66 block on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
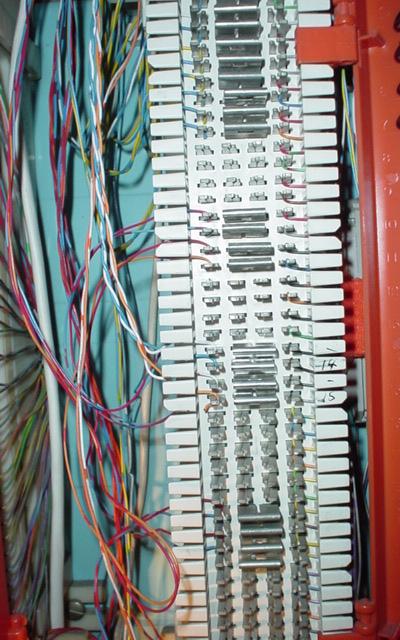 A 66 block is a type of
A 66 block is a type of
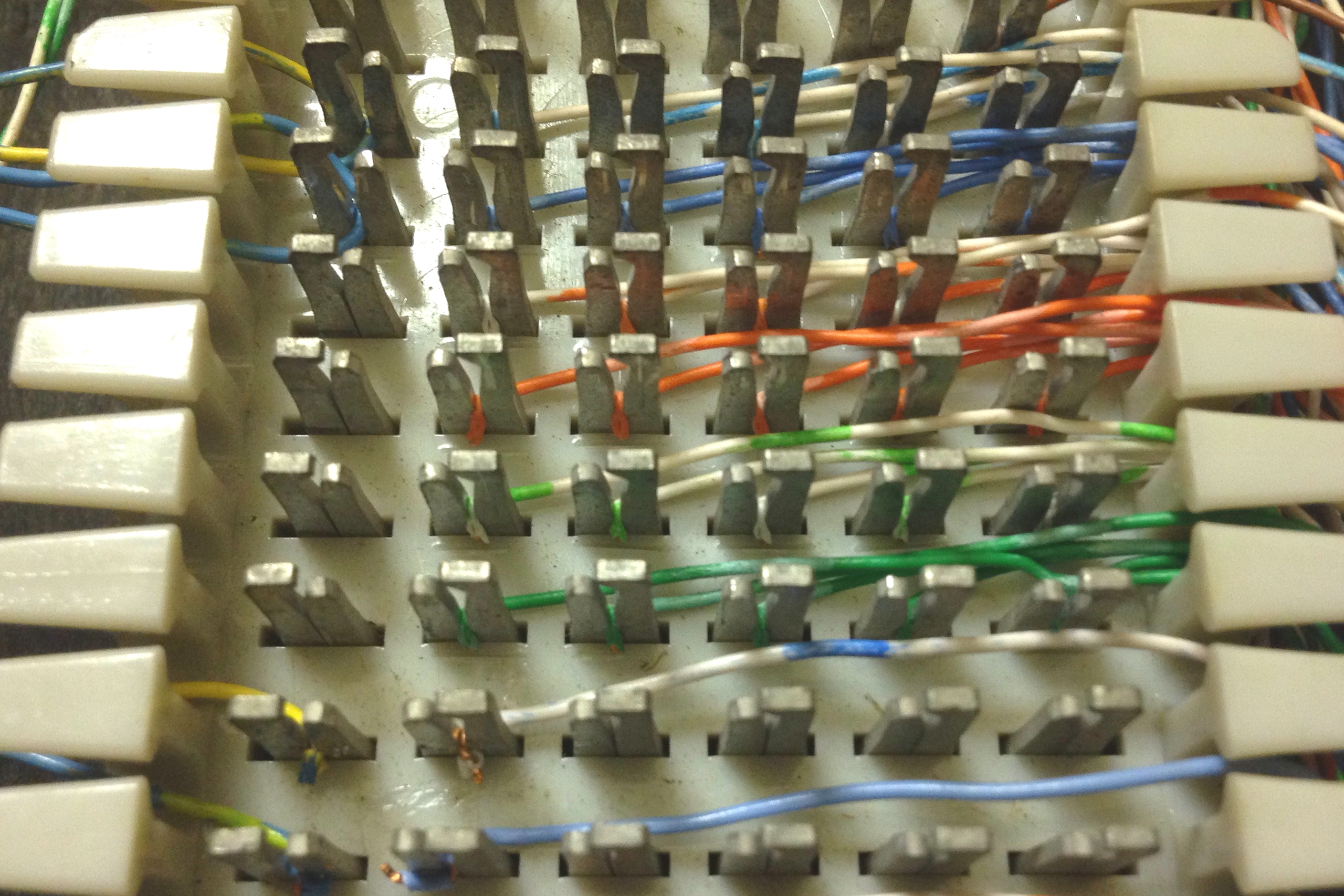 Circuit pairs are connected to the block with a punch-down tool by terminating the tip wire on the leftmost slot of one row and ring wire on the leftmost slot of the row beneath. Typically, a 25-pair cable coming from the phone company is punched down on the left side of a split-type block in pairs. The right hand side of the block is wired to the customer premises equipment with jumper wires. ''Bridging clips'' are used to connect the two center terminals, connecting the left-hand side of a split block with its right-hand side, thus completing the circuit. The clips form the point of interface between the subscriber and the provider. The bridging clips can be easily removed by either the subscriber or phone company personnel for trouble isolation, allowing the ability to split a circuit and determine in which direction trouble may exist. An orange insulating cover attached to a 66 block denotes its designation as a
Circuit pairs are connected to the block with a punch-down tool by terminating the tip wire on the leftmost slot of one row and ring wire on the leftmost slot of the row beneath. Typically, a 25-pair cable coming from the phone company is punched down on the left side of a split-type block in pairs. The right hand side of the block is wired to the customer premises equipment with jumper wires. ''Bridging clips'' are used to connect the two center terminals, connecting the left-hand side of a split block with its right-hand side, thus completing the circuit. The clips form the point of interface between the subscriber and the provider. The bridging clips can be easily removed by either the subscriber or phone company personnel for trouble isolation, allowing the ability to split a circuit and determine in which direction trouble may exist. An orange insulating cover attached to a 66 block denotes its designation as a
punch-down block
A punch-down block (also punchdown block, punch block, punchblock, quick-connect block and other variations) is a type of electrical connection often used in telephony. It is named because the solid copper wires are "punched down" into short ope ...
used to connect sets of wires in a telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most ...
system. Due to the proliferation of Voice over IP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also known as IP telephony, is a set of technologies used primarily for voice communication sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. VoIP enables voice calls to be transmitted as ...
(VoIP), 66 blocks are slowing becoming obsolete.
66 blocks are designed to terminate 20 through 24 AWG insulated solid copper wire. The 66 series connecting block, introduced in the Bell System
The Bell System was a system of telecommunication companies, led by the Bell Telephone Company and later by the AT&T Corporation, American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), that dominated the telephone services industry in North America fo ...
in 1962, was the first terminating device with insulation displacement connector technology. The term ''66 block'' reflects its Western Electric
Western Electric Co., Inc. was an American electrical engineering and manufacturing company that operated from 1869 to 1996. A subsidiary of the AT&T Corporation for most of its lifespan, Western Electric was the primary manufacturer, supplier, ...
model number.
66 E blocks are available pre-assembled with an RJ-21 female connector that accepts a quick connection to a 25-pair cable with a male end. These connections are typically made between the block and the customer-premises equipment
In telecommunications, a customer-premises equipment or customer-provided equipment (CPE) is any terminal and associated equipment located at a subscriber's premises and connected with a carrier's telecommunication circuit at the demarcation p ...
(CPE).
Types
66 blocks are manufactured in four common configurations: A, B, E and M. The A blocks have 25 slotted holes on the left side for positioning the incoming building cable with a 50 slot fanning strip on the right side for distribution cables. The B and M styles have 50 slot fanning strip on both sides. The B style is used mainly in distribution panels where several destinations (often 1A2 key telephones) need to connect to the same source. The M blocks are often used to connect a single instrument to such a distribution block. The E style has five columns of ten 2-clip rows and are used for transitioning from the 25-pair distribution cable to a 25-pair RJ21 style female ribbon connector. The 25-pair standard non-split 66 block contains 50 rows; each row has two (E) or four (M) or six (A) and (B) columns of clips that are electrically bonded. The 25-pair ''split 50'' 66 block is the industry standard for easy termination of voice cabling, and is a standard network termination by telephone companies—generally on commercial properties. Each row contains four (M) or six (B) clips, but the left-side clips are electrically isolated from the right-side clips. Smaller versions also exist with fewer rows for smaller-scale use, such as residential.Use
 Circuit pairs are connected to the block with a punch-down tool by terminating the tip wire on the leftmost slot of one row and ring wire on the leftmost slot of the row beneath. Typically, a 25-pair cable coming from the phone company is punched down on the left side of a split-type block in pairs. The right hand side of the block is wired to the customer premises equipment with jumper wires. ''Bridging clips'' are used to connect the two center terminals, connecting the left-hand side of a split block with its right-hand side, thus completing the circuit. The clips form the point of interface between the subscriber and the provider. The bridging clips can be easily removed by either the subscriber or phone company personnel for trouble isolation, allowing the ability to split a circuit and determine in which direction trouble may exist. An orange insulating cover attached to a 66 block denotes its designation as a
Circuit pairs are connected to the block with a punch-down tool by terminating the tip wire on the leftmost slot of one row and ring wire on the leftmost slot of the row beneath. Typically, a 25-pair cable coming from the phone company is punched down on the left side of a split-type block in pairs. The right hand side of the block is wired to the customer premises equipment with jumper wires. ''Bridging clips'' are used to connect the two center terminals, connecting the left-hand side of a split block with its right-hand side, thus completing the circuit. The clips form the point of interface between the subscriber and the provider. The bridging clips can be easily removed by either the subscriber or phone company personnel for trouble isolation, allowing the ability to split a circuit and determine in which direction trouble may exist. An orange insulating cover attached to a 66 block denotes its designation as a demarcation point
In telephony, the demarcation point is the point at which the public switched telephone network ends and connects with the customer's on-premises wiring. It is the dividing line which determines who is responsible for installation and mainte ...
by the local exchange carrier
Local exchange carrier (LEC) is a regulatory term in telecommunications for the local telephone company.
In the United States, wireline telephone companies are divided into two large categories: long-distance ( interexchange carrier, or IXCs) ...
.
Modern 110 blocks have largely supplanted 66 blocks for new commercial installations at the end of the 20th century, as the capability for a circuit to carry digital data overlaid its ability to carry analog voice conversations. 110 block termination is almost always compliant with Category 5 (or higher) and therefore capable of supporting 100 MHz (or faster) signaling. Compared to 110 and higher-density wire terminating blocks, 66 blocks are physically large; and because of their maximum 16 MHz Category 3 signaling compatibility, they are ill-suited for high speed (faster than 10BASE-T
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
) data circuits.
''Split 50'' 66 blocks are still used as network interface blocks in distribution frame
In telecommunications, a distribution frame is a passive device which terminates cables, allowing arbitrary interconnections to be made.
For example, the Main Distribution Frame (MDF) located at a telephone exchange, telephone central office te ...
s to interconnect circuits with bridging clips, but are primarily limited to narrowband
Narrowband signals are signals that occupy a narrow range of frequencies or that have a small fractional bandwidth. In the audio spectrum, ''narrowband sounds'' are sounds that occupy a narrow range of frequencies. In telephony, narrowband is ...
circuits such as POTS/DSL
Digital subscriber line (DSL; originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric di ...
, DS0, or DS1 circuits.
See also
* * RJ21 – Often used as a connector for pre-terminated 66 blocksNotes
References
{{Reflist Local loop Telephony equipment