2639 Planman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 639 ( DCXXXIX) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 639 ( DCXXXIX) was a
common year starting on Friday
A common year starting on Friday is any non-leap year (i.e. a year with 365 days) that begins on Friday, 1 January, and ends on Friday, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is C. The most recent year of such kind was 2021, and the next one wil ...
of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts ...
. The denomination 639 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian and Julian calendar, Julian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "o ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, the current year is numbered in the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Europe
*January 19
Events Pre-1600
* 379 – Emperor Gratian elevates Flavius Theodosius at Sirmium to '' Augustus'', and gives him authority over all the eastern provinces of the Roman Empire.
* 649 – Conquest of Kucha: The forces of Kucha surren ...
– Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the ...
dies after a 10-year reign as king of all the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
, in which his realm
A realm is a community or territory over which a sovereign rules. The term is commonly used to describe a monarchical or dynastic state. A realm may also be a subdivision within an empire, if it has its own monarch, e.g. the German Empire.
Etymo ...
has prospered. He is succeeded by Sigebert III
Sigebert III ( 630–656) was the Merovingian dynasty, Merovingian king of Austrasia from 633 to his death around 656. He was described as the first Merovingian ''roi fainéant'', or "do-nothing king", with the mayor of the palace in fact ruling ...
(age 9), independent ruler of Austrasia
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Francia, Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had ...
, and his half-brother Clovis II
Clovis II (633 – 657) was King of the Franks in Neustria and Burgundy, having succeeded his father Dagobert I in 639. His brother Sigebert III had been King of Austrasia since 634. He was initially under the regency of his mother Nanth ...
(age 2), who becomes king of Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks during the Early Middle Ages, in contrast to the eastern Frankish kingdom, Austrasia. It initially included land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, in the north of present-day ...
and Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
. Under the supervision of Pepin of Landen
Pepin I (also Peppin, Pipin, or Pippin) of Landen (c. 580 – 27 February 640), also called the Elder or the Old, was the Mayor of the palace of Austrasia under the Merovingian King Dagobert I from 623 to 629. He was also the Mayor for Sige ...
, Mayor of the Palace
Under the Merovingian dynasty, the mayor of the palace or majordomo,
( or ) was the manager of the household of the Frankish king. He was the head of the Merovingian administrative ladder and orchestrated the operation of the entire court. He ...
, the royal treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry; in a business context, corporate treasury.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be ...
is distributed between the two brothers and widowed queen Nanthild
Nanthild ( 610 – 642), also known as ''Nantéchilde'', ''Nanthechilde'', ''Nanthildis'', ''Nanthilde'', or ''Nantechildis'', was a Frankish queen consort and regent, the third of many consorts of Dagobert I, king of the Franks (629–639). She w ...
(regent
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
on Clovis' behalf).
Arabian Empire
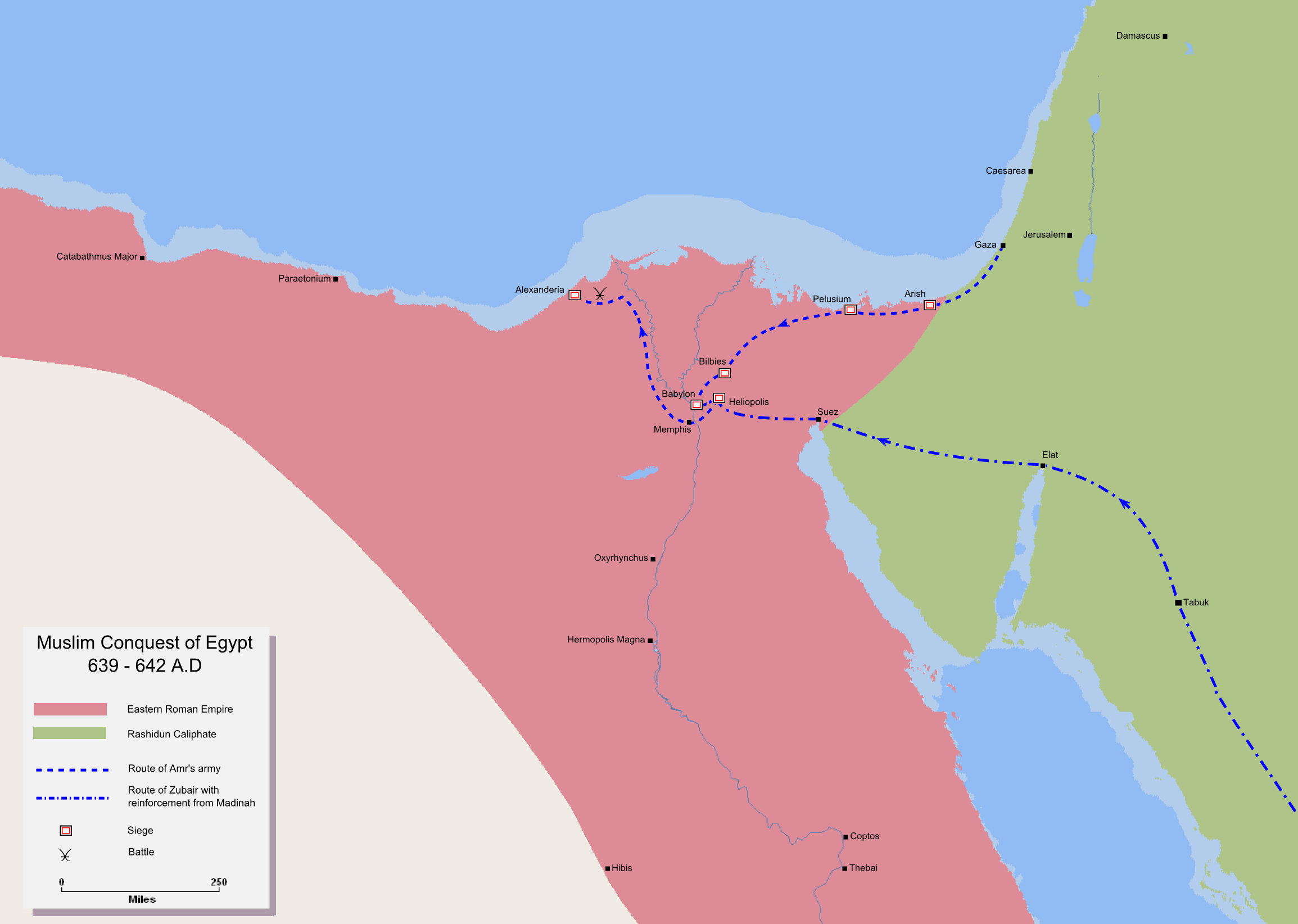
* Arab–Byzantine War: TheRashidun army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, grantin ...
(4,000 men), under the command of 'Amr ibn al-'As
Amr ibn al-As ibn Wa'il al-Sahmi (664) was an Arab commander and companion of Muhammad who led the Muslim conquest of Egypt and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Qurayshite, Amr embraced Islam in and wa ...
, invades Byzantine Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, l ...
. They capture the strategic town of Pelusium
Pelusium (Ancient Egyptian: ; /, romanized: , or , romanized: ; ; ; ; ) was an important city in the eastern extremes of Egypt's Nile Delta, to the southeast of the modern Port Said. It became a Roman provincial capital and Metropolitan arc ...
(Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the eas ...
) after a two-month siege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict charact ...
. Arab reinforcements led by Zubayr ibn al-Awwam
Al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam ibn Khuwaylid al-Asadi (; ) was an Arab Muslim commander in the service of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the caliphs Abu Bakr () and Umar () who played a leading role in the Ridda Wars, Ridda wars against rebel tribes in ...
are sent from Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
to assist Amr's army. The losses incurred by the Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s are ameliorated by Sinai Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
s, tribes of Rashida and Lakhm; they join the invaders in conquering Egypt.Alfred Butler, "The Invasion of Egypt", p. 213
* Hormuzan
Hormuzan (Middle Persian: ''Hormazdān'', New Persian: ) was a Persian aristocrat who served as the governor of Khuzestan, and was one of the Sasanian military officers at the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah. He was later taken prisoner by the Muslims ...
, Persian satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
of Susiana
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital of Elam and the winter ca ...
(vassal of the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
), revolts against the Muslims and raids Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. Arab forces under Abu Musa al-Asha'ari destroy Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
in the lower Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
.
* Plague of Emmaus
The plague of Amwas (), also spelled plague of Emmaus, was an ancient bubonic plague epidemic that afflicted Islamic Syria in 638–639, during the first plague pandemic and toward the end of the Muslim conquest of the region. It was likely a ree ...
: An epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
disease which has broken out in Emmaus
Emmaus ( ; ; ; ) is a town mentioned in the Gospel of Luke of the New Testament. Luke reports that Jesus appeared, after his death and resurrection, before two of his disciples while they were walking on the road to Emmaus.
Although its geograp ...
(Imwas
Imwas or Emmaus (), known in classical times as Nicopolis (), is an ethnically cleansed Palestinian village located southeast of the city of Ramla and from Jerusalem in the Latrun salient of the West Bank.Wareham and Gill, 1998, p. 108. It is ...
) in Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
strikes the city and the military camp
A military camp or bivouac is a semi-permanent military base, for the lodging of an army. Camps are erected when a military force travels away from a major installation or fort during training or operations, and often have the form of large cam ...
s of the Muslim Arabs
Arab Muslims () are the Arabs who adhere to Islam. They are the largest subdivision of the Arab people and the largest ethnic group among Muslims globally, followed by Bengalis and Punjabis. Likewise, they comprise the majority of the population ...
, killing most of its population (estimated at 25,000 people) until it subsides in October.
Asia
* TheXueyantuo
The Xueyantuo or Sir Tardush were an ancient Tiele people, Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, Eastern Göktürk ...
assaults the Chinese-conquered vassal of Eastern Tujue
The Eastern Turkic Khaganate ( zh, t=東突厥, p=Dōng Tūjué or Dōng Tújué) was a Turkic peoples, Turkic khaganate formed as a result of the internecine wars in the beginning of the 7th century (AD 581–603) after the First Turkic Kh ...
. Although simultaneously fighting in Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
against Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC – 668 AD) (; ; Old Korean: Guryeo) also later known as Goryeo (; ; Middle Korean: 고ᇢ롕〮, ''kwòwlyéy''), was a Korean kingdom which was located on the northern and central parts of the Korea, Korean Peninsula an ...
, Emperor Tai Zong commissions his famous general Li Shiji
Li Shiji (594?The ''Old Book of Tang'' indicated that Li Shiji was 75 at the time of his death, while the ''New Book of Tang'' indicated that Li Shiji was 85 at the time of his death. Compare ''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 67 with ''New Book of Tang ...
to fend off attacks in the campaign against Xueyantuo.
* An unsuccessful revolt of Prince Kürşat (of the Eastern Turks) breaks out in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
By topic
Religion
* Eligius succeedsAcarius
Acarius (died 14 March 642), venerated as Saint Acarius, was a monk of Luxeuil Abbey who became Bishop of Doornik and Noyon, which today are located on either side of the Franco-Belgian border.
Life
Acarius was born to a noble family of Burgundy ...
as bishop of Doornik and Noyon. He becomes constituted guardian of the towns of Vermandois
Vermandois was a French county that appeared in the Merovingian period. Its name derives from that of an ancient tribe, the Viromandui. In the 10th century, it was organised around two castellan domains: St Quentin (Aisne) and Péronne ( Som ...
, which also include Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
and Kortrijk
Kortrijk ( , ; or ''Kortrik''; ), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region, Flemish Provinces of Belgium, province of We ...
(Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
). Saint Quen of Rouen; trans. Jo Ann McNamara. "The life of Saint Eligius" (Vita Sanci Eligii)
* The First Cathedral of Santa Maria Assunta is founded by the exarch
An exarch (;
from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'') was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical.
In the late Roman Empire and early Byzantine Empire, ...
Isaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
of Ravenna
Ravenna ( ; , also ; ) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century until its Fall of Rome, collapse in 476, after which ...
on Torcello
Torcello (; ) is a sparsely populated island at the northern end of the Venetian Lagoon, in north-eastern Italy. It was first settled in 452 AD and has been referred to as the parent island from which Venice was populated. It was a town with ...
, confirming the island's importance as a centre of population in Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
at this date.
Births
*Aldegonde
Aldegund ( 639–684), also Aldegundis or Aldegonde, was a Frankish Benedictine abbess who is honored as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church in France and by the Orthodox Church.
Aldegund was closely related to the Merovingian royal family. H ...
, Frankish abbess
An abbess (Latin: ''abbatissa'') is the female superior of a community of nuns in an abbey.
Description
In the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and Eastern Catholic), Eastern Orthodox, Coptic, Lutheran and Anglican abbeys, the mod ...
(approximate date)
* Aldhelm
Aldhelm (, ; 25 May 709), Abbot of Malmesbury Abbey, Bishop of Sherborne, and a writer and scholar of Latin poetry, was born before the middle of the 7th century. He is said to have been the son of Kenten, who was of the royal house of Wessex ...
, bishop of Sherborne
The Bishop of Sherborne is an episcopal title which takes its name from the market town of Sherborne in Dorset, England. The see of Sherborne was established in around 705 by St Aldhelm, the Abbot of Malmesbury. This see was the mother diocese ...
(approximate date)
* Ecgberht of Ripon
Ecgberht (or Egbert, and sometimes referred to as Egbert of Rath Melsigi) (died 729) was an Anglo-Saxon monk of Northumbria. After studying at Lindisfarne and Rath Melsigi, he spent his life travelling among monasteries in northern Britain and a ...
, bishop of Lindisfarne
Lindisfarne, also known as Holy Island, is a tidal island off the northeast coast of England, which constitutes the civil parishes in England, civil parish of Holy Island in Northumberland. Holy Island has a recorded history from the 6th centu ...
(d. 729
Year 729 ( DCCXXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 729th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 729th year of the 1st millennium, the 29th year of the 8th century, and the 10th and ...
)
* Yeon Namsan
Yeon Namsan (淵男産, 연남산; 639–701) was the third son of the Goguryeo military leader and dictator Yeon Gaesomun (603?–665).
The course of his career shadowed closely that of his elder brother Yeon Namsaeng. From an early age he was ...
, military leader of Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC – 668 AD) (; ; Old Korean: Guryeo) also later known as Goryeo (; ; Middle Korean: 고ᇢ롕〮, ''kwòwlyéy''), was a Korean kingdom which was located on the northern and central parts of the Korea, Korean Peninsula an ...
(d. 701
__NOTOC__
Year 701 ( DCCI) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 701st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 701st year of the 1st millennium, the 1st year of the 8th century, and the ...
)
Deaths
*January 19
Events Pre-1600
* 379 – Emperor Gratian elevates Flavius Theodosius at Sirmium to '' Augustus'', and gives him authority over all the eastern provinces of the Roman Empire.
* 649 – Conquest of Kucha: The forces of Kucha surren ...
– Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the ...
, king of the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
(b. c. 603)
* February 3
Events Pre-1600
* 1047 – Drogo of Hauteville is elected as count of the Apulian Normans during the Norman conquest of Southern Italy.
* 1112 – Ramon Berenguer III, Count of Barcelona, and Douce I, Countess of Provence, marry, u ...
– K'inich Yo'nal Ahk I, ajaw
Ajaw or Ahau ('Lord') is a pre-Columbian Maya civilization, Maya political title attested from epigraphy, epigraphic inscriptions. It is also the name of the 20th day of the ''tzolkʼin'', the Maya divinatory calendar, on which a ruler's ''kʼatu ...
of Piedras Negras Piedras Negras may refer to:
* Piedras Negras, Coahuila, a city in the state of Coahuila, Mexico
** Piedras Negras Municipality, a municipality in Mexico, with the center in the eponymous city
* Piedras Negras (Maya site)
Piedras Negras is the ...
* November 27
Events Pre-1600
* AD 25 – Luoyang is declared capital of the Eastern Han dynasty by Emperor Guangwu of Han.
* 176 – Emperor Marcus Aurelius grants his son Commodus the rank of " Imperator" and makes him Supreme Commander of th ...
– Acarius
Acarius (died 14 March 642), venerated as Saint Acarius, was a monk of Luxeuil Abbey who became Bishop of Doornik and Noyon, which today are located on either side of the Franco-Belgian border.
Life
Acarius was born to a noble family of Burgundy ...
, bishop of Doornik and Noyon
* Suhayl ibn Amr
Suhayl ibn ʿAmr (), also known as Abū Yazīd, was a contemporary of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a prominent leader among the Quraysh tribe of Mecca. Clever and articulate, he was known as the '' Khatib'' (orator) of his tribe, and his o ...
(b. c. 556
__NOTOC__
Year 556 ( DLVI) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 556 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe f ...
)
* Abu Jandal ibn Suhayl
Al-ʿĀṣī ibn Suhayl (Arabic: العاصي ابن سهيل), better known as Abū Jandal (أبو جندل), was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, who was the first person returned to Mecca after the Treaty of Hudaybiyyah. Abu Jan ...
(b. 594
__NOTOC__
Year 594 ( DXCIV) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 594 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe f ...
- 601)
* Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah
ʿĀmir ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Jarrāḥ (; 583–639), better known as Abū ʿUbayda () was a Muslim commander and one of the Companions of the Prophet. He is mostly known for being one of the ten to whom Paradise was promised. He was comm ...
, commander of the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
(b. 583)
* Muadh ibn Jabal
Muʿādh ibn Jabal (; 603 – 639) was a (companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Muadh was an of the Banu Khazraj tribe and compiled the Quran with five companions while Muhammad was still alive. He acquired a reputation for knowledge.
Mu ...
, early Muslim scholar
* Shurahbil ibn Hasana
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Shuraḥbīl ibn Ḥasana () was one of the earliest Muslim converts, ''sahaba'' (companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad) and a key commander in the Rashidun army during the Muslim conquest of the Levant.
Early life
Shurahbil ...
, Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
general
* Yazid ibn Abi Sufyan
Yazid ibn Abi Sufyan ibn Harb ibn Umayya (; died 639) was a leading Arab Muslim commander in the conquest of Syria from 634 until his death in the plague of Amwas in 639. Following the capture of Damascus around 635, he was placed in command of ...
, general of the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit. "successors") — Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively — believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
* Faílbe Flann mac Áedo Duib, king of Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Nor ...
(Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
)
* Wang Gui, chancellor of the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
(b. 571
__NOTOC__
Year 571 (Roman numerals, DLXXI) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 571 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent ...
)
* Yang Gongren
Yang Guan (died 639), courtesy name Gongren, better known as Yang Gongren, formally Duke Xiao of Guan, was a Chinese military general and politician during the Sui dynasty, Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang dynasties, at one point serving as a chancello ...
, chancellor of the Tang dynasty
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:639