AND-OR-Invert on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
AND-OR-invert (AOI) logic and AOI gates are two-level compound (or complex) logic functions constructed from the combination of one or more
 The 2-1 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and
The 2-1 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and
 Real world examples of an 2-2 AOI gate are found in the CD4085B, SN74LS51, SN5450 logic ICs (see further below).
The 2-2 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and
Real world examples of an 2-2 AOI gate are found in the CD4085B, SN74LS51, SN5450 logic ICs (see further below).
The 2-2 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and
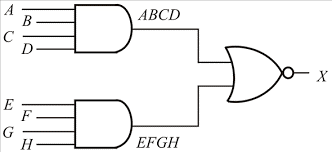 Real world examples of an 4-4 AOI gate is found in the CD4048B logic IC (see further below).
The 4-4 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and
Real world examples of an 4-4 AOI gate is found in the CD4048B logic IC (see further below).
The 4-4 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and

 AND-OR-invert (AOI) and OAI gates can be readily implemented in
AND-OR-invert (AOI) and OAI gates can be readily implemented in
File:Logique74ls51.svg, Schematic of SN74LS51 IC consists of a 3-3 AOI gate and 2-2 AOI gate
File:Ttl inside 7451.svg, Pinout of SN74LS51 IC
AND gate
The AND gate is a basic digital logic gate that implements the logical conjunction (∧) from mathematical logic AND gates behave according to their truth table. A HIGH output (1) results only if all the inputs to the AND gate are HIGH (1). If a ...
s followed by a NOR gate
The NOR (NOT OR) gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW (0); if one or both input is HIGH (1), a LOW o ...
(equivalent to an OR gate
The OR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical disjunction. The OR gate outputs "true" if any of its inputs is "true"; otherwise it outputs "false". The input and output states are normally represented by different voltage levels.
...
through an Inverter gate, which is the "OI" part of "AOI"). Construction of AOI cells is particularly efficient using CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
technology, where the total number of transistor gates can be compared to the same construction using NAND logic or NOR logic
A NOR gate or a NOT OR gate is a logic gate which gives a positive output only when both inputs are negative.
Like NAND gates, NOR gates are so-called " universal gates" that can be combined to form any other kind of logic gate. For example, t ...
. The complement of AOI logic is OR-AND-invert OR-AND-invert gates, or OAI-gates, are logic gates comprising OR gates followed by a NAND gate. They can be efficiently implemented in logic families like CMOS and Transistor–transistor logic, TTL. They are Duality_(mathematics)#Duality_in_logic_a ...
(OAI) logic, where the OR gates precede a NAND gate.
Overview
Mostlogic optimization
Logic optimization is a process of finding an equivalent representation of the specified logic circuit under one or more specified constraints. This process is a part of a logic synthesis applied in digital electronics and integrated circuit ...
result in a sum-of-products or product-of-sums logic expression.
AOI is used for sum-of-products, the variables are ANDed to form minterms which are ORed together then inverted:
* is known as a AOI 2-1 gate.
* is known as a AOI 2-2 gate.
* is known as a AOI 3-3 gate.
* is known as a AOI 4-4 gate.
* is known as a AOI 4-3-2 gate.
* and other variations.
Examples
AOI gates perform one or more AND operations followed by an OR operation then an inversion.2-1 AOI gate
truth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
:
:
2-2 AOI gate
truth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
:
:
3-3 AOI gate
Real world examples of an 3-3 AOI gate is found in the SN74LS51 logic IC (see further below). The 3-3 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation andtruth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
:
:
Its logic table would have 64 entries, but is not shown.
4-4 AOI gate
 Real world examples of an 4-4 AOI gate is found in the CD4048B logic IC (see further below).
The 4-4 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and
Real world examples of an 4-4 AOI gate is found in the CD4048B logic IC (see further below).
The 4-4 AOI gate can be represented by the following boolean equation and truth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
:
:
Its logic table would have 256 entries, but is not shown.
Extensions to multiple levels
It is possible to create multi-level compound gates, which combine the logic of AND-OR-Invert gates withOR-AND-invert OR-AND-invert gates, or OAI-gates, are logic gates comprising OR gates followed by a NAND gate. They can be efficiently implemented in logic families like CMOS and Transistor–transistor logic, TTL. They are Duality_(mathematics)#Duality_in_logic_a ...
gates. An example is shown below. The parts implementing the same logic have been put in boxes with the same color.
Electronic implementation
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
circuitry. AOI gates are particularly advantaged in that the total number of transistors (or gates) is less than if the AND, NOT, and OR functions were implemented separately. This results in increased speed, reduced power, smaller area, and potentially lower fabrication cost. For example, a 2-1 AOI gate can be constructed with 6 transistors in CMOS, compared to 10 transistors using a 2-input NAND gate (4 transistors), an inverter (2 transistors), and a 2-input NOR gate (4 transistors).
In NMOS logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits.
NMOS transistors operate by creating an inv ...
, the lower half of the CMOS circuit is used in combination with a load device or pull-up transistor (typically a depletion load or a dynamic load).
AOI gates are similarly efficient in transistor–transistor logic
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first "transistor") and the amplifying function (the second "transistor" ...
(TTL).
;Examples
CMOS 4000-series logic family:
* CD4085B = dual 2-2 AOI gate
* CD4086B = single expandable 2-2-2-2 AOI gate"
* CD4048B = single expandable 8-input 8-function with three-state output, 8 choices for gate type: 8 NOR / 8 OR / 8 NAND / 8 AND / 4-4 AND-OR-Invert / 4-4 AND-OR / 4-4 OR-AND-Invert / 4-4 OR-AND
TTL 7400-series logic family: (in past decades, a number of AOI parts were available in the 7400 family, but currently most are obsolete (no longer manufactured))
* SN5450 = dual 2-2 AOI gate, one is expandable (SN54 is military version of SN74)
* SN74LS51 = 2-2 AOI gate and 3-3 AOI gate
* SN54LS54 = single 2-3-3-2 AOI gate
See also
*List of 7400-series integrated circuits
The following is a list of 7400-series digital logic integrated circuits. In the mid-1960s, the original 7400-series integrated circuits were introduced by Texas Instruments with the prefix "SN" to create the name SN74xx. Due to the popularity of ...
* List of 4000-series integrated circuits
References
* *{{cite book , title=Application-Specific Integrated Circuits , last=John , first= Michael , year=1997 , url=http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH02/CH02.4.htm#pgfId=799 , accessdate= 2008-07-04 AOI gate