Abnormal Termination on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

 An operating system crash commonly occurs when a
An operating system crash commonly occurs when a
abend.org
This usage derives from the ''ABEND'' macro on IBM
on madisoncollege.edu Abends can be "soft" (allowing automatic recovery) or "hard" (terminating the activity). The term is jocularly claimed to be derived from the German word " Abend" meaning "evening"."Abend"
on dictionary.die.net
Picking Up The Pieces After A Computer Crash
{{DEFAULTSORT:Crash (Computing) Computer jargon Computer errors Software anomalies
 In
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not computer operator, operating, system administration, administering or computer programming, programming the computer. An application (app, application program, sof ...
or an operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic
A kernel panic (sometimes abbreviated as KP) is a safety measure taken by an operating system's Kernel (operating system), kernel upon detecting an internal Fatal system error, fatal error in which either it is unable to safely recover or con ...
or fatal system error
A fatal system error (also known as a system crash, stop error, kernel error, or bug check) occurs when an operating system halts because it has reached a condition where it can no longer operate safely (i.e., where critical data could be lost ...
.
Most crashes are the result of a software bug
A software bug is a design defect ( bug) in computer software. A computer program with many or serious bugs may be described as ''buggy''.
The effects of a software bug range from minor (such as a misspelled word in the user interface) to sev ...
. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter
The program counter (PC), commonly called the instruction pointer (IP) in Intel x86 and Itanium microprocessors, and sometimes called the instruction address register (IAR), the instruction counter, or just part of the instruction sequencer, ...
, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal or unauthorized
Authorization or authorisation (see spelling differences), in information security, computer security and IAM (Identity and Access Management), is the function of specifying rights/privileges for accessing resources, in most cases through an a ...
opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considered to be the cause of the crash, which is discovered through the process of debugging
In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the Root cause analysis, root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bug (engineering), bugs.
For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, control flow analysis, Logf ...
. The original bug can be far removed from the code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
that actually triggered the crash.
In early personal computers, attempting to write data to hardware addresses outside the system's main memory could cause hardware damage. Some crashes are exploitable and let a malicious program or hacker
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who achieves goals and solves problems by non-standard means. The term has become associated in popular culture with a security hackersomeone with knowledge of bug (computing), bugs or exp ...
execute arbitrary code
In computer security, arbitrary code execution (ACE) is an attacker's ability to run any commands or code of the attacker's choice on a target machine or in a target process. An arbitrary code execution vulnerability is a security flaw in softwar ...
, allowing the replication of viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almo ...
or the acquisition of data which would normally be inaccessible.
Application crashes
Anapplication
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a ...
typically crashes when it performs an operation that is not allowed by the operating system. The operating system then triggers an exception or signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
in the application. Unix applications traditionally responded to the signal by dumping core. Most Windows and Unix GUI
Gui or GUI may refer to:
People Surname
* Gui (surname), an ancient Chinese surname, ''xing''
* Bernard Gui (1261 or 1262–1331), inquisitor of the Dominican Order
* Luigi Gui (1914–2010), Italian politician
* Gui Minhai (born 1964), Ch ...
applications respond by displaying a dialogue box (such as the one shown in the accompanying image on the right) with the option to attach a debugger
A debugger is a computer program used to test and debug other programs (the "target" programs). Common features of debuggers include the ability to run or halt the target program using breakpoints, step through code line by line, and display ...
if one is installed. Some applications attempt to recover from the error and continue running instead of exiting.
An application can also contain code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
to crash after detecting a severe error.
Typical errors that result in application crashes include:
*attempting to read or write memory that is not allocated for reading or writing by that application (e.g., segmentation fault
In computing, a segmentation fault (often shortened to segfault) or access violation is a Interrupt, failure condition raised by hardware with memory protection, notifying an operating system (OS) the software has attempted to access a restricted ...
, x86-specific general protection fault
A general protection fault (GPF) in the x86 instruction set architectures (ISAs) is a fault (a type of interrupt) initiated by ISA-defined protection mechanisms in response to an access violation caused by some running code, either in the kern ...
)
*attempting to execute privileged or invalid instructions
*attempting to perform I/O operations on hardware devices to which it does not have permission to access
*passing invalid arguments to system calls
*attempting to access other system resources to which the application does not have permission to access
*attempting to execute machine instructions with bad arguments (depending on CPU architecture): divide by zero
In mathematics, division by zero, division where the divisor (denominator) is zero, is a unique and problematic special case. Using fraction notation, the general example can be written as \tfrac a0, where a is the dividend (numerator).
The u ...
, operations on denormal number
In computer science, subnormal numbers are the subset of denormalized numbers (sometimes called denormals) that fill the underflow gap around zero in floating-point arithmetic. Any non-zero number with magnitude smaller than the smallest positive ...
or NaN (not a number) values, memory access to unaligned addresses, etc.
Crash to desktop
A "crash to desktop" (CTD) is said to occur when aprogram
Program (American English; also Commonwealth English in terms of computer programming and related activities) or programme (Commonwealth English in all other meanings), programmer, or programming may refer to:
Business and management
* Program m ...
(commonly a video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
) unexpectedly quits, abruptly taking the user back to the desktop
A desktop traditionally refers to:
* The surface of a desk (often to distinguish office appliances that fit on a desk, such as photocopiers and printers, from larger equipment covering its own area on the floor)
Desktop may refer to various compu ...
. Usually, the term is applied only to crashes where no error is displayed, hence all the user sees as a result of the crash is the desktop. Many times there is no apparent action that causes a crash to desktop. During normal function, the program may freeze for a shorter period of time, and then close by itself. Also during normal function, the program may become a black screen and repeatedly play the last few seconds of sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
(depending on the size of the audio buffer
Buffer may refer to:
Science
* Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas
* Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH
* Lysis buffer, in cell biology
* Metal ion buffer
* Mineral redox buffer, in geology
Technology and engineeri ...
) that was being played before it crashes to desktop. Other times it may appear to be trigger
Trigger may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional entities
* Trigger (''Only Fools and Horses''), in the TV sitcom
* Trigger Argee, in science fiction short stories by James H. Schmitz
* Devil Trigger, a transformation ability of ...
ed by a certain action, such as loading an area.
CTD bugs are considered particularly problematic for users. Since they frequently display no error message, it can be very difficult to track down the source of the problem, especially if the times they occur and the actions taking place right before the crash do not appear to have any pattern or common ground. One way to track down the source of the problem for games is to run them in windowed-mode. Certain operating system versions may feature one or more tools to help track down causes of CTD problems.
Some computer programs such as ''StepMania
''StepMania'' is a cross-platform rhythm video game and engine. It was originally developed as a clone of Konami's arcade game series ''Dance Dance Revolution'', and has since evolved into an extensible rhythm game engine capable of supporting ...
'' and BBC's '' Bamzooki'' also crash to desktop if in full-screen, but display the error in a separate window when the user has returned to the desktop.
Web server crashes
The software running theweb server
A web server is computer software and underlying Computer hardware, hardware that accepts requests via Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, co ...
behind a website may crash, rendering it inaccessible entirely or providing only an error message instead of normal content.
For example, if a site is using an SQL database (such as MySQL
MySQL () is an Open-source software, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A rel ...
) for a script (such as PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared towards web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by the PHP Group. ...
) and that SQL database server crashes, then PHP
PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared towards web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by the PHP Group. ...
will display a connection error.
Operating system crashes

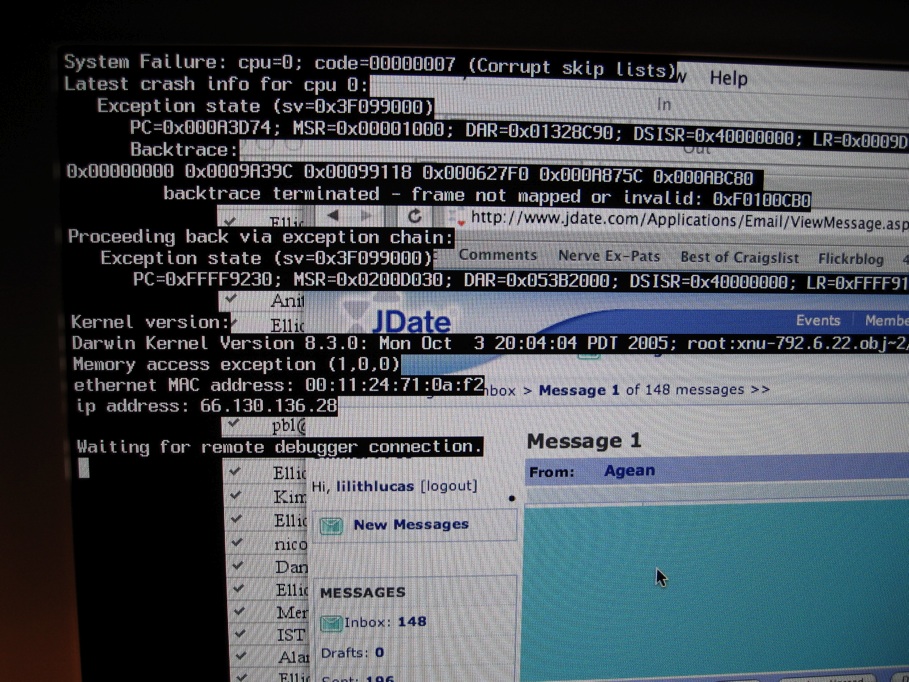
 An operating system crash commonly occurs when a
An operating system crash commonly occurs when a hardware exception
In computing and computer programming, exception handling is the process of responding to the occurrence of ''exceptions'' – anomalous or exceptional conditions requiring special processing – during the execution of a program. In general, an ...
occurs that cannot be handled. Operating system crashes can also occur when internal sanity-checking logic within the operating system detects that the operating system has lost its internal self-consistency.
Modern multi-tasking operating systems, such as Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, and macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
, usually remain unharmed when an application program crashes.
Some operating systems, e.g., z/OS
z/OS is a 64-bit operating system for IBM z/Architecture mainframes, introduced by IBM in October 2000. It derives from and is the successor to OS/390, which in turn was preceded by a string of MVS versions.Starting with the earliest:
...
, have facilities for Reliability, availability and serviceability
Reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS), also known as reliability, availability, and maintainability (RAM), is a computer hardware engineering term involving reliability engineering, high availability, and serviceability design. The p ...
(RAS) and the OS can recover from the crash of a critical component, whether due to hardware failure, e.g., uncorrectable ECC error, or to software failure, e.g., a reference to an unassigned page.
Abnormal end
An Abnormal end or ABEND is an abnormal termination ofsoftware
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, or a program crash. Errors or crashes on the Novell
Novell, Inc. () was an American software and services company headquartered in Provo, Utah, that existed from 1980 until 2014. Its most significant product was the multi-platform network operating system known as NetWare. Novell technolog ...
NetWare network operating system are usually called ABENDs. Communities of NetWare
NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol. The final update release was ver ...
administrators sprang up around the Internet, such aabend.org
This usage derives from the ''ABEND'' macro on IBM
OS/360
OS/360, officially known as IBM System/360 Operating System, is a discontinued batch processing operating system developed by IBM for their then-new System/360 mainframe computer, announced in 1964; it was influenced by the earlier IBSYS/IBJOB a ...
, ..., z/OS
z/OS is a 64-bit operating system for IBM z/Architecture mainframes, introduced by IBM in October 2000. It derives from and is the successor to OS/390, which in turn was preceded by a string of MVS versions.Starting with the earliest:
...
operating systems. Usually capitalized, but may appear as "abend". Some common ABEND codes are System ABEND 0C7 (data exception) and System ABEND 0CB (division by zero
In mathematics, division by zero, division (mathematics), division where the divisor (denominator) is 0, zero, is a unique and problematic special case. Using fraction notation, the general example can be written as \tfrac a0, where a is the di ...
).List of ABEND codeson madisoncollege.edu Abends can be "soft" (allowing automatic recovery) or "hard" (terminating the activity). The term is jocularly claimed to be derived from the German word " Abend" meaning "evening"."Abend"
on dictionary.die.net
Security and privacy implications of crashes
Depending on the application, the crash may contain the user's sensitive andprivate information
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
. Moreover, many software bugs which cause crashes are also exploitable for arbitrary code execution
In computer security, arbitrary code execution (ACE) is an attacker's ability to run any commands or code of the attacker's choice on a target machine or in a target process. An arbitrary code execution vulnerability is a security flaw in softwa ...
and other types of privilege escalation
Privilege escalation is the act of exploiting a Software bug, bug, a Product defect, design flaw, or a configuration oversight in an operating system or software application to gain elevated access to resource (computer science), resources that ar ...
. For example, a stack buffer overflow
In software, a stack buffer overflow or stack buffer overrun occurs when a program writes to a memory address on the program's call stack outside of the intended data structure, which is usually a fixed-length buffer.
Stack buffer overflow bugs ...
can overwrite the return address of a subroutine with an invalid value, which will cause, e.g., a segmentation fault
In computing, a segmentation fault (often shortened to segfault) or access violation is a Interrupt, failure condition raised by hardware with memory protection, notifying an operating system (OS) the software has attempted to access a restricted ...
, when the subroutine returns. However, if an exploit overwrites the return address with a valid value, the code in that address will be executed.
Crash reproduction
When crashes are collected in the field using acrash reporter
A crash reporter is usually a system software whose function is to identify reporting crash details and to alert when there are crashes, in production or on development / testing environments. Crash reports often include data such as stack trac ...
, the next step for developers is to be able to reproduce them locally. For this, several techniques exist:
STAR uses symbolic execution,
EvoCrash performs evolutionary search.
See also
*Copy protection
Copy protection, also known as content protection, copy prevention and copy restriction, is any measure to enforce copyright by preventing the reproduction of software, films, music, and other media.
Copy protection is most commonly found on vid ...
*Crash-only software
A crash-only software is a computer program that handle failures by simply restarting, without attempting any sophisticated recovery. Correctly written components of crash-only software can microreboot to a known-good state without the help of a ...
*Data loss
Data loss is an error condition in information systems in which information is destroyed by failures (like failed spindle motors or head crashes on hard drives) or neglect (like mishandling, careless handling or storage under unsuitable conditions) ...
* Guru Meditation
*Memory corruption
Memory corruption occurs in a computer program when the contents of a memory location are modified due to programmatic behavior that exceeds the intention of the original programmer or program/language constructs; this is termed as violation of m ...
*Memory protection
Memory protection is a way to control memory access rights on a computer, and is a part of most modern instruction set architectures and operating systems. The main purpose of memory protection is to prevent a process from accessing memory that h ...
*Page fault
In computing, a page fault is an exception that the memory management unit (MMU) raises when a process accesses a memory page without proper preparations. Accessing the page requires a mapping to be added to the process's virtual address space ...
*Reboot
In computing, rebooting is the process by which a running computer system is restarted, either intentionally or unintentionally. Reboots can be either a cold reboot (alternatively known as a hard reboot) in which the power to the system is physi ...
*Safe mode
Safe mode is a diagnosis, diagnostic mode of a computer operating system (OS). It can also refer to a mode of operation by application software. ''Safe mode'' is intended to help fix most, if not all, problems within an operating system. It is a ...
*Single-event upset
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (e.g. ions, electrons, photons) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microproce ...
*Storage violation
In computing a storage violation is a hardware or software fault that occurs when a task attempts to access an area of computer storage which it is not permitted to access.
Types of storage violation
Storage violation can, for instance, consist ...
*SIGILL
Signals are standardized messages sent to a running program to trigger specific behavior, such as quitting or error handling. They are a limited form of inter-process communication (IPC), typically used in Unix, Unix-like, and other POSIX-comp ...
* SystemRescue
*Undefined behavior
In computer programming, a program exhibits undefined behavior (UB) when it contains, or is executing code for which its programming language specification does not mandate any specific requirements. This is different from unspecified behavior, ...
Notes
References
External links
Picking Up The Pieces After A Computer Crash
{{DEFAULTSORT:Crash (Computing) Computer jargon Computer errors Software anomalies