3C 345 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 3C 345 is a
3C 345 is a
3C 345 on SIMBAD
{{Hercules (constellation), state=collapsed OVV quasars Blazars Hercules (constellation)
 3C 345 is a
3C 345 is a blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
/ flat spectrum radio quasar located in the constellation of Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
. It is noted for hosting a superluminal
Faster-than-light (superluminal or supercausal) travel and communication are the conjectural propagation of matter or information faster than the speed of light in vacuum (). The special theory of relativity implies that only particles with zero ...
jet and its variability in almost all wave bands.
Characteristics
3C 345 has anactive galactic nucleus
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that emits a significant amount of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum, with characteristics indicating that this luminosity is not produced by the stars. Such e ...
that has been categorised as a blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the ...
or as a flat spectrum radio quasar
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass rangi ...
. The host galaxy of 3C 345 is an E3 elliptical galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the three main galaxy morphological classification, classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hub ...
without prominent peculiar characteristics.
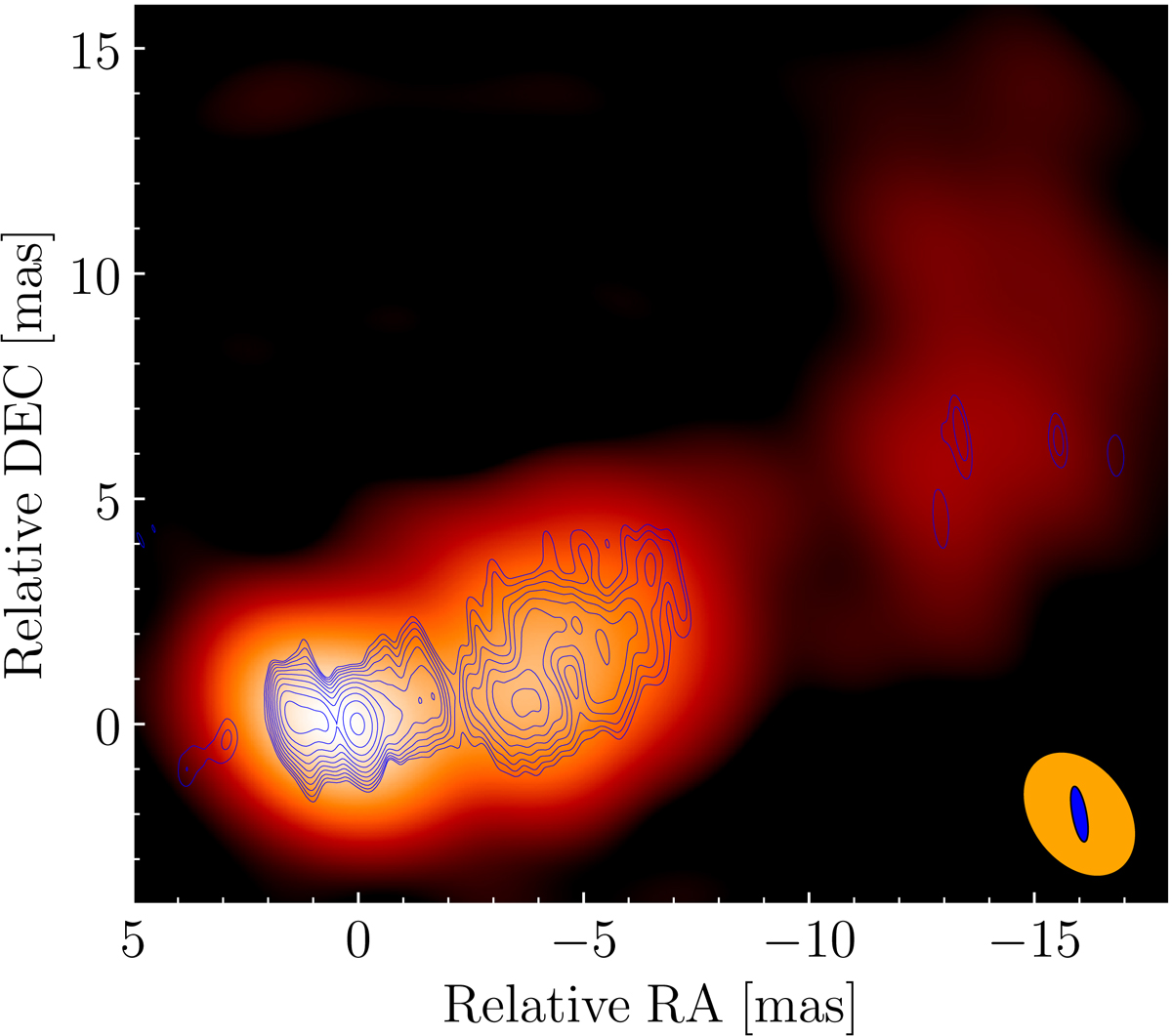
Superluminal jet
When observed inradio waves
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths ...
, 3C 345 features a compact region with a radio jet emanating from it for 3 arcseconds and ending at a hot spot. The jet appears straight for 4 milliarcseconds (mas) but then curves northwards. Hot spots are visible at the counterjet direction in radio images. There is also a faint halo. The jet has been found to emit X-rays, up until 0.2 arcseconds from a radio hot spot, which could be in reality a bend of the jet.
The radio jet exhibits superluminal motion
In astronomy, superluminal motion is the apparently faster-than-light motion seen in some radio galaxies, BL Lac objects, quasars, blazars and recently also in some galactic sources called microquasars. Bursts of energy moving out along the ...
for 0.12 to 12 mas, with apparent speeds that accelerate from ~5 c to ~15c within 0.3 mas. Within the jet lies a stationary feature ~0.1 mas (with corresponds to about 0.7 pc at the distance of 3C 345) from the core, which has also been found in other blazars. The viewing angle between the jet axis and the line of sight is calculated to be about 5°.
Variability
3C 345 has been known to fluctuate in brightness. For example, it brightened from magnitude 17.2 to 16.0 between 10 April 2018 and 8 May 2018 when observed in R band. A bright GeV gamma-ray flare was observed by theFermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (FGST, also FGRST), formerly called the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST), is a space observatory being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations from low Earth orbit. Its main instrument is ...
on 31 May 2017, as the flux increased by 40 times above average. The flares in 2009 were observed simultaneously in γ-rays, X-rays and optical/UV, while there was a lag before they were observed in radiowaves. A long term variability study indicates flares every 3.5 to 4 years, coinciding with the appearance of new features in the radio jets.
It has been suggested that the source of the fluctuation is the presence of a binary supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ...
, with the two similar black holes with masses about which are separated by around 0.33 pc and orbit each other with a period of 480 years. The second black hole perturbates the accretion disk
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is most frequently a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and ...
, resulting to fluctuations in activity. The X-rays observations indicate that the nuclear region is hidden behind a compton thick absorber with a column density of NH ≃ 1025 cm−2 that covers 75% to 85% of the X-rays source.
References
External links
3C 345 on SIMBAD
{{Hercules (constellation), state=collapsed OVV quasars Blazars Hercules (constellation)
345
The Year 345 ( CCCXLV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Amantius and Albinus (or, less frequently, year 1098 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 345 for ...