24-TET on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a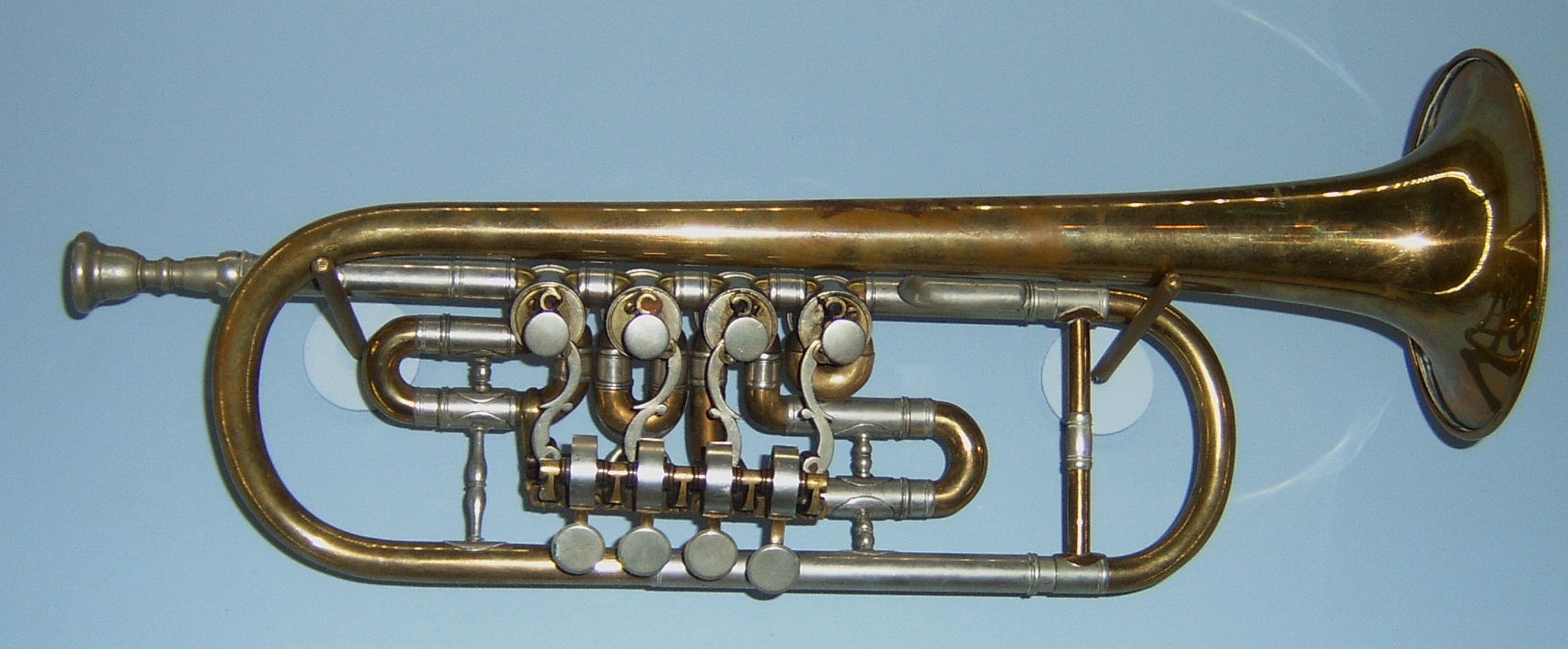  Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in
Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in
 The term ''quarter tone'' can refer to a number of different intervals, all very close in size. For example, some 17th- and 18th-century theorists used the term to describe the distance between a sharp and enharmonically distinct flat in mean-tone temperaments (e.g., D–E). In the quarter-tone scale, also called 24-tone equal temperament (24-TET), the quarter tone is 50 cents, or a frequency ratio of or approximately 1.0293, and divides the octave into 24 equal steps (
The term ''quarter tone'' can refer to a number of different intervals, all very close in size. For example, some 17th- and 18th-century theorists used the term to describe the distance between a sharp and enharmonically distinct flat in mean-tone temperaments (e.g., D–E). In the quarter-tone scale, also called 24-tone equal temperament (24-TET), the quarter tone is 50 cents, or a frequency ratio of or approximately 1.0293, and divides the octave into 24 equal steps (
 Any tunable musical instrument can be used to perform quarter tones, if two players and two identical instruments, with one tuned a quarter tone higher, are used. As this requires neither a special instrument nor special techniques, much quarter toned music is written for pairs of pianos, violins, harps, etc. The retuning of the instrument, and then returning it to its former pitch, is easy for violins, harder for harps, and slow and relatively expensive for pianos.
The following deals with the ability of single instruments to produce quarter tones. In Western instruments, this means "in addition to the usual 12-tone system". Because many musical instruments manufactured today (2018) are designed for the 12-tone scale, not all are usable for playing quarter tones. Sometimes special playing techniques must be used.
Conventional musical instruments that ''cannot'' play quarter tones (except by using special techniques—see below) include:
* Most standard or unmodified non-electronic keyboard instruments, such as
Any tunable musical instrument can be used to perform quarter tones, if two players and two identical instruments, with one tuned a quarter tone higher, are used. As this requires neither a special instrument nor special techniques, much quarter toned music is written for pairs of pianos, violins, harps, etc. The retuning of the instrument, and then returning it to its former pitch, is easy for violins, harder for harps, and slow and relatively expensive for pianos.
The following deals with the ability of single instruments to produce quarter tones. In Western instruments, this means "in addition to the usual 12-tone system". Because many musical instruments manufactured today (2018) are designed for the 12-tone scale, not all are usable for playing quarter tones. Sometimes special playing techniques must be used.
Conventional musical instruments that ''cannot'' play quarter tones (except by using special techniques—see below) include:
* Most standard or unmodified non-electronic keyboard instruments, such as
\relative c'
# Rast ():
#:C D E F G A B C (ascending)
#:C B A G F E D C (descending)
#:
\relative c'
#
\relative c'
# Segah (): E F G A B C D E
#:
\relative c'
# ‘Ajam ()
#Hoseyni
The Islamic philosopher and scientist
\relative c'
The quarter tone scale may be primarily a  Composer
Composer
\relative c'

quarter-tone / 24-edo
, ''TonalSoft.com'' {{Musical tuning Musical scales Quarter tones,
chromatic scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the ...
or an interval about half as wide (orally, or logarithmically) as a semitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between ...
, which itself is half a whole tone
In Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (). A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more deta ...
. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, and have 24 different pitches.
 Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in
Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in Persian traditional music
Persian traditional music or Iranian traditional music, also known as Persian classical music or Iranian classical music, refers to the classical music of Iran (historically known as '' Persia''). It consists of characteristics developed through ...
. However, the first evidenced proposal of the equally-tempered quarter tone scale, or 24 equal temperament, was made by 19th-century music theorists Heinrich Richter in 1823Julian Rushton
Julian Gordon Rushton (born 22 May 1941) is an English musicologist, born in Cambridge. He has contributed the entry on Mozart in ''The New Grove Dictionary of Opera'' and several other articles in ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians' ...
, "Quarter-Tone", ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language '' Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and t ...
'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie
Stanley John Sadie (; 30 October 1930 – 21 March 2005) was a British musicologist, music critic, and editor. He was editor of the sixth edition of the '' Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (1980), which was published as the first edition ...
and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan, 2001). and Mikhail Mishaqa about 1840. Composers who have written music using this scale include: Pierre Boulez
Pierre Louis Joseph Boulez (; 26 March 19255 January 2016) was a French composer, conductor and writer, and the founder of several musical institutions. He was one of the dominant figures of post-war contemporary classical music.
Born in Montb ...
, Julián Carrillo
Julián Carrillo Trujillo (January 28, 1875 – September 9, 1965) was a Mexican composer,Camp, Roderic Ai (1995). "Carrillo (Flores), Nabor" on ''Mexican Political Biographies, 1935–1993: Third Edition'', p. 121. . conductor, violin ...
, Mildred Couper
Mildred Couper (December 10, 1887 in Buenos Aires, Argentina – August 9, 1974 in Santa Barbara, United States) was a prominent composer and pianist, and one of the first American musicians to experiment with quarter-tone music. She was b ...
, George Enescu
George Enescu (; – 4 May 1955), known in France as Georges Enesco, was a Romanians, Romanian composer, violinist, pianist, conductor, teacher and statesman. He is regarded as one of the greatest musicians in Romanian history.
Biography
En ...
, Alberto Ginastera
Alberto Evaristo Ginastera (; April 11, 1916June 25, 1983) was an Argentine composer of classical music. He is considered to be one of the most important 20th-century classical music, 20th-century classical composers of the Americas.
Biography
G ...
, Gérard Grisey
Gérard Henri Grisey (; ; 17 June 1946 – 11 November 1998) was a twentieth-century French composer of contemporary classical music. His work is often associated with the Spectralist Movement in music, of which he was a major pioneer.
Biograp ...
, Alois Hába
Alois Hába (21 June 1893 – 18 November 1973) was a Czech composer, music theorist and teacher. He belongs to the important discoverers in modern classical music, and to the major composers of microtonal music, especially using the quarter-to ...
, Ljubica Marić
Ljubica Marić (Љубица Марић , 18 March 1909 – 17 September 2003) was a composer from Yugoslavia. She was a pupil of Josip Štolcer-Slavenski. She was known for being inspired by Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Eastern Orthodox Church, ...
, Charles Ives
Charles Edward Ives (; October 20, 1874May 19, 1954) was an American modernist composer, actuary and businessman. Ives was among the earliest renowned American composers to achieve recognition on a global scale. His music was largely ignored d ...
, Tristan Murail
Tristan Murail (born 11 March 1947) is a French composer associated with the " spectral" technique of composition. Among his compositions is the large orchestral work ''Gondwana''.
Early life and studies
Murail was born in Le Havre, France. His f ...
, Krzysztof Penderecki
Krzysztof Eugeniusz Penderecki (; 23 November 1933 – 29 March 2020) was a Polish composer and conductor. His best-known works include '' Threnody to the Victims of Hiroshima'', Symphony No. 3, his '' St Luke Passion'', '' Polish Requiem'', '' ...
, Giacinto Scelsi
Giacinto Francesco Maria Scelsi (; 8 January 1905 – 9 August 1988, sometimes cited as 8 August 1988) was an Italian composer who also wrote surrealist poetry in French.
He is best known for having composed music based around only one pitch, ...
, Ammar El Sherei
Ammar Ali Mohamed Ibrahim Ali Al Sherei () or more commonly known as Ammar El Sherei (16 April 1948 – 7 December 2012) was an Egyptian music icon, performer and composer.
Early life and education
Sherei was born blind on 16 April 1948 in t ...
, Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
, Tui St. George Tucker, Ivan Wyschnegradsky
Ivan Alexandrovich Wyschnegradsky ( ; September 29, 1979), was a Russian composer primarily known for his microtonal compositions. For most of his life, from 1920 onwards, Wyschnegradsky lived in Paris.
Life
Ivan Wyschnegradsky was born in Sai ...
, Iannis Xenakis
Giannis Klearchou Xenakis (also spelled for professional purposes as Yannis or Iannis Xenakis; , ; 29 May 1922 – 4 February 2001) was a Romanian-born Greek-French avant-garde composer, music theorist, architect, performance director and enginee ...
, and Seppe Gebruers
Seppe Gebruers (born May 9, 1990) is a Belgian musician, composer and improvisor. He is also a teacher and researcher at KASK conservatory Ghent. Gebruers plays both solo and in bands. His work ranges from jazz to contemporary classical music.
G ...
(See List of quarter tone pieces.)
Types
Equal-tempered tuning systems
 The term ''quarter tone'' can refer to a number of different intervals, all very close in size. For example, some 17th- and 18th-century theorists used the term to describe the distance between a sharp and enharmonically distinct flat in mean-tone temperaments (e.g., D–E). In the quarter-tone scale, also called 24-tone equal temperament (24-TET), the quarter tone is 50 cents, or a frequency ratio of or approximately 1.0293, and divides the octave into 24 equal steps (
The term ''quarter tone'' can refer to a number of different intervals, all very close in size. For example, some 17th- and 18th-century theorists used the term to describe the distance between a sharp and enharmonically distinct flat in mean-tone temperaments (e.g., D–E). In the quarter-tone scale, also called 24-tone equal temperament (24-TET), the quarter tone is 50 cents, or a frequency ratio of or approximately 1.0293, and divides the octave into 24 equal steps (equal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencie ...
). In this scale the quarter tone is the smallest step. A semitone is thus made of two steps, and three steps make a three-quarter tone or neutral second
In music theory, a neutral interval is an interval that is neither a major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in equal temperament, a major third is 400 cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral ...
, half of a minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a interval (music), musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval (music)#Number, interval numb ...
. The 8-TET scale is composed of three-quarter tones. Four steps make a whole tone.
Quarter tones and intervals close to them also occur in a number of other equally tempered tuning systems. 22-TET contains an interval of 54.55 cents, slightly wider than a quarter-tone, whereas 53-TET has an interval of 45.28 cents, slightly smaller. 72-TET also has equally tempered quarter-tones, and indeed contains three quarter-tone scales, since 72 is divisible by 24. The smallest interval in 31 equal temperament
In music, 31 equal temperament, which can also be abbreviated (31 tone ) or (equal division of the octave), also known as tricesimoprimal, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 31 equally-proportioned steps (e ...
(the "diesis" of 38.71 cents) is half a chromatic semitone
In modern Western tonal music theory an augmented unison or augmented prime is the interval between two notes on the same staff position, or denoted by the same note letter, whose alterations cause them, in ordinary equal temperament, to be one ...
, one-third of a diatonic semitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest interval (music), musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most Consonance and dissonance#Dissonance, dissonant when sounde ...
and one-fifth of a whole tone, so it may function as a quarter tone, a fifth-tone ''or'' a sixth-tone.
Just intonation tuning systems
Injust intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in thi ...
the quarter tone can be represented by the septimal quarter tone
A septimal quarter tone (in music) is an Interval (music), interval with the ratio of 36:35, which is the difference between the septimal minor third and the Just minor third, or about 48.77 Cent (music), cents wide. The name derives from the in ...
, 36:35 (48.77 cents), or by the undecimal quarter tone (i.e. the thirty-third harmonic), 33:32 (53.27 cents), approximately half the semitone of 16:15 or 25:24. The ratio of 36:35 is only 1.23 cents narrower than a 24-TET quarter tone. This just ratio is also the difference between a minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a interval (music), musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval (music)#Number, interval numb ...
(6:5) and septimal minor third
Septimal may refer to:
*Septimal chromatic semitone, the interval 21:20, about 84.47 cents
*Septimal comma, a small musical interval in just intonation divisible by 7
*Septimal diatonic semitone, the interval 15:14, about 119.44 cents
*S ...
(7:6).
Composer Ben Johnston, to accommodate the just septimal quarter tone, uses a small "7" () as an accidental to indicate a note is lowered 49 cents, or an upside down "7" () to indicate a note is raised 49 cents, or a ratio of 36:35. Fonville, John (Summer, 1991). "Ben Johnston's Extended Just Intonation: A Guide for Interpreters", p. 114, ''Perspectives of New Music
''Perspectives of New Music'' (PNM) is a peer-reviewed academic journal specializing in music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Musi ...
'', vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 106–137. Johnston uses an upward and downward arrow to indicate a note is raised or lowered by a ratio of 33:32, or 53 cents. The Maneri-Sims notation system designed for 72-et uses the accidentals and for a quarter tone (36:35 or 48.77 cents) up and down.
Playing quarter tones
 Any tunable musical instrument can be used to perform quarter tones, if two players and two identical instruments, with one tuned a quarter tone higher, are used. As this requires neither a special instrument nor special techniques, much quarter toned music is written for pairs of pianos, violins, harps, etc. The retuning of the instrument, and then returning it to its former pitch, is easy for violins, harder for harps, and slow and relatively expensive for pianos.
The following deals with the ability of single instruments to produce quarter tones. In Western instruments, this means "in addition to the usual 12-tone system". Because many musical instruments manufactured today (2018) are designed for the 12-tone scale, not all are usable for playing quarter tones. Sometimes special playing techniques must be used.
Conventional musical instruments that ''cannot'' play quarter tones (except by using special techniques—see below) include:
* Most standard or unmodified non-electronic keyboard instruments, such as
Any tunable musical instrument can be used to perform quarter tones, if two players and two identical instruments, with one tuned a quarter tone higher, are used. As this requires neither a special instrument nor special techniques, much quarter toned music is written for pairs of pianos, violins, harps, etc. The retuning of the instrument, and then returning it to its former pitch, is easy for violins, harder for harps, and slow and relatively expensive for pianos.
The following deals with the ability of single instruments to produce quarter tones. In Western instruments, this means "in addition to the usual 12-tone system". Because many musical instruments manufactured today (2018) are designed for the 12-tone scale, not all are usable for playing quarter tones. Sometimes special playing techniques must be used.
Conventional musical instruments that ''cannot'' play quarter tones (except by using special techniques—see below) include:
* Most standard or unmodified non-electronic keyboard instruments, such as piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
s, organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
, and accordion
Accordions (from 19th-century German language, German ', from '—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a Reed (mou ...
s
* Fret
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical inst ...
ted string instruments
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Musicians play some ...
such as guitars
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
, bass guitars
The bass guitar (), also known as the electric bass guitar, electric bass, or simply the bass, is the lowest-pitched member of the guitar family. It is similar in appearance and construction to an electric but with a longer neck and scale leng ...
, and ukulele
The ukulele ( ; ); also called a uke (informally), is a member of the lute (ancient guitar) family of instruments. The ukulele is of Portuguese origin and was popularized in Hawaii. The tone and volume of the instrument vary with size and con ...
s (though on these it is possible to play quarter tones by pitch-bending, with special tunings, or with customized necks)
* Pitched percussion instruments
Pitch may refer to:
Acoustic frequency
* Pitch (music), the perceived frequency of sound including "definite pitch" and "indefinite pitch"
** Absolute pitch or "perfect pitch"
** Pitch class, a set of all pitches that are a whole number of octav ...
, if standard techniques are used, and if the instruments are not tunable
* Western wind instruments
A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator (usually a tube) in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into (or over) a mouthpiece set at or near the end of the resonator. The pitch ...
that use keys or valves
** Woodwind instruments
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments.
Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and Ree ...
, such as clarinets, saxophones, flutes, and oboes (though with many of these, it is still possible using non-standard techniques such as special fingerings or by the player manipulating their embouchure
Embouchure () or lipping is the use of the lips, facial muscles, tongue, and teeth in playing a wind instrument. This includes shaping the lips to the mouthpiece (woodwind), mouthpiece of a woodwind or brass instrument. The word is of French lan ...
, to play at least ''some'' quarter tones, if not a whole scale)
** Valved brass instruments (trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz musical ensemble, ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest Register (music), register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitche ...
, tuba
The tuba (; ) is the largest and lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in th ...
) (though, as with woodwinds, embouchure manipulation, as well as harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
tones that fall closer to quarter-tones than half-tones, make quarter-tone scales possible; the horn
Horn may refer to:
Common uses
* Horn (acoustic), a tapered sound guide
** Horn antenna
** Horn loudspeaker
** Vehicle horn
** Train horn
*Horn (anatomy), a pointed, bony projection on the head of various animals
* Horn (instrument), a family ...
technique of adjusting pitch with the right hand in the bell makes this instrument an exception)
* Harmonica
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica incl ...
(although note bending is a common technique)
Conventional musical instruments that ''can'' play quarter tones include
* Electronic instruments:
** Synthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
s, using either special keyboard controllers or continuous-pitch controllers such as fingerboard controllers, or when controlled by a sequencer capable of outputting quarter-tone control signals.
** Theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named aft ...
s and other continuously pitched instruments
* Fretless string instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Musicians play some ...
s, such as the violin family
The violin family of musical instruments was developed in Italy in the 16th century. At the time the name of this family of instruments was viole da braccio which was used to distinguish them from the viol family (viole ''da gamba''). The standa ...
, fretless guitar
A fretless guitar is a guitar with a fingerboard without frets, typically a standard instrument that has had the frets removed, though some custom-built and commercial fretless guitars are occasionally made.
The classic fretless guitar was first ...
s, fretless electric basses, ouds, and members of the huqin
''Huqin'' () is a family of bowed string instruments, more specifically, a spike fiddle popularly used in Chinese music. The instruments consist of a round, hexagonal, or octagonal sound box at the bottom with a neck attached that protrudes ...
family of instruments.
* String instruments with movable frets (such as the sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form in 19th-century India. Khusrau K ...
)
* Specially fretted string instruments (such as the Turkish bağlama
The bağlama or saz is a family of plucked string instruments and long-necked lutes used in Europe, Balkans, Caucasus, Middle East, Khazar, Central Asia including Germany, France, Belgium, TRNC, Netherlands, Albania, Greece,Bosnia, Serbia, Croat ...
).
* Fretted string instruments specially tuned to quarter tones
* Pedal steel guitar
The pedal steel guitar is a console steel guitar with pedals and knee levers that change the pitch of certain strings, enabling more varied and complex music to be played than with other steel guitar designs. Like all steel guitars, it can play ...
* certain non-valved wind instruments, like Duduk
The duduk ( ; ) or tsiranapogh (, meaning "apricot-made wind instrument"), is a double reed woodwind instrument made of apricot wood originating from Armenia. Variations of the Armenian duduk appear throughout the Caucasus, the Balkans, and the ...
* Wind instruments whose main means of tone-control is a slide, such as trombone
The trombone (, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the Brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's lips vibrate inside a mouthpiece, causing the Standing wave, air c ...
s, the tromboon invented by P. D. Q. Bach
P. D. Q. Bach is a fictional composer created by the American composer and musical satirist Peter Schickele for a five-decade career performing the "discovered" works of the "only forgotten son" of the Bach family. Schickele's music combines Par ...
, the slide trumpet
The slide trumpet is an early type of trumpet fitted with a movable section of telescopic tubing, similar to the slide of a trombone. Eventually, the slide trumpet evolved into the sackbut, which evolved into the modern-day trombone. The key dif ...
and the slide whistle
A slide whistle (variously known as a swanee or swannee whistle, lotus flute, piston flute, or jazz flute) is a wind instrument consisting of a fipple like a recorder's and a tube with a piston in it. Thus it has an air reed like some woodwi ...
* Specially keyed woodwind instruments. A quarter tone clarinet was built by Fritz Schüller (1883–1977) of Markneukirchen
Markneukirchen () is a town in the Vogtlandkreis district, in Saxony, Germany, close to the Czech Republic, Czech border. It lies in the Elster Mountains (part of the Fichtel Mountains), southeast of Plauen, and northeast of Aš (Czech Republic) ...
, and a quarter tone mechanism for flutes by Eva Kingma.
* Valved brass instruments with extra, quarter-tone valves, and natural brass instruments that play through the 11th and 13th partials of the harmonic series
* Voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
* Kazoo
The kazoo is a musical instrument that adds a ''buzzing'' timbral quality to a player's voice when the player vocalizes into it. It is a type of '' mirliton'' (itself a membranophone), one of a class of instruments that modify the player's v ...
* Pitched percussion instruments
Pitch may refer to:
Acoustic frequency
* Pitch (music), the perceived frequency of sound including "definite pitch" and "indefinite pitch"
** Absolute pitch or "perfect pitch"
** Pitch class, a set of all pitches that are a whole number of octav ...
, when tuning permits (e.g., timpani), or using special techniques
Other instruments can be used to play quarter tones when using audio signal processing
Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. Audio signals are electronic representations of sound waves—longitudinal waves which travel through air, consisting ...
effects such as pitch shifting
Pitch shifting is a sound recording technique in which the original pitch of a sound is raised or lowered. Effects units that raise or lower pitch by a pre-designated musical interval ( transposition) are known as pitch shifters.
Pitch and t ...
.
Quarter-tone pianos have been built, which consist essentially of two pianos with two keyboards stacked one above the other in a single case, one tuned a quarter tone higher than the other.
Music of the Middle East
Many Persian dastgah and Arabic ''maqamat'' contain intervals of three-quarter tone size; a short list of these follows. #Bayati
Bayati () is one of the oldest forms of Azerbaijani folk poetry. A bayati consists of four lines, each of which has seven syllables. The rhyme scheme is AABA. Anonymous bayati have been collected as folk wisdom in editions such as {{langx, az, ...
(): D E F G A B C D
#:Saba
Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Șaba or Șaba-Târg, the Romanian name for Shabo, a village in Ukraine
* Saba, ...
(): D E F G A B C D
#:Al-Farabi
file:A21-133 grande.webp, thumbnail, 200px, Postage stamp of the USSR, issued on the 1100th anniversary of the birth of Al-Farabi (1975)
Abu Nasr Muhammad al-Farabi (; – 14 December 950–12 January 951), known in the Greek East and Latin West ...
described a number of intervals in his work in music, including a number of quarter tones.
Assyrian/Syriac Church Music Scale:
# Qadmoyo (Bayati)
# Trayono (Hussayni)
# Tlithoyo (Segah)
# Rbiʿoyo (Rast)
# Hmishoyo
# Shtithoyo (ʿAjam)
# Shbiʿoyo
# Tminoyo
Quarter-tone scale
Known as ''gadwal'' in Arabic, the quarter-tone scale was developed in the Middle East in the eighteenth century and many of the first detailed writings in the nineteenth century Syria describe the scale as being of 24 equal tones. The invention of the scale is attributed to Mishaqa who wrote a book devoted to the topic but made clear that his teacher, Sheikh Muhammad al-Attar (1764–1828), was one among many already familiar with the concept.theoretical
A theory is a systematic and rational form of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the conclusions derived from such thinking. It involves contemplative and logical reasoning, often supported by processes such as observation, experimentation, ...
construct in Arabic music. The quarter tone gives musicians a "conceptual map" they can use to discuss and compare intervals by number of quarter tones, and this may be one of the reasons it accompanies a renewed interest in theory, with instruction in music theory a mainstream requirement since that period.
Previously, pitches of a mode were chosen from a scale consisting of seventeen tones, developed by Safi al-Din al-Urmawi
Safi al-Din al-Urmawi al-Baghdadi () or Safi al-Din Abd al-Mu'min ibn Yusuf ibn al-Fakhir al-Urmawi al-Baghdadi (born c. 1216 AD in Urmia, died in 1294 AD in Baghdad) was a musician and writer on the theory of music.
Background and life
Safi ...
in the thirteenth century.
Charles Ives
Charles Edward Ives (; October 20, 1874May 19, 1954) was an American modernist composer, actuary and businessman. Ives was among the earliest renowned American composers to achieve recognition on a global scale. His music was largely ignored d ...
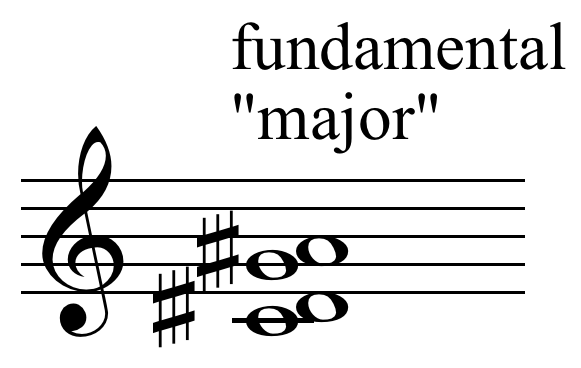
chose the chord C–D–F–G–B as good possibility for a "secondary" chord in the quarter-tone scale, akin to the minor chord of traditional tonality. He considered that it may be built upon any degree of the quarter tone scale Here is the secondary "minor" and its "first inversion":
In popular Western music
The bass descent ofNancy Sinatra
Nancy Sandra Sinatra (born June 8, 1940) is an American singer, actress, film producer and author. She is the elder daughter of Frank Sinatra and Nancy Sinatra ( Barbato) and is known for her 1965 signature hit " These Boots Are Made for Walki ...
's version of "These Boots Are Made for Walkin'
"These Boots Are Made for Walkin' is a hit song written by Lee Hazlewood and recorded by American singer Nancy Sinatra. It charted on January 22, 1966, and reached No.1 in the United States ''Billboard'' Hot 100 and in the UK Singles Chart. ...
includes quarter tone descents.
Several quarter-tone albums have been recorded by Jute Gyte, a one-man avantgarde black metal band from Missouri, US.
Another quartertone metal album was issued by the Swedish band Massive Audio Nerve.
Australian psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music Music genre, genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelia, psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound ...
band King Gizzard & the Lizard Wizard
King Gizzard & the Lizard Wizard (KGLW) are an Australian rock band formed in 2010 in Melbourne, Victoria. The band's current lineup consists of Stu Mackenzie (vocals, guitar), Ambrose Kenny-Smith (vocals, harmonica, keyboards), Cook Craig ( ...
's albums '' Flying Microtonal Banana'', K.G., and L.W. heavily emphasize quarter-tones and used a custom-built guitar in 24 tuning.
Jazz violinist / violist Mat Maneri
Mat Maneri (born October 4, 1969) is an American composer, violin, and viola player. He is the son of the saxophonist Joe Maneri and Sonja Maneri.
Career
Maneri has recorded with Cecil Taylor, Guerino Mazzola, Matthew Shipp, Joe Morris, G ...
, in conjunction with his father Joe Maneri
Joseph Gabriel Esther Maneri (February 9, 1927 – August 24, 2009), was an American jazz composer, saxophone and clarinet player. Violinist Mat Maneri is his son.
Boston Microtonal Society
In 1988, Maneri founded the Boston Microtonal Society, ...
, made a crossover fusion album, ''Pentagon'' (2005), that featured experiments in hip hop with quarter tone pianos, as well as electric organ and mellotron
The Mellotron is an electro-mechanical musical instrument developed in Birmingham, England, in 1963. It is played by pressing its keys, each of which causes a length of magnetic tape to contact a Capstan (tape recorder), capstan, which pulls i ...
textures, along with distorted trombone, in a post-Bitches Brew type of mixed jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
/ rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wale ...
.
Later, Seppe Gebruers
Seppe Gebruers (born May 9, 1990) is a Belgian musician, composer and improvisor. He is also a teacher and researcher at KASK conservatory Ghent. Gebruers plays both solo and in bands. His work ranges from jazz to contemporary classical music.
G ...
started playing and improvising with two pianos tuned a quarter-tone apart. In 2019 he started a research project at the Royal Conservatory of Ghent
The Royal Conservatory of Ghent () is a historic conservatory and a royally chartered musical institution in Ghent, Belgium. It is now a part of the University College Ghent.
History
The Royal Conservatory of Ghent is a royally chartered music ...
, titled 'Unexplored possibilities of contemporary improvisation and the influence of microtonality in the creation process'.
With two pianos tuned a quarter tone apart Gebruers recorded 'The Room: Time & Space' (2018) in a trio formation with drummer Paul Lovens
Paul Lovens (born 6 June 1949) is a German musician. He plays drums, percussion, singing saw, and cymbals. He has performed with the Aardvark Jazz Orchestra and Berlin Contemporary Jazz Orchestra.
He was born in Aachen, Germany. In the early ...
and bassist Hugo Anthunes. In his solo project 'Playing with standards' (album release January 2023), Gebruers plays with famous songs including jazz standards. With Paul Lytton and Nils Vermeulen he forms a 'Playing with standards' trio.
Ancient Greek tetrachords
The Genus (music)#Enharmonic, enharmonic genus of the Ancient Greece, Greek tetrachord consisted of a ditone or an approximate major third, and asemitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between ...
, which was divided into two microtones. Aristoxenos, Didymos (music theorist), Didymos and others presented the semitone as being divided into two approximate quarter tone intervals of about the same size, while other ancient Greek theorists described the microtones resulting from dividing the semitone of the enharmonic genus as unequal in size (i.e., one smaller than a quarter tone and one larger).

Interval size in equal temperament
Here are the sizes of some common intervals in a 24-note equally tempered scale, with the interval names proposed byAlois Hába
Alois Hába (21 June 1893 – 18 November 1973) was a Czech composer, music theorist and teacher. He belongs to the important discoverers in modern classical music, and to the major composers of microtonal music, especially using the quarter-to ...
(neutral third, etc.) and Ivan Wyschnegradsky
Ivan Alexandrovich Wyschnegradsky ( ; September 29, 1979), was a Russian composer primarily known for his microtonal compositions. For most of his life, from 1920 onwards, Wyschnegradsky lived in Paris.
Life
Ivan Wyschnegradsky was born in Sai ...
(major fourth, etc.):
:
Moving from Equal temperament, 12-TET to 24-TET allows the better approximation of a number of intervals. Intervals matched particularly closely include the neutral second
In music theory, a neutral interval is an interval that is neither a major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in equal temperament, a major third is 400 cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral ...
, neutral third, and (11:8) ratio, or the 11th harmonic. The septimal minor third
Septimal may refer to:
*Septimal chromatic semitone, the interval 21:20, about 84.47 cents
*Septimal comma, a small musical interval in just intonation divisible by 7
*Septimal diatonic semitone, the interval 15:14, about 119.44 cents
*S ...
and septimal major third are approximated rather poorly; the (13:10) and (15:13) ratios, involving the 13th harmonic, are matched very closely. Overall, 24-TET can be viewed as matching the 11th and 13th harmonics more closely than the 7th.
See also
* Musical temperament * List of quarter tone pieces * List of meantone intervals * 53 equal temperament#Holdrian comma, Holdrian Comma * Koron (music), Koron, Sori (music), SoriReferences
Further reading
* * * * * * * * *External links
quarter-tone / 24-edo
, ''TonalSoft.com'' {{Musical tuning Musical scales Quarter tones,