
The form of such dark clouds is very irregular: they have no clearly defined outer boundaries and sometimes take on convoluted serpentine shapes. The largest dark nebulae are visible to the naked eye, appearing as dark patches against the brighter background of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked ey ...
like the Coalsack Nebula
The Coalsack Nebula (Southern Coalsack, or simply the Coalsack) is a prominent dark nebula in the skies, being easily visible to the naked eye as a dark patch obscuring a brief section of Milky Way stars as they cross their southernmost region of ...
and the Great Rift. These naked-eye objects are sometimes known as dark cloud constellations and take on a variety of names.
In the inner outer molecular regions of dark nebulae, important events take place, such as the formation of stars and masers
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, James ...
.




Image gallery
LDN 1768 LDN is usually contractional slang for London, UK.
LDN may also refer to: Arts and media
* London Daily News, former newspaper
* BBC London (formerly ''BBC LDN''), broadcasting body
* "LDN" (song), a 2006 single by Lily Allen
Language
* Láadan, ...
contains protostars.
File:A Hole in the Sky.jpg, Dark nebula called LDN1774, taken by the Wide Field Imager, an instrument mounted on ESO
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 member states for ground-based ast ...
’s 2.2-meter MPG/ESO telescope at La Silla.
File:The dark nebula LDN 483.jpg, Dark nebula LDN 483 is located about 700 light-years away in the constellation of Serpens
Serpens ( grc, , , the Serpent) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International ...
(The Serpent).
File:The Dark Cloud Lupus 4.jpg, Lupus 4 is a dense pocket of gas and dust where new stars are expected to form.
See also
*List of dark nebulae
This is a list of dark nebulae (absorption nebulae), also called "dark clouds".
List
* E Nebula (Barnard 142 and 143)
* Barnard 68, possibly the closest to Earth at about 400 light-years.
* Bernes 157 (Sandqvist and Lindroos, SL 39-41), another ...
* Bok globule
In astronomy, Bok globules are isolated and relatively small dark nebulae, containing dense cosmic dust and gas from which star formation may take place. Bok globules are found within H II regions, and typically have a mass of about 2 to 50 so ...
* Dark Cloud (disambiguation) ''Dark Cloud'' is the first in a series of console role-playing games. Its spiritual sequel is ''Dark Cloud 2'' or ''Dark Chronicle''.
Dark cloud or dark clouds may also refer to:
* Dark nebula or ''dark cloud'', a type of interstellar cloud
* Dark ...
References
{{Authority control Nebulae Cosmic dust