A. B. Rogers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
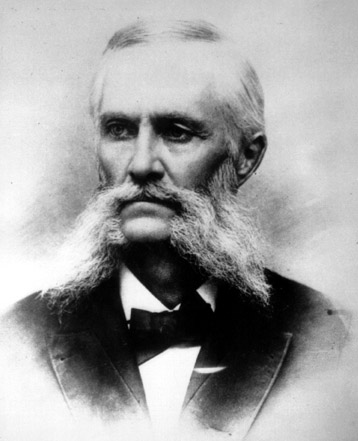 Albert Bowman Rogers (28 May 1829 – 4 May 1889), commonly known as Major A.B. Rogers, was an American
Albert Bowman Rogers (28 May 1829 – 4 May 1889), commonly known as Major A.B. Rogers, was an American
 Albert Bowman Rogers (28 May 1829 – 4 May 1889), commonly known as Major A.B. Rogers, was an American
Albert Bowman Rogers (28 May 1829 – 4 May 1889), commonly known as Major A.B. Rogers, was an American surveyor
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. These points are usually on the ...
now best remembered for his discovery of the Rogers Pass in British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Canada. He also has the distinction of having Rogers Pass in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
of Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, an ...
named after him, following his description of the pass in 1887.
Early life
Born in Orleans,Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
in 1829, he attended Brown University
Brown University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Providence, Rhode Island, United States. It is the List of colonial colleges, seventh-oldest institution of higher education in the US, founded in 1764 as the ' ...
, but transferred after one year to Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
, where he obtained a degree in Engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
. Rogers served with the U.S.
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
during the Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, was a conflict initially fought by European colonial empires, the United States, and briefly the Confederate States of America and Republic of Texas agains ...
, attaining the rank of major
Major most commonly refers to:
* Major (rank), a military rank
* Academic major, an academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits
* People named Major, including given names, surnames, nicknames
* Major and minor in musi ...
during the 1862 Dakota Sioux
The Dakota (pronounced , or ) are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided into the Eastern Dakota and the Wester ...
uprising
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
.
Surveys for the Canadian Pacific Railway
His initial engineering experience was primarily on the Americanprairies
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
surveying for the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad
The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), better known as the Milwaukee Road , was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986.
The company experienced financi ...
. Nevertheless, James Jerome Hill
James Jerome Hill (September 16, 1838 – May 29, 1916) was a Canadian-American railway director. He was the chief executive officer of a family of lines headed by the Great Northern Railway, which served a substantial area of the Upper Midwest ...
of the Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway () , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Kansas City, Canadian Pacific Ka ...
hired Rogers in April 1881 to find a rail route through the Selkirk and Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
. Rogers carefully studied the reports of earlier surveyors, particularly those of Walter Moberly from 1865. Moberly's assistant Albert Perry had previously described the approach to a potential pass from the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook language, Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin language, Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river headwater ...
along the Illecillewaet River
The Illecillewaet River is a tributary of the Columbia River located in British Columbia, Canada. Fed by the Illecillewaet Glacier in Glacier National Park, the river flows approximately to the southwest, (Some secondary sources state that he only saw the pass from a distance, but this is contradicted by first-hand reports.) Running out of food, the party turned back west. Although they had found a pass, they had been unable to explore its eastern approach, a distance of from the junction of the
Biography at the ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rogers, Albert Bowman 1829 births 1889 deaths American civil engineers American people in rail transportation Canadian Pacific Railway people Explorers of British Columbia Explorers of Montana People from Orleans, Massachusetts Yale University alumni
Beaver
Beavers (genus ''Castor'') are large, semiaquatic rodents of the Northern Hemisphere. There are two existing species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers are the second-large ...
and Columbia Rivers. Returning in 1882, he approached from the east, following the Beaver River. On July 24, 1882, he reached the same pass, confirming its existence and the feasibility of a railway route.
In gratitude, the Canadian Pacific named the pass for him and presented Rogers with a cheque for $5,000. Rogers initially refused to cash the cheque, preferring rather to display it in a frame. It was not until Van Horne promised him a gold watch as a souvenir that he consented to cash the cheque.
Rogers was a tough task master and was disliked by many of those who worked under him. They suffered under basic and meagre food supplies while being driven to continue on. One party avoided starvation by sheer luck when they were able to quickly canoe downstream.
Post Rogers Pass
In 1887, while surveying again for James J. Hill, but this time for the Great Northern Railway, he was searching for a pass over the continental divide and located Rogers Pass in Montana. Though the Great Northern eventually selectedMarias Pass
Marias Pass (elevation ) is a mountain pass in the Rocky Mountains in the western US state of Montana. Lying on the southern border of
Glacier National Park, it is traversed by US Highway 2 and by the BNSF Hi-Line Subdivision.
The pass is ...
, to the north of Rogers Pass, as the continental divide pass for their transcontinental rail route, the Great Northern named Rogers Pass in Montana for the surveyor. Rogers Pass in Montana became the route of Montana Highway 200, the highway route between Great Falls and Missoula, Montana.
His surveying career was curtailed after he was badly injured falling from his horse while surveying the right-of-way for the Great Northern Railway near Coeur d'Alene, Idaho
Coeur d'Alene ( ; ) is a city and the county seat of Kootenai County, Idaho, United States. It is the most populous city in North Idaho and the principal city of the Coeur d'Alene Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 54,628 at th ...
. He died 4 May 1889 at Waterville, Minnesota
Waterville is a city in Le Sueur County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 1,868 at the 2010 census. It is close to Sakatah Lake State Park on the Cannon River.
Waterville has a yearly celebration called "Bullhead Days," and it ...
, where he spent retirement at the home of his brother. Although some sources report that he died as a result of his injuries, others indicate that he suffered from cancer of the stomach
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
.
References
External links
Biography at the ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rogers, Albert Bowman 1829 births 1889 deaths American civil engineers American people in rail transportation Canadian Pacific Railway people Explorers of British Columbia Explorers of Montana People from Orleans, Massachusetts Yale University alumni