4-Quinolones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
4-Quinolone is an 
organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
derived from quinoline
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only sl ...
. It and 2-quinolone
2-Quinolone is an organic compound related structurally to quinoline. It is the majority tautomer in equilibrium with 2-quinolinol. The compound can be classified as a cyclic amide, and as such is used as an isostere for peptides and other phar ...
are the two most important parent (meaning simplified) quinolones. 4-Quinolone exists in equilibrium with a minor tautomer, 4-hydroxyquinoline (CAS#611-36-9). Aside from pedagogical interest, 4-quinolone is of little intrinsic value but its derivatives, the 4-quinolone antibiotics, represent a large class of important drugs.

Synthesis
Thechemical synthesis
Chemical synthesis (chemical combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses ...
of quinolones often involves ring-closing reactions.{{cite journal, title=Co(III)-Catalyzed Enaminone-Directed C-H Amidation for Quinolone Synthesis, author=Shi, Pengfei, author2=Wang, Lili, author3=Chen, Kehao, author4=Wang, Jie, author5=Zhu, Jin, journal= Organic Letters, year=2017, volume=19, issue=9, pages=2418–2421, pmid=28425721, doi=10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00968 Such reactions often install a hydroxyl group (an –OH functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
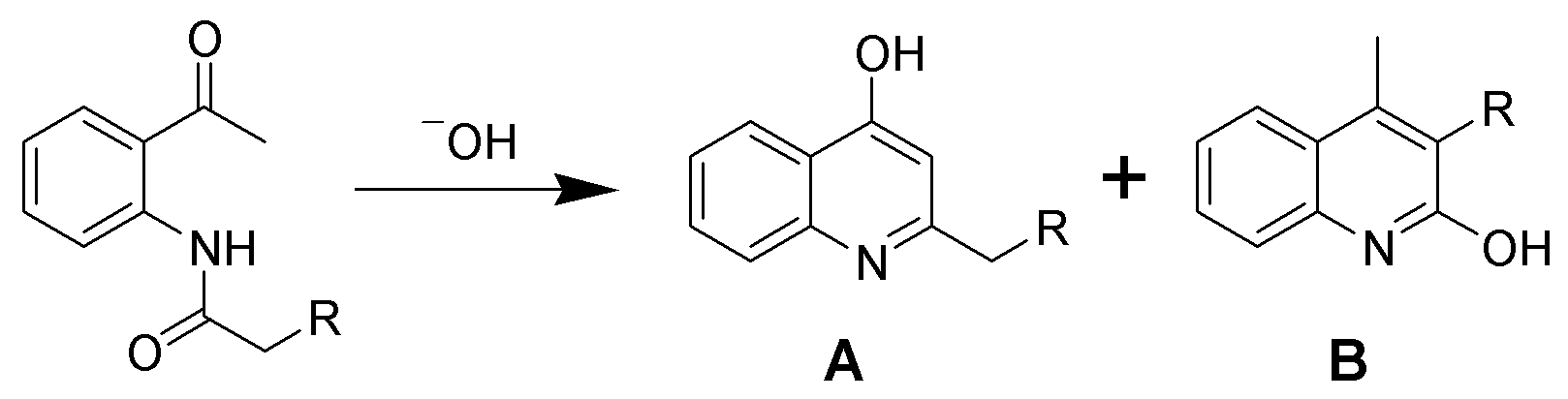
) on the carbon across from the ring nitrogen (i.e., the C-4 positions). An example of such a synthesis is the Camps cyclization, which, depending on starting materials and reaction conditions, can give both 2-hydroxyquinolines (B) and 4-hydroxyquinolines (A) as shown. The hydroxyquinolines tautomerize to the quinolones.

References