AIM-54A Phoenix on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The AIM-54 Phoenix is an American active radar-guided, beyond-visual-range
 In the early 1960s, the U.S. Navy made the next interceptor attempt with the F-111B, and they needed a new missile design. At the same time, the
In the early 1960s, the U.S. Navy made the next interceptor attempt with the F-111B, and they needed a new missile design. At the same time, the
 The Phoenix has several guidance modes and achieves its longest range by using mid-course updates from the F-14A/B AWG-9 radar (APG-71 radar in the F-14D) as it climbs to cruise between and at close to Mach 5. The Phoenix uses this high altitude to maximize its range by reducing atmospheric drag. At around from the target, the missile activates its own radar to provide terminal guidance."AIM-54"
The Phoenix has several guidance modes and achieves its longest range by using mid-course updates from the F-14A/B AWG-9 radar (APG-71 radar in the F-14D) as it climbs to cruise between and at close to Mach 5. The Phoenix uses this high altitude to maximize its range by reducing atmospheric drag. At around from the target, the missile activates its own radar to provide terminal guidance."AIM-54"
(2004). Directory of US Military Rockets and Missiles. Retrieved 28 November 2010. Minimum engagement range for the Phoenix is around ; at this range active homing would initiate upon launch. If the AWG-9 radar lost radar lock on a target before the missile had activated its own radar, the missile proceeded on a ballistic trajectory with no further guidance, known as 'going dumb'.
 * On January 5, 1999, a pair of US F-14s fired two Phoenixes at Iraqi MiG-25s southeast of Baghdad. Both AIM-54s' rocket motors failed and neither missile hit its target.
* On September 9, 1999, another US F-14 launched an AIM-54 at an Iraqi MiG-23 that was heading south into the no-fly zone from Al Taqaddum air base west of Baghdad. The missile missed, eventually going into the ground after the Iraqi fighter reversed course and fled north.
* On January 5, 1999, a pair of US F-14s fired two Phoenixes at Iraqi MiG-25s southeast of Baghdad. Both AIM-54s' rocket motors failed and neither missile hit its target.
* On September 9, 1999, another US F-14 launched an AIM-54 at an Iraqi MiG-23 that was heading south into the no-fly zone from Al Taqaddum air base west of Baghdad. The missile missed, eventually going into the ground after the Iraqi fighter reversed course and fled north.
 The AIM-54 Phoenix was retired from USN service on September 30, 2004. F-14 Tomcats were retired on September 22, 2006. They were replaced by shorter-range
The AIM-54 Phoenix was retired from USN service on September 30, 2004. F-14 Tomcats were retired on September 22, 2006. They were replaced by shorter-range
 On January 7, 1974, as part of Project ''Persian King'', the Air force history of Iran#Imperial era, Imperial Iranian Air Force placed an order for 424 AIM-54As, later increasing it by 290 missiles that June. Of the initial order, 274 missiles and 10 training rounds were delivered for US$150 million, until the Iranian Revolution, 1979 Revolution ended deliveries and left the remaining 150 missiles embargoed and the additional order of 290 cancelled.
According to Tom Cooper and Farzad Bishop, during the
On January 7, 1974, as part of Project ''Persian King'', the Air force history of Iran#Imperial era, Imperial Iranian Air Force placed an order for 424 AIM-54As, later increasing it by 290 missiles that June. Of the initial order, 274 missiles and 10 training rounds were delivered for US$150 million, until the Iranian Revolution, 1979 Revolution ended deliveries and left the remaining 150 missiles embargoed and the additional order of 290 cancelled.
According to Tom Cooper and Farzad Bishop, during the
 ;: Original model that became operational with the U.S. Navy in about 1974, and it was also exported to Iran before the Iran hostage crisis beginning in 1979.
;: Also known as the 'Dry' missile. A version with simplified construction and no coolant conditioning. Did not enter series production. Developmental work started in January 1972. 7 X-AIM-54B missiles were created for testing, 6 of them by modifying pilot production IVE/PIP rounds. After two successful test firings, the 'Dry' missile effort was cancelled for being "not cost effective"..
;: The only improved model that was ever produced. It used digital electronics in the place of the analog electronics of the AIM-54A. This model had better abilities to shoot down low and high-altitude
;: Original model that became operational with the U.S. Navy in about 1974, and it was also exported to Iran before the Iran hostage crisis beginning in 1979.
;: Also known as the 'Dry' missile. A version with simplified construction and no coolant conditioning. Did not enter series production. Developmental work started in January 1972. 7 X-AIM-54B missiles were created for testing, 6 of them by modifying pilot production IVE/PIP rounds. After two successful test firings, the 'Dry' missile effort was cancelled for being "not cost effective"..
;: The only improved model that was ever produced. It used digital electronics in the place of the analog electronics of the AIM-54A. This model had better abilities to shoot down low and high-altitude

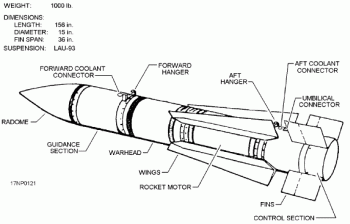 The following is a list of AIM-54 Phoenix specifications:
* Primary function: long-range, air-launched, air-intercept missile
* Contractor: Hughes Aircraft Company and Raytheon Corporation
* Unit cost: about $477,000, but this varied greatly
* Power plant: solid propellant rocket motor built by Hercules Inc., Hercules Incorporated
* Length:
* Weight:
* Diameter:
* Wing span:
* Range: over (actual range is classified)
* Speed: 3,000+ mph (4,680+ km/h)
* Guidance system: semi-active and active radar homing
* Warheads: proximity fuze, high explosive
* Warhead weight:
* Users: US (U.S. Navy), Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, IRIAF)
* Date deployed: 1974
* Date retired (U.S.): September 30, 2004
The following is a list of AIM-54 Phoenix specifications:
* Primary function: long-range, air-launched, air-intercept missile
* Contractor: Hughes Aircraft Company and Raytheon Corporation
* Unit cost: about $477,000, but this varied greatly
* Power plant: solid propellant rocket motor built by Hercules Inc., Hercules Incorporated
* Length:
* Weight:
* Diameter:
* Wing span:
* Range: over (actual range is classified)
* Speed: 3,000+ mph (4,680+ km/h)
* Guidance system: semi-active and active radar homing
* Warheads: proximity fuze, high explosive
* Warhead weight:
* Users: US (U.S. Navy), Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, IRIAF)
* Date deployed: 1974
* Date retired (U.S.): September 30, 2004
NASA Dryden Flight Research Center – Phoenix Missile Hypersonic Testbed
{{DEFAULTSORT:AIM-054 Cold War air-to-air missiles of the United States Beyond-visual-range air-to-air missiles Raytheon Company products Military equipment introduced in the 1970s
air-to-air missile
An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft (including unmanned aircraft such as cruise missiles). AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid-fuel roc ...
(AAM), carried in clusters of up to six missiles on the Grumman F-14 Tomcat
The Grumman F-14 Tomcat is an American carrier-capable supersonic aircraft, supersonic, twinjet, twin-engine, Tandem#Aviation, tandem two-seat, twin-tail, all-weather-capable variable-sweep wing fighter aircraft. The Tomcat was developed for t ...
, its only operational launch platform.
The AIM-54 Phoenix was the United States' only operational long-range AAM during its service life; its operational capabilities were supplemented by the AIM-7 Sparrow
The AIM-7 Sparrow (Air Intercept Missile) is an American medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile operated by the United States Air Force, United States Navy, United States Marine Corps, and various other air forces and navies. Sp ...
(and later, the AIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile (AMRAAM) ( ) is an American Beyond-visual-range missile, beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It uses active transmit-receive radar guidance ...
), which served as the primary medium-range AAM and the AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder is a short-range air-to-air missile. Entering service with the United States Navy in 1956 and the Air Force in 1964, the AIM-9 is one of the oldest, cheapest, and most successful air-to-air missiles. Its latest variants rema ...
, serving as the primary short-range or "dogfight" AAM. The combination of Phoenix missile and the Tomcat's AN/AWG-9 guidance radar meant that it was the first aerial weapons system that could simultaneously engage multiple targets. Due to its active radar tracking, the brevity code " Fox Three" was used when firing the AIM-54. The act of the missile achieving a radar lock with its own radar is known under brevity as "Going Pitbull".
Both the missile and the aircraft were used by Iran and the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
(USN). In US service both are now retired, the AIM-54 Phoenix in 2004 and the F-14 in 2006. They were replaced by the shorter-range AIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile (AMRAAM) ( ) is an American Beyond-visual-range missile, beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It uses active transmit-receive radar guidance ...
, employed on the F/A-18 Hornet
The McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet is an all-weather supersonic, twinjet, twin-engine, carrier-based aircraft, carrier-capable, Multirole combat aircraft, multirole combat aircraft, designed as both a Fighter aircraft, fighter and attack airc ...
and F/A-18E/F Super Hornet
The Boeing F/A-18E and F/A-18F Super Hornet are a series of American supersonic twinjet, twin-engine, Carrier-based aircraft, carrier-capable, Multirole combat aircraft, multirole fighter aircraft derived from the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Ho ...
; in its AIM-120D version, the latest version of the AMRAAM just matches the Phoenix's maximum range. In July 2024, the USN announced the operational fielding of the AIM-174
The AIM-174B Gunslinger is a long-range air-to-air missile (AAM) developed by U.S. defense contractor Raytheon and used by the United States Navy (USN). The AIM-174B is a derivative of the RIM-174B Standard Extended Range Active Missile (ERAM, ...
, the "Air-Launched Configuration" of the RIM-174 Standard ERAM
The RIM-174 Standard Extended Range Active Missile (ERAM), or Standard Missile 6 (SM-6), is a missile in current production for the United States Navy (USN). It was designed for extended-range anti-air warfare (ER-AAW) purposes, providing cap ...
, the first dedicated long-range AAM to be fielded by the U.S. military since the AIM-54's retirement. While details regarding the AIM-174's range are unconfirmed, certain surface-launched RIM-174 variants are capable of launches. With the benefit of being launched already at-speed and at-altitude (where the air is thinner and thus easier to fly through), combined with additional lofting
Lofting is a Technical drawing, drafting technique to generate curved lines. It is used in plans for streamlined objects such as aircraft and boats. The lines may be drawn on wood and the wood then cut for advanced woodworking. The technique can be ...
, the AIM-174's range may extend to several hundred miles, though the USN has confirmed a range of , about a 30% increase in range over the AIM-54C.
The AIM-54 has been used in 62 air-to-air strikes, all by Iran during the eight-year Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
.Cooper, Tom; Bishop, Farzad. ''Iranian F-14 Tomcat Units in Combat'', p. 85. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2004. . Following the retirement of the F-14 by the USN, the weapon's only current operator is the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force
The Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (IRIAF; ) is the air force, aviation branch of the Islamic Republic of Iran Army. The present air force was created when the Imperial Iranian Air Force was renamed in 1979 following the Iranian Revoluti ...
.
Development
Background
Since 1951, the Navy faced the initial threat from the Tupolev Tu-4K 'Bull' carryinganti-ship missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM or ASM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea-skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. ...
s or nuclear bombs.
Eventually, during the height of the Cold War, the threat would have expanded into regimental-size raids of Tu-16 Badger
The Tupolev Tu-16 (USAF/DOD reporting name Type 39; NATO reporting name: Badger) is a twin-engined jet strategic heavy bomber used by the Soviet Union. It has been flown for almost 70 years. While many aircraft in Soviet service were retired af ...
and Tu-22M Backfire
The Tupolev Tu-22M (; NATO reporting name: Backfire) is a supersonic, variable-sweep wing, long-range strategic and maritime strike bomber developed by the Tupolev, Tupolev Design Bureau in the 1960s. The bomber was reported as being designated ...
bombers equipped with low-flying, long-range, high-speed, nuclear-armed cruise missiles and considerable electronic countermeasures
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to countermeasure, trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny ...
(ECM) of various types. This combination was considered capable of saturating fleet defenses and threatening carrier groups.
The Navy would require a long-range, long-endurance interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are c ...
to defend carrier battle groups against this threat. The proposed Douglas F6D Missileer
The Douglas F6D Missileer was a proposed carrier-based fleet defense fighter designed by Douglas Aircraft Company in response to a 1959 United States Navy requirement. It was designed to be able to loiter for extended periods at a relatively lo ...
was intended to fulfill this mission and oppose the attack as far as possible from the fleet it was defending. The weapon needed for interceptor aircraft, the Bendix AAM-N-10 Eagle
The AAM-N-10 Eagle was a long-range air-to-air missile developed by the Bendix Corporation for use by the United States Navy. Intended for carriage by the Douglas F6D Missileer fleet defense fighter, the Eagle program was cancelled before testing ...
, was to be an air-to-air missile of unprecedented range when compared to contemporary AIM-7 Sparrow
The AIM-7 Sparrow (Air Intercept Missile) is an American medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile operated by the United States Air Force, United States Navy, United States Marine Corps, and various other air forces and navies. Sp ...
missiles. It would work together with Westinghouse AN/APQ-81 radar. The Missileer project was cancelled in December 1960.
AIM-54
 In the early 1960s, the U.S. Navy made the next interceptor attempt with the F-111B, and they needed a new missile design. At the same time, the
In the early 1960s, the U.S. Navy made the next interceptor attempt with the F-111B, and they needed a new missile design. At the same time, the USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
canceled the projects for their land-based high-speed interceptor aircraft, the North American XF-108 Rapier
The North American XF-108 Rapier was a proposed long-range, high-speed interceptor aircraft designed by North American Aviation intended to defend the United States from supersonic Soviet Union, Soviet strategic bombers. The aircraft would hav ...
and the Lockheed YF-12
The Lockheed YF-12 is an American Mach number, Mach 3+ capable, high-altitude interceptor aircraft, interceptor prototype, developed and manufactured by American aerospace company Lockheed Corporation.
The interceptor was developed duri ...
, and left the capable AIM-47 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control sys ...
missile at a quite advanced stage of development, but with no effective launch platform.
The AIM-54 Phoenix, developed for the F-111B fleet air defense fighter, had an airframe with four cruciform fins that was a scaled-up version of the AIM-47. One characteristic of the Missileer ancestry was that the radar sent it mid-course correction
Command guidance is a type of missile guidance in which a ground station or aircraft relay signals to a guided missile via radio control or through a wire connecting the missile to the launcher and tell the missile where to steer to intercept its ...
s, which allowed the fire control system to "loft
A loft is a building's upper storey or elevated area in a room directly under the roof (American usage), or just an attic: a storage space under the roof usually accessed by a ladder (primarily British usage). A loft apartment refers to large ...
" the missile up over the target into thinner air where it had better range.
The F-111B was canceled in 1968. Its weapons system, the AIM-54 working with the AWG-9 radar, migrated to the new U.S. Navy fighter project, the VFX, which would later become the F-14 Tomcat
The Grumman F-14 Tomcat is an American carrier-capable supersonic, twin-engine, tandem two-seat, twin-tail, all-weather-capable variable-sweep wing fighter aircraft. The Tomcat was developed for the United States Navy's Naval Fighter Experi ...
.
The AIM-54 Phoenix was also considered by the Royal Air Force to be used on Avro Vulcan
The Avro Vulcan (later Hawker Siddeley Vulcan from July 1963) was a jet-powered, tailless, delta-wing, high-altitude, strategic bomber, which was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) from 1956 until 1984. Aircraft manufacturer A.V. Roe ...
bomber planes as part of an air defence aircraft. This missileer conversion would have used 12 missiles onboard and an extensive modification to the Vulcan's radar.
In 1977, development of a significantly improved Phoenix version, the AIM-54C, was developed to better counter projected threats from tactical anti-naval aircraft and cruise missiles, and its final upgrade included a re-programmable memory capability to keep pace with emerging ECM.
Usage in comparison to other weapon systems
The AIM-54/AWG-9 combination had multiple track (up to 24 targets) and multiple launch (up to six Phoenixes can be launched nearly simultaneously) capability, regardless ofweather conditions
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the ...
or heavy enemy electronic warfare, known as jamming. The large missile is equipped with a conventional warhead
A warhead is the section of a device that contains the explosive agent or toxic (biological, chemical, or nuclear) material that is delivered by a missile, rocket (weapon), rocket, torpedo, or bomb.
Classification
Types of warheads include:
*E ...
.
The AIM-54 is designed for ejection launch, where a Pyrotechnics, pyrotechnic charge forcefully jettisons it from either a LAU-93 or a LAU-132 launcher before its solid propellant rocket motor ignites.
On the F-14, four missiles can be carried under the fuselage tunnel attached to special aerodynamic pallets, plus two under glove stations. A full load of six Phoenix missiles and the unique launch rails weighs in at over , about twice the weight of Sparrows, putting it above the allowable bringback load (which also would include enough fuel for go-around attempts). As such, carrying six Phoenix missiles would necessitate the Jettison (aviation), jettison of at least some of the Phoenix missiles if they were not used. The most common air superiority payload was a mix of two Phoenix, three AIM-7 Sparrow, Sparrow, and two AIM-9 Sidewinder, Sidewinder missiles.
Most other US aircraft relied on the smaller, Semi-active radar homing, semi-active medium-range AIM-7 Sparrow
The AIM-7 Sparrow (Air Intercept Missile) is an American medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile operated by the United States Air Force, United States Navy, United States Marine Corps, and various other air forces and navies. Sp ...
. Semi-active guidance meant the aircraft no longer had a search capability while supporting the launched Sparrow, reducing situational awareness.
The Tomcat's radar could track up to 24 targets in track-while-scan mode, with the AWG-9 selecting up to six potential targets for the missiles. The pilot or radar intercept officer (RIO) could then launch the Phoenix missiles once parameters were met. The large tactical information display (TID) in the RIO's cockpit gave information to the aircrew (the pilot had the ability to monitor the RIO's display) and the radar could continually search and track multiple targets after Phoenix missiles were launched, thereby maintaining situational awareness of the battlespace.
The Link 4 datalink allowed US Navy Tomcats to share information with the E-2 Hawkeye, E-2C Hawkeye airborne early warning, AEW aircraft. During Operation Desert Shield (Gulf War), Desert Shield in 1990, the Link 4A was introduced; this allowed the Tomcats to have a fighter-to-fighter datalink capability, further enhancing overall situational awareness. The F-14D entered service with Joint Tactical Information Distribution System, JTIDS that brought the even better Link 16 datalink "picture" to the cockpit.
Active guidance
(2004). Directory of US Military Rockets and Missiles. Retrieved 28 November 2010. Minimum engagement range for the Phoenix is around ; at this range active homing would initiate upon launch. If the AWG-9 radar lost radar lock on a target before the missile had activated its own radar, the missile proceeded on a ballistic trajectory with no further guidance, known as 'going dumb'.
Service history
U.S. combat experience
 * On January 5, 1999, a pair of US F-14s fired two Phoenixes at Iraqi MiG-25s southeast of Baghdad. Both AIM-54s' rocket motors failed and neither missile hit its target.
* On September 9, 1999, another US F-14 launched an AIM-54 at an Iraqi MiG-23 that was heading south into the no-fly zone from Al Taqaddum air base west of Baghdad. The missile missed, eventually going into the ground after the Iraqi fighter reversed course and fled north.
* On January 5, 1999, a pair of US F-14s fired two Phoenixes at Iraqi MiG-25s southeast of Baghdad. Both AIM-54s' rocket motors failed and neither missile hit its target.
* On September 9, 1999, another US F-14 launched an AIM-54 at an Iraqi MiG-23 that was heading south into the no-fly zone from Al Taqaddum air base west of Baghdad. The missile missed, eventually going into the ground after the Iraqi fighter reversed course and fled north.
 The AIM-54 Phoenix was retired from USN service on September 30, 2004. F-14 Tomcats were retired on September 22, 2006. They were replaced by shorter-range
The AIM-54 Phoenix was retired from USN service on September 30, 2004. F-14 Tomcats were retired on September 22, 2006. They were replaced by shorter-range AIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile (AMRAAM) ( ) is an American Beyond-visual-range missile, beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It uses active transmit-receive radar guidance ...
s, employed on the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet
The Boeing F/A-18E and F/A-18F Super Hornet are a series of American supersonic twinjet, twin-engine, Carrier-based aircraft, carrier-capable, Multirole combat aircraft, multirole fighter aircraft derived from the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Ho ...
.
Despite the much-vaunted capabilities, the Phoenix was rarely used in combat, with only two confirmed launches and no confirmed targets destroyed in US Navy service. The USAF F-15 Eagle had responsibility for overland combat air patrol duties in Operation Desert Storm in 1991, primarily because of the onboard F-15 identification friend or foe, IFF capabilities. The Tomcat did not have the requisite IFF capability mandated by the Joint Force Air Component Commander (JFACC) to satisfy the rules of engagement to utilize the Phoenix capability at beyond visual range. The AIM-54 was not adopted by any foreign nation besides Iran, or any other US armed service, and was not used on any aircraft other than the F-14.
Iranian combat experience
 On January 7, 1974, as part of Project ''Persian King'', the Air force history of Iran#Imperial era, Imperial Iranian Air Force placed an order for 424 AIM-54As, later increasing it by 290 missiles that June. Of the initial order, 274 missiles and 10 training rounds were delivered for US$150 million, until the Iranian Revolution, 1979 Revolution ended deliveries and left the remaining 150 missiles embargoed and the additional order of 290 cancelled.
According to Tom Cooper and Farzad Bishop, during the
On January 7, 1974, as part of Project ''Persian King'', the Air force history of Iran#Imperial era, Imperial Iranian Air Force placed an order for 424 AIM-54As, later increasing it by 290 missiles that June. Of the initial order, 274 missiles and 10 training rounds were delivered for US$150 million, until the Iranian Revolution, 1979 Revolution ended deliveries and left the remaining 150 missiles embargoed and the additional order of 290 cancelled.
According to Tom Cooper and Farzad Bishop, during the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
AIM-54s fired by Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, IRIAF Tomcats achieved 78 victories against Iraqi Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21, MiG-21s, Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23, MiG-23s, Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25, MiG-25s, Tupolev Tu-22, Tu-22s, Sukhoi Su-17, Su-20/22s, Dassault Mirage F1, Mirage F 1s, Dassault-Breguet Super Étendard, Super Étendards, and even two Exocet, AM-39 Exocets and a Silkworm (missile), C-601. This includes two occasions where one AIM-54 was responsible for the downing of two Iraqi aircraft, as well as an incident on January 7, 1981, where a Phoenix fired at a four-ship of MiG-23s downed three and damaged the fourth.
The US refused to supply spare parts and maintenance after the 1979 Revolution, except for a brief period during the Iran–Contra affair. According to Cooper, the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force kept its F-14 fighters and AIM-54 missiles in regular use during the entire Iran–Iraq War, though periodic lack of spares grounded large parts of the fleet at times. During late 1987, the stock of AIM-54 missiles was at its lowest, with fewer than 50 operational missiles available. The missiles needed fresh Molten-salt battery, thermal batteries that could only be purchased from the US. Iran found a clandestine buyer that supplied it with batteries, which cost up to US$10,000 each. Iran received spares and parts for both the F-14s and AIM-54s from various sources during the Iran–Iraq War, and has received more spares after the conflict. Iran started a program to build spares for the planes and missiles, and although there are claims that it no longer relies on outside sources to keep its F-14s and AIM-54s operational, there is evidence that Iran continues to procure parts clandestinely.
Both the F-14 Tomcat and the AIM-54 Phoenix missile continue in the service of the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force. Iran claimed to be working on building an equivalent missile and in 2013 unveiled the Fakour-90, an upgraded and reverse-engineered version of the Phoenix.
Variants
 ;: Original model that became operational with the U.S. Navy in about 1974, and it was also exported to Iran before the Iran hostage crisis beginning in 1979.
;: Also known as the 'Dry' missile. A version with simplified construction and no coolant conditioning. Did not enter series production. Developmental work started in January 1972. 7 X-AIM-54B missiles were created for testing, 6 of them by modifying pilot production IVE/PIP rounds. After two successful test firings, the 'Dry' missile effort was cancelled for being "not cost effective"..
;: The only improved model that was ever produced. It used digital electronics in the place of the analog electronics of the AIM-54A. This model had better abilities to shoot down low and high-altitude
;: Original model that became operational with the U.S. Navy in about 1974, and it was also exported to Iran before the Iran hostage crisis beginning in 1979.
;: Also known as the 'Dry' missile. A version with simplified construction and no coolant conditioning. Did not enter series production. Developmental work started in January 1972. 7 X-AIM-54B missiles were created for testing, 6 of them by modifying pilot production IVE/PIP rounds. After two successful test firings, the 'Dry' missile effort was cancelled for being "not cost effective"..
;: The only improved model that was ever produced. It used digital electronics in the place of the analog electronics of the AIM-54A. This model had better abilities to shoot down low and high-altitude anti-ship missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM or ASM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea-skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. ...
s. It was designed for greater service life, reliability, and utilized less parts. It also included a Built-in self-test, built in self-test (BIST/BIT) and missile on-aircraft test capability. This model took over from the AIM-54A beginning in 1986.
;/sealed round: More capabilities in electronic counter-countermeasures. It did not require coolant during flight. The Missile was deployed from 1988 onwards. Because the AIM-54 ECCM/Sealed received no coolant, F-14s carrying this version of the missile could not exceed a specified airspeed.
There were also test, evaluation, ground training, and captive air training versions of the missile; designated ATM-54, AEM-54, DATM-54A, and CATM-54. The flight versions had A and C versions. The DATM-54 was not made in a C version as there was no change in the ground handling characteristics.
;: A 1970s proposal for a ship launched version of the Phoenix as an alternative/replacement for the RIM-7 Sea Sparrow, Sea Sparrow point defense system. It would also have provided a medium-range SAM capability for smaller and/or non-Aegis equipped vessels (such as the Aircraft Carrier (Medium), CVV). The Sea Phoenix system would have included a modified shipborne version of the AN/AWG-9 radar. Hughes Aircraft touted the fact that 27 out of 29 major elements of the standard (airborne) AN/AWG-9 could be used in the shipborne version with little modification. Each system would have consisted of one AWG-9 radar, with associated controls and displays, and a fixed 12-cell launcher for the Phoenix missiles. In the case of an aircraft carrier, for example, at least three systems would have been fitted in order to give overlapping coverage throughout the full 360°.. Both land and ship based tests of modified Phoenix (AIM-54A) missiles and a containerised AWG-9 (originally the 14th example off the AN/AWG-9 production line) were successfully carried out from 1974 onwards..
;AIM-54B: A land based version for the United States Marine Corps, USMC was also proposed. It has been suggested that the AIM-54B would have been used in operational Sea Phoenix systems, although that version had been cancelled by the second half of the 1970s. Ultimately, a mix of budgetary and political issues meant that, despite being technically and operationally attractive, further development of the Sea Phoenix did not proceed.
;: In February 2013 Iran reportedly tested an indigenous long-range air-to-air missile. In September 2013 it displayed the Fakour-90 on a military parade. It looked almost identical to the AIM-54 Phoenix. In July 2018 as reported by Jane's, Iran started mass production of the Fakour-90.
Operators

Current operators
* –Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force
The Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (IRIAF; ) is the air force, aviation branch of the Islamic Republic of Iran Army. The present air force was created when the Imperial Iranian Air Force was renamed in 1979 following the Iranian Revoluti ...
Former operators
* - Air force history of Iran#Imperial era, Imperial Iranian Air Force * –United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
: Retired in 2004
Characteristics
 The following is a list of AIM-54 Phoenix specifications:
* Primary function: long-range, air-launched, air-intercept missile
* Contractor: Hughes Aircraft Company and Raytheon Corporation
* Unit cost: about $477,000, but this varied greatly
* Power plant: solid propellant rocket motor built by Hercules Inc., Hercules Incorporated
* Length:
* Weight:
* Diameter:
* Wing span:
* Range: over (actual range is classified)
* Speed: 3,000+ mph (4,680+ km/h)
* Guidance system: semi-active and active radar homing
* Warheads: proximity fuze, high explosive
* Warhead weight:
* Users: US (U.S. Navy), Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, IRIAF)
* Date deployed: 1974
* Date retired (U.S.): September 30, 2004
The following is a list of AIM-54 Phoenix specifications:
* Primary function: long-range, air-launched, air-intercept missile
* Contractor: Hughes Aircraft Company and Raytheon Corporation
* Unit cost: about $477,000, but this varied greatly
* Power plant: solid propellant rocket motor built by Hercules Inc., Hercules Incorporated
* Length:
* Weight:
* Diameter:
* Wing span:
* Range: over (actual range is classified)
* Speed: 3,000+ mph (4,680+ km/h)
* Guidance system: semi-active and active radar homing
* Warheads: proximity fuze, high explosive
* Warhead weight:
* Users: US (U.S. Navy), Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, IRIAF)
* Date deployed: 1974
* Date retired (U.S.): September 30, 2004
See also
References
External links
NASA Dryden Flight Research Center – Phoenix Missile Hypersonic Testbed
{{DEFAULTSORT:AIM-054 Cold War air-to-air missiles of the United States Beyond-visual-range air-to-air missiles Raytheon Company products Military equipment introduced in the 1970s