Abortion In Ohio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Abortion in
Abortion in
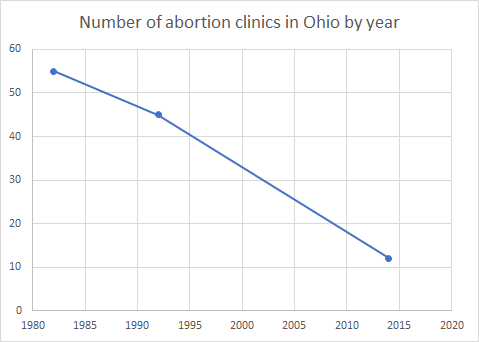 Between 1982 and 1992, the number of
Between 1982 and 1992, the number of
71-year-old admits to vandalism on Planned Parenthood building
,
Judge grants probation to 71-year-old woman who vandalized Planned Parenthood building
, ''Columbus Dispatch'' (November 15, 2016). Jackson was sentenced to probation, with the judge citing her struggle with serious mental illness as a mitigating factor.
Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
is legal on request up to the point of fetal viability
Fetal viability is the ability of a human fetus to survive outside the uterus. Viability depends upon factors such as birth weight, gestational age, and the availability of advanced medical care. In low-income countries, more than 90% of extr ...
(roughly 23 weeks) as a result of abortion rights being placed into the Ohio State Constitution
The Constitution of the State of Ohio is the basic governing document of the State of Ohio, which in 1803 became the 17th state to join the United States of America. Ohio has had three constitutions since statehood was granted.
Ohio was created ...
by November 2023 Ohio Issue 1, adopted by 56% of voters.
Planned Parenthood
The Planned Parenthood Federation of America, Inc. (PPFA), or simply Planned Parenthood, is an American nonprofit organization
and the ACLU
The American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) is an American nonprofit civil rights organization founded in 1920. ACLU affiliates are active in all 50 states, Washington, D.C., and Puerto Rico. The budget of the ACLU in 2024 was $383 million.
...
are advocating in court to have other pre-amendment restrictions nullified, such as a 24-hour waiting period, laws prohibiting advanced practice nurses and similar healthcare providers from prescribing abortion medications, and a law prohibiting the prescription of mifepristone
Mifepristone, and also known by its developmental code name RU-486, is a drug typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days (9 wee ...
(which is commonly used for medication abortion
A medical abortion, also known as medication abortion or non-surgical abortion, occurs when drugs (medication) are used to bring about an abortion. Medical abortions are an alternative to surgical (also called procedural or instrumentation) a ...
) for any off-label Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication (medicine), indication or in an unapproved age group, dose (biochemistry), dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) ca ...
use.
Current Ohio law
Due to November 2023 Ohio Issue 1, abortions up tofetal viability
Fetal viability is the ability of a human fetus to survive outside the uterus. Viability depends upon factors such as birth weight, gestational age, and the availability of advanced medical care. In low-income countries, more than 90% of extr ...
are legal in Ohio. Ohio has multiple layers of law on abortion, resulting from multiple laws passed over the decades. However, these laws are no longer enforceable.
A " heartbeat bill" that banned abortions after six weeks of gestational age
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method, if available. Such metho ...
that was enacted before Issue 1 was challenged in court, with the Attorney General of Ohio
The Ohio attorney general is the chief legal officer of the state of Ohio in the United States. The office is filled by general election, held every four years. The Ohio attorney general is Republican Dave Yost.
History
The office of the att ...
and other Republican leaders in Ohio defending it in court. The six-week abortion ban was struck down by an Ohio judge in October 2024.
Laws no longer enforceable
On April 11, 2019, Ohio GovernorMike DeWine
Richard Michael DeWine ( ; born January 5, 1947) is an American politician and attorney serving as the 70th List of governors of Ohio, governor of Ohio since 2019. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served a ...
signed the ''Human Rights and Heartbeat Protection Act'', which banned abortion in Ohio after any embryonic cardiac activity is detected. No exceptions were made for rape, incest or fetal inviability; the only exception, according to ORC 2919.193(B), is a medical emergency, defined in 2919.16(F) & (K) as "serious risk of the substantial and irreversible impairment of a major bodily function of the pregnant woman."
Included in this law, ORC 2919.198, was a section called "Immunity of pregnant woman." This section overrides penalties for pregnant women who undertake an abortion ''after embryonic cardiac activity'' had been detected. This release of penalties did not extend to physicians or doctors who administered the abortion past detectable cardiac activity.
The law only went into effect on June 24, 2022, after the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
overturned ''Roe v. Wade
''Roe v. Wade'', 410 U.S. 113 (1973),. was a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States protected the right to have an ...
''. On October 7, a judge granted a motion for preliminary injunction against the abortion bans. The decision meant abortions through 22 weeks gestation could continue, in keeping with state law in place before the ban.
Context
According to a 2017 report from theCenter for Reproductive Rights
The Center for Reproductive Rights (CRR) is a global legal advocacy organization, headquartered in New York City, that seeks to advance reproductive rights, such as abortion. The organization's stated mission is to "use the law to advance reprod ...
and Ibis Reproductive Health, states that tried to pass additional constraints on a woman's ability to access legal abortions had fewer policies supporting women's health, maternal
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of gestatio ...
health and children's health. These states also tended to resist expanding Medicaid, family leave, medical leave, and sex education in public schools. According to Megan Donovan, a senior policy manager at the Guttmacher Institute
The Guttmacher Institute is a research and policy NGO that aims to improve sexual health and expand reproductive rights worldwide. The organization was started in 1968 as part of Planned Parenthood; it became independent from Planned Parenthood ...
, states with legislation that protects a woman's right to access abortion services have the lowest rates of infant mortality in the United States. In 2017, Georgia, Ohio, Missouri, Louisiana, Alabama and Mississippi had among the highest rates of infant mortality in the United States. In 2017, Ohio had an infant mortality rate of 7.2 deaths per 1,000 live births.
In the 2022 Ohio child-rape and Indiana abortion case
On June 30, 2022, a ten-year-old girl from Columbus, Ohio, United States, traveled to Indiana to get an abortion because abortion law in Ohio did not provide an exception for minor children who became pregnant because of rape. Her case drew nat ...
a ten-year-old girl from Columbus, Ohio
Columbus (, ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities in Ohio, most populous city of the U.S. state of Ohio. With a 2020 United States census, 2020 census population of 905,748, it is the List of United States ...
traveled to Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
to get an abortion because the 6-week abortion ban passed did not provide an exception for those who became pregnant because of rape. This includes those who are children or are otherwise minors. Her case drew national attention and commentary from public figures, due in part to its proximity to the June 24, 2022, decision of the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
in ''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization
''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization'', 597 U.S. 215 (2022), is a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States, United States Supreme Court in which the court held ...
'', which overturned ''Roe v. Wade
''Roe v. Wade'', 410 U.S. 113 (1973),. was a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States protected the right to have an ...
'' and allowed states, including Ohio, to impose unlimited limitations on abortion access.
In September 2022, shortly after Ohio's 6-week abortion ban went into effect, a woman made national news when she almost bled to death after an Ohio hospital refused to treat her miscarriage. In late September 2022, abortion providers filed affidavits in Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
as part of a lawsuit aimed at stopping enforcement of the 6-week abortion ban. The affidavits detailed instances of minors who had been sexually assaulted having to leave the state to obtain abortions, several women who threatened suicide or self-harm because of the inability to receive an abortion, and women with cancer who were refused abortions and could not receive cancer treatment while pregnant.
In the year following the overturn of Roe v. Wade in 2022, 210 pregnant women in a dozen states were criminally charged for conduct associated with their pregnancy, pregnancy loss or birth. Six states — Alabama, Mississippi, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina and Texas — accounted for most cases.
In September 2023, 34 year old Brittany Watts of Warren, Ohio
Warren is a city in Trumbull County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. The population was 39,201 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Located along the Mahoning River, Warren lies approximately northwest of Youngstown, Ohio, Y ...
was arrested after having a miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
at home and was charged with "abusing a corpse". An Ohio grand jury later dismissed the charges.
History
Legislative history
By the end of the 1800s, all states in the Union except Louisiana had therapeutic exceptions in their legislative bans on abortions. In 1978,Akron
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 census. The Akron metropolitan area, covering Summit and Portage counties, had ...
, Ohio, passed a city ordinance that restricted abortion rights.
The state was one of 23 states in 2007 to have a detailed abortion-specific informed consent requirement. Mississippi, Nebraska, North Dakota and Ohio all had statutes in 2007 that required specific informed consent on abortion but also, by statute, allowed medical doctors performing abortions to disassociate themselves with the anti-abortion
Anti-abortion movements, also self-styled as pro-life movements, are involved in the abortion debate advocating against the practice of abortion and its Abortion by country, legality. Many anti-abortion movements began as countermovements in r ...
materials they were required to provide to their female patients. The Ohio legislature was one of five states nationwide that tried, and failed, to pass a "fetal heartbeat" bill in 2013. Only North Dakota successfully passed such a law, but it was later struck down by the courts. They tried with this type of legislation again unsuccessfully in 2018.
Among those who believe that abortion is murder, some believe it may be appropriate to punish it with death. While attempts to criminalize abortion generally focus on the doctor, Texas state Rep. Tony Tinderholt (R) introduced a bill in 2017 and 2019 that may enable the death penalty in Texas for women who have abortions, and the Ohio legislature considered a similar bill in 2018.
In Ohio, a "fetal heartbeat" law, HB 125, was introduced in the state legislature in October 2011. It was the only state in the country to try to pass such legislation that year. The bill was shelved by the Republican majority Senate to avoid controversy. This bill was notably supported by John C. Willke. A related law was signed in Ohio in 2013 by Governor John Kasich
John Richard Kasich Jr. ( ; born May 13, 1952) is an American politician and author who was the 69th governor of Ohio from 2011 to 2019, a member of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1983 to 2001, and a Republican candidate for the pre ...
, which mandates, among other things, that doctors who do not test for embryonic cardiac activity when a patient seeks an abortion, tell the patient in writing if there is embryonic cardiac activity, and then tell them the statistical likelihood that the fetus could be carried to term, are subject to criminal penalties; specifically, "The doctor's failure to do so would be a first-degree misdemeanor, carrying up to six months in jail, for the first violation and a fourth-degree felony, carrying up to 18 months in jail, for subsequent violations." A bill similar to the 2011–2012 bill was introduced by Christina Hagan in 2013, titled HB 248. A further "fetal heartbeat" law was introduced on August 14, 2013, by Lynn Wachtmann and others. In 2013, Ohio passed a Targeted Regulation of Abortion Providers (TRAP) bill containing provisions related to admitting privileges and licensing and requiring clinics to have a transfer agreement with a hospital. "Fetal heartbeat" bills appeared again in the state legislature in 2014. On March 25, 2015, another "heartbeat" bill (House Bill 69) passed the Ohio House of Representatives. ''The Guardian'' reported that "The bill is unlikely to go any further, facing stiff opposition in the senate as well as from John Kasich, the Republican governor of Ohio." On December 6, 2016, the Ohio Senate added a heartbeat ban provision to an unrelated bill, House Bill 493, previously passed by the Ohio House of Representatives. The bill
''The Bill'' is a British police procedural television series, broadcast on ITV (TV network), ITV from 16 October 1984 until 31 August 2010. The programme originated from a one-off drama, "Woodentop (The Bill), Woodentop" (part of the ''Storyb ...
was returned to the House and passed by the House the same day. The bill as passed would make abortion after the detection of embryonic cardiac activity a fifth-degree felony except in cases where a physician judges the abortion necessary "to prevent the death of the pregnant woman or to prevent a serious risk of the substantial and irreversible impairment of a major bodily function of the pregnant woman." On December 13, 2016, Kasich vetoed the bill. Attempts to pass a "fetal heartbeat" law continued in 2016, with Ohio being one of eight states nationwide that tried and failed to pass such legislation.
In early 2018, the House considered a bill passed by the Senate to ban abortion after 13 weeks and require that fetal remains be cremated or buried. In 2018, the state was one of eleven where the legislature introduced a bill that failed to pass that would have banned abortion in almost all cases.
Nationally, 2019 was one of the most active years for state legislatures in terms of trying to pass abortion rights restrictions. State governments with Republican majorities started to push these bills after Brett Kavanaugh
Brett Michael Kavanaugh (; born February 12, 1965) is an American lawyer and jurist serving as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was nominated by President Donald Trump on July 9, 2018, and has served since Oct ...
was confirmed as a US Supreme Court judge, replacing the more liberal Anthony Kennedy
Anthony McLeod Kennedy (born July 23, 1936) is an American attorney and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1988 until his retirement in 2018. He was nominated to the court in 1987 by Pres ...
. These state governments generally saw this as a positive sign that new moves to restrict abortion rights would be less likely to face resistance in the courts. Two "fetal heartbeat" bills were introduced in the Ohio General Assembly
The Ohio General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Ohio. It consists of the 99-member Ohio House of Representatives and the 33-member Ohio Senate. Both houses of the General Assembly meet at the Ohio Statehouse in Colu ...
in 2019, marking the 133rd Session of the Ohio General Assembly as the fifth time such legislation has been proposed in the state. On February 11, 2019, Candice Keller
Candice Keller (born ) is an American politician and former state representative for the 53rd District of the Ohio House of Representatives, which includes part of Butler County, Ohio, Butler County. A Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
and Ron Hood filed HB 68, which was introduced in the Ohio House of Representatives
The Ohio House of Representatives is the lower house of the Ohio General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Ohio; the other house of the bicameral legislature being the Ohio Senate.
The House of Representatives first met in ...
on February 12, 2019. On February 12, 2019, Kristina Roegner filed SB 23 in the Ohio Senate
The Ohio Senate is the upper house of the Ohio General Assembly. The State Senate, which meets in the Ohio Statehouse in Columbus, first convened in 1803. Senators are elected for four year terms, staggered every two years such that half of t ...
; the bill was referred to the Health, Human Services and Medicaid Committee on February 13, 2019. On February 21, 2019, the President of the Ohio Senate, Larry Obhof pledged to pass SB 23 out of the upper chamber stating, "We are going to pass that bill by the middle of March. I have no doubt at all." On March 13, 2019, SB 23 was passed out of the Ohio Senate by a vote of 19 to 13. The next month, the Ohio House amended the bill, and passed it, 56–40; the changes were ratified in the Senate, 18–13. The bill was signed into law by Governor Mike DeWine
Richard Michael DeWine ( ; born January 5, 1947) is an American politician and attorney serving as the 70th List of governors of Ohio, governor of Ohio since 2019. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served a ...
on April 11, 2019. At the time the bill passed, only 27% of the state legislators were female. The law, slated to go into effect in July 2019, would make abortion illegal after embryonic cardiac activity can be detected, usually between five or six weeks into the pregnancy. No exceptions for cases of rape or incest are made.
In July 2019 a federal judge temporarily enjoined the state's officials, and the County Prosecutors of Cuyahoga, Hamilton, Franklin, Richland, Mahoning, Montgomery, and Lucas Counties, from enforcing this prohibition against the state's abortion providers. This injunction does not, however, prevent County Prosecutors outside Cuyahoga, Hamilton, Franklin, Richland, Mahoning, Montgomery, and Lucas Counties from enforcing the criminal prohibition on post-embryonic cardiac activity abortions, nor does it prevent them from prosecuting individuals or organizations that aid or abet abortions after embryonic cardiac activity, which remains a criminal offense under Ohio law.
In November 2019, a bill was introduced by Candice Keller
Candice Keller (born ) is an American politician and former state representative for the 53rd District of the Ohio House of Representatives, which includes part of Butler County, Ohio, Butler County. A Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
and Ron Hood, House Bill 413, which would if made into law ban abortion outright and require doctors to reimplant an ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these sympto ...
, a medical procedure that obstetricians and gynecologists contend is currently impossible.
In 2020 a bill was signed into law in Ohio requiring all aborted fetal tissue to be cremated or buried.
In 2021 the city of Lebanon, Ohio
Lebanon is a city in Warren County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. The population was 20,841 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is part of the Cincinnati metropolitan area.
History
Lebanon is in the Symmes Purchase. Th ...
, passed an ordinance whereby abortion at all stages of pregnancy was outlawed. Mason, Ohio
Mason is a city in southwestern Warren County, Ohio, United States, approximately north of downtown Cincinnati. As of the United States Census 2020, 2020 census, Mason's population was 34,792. It is home to Kings Island amusement park and one of ...
, also banned abortion at all stages in 2021, but its ordinance was repealed later that year.
August 2023 Ohio Issue 1 was put to referendum on August 8, 2023, and would have made it harder for voter-led initiatives to be proposed and approved. The issue was widely seen as being related to the issue of abortion, as November 2023 Ohio Issue 1, a referendum to restore ''Roe v. Wade''-era access to abortion in the state, was slated to appear on the November 2023 ballot, along with future proposals to raise the minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. List of countries by minimum wage, Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation b ...
. The intent of this initiative, according to its creator, Republican State Representative
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United St ...
Brian Stewart, was to "top
Top most commonly refers to:
* Top, a basic term of orientation, distinguished from bottom, front, back, and sides
* Spinning top, a ubiquitous traditional toy
* Top (clothing), clothing designed to be worn over the torso
* Mountain top, a moun ...
a whole host of eferendumissues that we know are coming down the pike" including redistricting
Redistricting in the United States is the process of drawing electoral district boundaries. For the United States House of Representatives, and state legislatures, redistricting occurs after each ten-year census.
The U.S. Constitution in Art ...
, minimum wages
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. Bec ...
, qualified immunity
In the United States, qualified immunity is a legal principle of federal law that grants government officials performing discretionary (optional) functions immunity from lawsuits for damages unless the plaintiff shows that the official violated "c ...
, and, most notably, abortion rights
Abortion-rights movements, also self-styled as pro-choice movements, are movements that advocate for legal access to induced abortion services, including elective abortion. They seek to represent and support women who wish to terminate their p ...
. Of the more than 3 million votes counted, 57% were "no" votes and 43% voted "yes".
November 2023 referendum
November 2023 Ohio Issue 1 was a statewide referendum on whether to amend the state constitution to include a right to abortion and other reproductive healthcare. Ohio was the only state in 2023 to consider a statewide constitutional right to abortion. Issue 1 was written to undo a 2019 trigger law, which was triggered by Dobbs, banning all abortion after six weeks — a so-called heartbeat law — with no exceptions for rape or incest; it included language that allowed Ohioans to "make and carry out one’s own reproductive decisions" to the point of viability. Viability is a medical concept determined by a physician and as of 2023 is generally considered to be between 22 and 24 weeks gestation. The initiative was also written to grant exceptions for later abortions to protect the life of the pregnant individual. The initiative was also designed to provide legal protections to anyone aiding someone in accessing abortion. Ohio's ballot board, which had a Republican majority, changed language in the ballot initiative to replace the word "fetus" with "unborn child" and to omit references tobirth control
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
.
The amendment was passed 56.78% to 43.22% with turnout that was heavy for an off-year election
An off-year election in the United States typically refers to a general election held in an odd-numbered year when neither a presidential election nor a midterm election takes place. At times, the term "off-year" may also be used to refer to ...
.
Judicial history
In 1913 in the case of '' State v. Tipple'', the Ohio Supreme Court said, "The reason and policy of the statute are to protect women and unborn babes from dangerous criminal practice, and to discourage secret immorality between the sexes, and a vicious and craven custom amongst married pairs who wish to evade the responsibilities of rearing offspring." TheUS Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
's decision in 1973's ''Roe v. Wade
''Roe v. Wade'', 410 U.S. 113 (1973),. was a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States protected the right to have an ...
'' ruling meant the state could no longer regulate abortion in the first trimester; however, the Supreme Court overturned ''Roe v. Wade
''Roe v. Wade'', 410 U.S. 113 (1973),. was a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court ruled that the Constitution of the United States protected the right to have an ...
'' in ''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization
''Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization'', 597 U.S. 215 (2022), is a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States, United States Supreme Court in which the court held ...
'', later in 2022.
In '' Akron v. Akron Center for Reproductive Health'', 462 U.S. 416 (1983), the Supreme Court declared unconstitutional an ordinance requiring second-trimester abortions to be performed in hospitals, and requiring patients seeking abortions to be informed of the status of the pregnancy, stage of fetal development, expected date of viability, health risks of abortion, and the availability of adoption agencies and childbirth resources. The Supreme Court also declared unconstitutional provisions in the ordinance requiring women to wait 24 hours after seeking an abortion, requiring parental consent for minors seeking abortions, and requiring that aborted fetuses be disposed of in a "humane" and "sanitary" manner.
The Supreme Court later overruled ''Akron v. Akron Center for Reproductive Health'', 462 U.S. 416 (1983), in ''Planned Parenthood v. Casey
''Planned Parenthood v. Casey'', 505 U.S. 833 (1992), was a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States in which the Court upheld the right to have an abortion as established by the "essential holding" of '' Roe v. Wade'' (1973) ...
'', 505 U.S. 833 (1992).
In August 2024, a county judge in Ohio blocked the state's 24 hour waiting period for obtaining an abortion, citing that it was unconstitutional under November 2023 Ohio Issue 1. A few weeks later, another county judge in Ohio struck down two laws that restricted access to mifepristone
Mifepristone, and also known by its developmental code name RU-486, is a drug typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days (9 wee ...
.
In October 2024, the six week abortion ban was struck down by an Ohio judge, citing that it was unconstitutional under November 2023 Ohio Issue 1.
Clinic history
 Between 1982 and 1992, the number of
Between 1982 and 1992, the number of abortion clinic
An abortion clinic or abortion provider is a medical facility that provides abortions. Such clinics may be public medical centers, private medical practices or nonprofit organizations such as Planned Parenthood.
Statistics
Canada
*There were ...
s in the state decreased by ten, going from 55 in 1982 to 45 in 1992. In 2014, there were twelve abortion clinics in the state. In 2014, 93% of the counties in the state did not have an abortion clinic. That year, 56% of women in the state aged 15–44 lived in a county without an abortion clinic. In March 2016, there were 28 Planned Parenthood
The Planned Parenthood Federation of America, Inc. (PPFA), or simply Planned Parenthood, is an American nonprofit organization
clinics in the state. In 2017, there were 27 Planned Parenthood clinics serving a population of 2,585,171 women aged 15–49. Three of the Planned Parenthood clinics offered abortion services.
Statistics
In the period between 1972 and 1974, the state had an illegal abortion mortality rate per million women aged 15–44 of between 0.1 and 0.9. In 1990, 1,314,000 women in the state faced the risk of an unintended pregnancy. In 2010, the state had nine publicly funded abortions, of which nine were federally funded and none were state funded. In 2014, 48% of adults said in a poll by thePew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. The 2023 American Values Atlas reported that, in their most recent survey, 64% of Ohioans said that abortion should be legal in all or most cases.
The number of abortion clinic
An abortion clinic or abortion provider is a medical facility that provides abortions. Such clinics may be public medical centers, private medical practices or nonprofit organizations such as Planned Parenthood.
Statistics
Canada
*There were ...
s in Ohio has declined over the years, with 55 in 1982, 45 in 1992 and 12 in 2014. There were 21,186 legal abortions in 2014 and 20,976 in 2015.
Abortion rights views and activities
Protests
Women from the state participated in marches supporting abortion rights as part of a #StoptheBans movement in May 2019. In May 2019, women participated in a heartbeat ban bill protest in Cleveland as part of #StoptheBans movement. It was organized by NARAL Pro Choice Ohio, Planned Parenthood Advocates of Ohio andCleveland State University
Cleveland State University (CSU) is a public research university in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It was established in 1964 and opened for classes in 1965 after acquiring the entirety of Fenn College, a private school that had been in oper ...
students. A #StoptheBans protest in Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
saw dozens of people participating outside the Hamilton County Courthouse where they chanted "Right to life, that's a lie, you don't care if women die".
Following the overturn of Roe v. Wade on June 24, 2022, hundreds of abortion rights protesters gathered at the Ohio State Capitol in Columbus. Other protests were held in Akron
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 census. The Akron metropolitan area, covering Summit and Portage counties, had ...
, Bowling Green
A bowling green is a finely laid, close-mown and rolled stretch of turf for playing the game of bowls.
Before 1830, when Edwin Beard Budding of Thrupp, near Stroud, UK, invented the lawnmower, lawns were often kept cropped by grazing sheep ...
, Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
, and Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
. On July 10, a group of abortion rights protesters in Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
camped out in front of City Hall for a week.
On July 5, 2023, Ohioans United For Reproductive Rights submitted over 700,000 signatures to the Ohio Secretary of State for their petition to get abortion rights on the November 2023 ballot, more than the 414,000 signatures required.
Attacks on abortion clinics
The first clinic arson occurred inOregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
in March 1976 and the first bombing occurred in February 1978 in Ohio. In 1978, there were three arson attacks and four bomb attacks on abortion facilities in the United States. Of these seven attacks, all but two took place in Ohio. These seven attacks caused combined damage of US$800,000.
In 1977, there were four arson attacks on abortion clinics. These took place in Minnesota, Vermont, Nebraska and Ohio. Combined, they caused over US$1.1 million in damage. By 2000, an act of violence had taken place at an abortion clinic in Shelby County, Ohio. On March 7, 2016, Rachel Ann Jackson, 71, vandalized a Planned Parenthood clinic in Columbus, Ohio
Columbus (, ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities in Ohio, most populous city of the U.S. state of Ohio. With a 2020 United States census, 2020 census population of 905,748, it is the List of United States ...
, with the message "SATAN DEN OF BABY KILLERS..." She pleaded guilty to felony counts of breaking and entering and vandalism and a misdemeanor count of aggravated trespass.,
WCMH
WCMH-TV (channel 4) is a television station in Columbus, Ohio, United States, affiliated with NBC and owned by Nexstar Media Group. The station's studios are located on Olentangy River Road near the Ohio State University campus, and its transm ...
(August 8, 2016).John FuttyJudge grants probation to 71-year-old woman who vandalized Planned Parenthood building
, ''Columbus Dispatch'' (November 15, 2016). Jackson was sentenced to probation, with the judge citing her struggle with serious mental illness as a mitigating factor.
Local ordinances
In 1978,Akron, Ohio
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Akron metr ...
, passed a city ordinance that restricted abortion rights. Its provisions included requiring all abortions beyond the first trimester of pregnancy to be performed in a hospital; a doctor to inform the patient of the status of fetal development, risks of abortion, and childbirth and adoption resources; and a 24-hour waiting period. The ordinance was ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
in '' City of Akron v. Akron Center for Reproductive Health''.
The city of Lebanon, Ohio
Lebanon is a city in Warren County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. The population was 20,841 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is part of the Cincinnati metropolitan area.
History
Lebanon is in the Symmes Purchase. Th ...
, in 2021 outlawed most abortions within its city boundaries and declared itself a "sanctuary city for the unborn". The Lebanon ordinance declares abortion to be "a murderous act of violence that purposefully and knowingly terminates a human life," and it outlaws abortion "at all times and at all stages of pregnancy." The only exception is for abortions performed "in response to a life-threatening physical condition aggravated by, caused by, or arising from a pregnancy" that "places the woman in danger of death or a serious risk of substantial impairment of a major bodily function unless an abortion is performed." The ordinance was adopted by a unanimous vote of the Lebanon city council on May 25, 2021.
The city council of Mason adopted a similar ordinance outlawing most abortions within city limits on October 25, 2021. The ordinance also declares abortion-inducing drugs to be contraband and outlaws their possession and distribution within city limits. Violators are subject to punishment of up to 180 days in jail and a fine of up to $1,000. On December 13, 2021, the city council of Mason voted to repeal this ordinance.
See also
*2022 Ohio child-rape and Indiana abortion case
On June 30, 2022, a ten-year-old girl from Columbus, Ohio, United States, traveled to Indiana to get an abortion because abortion law in Ohio did not provide an exception for minor children who became pregnant because of rape. Her case drew nat ...
* November 2023 Ohio Issue 1
References
{{OhioOhio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
Healthcare in Ohio
Women in Ohio