256-QAM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of
 In a QAM signal, one carrier lags the other by 90°, and its amplitude modulation is customarily referred to as the in-phase component, denoted by The other modulating function is the
In a QAM signal, one carrier lags the other by 90°, and its amplitude modulation is customarily referred to as the in-phase component, denoted by The other modulating function is the  The addition of two sinusoids is a linear operation that creates no new frequency components. So the bandwidth of the composite signal is comparable to the bandwidth of the DSB (double-sideband) components. Effectively, the spectral redundancy of DSB enables a doubling of the information capacity using this technique. This comes at the expense of demodulation complexity. In particular, a DSB signal has zero-crossings at a regular frequency, which makes it easy to recover the phase of the carrier sinusoid. It is said to be
The addition of two sinusoids is a linear operation that creates no new frequency components. So the bandwidth of the composite signal is comparable to the bandwidth of the DSB (double-sideband) components. Effectively, the spectral redundancy of DSB enables a doubling of the information capacity using this technique. This comes at the expense of demodulation complexity. In particular, a DSB signal has zero-crossings at a regular frequency, which makes it easy to recover the phase of the carrier sinusoid. It is said to be
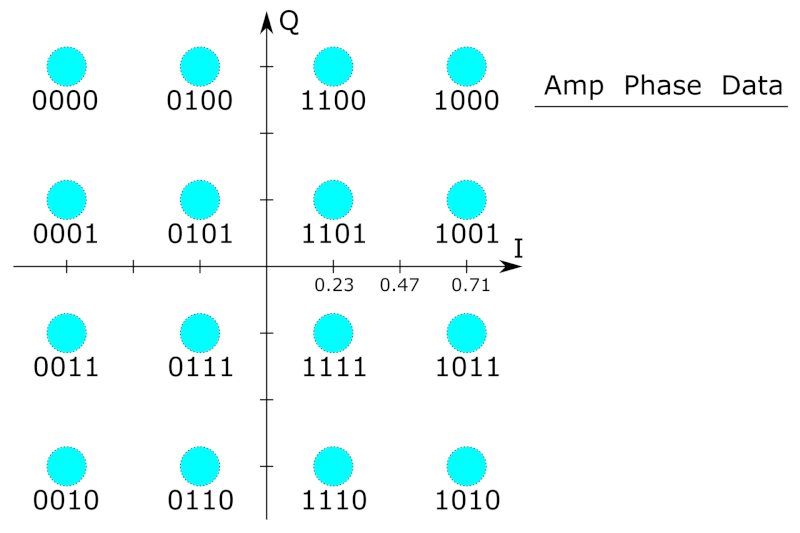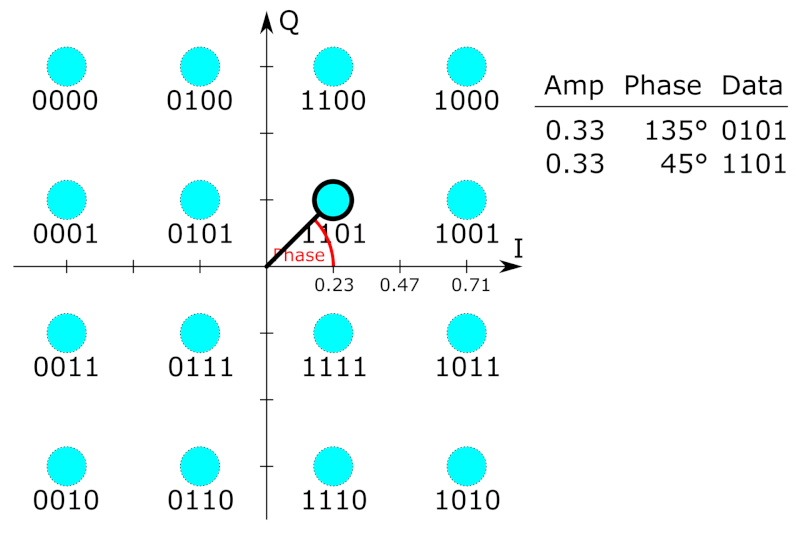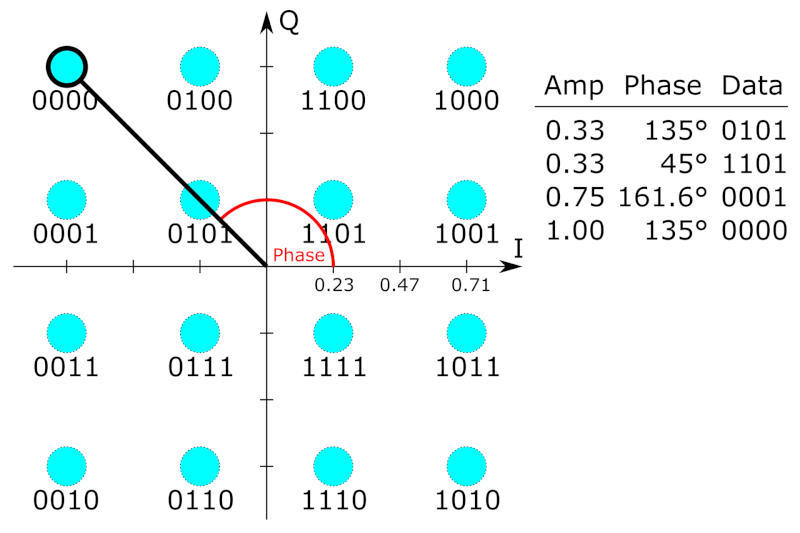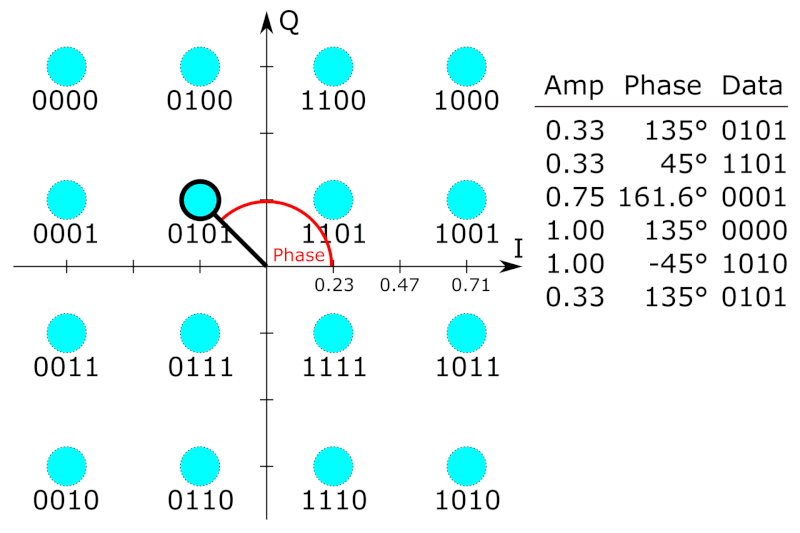
 As in many digital modulation schemes, the
As in many digital modulation schemes, the
ANSI/SCTE 07 2013
In the UK, 64-QAM is used for Communication systems designed to achieve very high levels of
Communication systems designed to achieve very high levels of
QAM Demodulation
Interactive webdemo of QAM constellation with additive noise
Institute of Telecommunicatons, University of Stuttgart
QAM bit error rate for AWGN channel – online experiment
How imperfections affect QAM constellation
Microwave Phase Shifters
Overview by Herley General Microwave
Simulation of dual-polarization QPSK (DP-QPSK) for 100G optical transmission
{{DEFAULTSORT:Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Radio modulation modes Data transmission
digital modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
methods and a related family of analog modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
methods widely used in modern telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit stream
A bitstream (or bit stream), also known as binary sequence, is a sequence of bits.
A bytestream is a sequence of bytes. Typically, each byte is an 8-bit quantity, and so the term octet stream is sometimes used interchangeably. An octet may ...
s, by changing (''modulating'') the amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
s of two carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or freq ...
s, using the amplitude-shift keying
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, a Symbol rate, symbol, representing one or more bits, is sent by transmitting a fixed-a ...
(ASK) digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion t ...
(AM) analog modulation scheme. The two carrier waves are of the same frequency and are out of phase
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a s ...
with each other by 90°, a condition known as orthogonality
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of '' perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendicular'' is more specifically ...
or quadrature. The transmitted signal is created by adding the two carrier waves together. At the receiver, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated) because of their orthogonality. Another key property is that the modulations are low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveforms compared to the carrier frequency, which is known as the narrowband assumption.
Phase modulation
Phase modulation (PM) is a signal modulation method for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal f ...
(analog PM) and phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency carrier wave. The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. I ...
(digital PSK) can be regarded as a special case of QAM, where the amplitude of the transmitted signal is a constant, but its phase varies. This can also be extended to frequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proporti ...
(FM) and frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is encoded on a carrier signal by periodically shifting the frequency of the carrier between several discrete frequencies. The technology is used fo ...
(FSK), for these can be regarded as a special case of phase modulation.
QAM is used extensively as a modulation scheme for digital communications system
A communications system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. Commu ...
s, such as in 802.11
IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer c ...
Wi-Fi standards. Arbitrarily high spectral efficiencies can be achieved with QAM by setting a suitable constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
size, limited only by the noise level and linearity of the communications channel. QAM is being used in optical fiber systems as bit rates increase; QAM16 and QAM64 can be optically emulated with a three-path interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
.
Demodulation
 In a QAM signal, one carrier lags the other by 90°, and its amplitude modulation is customarily referred to as the in-phase component, denoted by The other modulating function is the
In a QAM signal, one carrier lags the other by 90°, and its amplitude modulation is customarily referred to as the in-phase component, denoted by The other modulating function is the quadrature component
A sinusoid with modulation can be decomposed into, or synthesized from, two amplitude-modulated sinusoids that are in quadrature phase, i.e., with a phase offset of one-quarter cycle (90 degrees or /2 radians). All three sinusoids have the sam ...
, So the composite waveform is mathematically modeled as:
: or:
where is the carrier frequency. At the receiver, a coherent demodulator multiplies the received signal separately with both a cosine
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side opposite that ...
and sine
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side opposite th ...
signal to produce the received estimates of and . For example:
:
Using standard trigonometric identities
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Geometrically, these are identities involvin ...
, we can write this as:
:
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
ing removes the high frequency terms (containing ), leaving only the term. This filtered signal is unaffected by showing that the in-phase component can be received independently of the quadrature component. Similarly, we can multiply by a sine wave and then low-pass filter to extract
self-clocking
In telecommunications and electronics, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal or other source of Synchronization (computer science), synchronization. This is usually done by including embedd ...
. But the sender and receiver of a quadrature-modulated signal must share a clock or otherwise send a clock signal. If the clock phases drift apart, the demodulated ''I'' and ''Q'' signals bleed into each other, yielding crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, ...
. In this context, the clock signal is called a "phase reference". Clock synchronization is typically achieved by transmitting a burst subcarrier
A subcarrier is a sideband of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio bro ...
or a pilot signal
In telecommunications, a pilot signal is a signal, usually a single frequency, transmitted over a communications system for supervisory, control, equalization, continuity, synchronization, or reference purposes.
Uses in different communicat ...
. The phase reference for NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.
In 1953, a second ...
, for example, is included within its colorburst
Colorburst is an analog and composite video signal generated by a video-signal generator used to keep the chrominance subcarrier synchronized in a color television signal. By synchronizing an oscillator with the colorburst at the back p ...
signal.
Analog QAM is used in:
* NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.
In 1953, a second ...
and PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a color encoding system for analog television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
analog color television
Color television (American English) or colour television (British English) is a television transmission technology that also includes color information for the picture, so the video image can be displayed in color on the television set. It improv ...
systems, where the I- and Q-signals carry the components of chroma (colour) information. The QAM carrier phase is recovered from a special colorburst transmitted at the beginning of each scan line.
* C-QUAM
C-QUAM (Compatible QUadrature Amplitude Modulation) is the method of AM stereo broadcasting used in Canada, the United States and most other countries. It was invented in 1977 by Norman Parker, Francis Hilbert, and Yoshio Sakaie, and published in ...
("Compatible QAM") is used in AM stereo
AM stereo is a term given to a series of mutually incompatible techniques for radio broadcasting stereo audio in the AM band in a manner that is compatible with standard AM receivers. There are two main classes of systems: independent sideban ...
radio to carry the stereo difference information.
Fourier analysis
ApplyingEuler's formula
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that, for ...
to the sinusoids in , the positive-frequency portion of (or analytic representation) is:
:
where denotes the Fourier transform, and and are the transforms of and This result represents the sum of two DSB-SC signals with the same center frequency. The factor of represents the 90° phase shift that enables their individual demodulations.
Digital QAM

constellation diagram
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional ''xy''-plane scatter diagram in the co ...
is useful for QAM. In QAM, the constellation points are usually arranged in a square grid with equal vertical and horizontal spacing, although other configurations are possible (e.g. a hexagonal or triangular grid). In digital telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
the data is usually binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical op ...
, so the number of points in the grid is typically a power of 2 (2, 4, 8, …), corresponding to the number of bits per symbol. The simplest and most commonly used QAM constellations consist of points arranged in a square, i.e. 16-QAM, 64-QAM and 256-QAM (even powers of two). Non-square constellations, such as Cross-QAM, can offer greater efficiency but are rarely used because of the cost of increased modem complexity.
By moving to a higher-order constellation, it is possible to transmit more bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
s per symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
. However, if the mean energy of the constellation is to remain the same (by way of making a fair comparison), the points must be closer together and are thus more susceptible to noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
and other corruption; this results in a higher bit error rate
In digital transmission, the number of bit errors is the number of received bits of a data stream over a communication channel that have been altered due to noise, interference, distortion or bit synchronization errors.
The bit error rate (BER) ...
and so higher-order QAM can deliver more data less reliably than lower-order QAM, for constant mean constellation energy. Using higher-order QAM without increasing the bit error rate requires a higher signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to noise power, often expressed in deci ...
(SNR) by increasing signal energy, reducing noise, or both.
If data rates beyond those offered by 8- PSK are required, it is more usual to move to QAM since it achieves a greater distance between adjacent points in the I-Q plane by distributing the points more evenly. The complicating factor is that the points are no longer all the same amplitude and so the demodulator
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content from ...
must now correctly detect both phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
and amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
, rather than just phase.
64-QAM and 256-QAM are often used in digital cable
Digital cable is the distribution of cable television using digital data and video compression. The technology was first developed by General Instrument. By 2000, most cable companies offered digital features, eventually replacing their previo ...
television and cable modem
A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG) and coaxial cable infrastructure. Cable modems are pri ...
applications. In the United States, 64-QAM and 256-QAM are the mandated modulation schemes for digital cable
Digital cable is the distribution of cable television using digital data and video compression. The technology was first developed by General Instrument. By 2000, most cable companies offered digital features, eventually replacing their previo ...
(see QAM tuner) as standardised by the SCTE in the standarANSI/SCTE 07 2013
In the UK, 64-QAM is used for
digital terrestrial television
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV, DTT, or DTTB) is a technology for terrestrial television, in which television stations broadcast television content in a digital signal, digital format. Digital terrestrial television is a major technologica ...
(Freeview Freeview may refer to:
*Freeview (Australia), the marketing name for the digital terrestrial television platform in Australia
*Freeview (New Zealand), a digital satellite and digital terrestrial television platform in New Zealand
*Freeview (UK), a ...
) whilst 256-QAM is used for Freeview-HD.
 Communication systems designed to achieve very high levels of
Communication systems designed to achieve very high levels of spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system. It is a measure of how efficiently a limited frequency spectrum i ...
usually employ very dense QAM constellations. For example is ADSL
Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over Copper wire, copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem ...
technology for copper twisted pairs, whose constellation size goes up to 32768-QAM (in ADSL terminology this is referred to as bit-loading, or bit per tone, 32768-QAM being equivalent to 15 bits per tone).
Ultra-high capacity microwave backhaul systems also use 1024-QAM. With 1024-QAM, adaptive coding and modulation
Adaptation, in biology, is the process or trait by which organisms or population better match their environment
Adaptation may also refer to:
Arts
* Adaptation (arts), a transfer of a work of art from one medium to another
** Film adaptation, ...
(ACM) and XPIC, vendors can obtain gigabit capacity in a single 56 MHz channel.
Interference and noise
In moving to a higher order QAM constellation (higher data rate and mode) in hostile RF/microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
QAM application environments, such as in broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), ...
or telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
, multipath interference
In radio communication, multipath is the radio propagation, propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna (electronics), antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionosph ...
typically increases. There is a spreading of the spots in the constellation, decreasing the separation between adjacent states, making it difficult for the receiver to decode the signal appropriately. In other words, there is reduced noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
immunity. There are several test parameter measurements which help determine an optimal QAM mode for a specific operating environment. The following three are most significant:
* Carrier/interference ratio
* Carrier-to-noise ratio
In telecommunications, the carrier-to-noise ratio, often written CNR or ''C/N'', is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a modulated signal. The term is used to distinguish the CNR of the radio frequency passband signal from the SNR of an analog ...
* Threshold-to-noise ratio
See also
*Amplitude and phase-shift keying
Amplitude and phase-shift keying (APSK) is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by modulating both the amplitude and the phase of a carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic wa ...
or asymmetric phase-shift keying (APSK)
* Carrierless amplitude phase modulation (CAP)
*
* In-phase and quadrature components
A sinusoid with modulation can be decomposed into, or synthesized from, two amplitude-modulated sinusoids that are in quadrature phase, i.e., with a phase offset of one-quarter cycle (90 degrees or /2 radians). All three sinusoids have the sam ...
* Modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
for other examples of modulation techniques
* Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency carrier wave. The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. I ...
* QAM tuner for HDTV
* Random modulation
References
Further reading
* *External links
QAM Demodulation
Interactive webdemo of QAM constellation with additive noise
Institute of Telecommunicatons, University of Stuttgart
QAM bit error rate for AWGN channel – online experiment
How imperfections affect QAM constellation
Microwave Phase Shifters
Overview by Herley General Microwave
Simulation of dual-polarization QPSK (DP-QPSK) for 100G optical transmission
{{DEFAULTSORT:Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Radio modulation modes Data transmission