2015 Nepal Earthquake on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The April 2015 Nepal earthquake (also known as the Gorkha earthquake) killed 8,962 people and injured 21,952 across the countries of Nepal, India, China and Bangladesh. It occurred at on Saturday 25 April 2015, with a magnitude of Mw 7.8–7.9 or Ms 8.1 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of X (''Extreme''). Its
 The earthquake occurred on 25 April 2015 at NST (06:11:25 UTC) at a depth of approximately (which is considered shallow and therefore more damaging than quakes that originate deeper in the ground), with its
The earthquake occurred on 25 April 2015 at NST (06:11:25 UTC) at a depth of approximately (which is considered shallow and therefore more damaging than quakes that originate deeper in the ground), with its
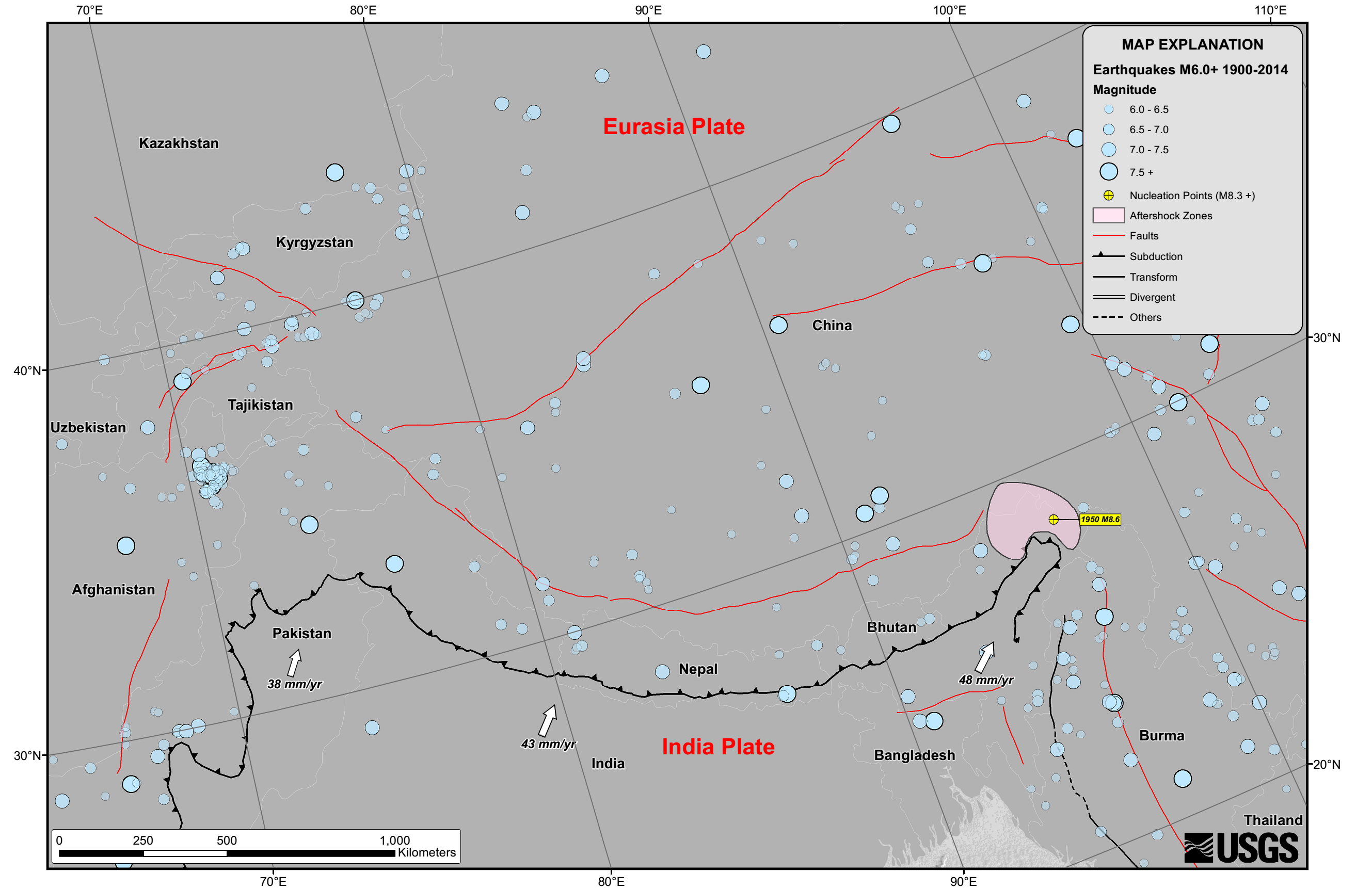 Nepal lies towards the southern limit of the diffuse continental collision">collisional boundary where the
Nepal lies towards the southern limit of the diffuse continental collision">collisional boundary where the
 According to the
According to the
 A series of aftershocks began immediately after the mainshock, at intervals of 15–30 minutes, with one aftershock reaching 6.6Mw within 34 minutes of the initial quake. A major aftershock of magnitude 6.9 Mw occurred on 26 April 2015 in the same region at 12:54 NST (07:08 UTC), with an epicenter located about south of Kodari, Nepal. The aftershock caused fresh avalanches on Mount Everest and was felt in many places in northern India including
A series of aftershocks began immediately after the mainshock, at intervals of 15–30 minutes, with one aftershock reaching 6.6Mw within 34 minutes of the initial quake. A major aftershock of magnitude 6.9 Mw occurred on 26 April 2015 in the same region at 12:54 NST (07:08 UTC), with an epicenter located about south of Kodari, Nepal. The aftershock caused fresh avalanches on Mount Everest and was felt in many places in northern India including
some 30 months later
found only 12% of the reconstruction money had been distributed, and those without land were locked out of financial support, exacerbating the social divide and feeding marginalization.
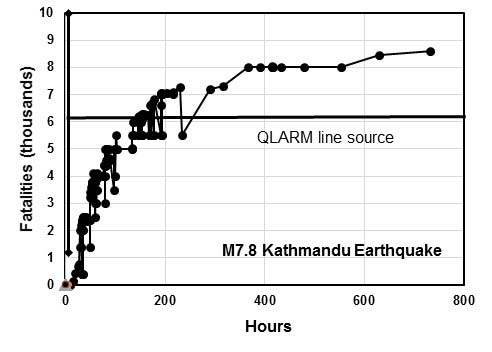 After the rupture area of the Kathmandu 2015 earthquake had been derived and the intensities of shaking had been mapped, a line source model for losses could be constructed with energy being radiated along the entire rupture. The fatalities estimated in this way by QLARM agree with those reported in the end. The figure shows reports of fatalities as a function of time. News reports significantly underestimated the actual numbers of fatalities for several days.
''
After the rupture area of the Kathmandu 2015 earthquake had been derived and the intensities of shaking had been mapped, a line source model for losses could be constructed with energy being radiated along the entire rupture. The fatalities estimated in this way by QLARM agree with those reported in the end. The figure shows reports of fatalities as a function of time. News reports significantly underestimated the actual numbers of fatalities for several days.
''
File:Nepal Earthquake 2015 01.jpg, Building damage as a result of the earthquake
File:Gorkha Earthquake Effect.jpg, Damaged building in Balaju area
 Concern was expressed that harvests could be reduced or lost this season as people affected by the earthquake would have only a short time to plant crops before the onset of the
Concern was expressed that harvests could be reduced or lost this season as people affected by the earthquake would have only a short time to plant crops before the onset of the
epicenter
The epicenter (), epicentre, or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates.
Determination
The primary purpose of a ...
was east of Gorkha District
Gorkha District (), a part of Gandaki Province, is one of seventy-seven districts of Nepal, and the fourth largest district of the country in terms of area. It is historically linked with the creation of modern Nepal and the name of the legenda ...
at Barpak, Gorkha, roughly northwest of central Kathmandu
Kathmandu () is the capital and largest city of Nepal, situated in the central part of the country within the Kathmandu Valley. As per the 2021 Nepal census, it has a population of 845,767 residing in 105,649 households, with approximately 4 mi ...
, and its hypocenter
A hypocenter or hypocentre (), also called ground zero or surface zero, is the point on the Earth's surface directly below a nuclear explosion, meteor air burst, or other mid-air explosion. In seismology, the hypocenter of an earthquake is its ...
was at a depth of approximately . It was the worst natural disaster to strike Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
since the 1934 Nepal–India earthquake. The ground motion recorded in Kathmandu, the capital of Nepal, was of low frequency, which, along with its occurrence at an hour when many people in rural areas were working outdoors, decreased the loss of human lives.
The earthquake triggered an avalanche on Mount Everest, killing 22 people, the deadliest incident on the mountain on record. The earthquake triggered another huge avalanche in the Langtang
Langtang Valley () also known as Lamtang Valley is a Himalayan valley in the mountains of north-central Nepal, known for its trekking routes and natural environment.
Administrative
The Langtang Valley lies in Rasuwa District, Rasuwa dist ...
valley, where 250 people were reported missing.
Hundreds of thousands of Nepalese were made homeless with entire villages flattened across many districts of the country. Centuries-old buildings were destroyed at UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
s in the Kathmandu Valley
The Kathmandu Valley (), also known as the Nepal Valley or Nepa Valley (, Newar language, Nepal Bhasa: 𑐣𑐾𑐥𑐵𑑅 𑐐𑐵𑑅, नेपाः गाः), National Capital Area, is a bowl-shaped valley located in the Himalayas, Hima ...
, including some at the Kathmandu Durbar Square
Kathmandu Durbar Square (Nepal Bhasa: येँ लायकु/𑐥𑐾𑑄 𑐮𑐵𑐫𑐎𑐹, Nepali: हनुमानढोका दरबार; ''Basantapur Durbar Kshetra'') is a historically and culturally significant site in Kathma ...
, the Patan Durbar Square, the Bhaktapur Durbar Square
Bhaktapur Durbar Square (Newar language, Nepal Bhasa: ) is a former royal palace complex located in Bhaktapur, Nepal. It housed the Malla dynasty (Nepal), Malla kings of Nepal from 14th to 15th century and the kings of the Kingdom of Bhaktapur f ...
, the Changu Narayan Temple, the Boudhanath stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
, and the Swayambhunath stupa. Geophysicists and other experts had warned for decades that Nepal was vulnerable to a deadly earthquake, particularly because of its geology, urbanization, and architecture. Dharahara
Dharahara or ''Bhimsen Stambha'' (; or ), is a tower at the centre of Sundhara, Kathmandu, Nepal. It was first built in 1832 by ''Mukhtiyar'' (equivalent to Prime Minister) Bhimsen Thapa under the commission of Queen Lalit Tripurasundari and ...
, also called Bhimsen Tower, a nine-storey tall tower, was destroyed. It was a part of the architecture of Kathmandu recognized by UNESCO.
Continued aftershock
In seismology, an aftershock is a smaller earthquake that follows a larger earthquake, in Epicenter, the same area of the Mainshock, main shock, caused as the displaced Crust (geology), crust adjusts to the effects of the main shock. Large earthq ...
s occurred throughout Nepal at intervals of 15–20 minutes, with one shock reaching a magnitude of 6.7 on 26 April at NST. The country also had a continued risk of landslides.
A major aftershock occurred on 12 May 2015 at with a moment magnitude (Mw) of 7.3. The epicenter was near the Chinese border between the capital of Kathmandu and Mount Everest. More than 200 people were killed and over 2,500 were injured by this aftershock, and many were left homeless.
Earthquake
 The earthquake occurred on 25 April 2015 at NST (06:11:25 UTC) at a depth of approximately (which is considered shallow and therefore more damaging than quakes that originate deeper in the ground), with its
The earthquake occurred on 25 April 2015 at NST (06:11:25 UTC) at a depth of approximately (which is considered shallow and therefore more damaging than quakes that originate deeper in the ground), with its epicentre
The epicenter (), epicentre, or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates.
Determination
The primary purpose of a s ...
approximately southeast of Lamjung
Lamjung District ( ), a part of Gandaki Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Besisahar as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 167,724. lies in the mid-hills of Nepal spa ...
, Nepal, lasting approximately 50 seconds. The earthquake was initially reported as 7.5 by the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ...
(USGS) before it was quickly upgraded to 7.8, while the Global Centroid Moment Tensor (GCMT) reported a magnitude of 7.9. The China Earthquake Networks Center (CENC) reported the earthquake's magnitude to be 8.1 . The India Meteorological Department
India Meteorological Department (IMD) is an Indian agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India. It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology. IMD is headquar ...
(IMD) said two powerful quakes were registered in Nepal at 06:11 UTC and 06:45 UTC. The first quake had its epicenter was identified at a distance of 80 km to the northwest of Kathmandu
Kathmandu () is the capital and largest city of Nepal, situated in the central part of the country within the Kathmandu Valley. As per the 2021 Nepal census, it has a population of 845,767 residing in 105,649 households, with approximately 4 mi ...
, the capital of Nepal. Bharatpur was the nearest major city to the main earthquake, as the crow flies from the epicenter. The second earthquake was somewhat less powerful at 6.6 . It occurred east of Kathmandu and its seismic focus lay at a depth of below the earth's surface. Over 38 aftershocks of magnitude 4.5 or greater occurred in the day following the initial earthquake, including one of 6.8 .
According to the USGS, the earthquake was caused by a sudden thrust, a short sharp thrust that caught many unsuspected and dies to this thrust only, along the major fault line where the Indian plate
The Indian plate (or India plate) is or was a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana an ...
, carrying India, is slowly diving underneath the Eurasian plate, carrying much of Europe and Asia. Kathmandu, situated on a block of crust approximately 120 km (74 miles) wide and 60 km (37 miles) long, rapidly shifted 3 m (10 ft) to the south in a matter of just 30 seconds.
The risk of a large earthquake was well known beforehand. In 2013, in an interview with seismologist Vinod Kumar Gaur, ''The Hindu'' quoted him as saying, "Calculations show that there is sufficient accumulated energy n the Main Frontal Thrust">Main_Frontal_Thrust.html" ;"title="n the Main Frontal Thrust">n the Main Frontal Thrust now to produce an 8-magnitude earthquake. I cannot say when. It may not happen tomorrow, but it could possibly happen sometime this century, or wait longer to produce a much larger one." According to Brian Tucker, founder of a nonprofit organization devoted to reducing casualties from natural disasters, some government officials had expressed confidence that such an earthquake would not occur again. Tucker recounted a conversation he had with a government official in the 1990s who said, "We don't have to worry about earthquakes anymore, because we already had an earthquake." The previous earthquake to which he referred occurred in 1934. In fact, the 600-km-long Central Himalayan Gap hadn't ruptured 1505 Lo Mustang earthquake">since 1505.
Geology
 Nepal lies towards the southern limit of the diffuse continental collision">collisional boundary where the
Nepal lies towards the southern limit of the diffuse continental collision">collisional boundary where the Indian plate
The Indian plate (or India plate) is or was a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana an ...
underthrusts the Eurasian plate, occupying the central sector of the Himalayan arc, nearly one-third of the long Himalayas. Geologically, the Nepal Himalayas are subdivided into five tectonic zones from north to south, east to west, and almost parallel to sub-parallel. These five distinct morpho-geotectonic zones are: (1) Terai Plain; (2) Sub Himalaya (Siwalik Hills, Shivalik Range); (3) Lesser Himalaya (Mahabharat Range and mid valleys); (4) Higher Himalaya; and (5) Inner Himalaya (Tibetan Tethys). Each of these zones is clearly identified by its morphological, geological, and tectonic features.
The convergence rate between the plates in central Nepal is about per year. The location, magnitude, and focal mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the Fault (geology)#Slip.2C heave.2C throw, deformation in the Hypocenter, source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a Fault (geology), fault-related event, it refers to the ori ...
of the earthquake suggest that it was caused by a slip along the Main Frontal Thrust.
The earthquake's effects were amplified in Kathmandu as it sits on the Kathmandu Basin, which contains up to of sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s, representing the infilling of a lake.
Based on a study published in 2014, of the Main Frontal Thrust, on average a great earthquake occurs every 750 ± 140 and 870 ± 350 years in the east Nepal region. A study from 2015 found a 700-year delay between earthquakes in the region. The study also suggests that because of tectonic stress buildup, the 1934 earthquake and the 2015 quake are connected, following a historic earthquake pattern. A 2016 study on historical great (M ≥ 8) earthquake pairs and cycles found that associated great earthquakes are likely to occur in the West China region through the 2020s.
Intensity
 According to the
According to the USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an government agency, agency of the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geograp ...
website, the maximum intensity was VIII (''Severe''), however certain reports state an intensity of X (''Extreme'') or higher. In most of Kathmandu the intensity was VIII-IX, as evidenced by the numerous undamaged water towers installed on top of undamaged multi story buildings. Tremors were felt in the neighboring Indian states of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
, Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
, Odisha
Odisha (), formerly Orissa (List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2011), is a States and union territories of India, state located in East India, Eastern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by ar ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the ...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in East India, eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north ...
, Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand (, ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2007), is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the n ...
, Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
, in the National Capital Region around New Delhi
New Delhi (; ) is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the Government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Parliament ...
and as far south as Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
. Damage was extensive in northern Bihar and minor damage was also reported from parts of Odisha. Shaking was felt in high-rise buildings as far as Kochi
Kochi ( , ), List of renamed Indian cities and states#Kerala, formerly known as Cochin ( ), is a major port city along the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea. It is part of the Ernakulam district, district of Ernakulam in the ...
in the southern state of Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
. The intensity in Patna
Patna (; , ISO 15919, ISO: ''Paṭanā''), historically known as Pataliputra, Pāṭaliputra, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, ...
was V (''Moderate''). The intensity was IV (''Light'') in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Dhaka ( or ; , ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital city, capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh. It is one of the list of largest cities, largest and list o ...
. The earthquake was also experienced across southwest China
Southwestern China () is a region in the People's Republic of China. It consists of five provincial administrative regions, namely Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Xizang.
Geography
Southwestern China is a rugged and mountainous region, ...
, ranging from the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the ...
to Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
, which is away from the epicenter. Tremors were felt in Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
.
Aftershocks
Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
, Siliguri
Siliguri (, ; ), also known as Shiliguri, is a major Tier ii cities in india, tier-II city in West Bengal. It forms the twin cities, Twin Cities with the neighbouring city of Jalpaiguri. The city spans areas of the Darjeeling district, Darjeel ...
, Jalpaiguri, and Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
. The aftershock caused a landslide on the Koshi Highway
Koshi Highway or NH08 (previously: H08) () is a 390 km long highway located in Koshi Province. It is a north-south highway which is understood to be the shortest highway connecting India to China across the Himalayan mountains in Nepal. Ran ...
, which blocked the section of the road between Bhedetar and Mulghat.
A model of GeoGateway, based on a United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ...
mechanism of a near-horizontal fault as well as the location of aftershocks showed that the fault had an 11° dip towards the north, striking at 295°, was wide, long, and had a dip slip of . The USGS says the aftershock registered at a shallow depth of .
As of 24 May 2016, 459 aftershocks had occurred with different epicenters and magnitudes equal to or above 4 Mw (out of which 51 aftershocks are equal to or above 5 Mw and 5 aftershocks above 6 Mw) and more than 20,000 aftershocks less than 4 Mw.
12 May 2015 earthquake
A second major earthquake occurred on 12 May 2015 at 12:50 NST with a moment magnitude (Mw) of 7.3Mw 18 km (11 mi) southeast of Kodari. The epicenter was near the Chinese border between the capital city ofKathmandu
Kathmandu () is the capital and largest city of Nepal, situated in the central part of the country within the Kathmandu Valley. As per the 2021 Nepal census, it has a population of 845,767 residing in 105,649 households, with approximately 4 mi ...
and Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
. It struck at a depth of 18.5 km (11.5 miles). This earthquake occurred along the same fault as the original magnitude 7.8 earthquake of 25 April but further to the east. As such, it is considered an aftershock
In seismology, an aftershock is a smaller earthquake that follows a larger earthquake, in Epicenter, the same area of the Mainshock, main shock, caused as the displaced Crust (geology), crust adjusts to the effects of the main shock. Large earthq ...
of the 25 April quake. Tremors were also felt in northern parts of India including Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
and other North-Indian States. At least 153 people died in Nepal as a result of the aftershock and about 2,500 were injured. 62 others died in India, two in Bangladesh, and one in China.
Aftermath
Disastrous events in very poor and politically paralyzed nations such as Nepal often become a long drawn out chain of events, in that one disaster feeds into another for years or even decades on end. The aftereffects of the earthquake had subsequent effects on a myriad of things:human trafficking
Human trafficking is the act of recruiting, transporting, transferring, harboring, or receiving individuals through force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of exploitation. This exploitation may include forced labor, sexual slavery, or oth ...
, labour cost and availability, rental and property cost burdens, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, private and public debt burdens, mental health, politics, tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ...
, disease, and damage to the healthcare system. A survesome 30 months later
found only 12% of the reconstruction money had been distributed, and those without land were locked out of financial support, exacerbating the social divide and feeding marginalization.
More direct effects
Some disasters that came with the monsoon season were suspected to be related to the earthquake. There was a landslip on 11 June, killing 53 people. Meanwhile, a glacial lake had burst in the particularly hard-hit Solukhumbhu district. Whether or not the quake contributed to such events is often unknown and unresearched, but it is certainly possible.Casualties
Nepal
The earthquake killed at least 8,857 people in Nepal and injured nearly three times as many. The rural death toll may have been minimized by the fact that most villagers were outdoors working when the quake hit. As of 15 May, 6,271 people, including 1,700 from the 12 May aftershock, were still receiving treatment for their injuries. Nearly 3.5 million people were left homeless, causing around 2.6 million internal displacements. The example of this earthquake shows that loss calculations for hypothetical likely future earthquakes can be reasonably reliable. In 2005, the expected numbers of fatalities due to a hypothetical scenario earthquake near Kathmandu for M8.1 was published. The fatalities at that time were estimated between 21,000 and 42,000. The M7.8 earthquake of 25 April 2015 killed about 8,800 people because it occurred on a Saturday and so many buildings that collapsed, such as schools and municipal buildings, were empty, reducing the death toll. In addition, the epicentre of the earthquake was in a rural setting, so the worst hit districts had low population densities and most of the population was outside when the earthquake hit. Had the earthquake occurred at night or during the working week, when many more people were inside vulnerable buildings, the death toll would have likely been much closer to the modelled estimate. After the rupture area of the Kathmandu 2015 earthquake had been derived and the intensities of shaking had been mapped, a line source model for losses could be constructed with energy being radiated along the entire rupture. The fatalities estimated in this way by QLARM agree with those reported in the end. The figure shows reports of fatalities as a function of time. News reports significantly underestimated the actual numbers of fatalities for several days.
''
After the rupture area of the Kathmandu 2015 earthquake had been derived and the intensities of shaking had been mapped, a line source model for losses could be constructed with energy being radiated along the entire rupture. The fatalities estimated in this way by QLARM agree with those reported in the end. The figure shows reports of fatalities as a function of time. News reports significantly underestimated the actual numbers of fatalities for several days.
''The Himalayan Times
''The Himalayan Times'' is an English-language broadsheet newspaper published and distributed daily in Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the ...
'' reported that as many as 20,000 foreign nationals may have been visiting Nepal at the time of the earthquake, although reports of foreign deaths were relatively low.
India
A total of 78 deaths were reported in India – including 58 in Bihar, 16 in Uttar Pradesh, 3 in West Bengal and 1 in Rajasthan.China
Twenty-seven people were confirmed dead, 383 were injured and 4 were missing, all from theTibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), often shortened to Tibet in English or Xizang in Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China. It was established in 1965 to replace the ...
.
The quake destroyed 2,500 houses and damaged 24,700 others across 19 counties in Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
, affecting nearly 300,000 people, among whom 47,500 were displaced, while A total of 82 temples were also damaged. The counties of Gyirong, Nyalam and Tingri in Xigazê were worst hit, where nearly 80 percent of the houses in the three counties collapsed.
Bangladesh
Four people were killed and 18 districts were affected by the earthquake in Bangladesh. A six-story building partially collapsed and two garment factories tilted inDhaka
Dhaka ( or ; , ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital city, capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh. It is one of the list of largest cities, largest and list o ...
. A 22-year-old man died when trying to flee the Dhaka Medical College in a panic. In Tangail
Tangail (, ) is a city of Tangail District in central Bangladesh. A significant city in Bangladesh, Tangail lies on the bank of the Louhajang River, northwest of Dhaka, the nation's capital.
Etymology
''Tangail'' originates from the Beng ...
, a woman died trying to escape a building. Another woman was crushed to death by a collapsed wall while a teacher died of a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
during the earthquake.
Avalanches on Mount Everest
This earthquake causedavalanche
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a Grade (slope), slope, such as a hill or mountain. Avalanches can be triggered spontaneously, by factors such as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, othe ...
s on Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
. At least 19 died, with at least 120 others injured or missing.
Landslides in the Langtang Valley
In the Langtang valley located in Langtang National Park, 329 people were reported missing after an avalanche hit the village of Ghodatabela and the village of Langtang. The avalanche was estimated to have been two to three kilometres wide. Ghodatabela was an area popular on the Langtang trekking route. The village of Langtang was destroyed by the avalanche. Smaller settlements on the outskirts of Langtang were buried during the earthquake, such as Chyamki, Thangsyap, and Mundu. Twelve locals and two foreigners were believed to have survived. Smallerlandslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides ...
s occurred in the Trishuli River Valley with reports of significant damage at Mailung, Simle, and Archale. On 4 May it was announced that 52 bodies had been found in the Langtang area, of which seven were of foreigners.
According to geological models, the frequency and intensity of future landslides in the Langtang Valley is due to increase in the coming decades. This is attributable directly to the effect of the earthquake, which caused widespread fracturing in the grounds of the Langtang area.
Damage
Thousands of houses were destroyed across many districts of the country, with entire villages flattened, especially those near the epicenter. TheTribhuvan International Airport
Tribhuvan International Airport (, , colloquially referred to as TIA) is an international airport located in Kathmandu, Bagmati, Nepal. It has a tabletop runway, a domestic terminal and an international terminal. As the country's main internat ...
serving Kathmandu was closed immediately after the earthquake, but was re-opened later in the day for relief operations and, later, for some commercial flights. It subsequently shut down operations sporadically due to aftershocks, and on 3 May was closed temporarily to the largest planes for fear of runway damage. During strong aftershocks, the airport opened all boarding-lounge exit doors onto the tarmac, allowing people who were waiting post security and immigration to flee to the open spaces of the runway tarmac. Many remained outside as planes were delayed and the airport swelled to capacity. The airport facilities suffered damage and there was no running water or operating toilets in the airport lounges. Few airport workers were at their posts; most were killed in the earthquake or had to deal with its aftereffects.
Flights resumed from Pokhara, to the west of the epicentre, on 27 April.
Several of the churches in the Kathmandu valley were destroyed. As Saturday is the principal day of Christian worship in Nepal, 500 people were reported to have died in the collapses.
Several temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
s on Kathmandu Durbar Square
Kathmandu Durbar Square (Nepal Bhasa: येँ लायकु/𑐥𑐾𑑄 𑐮𑐵𑐫𑐎𑐹, Nepali: हनुमानढोका दरबार; ''Basantapur Durbar Kshetra'') is a historically and culturally significant site in Kathma ...
, a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
, collapsed, as did the Dharahara
Dharahara or ''Bhimsen Stambha'' (; or ), is a tower at the centre of Sundhara, Kathmandu, Nepal. It was first built in 1832 by ''Mukhtiyar'' (equivalent to Prime Minister) Bhimsen Thapa under the commission of Queen Lalit Tripurasundari and ...
tower, built in 1832; the collapse of the latter structure killed at least 180 people, Manakamana Temple in Gorkha, previously damaged in an earlier quake, tilted several inches further. The northern side of Janaki Mandir in Janakpur
Janakpurdham or Janakpur (), is the capital city of Madhesh Province. This sub-metropolitan city is a central hub for the Maithili language, as well as for religious and cultural tourism in Nepal.
The city was founded in the early 18th centur ...
was reported to have been damaged. Several temples, including Kasthamandap, Panchtale temple, the top levels of the nine-story Basantapur Durbar, the Dasa Avtar temple and two shrines located behind the Shiva Parvati temple were demolished by the quake. Some other monuments including the Taleju Bhawani Temple partially collapsed.
The top of the Jaya Bageshwari Temple in Gaushala and some parts of the Pashupatinath Temple
Shri Pashupatinātha Temple () is a revered Hindu temple dedicated to Pashupati, a manifestation of the god Śiva. Located on the banks of the sacred Bagmati River in Kathmandu, Nepal, the temple is one of the oldest and most significant religiou ...
, Swyambhunath, Boudhanath Stupa, Ratna Mandir, inside Rani Pokhari, and Durbar High School have been destroyed.
In Patan, the Char Narayan Mandir, the statue of Yog Narendra Malla, a pati inside Patan Durbar Square, the Taleju Temple, the Hari Shankar, Uma Maheshwar Temple and the Machhindranath Temple in Bungamati were destroyed. In Tripureshwar, the Kal Mochan Ghat, a temple inspired by Mughal architecture, was completely destroyed and the nearby Tripura Sundari also suffered significant damage. In Bhaktapur, several monuments, including the Phasi Deva temple, the Chardham temple and the 17th century Vatsala Durga Temple were fully or partially destroyed.
Outside the Valley, the Manakamana Temple in Gorkha, the Gorkha Durbar, the Palanchok Bhagwati, in Kabhrepalanchok District, the Rani Mahal in Palpa District
Palpa District (, a part of Lumbini Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, a landlocked country of South Asia. The district, with Tansen as its headquarters, covers an area of and has a population (2021) of 245,027.
Palpa ...
, the Churiyamai in Makwanpur District
Makwanpur District (; ), in Bagmati Province, earlier a part of Narayani Zone, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The city of Hetauda serves as the district headquarters and also as the provincial headquarters. The district covers a ...
, the Dolakha Bhimsensthan in Dolakha District
Dolakha, often known as Dolkha or Dholkha (Nepal Bhasa:दोलखा जिल्ला)), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Charikot as its district headqu ...
, and the Nuwakot Durbar suffered varying degrees of damage. Historian Prushottam Lochan Shrestha stated, "We have lost most of the monuments that had been designated as World Heritage Sites in Kathmandu
Kathmandu () is the capital and largest city of Nepal, situated in the central part of the country within the Kathmandu Valley. As per the 2021 Nepal census, it has a population of 845,767 residing in 105,649 households, with approximately 4 mi ...
, Bhaktapur
Bhaktapur (Nepali language, Nepali and Sanskrit: भक्तपुर, ; "City of Devotees"), known locally as Khwopa (Nepal Bhasa: , ) and historically called Bhadgaon, is a city in the east corner of the Kathmandu Valley in Nepal located abou ...
and Lalitpur District, Nepal
Lalitpur District (, in Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Lalitpur, Nepal, Lalitpur as its district headquarters, covers an area of and has a population (2001) of 337, ...
. They cannot be restored to their original states." The northeastern parts of India also received major damage. Heavy shocks were felt in the states of Uttrakhand, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal and others. Huge damage was caused to the property and the lives of the people.
Economic loss
 Concern was expressed that harvests could be reduced or lost this season as people affected by the earthquake would have only a short time to plant crops before the onset of the
Concern was expressed that harvests could be reduced or lost this season as people affected by the earthquake would have only a short time to plant crops before the onset of the Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
rains.
Nepal, with a total Gross Domestic Product of US$19.921 billion (according to a 2012 estimate), is one of Asia's poorest countries, and has little ability to fund a major reconstruction effort on its own. Even before the quake, the Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank is headquartered in Metro Manila, Philippines and maintains 31 field offices around the world.
The bank was establishe ...
estimated that it would need to spend about four times more than it currently does annually on infrastructure through to 2020 to attract investment. The U.S. Geological Survey initially estimated economic losses from the tremor at 9 per cent to 50 per cent of gross domestic product, with a best guess of 35 per cent. "It's too hard for now to tell the extent of the damage and the effect on Nepal's GDP", according to Hun Kim, an Asian Development Bank (ADB) official. The ADB said on the 28th that it would provide a US$3 million grant to Nepal for immediate relief efforts, and up to US$200 million for the first phase of rehabilitation.
Rajiv Biswas, an economist at a Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
-based consultancy, said that rebuilding the economy will need international effort over the next few years as it could "easily exceed" US$5 billion.
More recent studies estimate the damage from the earthquake to be closer to US$10 billion (which would be around 50% of Nepals GDP at the time).
Social effects
It was reported that the survivors were preyed upon by human traffickers involved in the supply of girls and women to the brothels of South Asia. These traffickers took advantage of the chaos that resulted from the aftermath of the earthquake. The most affected were women from poor communities who lost their homes. In response to the unsafe conditions of the temporary campsites, international organizations implemented Safety Committees which were provided cash grants for necessities like additional toilets and bathrooms.Most affected
Single women had very little access to relief, according to a report by the Inter-party Women's Alliance (IPWA). The report also found that violence and rapes against women and minors have increased after the earthquake. Additionally, the earthquake has significantly affected certain groups of people. Tibeto-Burman peoples were hardest hit as they tend to inhabit the higher slopes of mountains as opposed to the central valleys and are less educated and connected. All of these factors make them harder to access. According to a government survey, malnutrition in children has worsened considerably some 3 months after the quake, with the most undernourished being Tamang and Chepang peoples.http://www.ekantipur.com/2015/07/30/national/malnutrition-stalks-quake-hit-kids/408642.html The Kathmandu Post: Malnutrition stalks quake-hit kids Before the quake, 41 percent of children under five were stunted, 29 percent were underweight and 11 percent were emaciated, according to the World Food Programme.Disease
Though a feared mass cholera outbreak failed to materialize (there were sporadic reports), other outbreaks were reported. At least 13 people died ofscrub typhus
Scrub typhus or bush typhus is a form of typhus caused by the intracellular parasite '' Orientia tsutsugamushi'', a Gram-negative α-proteobacterium of family Rickettsiaceae first isolated and identified in 1930 in Japan.Edmond Fernandes and Prakash Narayan stated that elderly care in disaster was more important than women and child focused one for Nepal earthquake and absence of military support for medical aid providers impacted relief work.
Rescue and relief
About 90% of soldiers from theNepalese Army
The Nepali Army (), also referred to as the Gorkhali Army (; see ''Gurkha, Gorkhas''), formally known as "Royal Nepal Army" is the Ground warfare, land Military branch, service branch of the Nepalese Armed Forces, Nepali Armed Forces. After t ...
were sent to the stricken areas in the aftermath of the earthquake under Operation Sankat Mochan
Operation Sankat Mochan ( Nepali: संकट मोचन, Operation Crisis Relief) is a Nepal Army earthquake relief operation following the April 2015 Nepal earthquake; the Nepal Army has deployed 90 percent of its force.
As of 1 May international aid agencies like
USGS Earthquake Hazards Program
on USGS Website
National Seismological Center
Nepali National Seismological Centre
Tectonics & Earthquakes of Himalaya and the 2015 Earthquake in Nepal
–
The 25 April 2015, Gorkha, Nepal, Earthquake: An Expected Event that Defied Expectations
– United States Geological Survey * *
Nepal Earthquake Open Data Portal
() by National Planning Commission has
SOAS Digital Collections
{{Himalayan earthquakes Nepal,04 Nepal earthquake 2010s in Tibet 2015 in China Nepal earthquake Nepal earthquake Nepal earthquake Nepal earthquake Earthquakes in Bangladesh 2015, 04 Earthquakes in India Earthquakes in Tibet Natural disasters in Bihar Nepal earthquake Buried rupture earthquakes
Médecins Sans Frontières
(MSF; pronounced ), known in some English-speaking settings as Doctors Without Borders, is a charity that provides humanitarian medical care. It is a non-governmental organisation (NGO) of French origin known for its projects in conflict zo ...
and the Red Cross
The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 16million volunteering, volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ...
were able to start medically evacuating the critically wounded by helicopter from outlying areas, initially cut-off from the capital city, Kathmandu, and treating others in mobile and makeshift facilities. There was concern about epidemics due to the shortage of clean water, the makeshift nature of living conditions and the lack of toilets.
Emergency workers were able to identify four men who had been trapped in rubble, and rescue them, using advanced heartbeat detection. The four men were trapped in up to ten feet of rubble in the village of Chautara, north of Kathmandu. An international team of rescuers from several countries using FINDER devices found two sets of men under two different collapsed buildings.
Volunteers used crisis mapping
Crisis mapping (also known as disaster mapping) is the real-time gathering, display and analysis of data during a crisis, usually a natural disaster or social/political conflict (violence, elections, etc.). Crisis mapping projects usually allow ...
to help plan emergency aid work. Local organization Kathmandu Living Labs helped coordinate local knowledge on the ground and collaborated with international crisis mapping and humanitarian organizations. Public volunteers from around the world participated in crowdmapping and added details into online maps. Information was mapped from data input from social media, satellite pictures and drones of passable roads, collapsed houses, stranded, shelterless and starving people, who needed help, and from messages and contact details of people willing to help. On-site volunteers verified these mapping details wherever they could to reduce errors. The technologies used by Kathmandu Living Labs were built on top of existing open source solutions which allowed them to work in a fast and cost effective manner.
Digital mappers, through the Kathmandu Living Labs, were already charting the densely populated Kathmandu Valley, and then focused on earthquake relief. "They were doing an inventory in the poorer communities where they didn't have a very good sense of the quality of buildings," says Cowan, whose students helped add Kathmandu's buildings and roads to OpenStreetMap. First responders, from Nepalese citizens to the Red Cross, the Nepal army and the United Nations used this data. The Nepal earthquake crisis mapping utilized experience gained and lessons learned about planning emergency aid work from earthquakes in Haiti and Indonesia.
India pledged to donate $1 billion in cash and materials to Nepal. India's External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj said "I am happy to announce Government of India's pledge for Nepal's post-earthquake reconstruction of Nepali Rupees 10,000 crores, equivalent to one billion US dollars, one fourth of it as Grant." The International Conference on Nepal's Reconstruction has been organised by the Nepalese government to raise funds for rebuilding the country.
Reports are also coming in of sub-standard relief materials and inedible food being sent to Nepal by many of the foreign aid agencies.
A United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionar ...
helicopter crashed on 12 May while involved in delivering relief supplies. The Bell UH-1Y Venom
The Bell UH-1Y Venom (also called Super Huey) is a twin-engine, 4-blade, medium-sized utility helicopter built by Bell Helicopter under the H-1 upgrade program of the United States Marine Corps. One of the latest members of the numerous Bell H ...
crashed at Charikot, roughly 45 miles (72 kilometres) east of Kathmandu. Two Nepalese soldiers and six American Marines died in the crash.
Need-fulfillment application, Getmii, launched a special pilot version in partnership with the Red Cross to double daily blood donors at the Kathmandu donation center using the app.
Imaging technologies such as satellites and smartphones, were instrumental to relief efforts in Nepal. GLIMS, group of volunteer scientists from nine nations, were able to provide rapid, systematic mapping of the damaged area, allowing the investigation of earthquake-induced geo-hazard processes that provided information to relief and recovery officials on the same timeframe as those operations were occurring.
Charities and Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project or venture by raising money from a large number of people, typically via the internet. Crowdfunding is a form of crowdsourcing and Alternative Finance, alternative finance, to fund projects "withou ...
platforms received over $230 million in donations from support groups. The money was used to provide medical supplies, for reconstruction of damaged buildings including schools and hospitals, and building orphanages for the victims among other things.
Repair and reconstruction
Monuments
UNESCO and the Ministry of Culture began strengthening damaged monuments in danger of collapsing before the monsoon season. Subsequent restoration of collapsed structures, including historic houses is planned. Architectural drawings exist that provide plans for reconstruction. According to UNESCO, more than 30 monuments in the Kathmandu Valley collapsed in the quakes, and another 120 incurred partial damage. Repair estimates are $160 million to restore 1,000 damaged and destroyed monasteries, temples, historic houses, and shrines across the country. The destruction is concentrated in the Kathmandu Valley. UNESCO designated seven groups of multi-ethnic monuments clustered in the valley as a single World Heritage Site, includingSwayambhu
Svayambhu () is a Sanskrit word that means "self-born", "self-manifested", "self-existing", or "that that is created by its own accord". Various deities and entities featured in Hindu literature and tradition are regarded to be svayambhu, such as ...
, the three squares namely Durbar square of Kathmandu, Patan Durbar Square, and Bhaktapur Durbar Square
Bhaktapur Durbar Square (Newar language, Nepal Bhasa: ) is a former royal palace complex located in Bhaktapur, Nepal. It housed the Malla dynasty (Nepal), Malla kings of Nepal from 14th to 15th century and the kings of the Kingdom of Bhaktapur f ...
, and the Hindu temples of Pashupatinath and Changu Narayan. Out of them only three were damaged in the quakes—three Durbar squares, the temple of Changu Narayan, and the 1655 temple in Sankhu. Drones fly above cultural heritage sites to provide 3D images of the damage to use for planning repairs.
Nepal Rural Housing Reconstruction Program
After an international donors conference held in Kathmandu on 25 June 2015 a multi donor trust fund of US$4.4 billion was established to aid the reconstruction of affected housing in 14 districts of Nepal. This covered 66 per cent of the country's total recovery and reconstruction needs of US$6.7 billion. Implementation of the Program consisted of five phases i.e. Survey, Identification and Validation, Enrollment, Reconstruction and Completion. The data collection for the program was done digitally using tablets and resulted in collection of over 10 TB of data. The data was openly released to the public by the National Planning Commission and is available for download on their website.International aid
A total of $3bn was pledged by donors to help rebuild Nepal.UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
said close to 1.7 million children had been driven out into the open, and were in desperate need of drinking water, psychological counsel, temporary shelters, sanitation and protection from disease outbreak. It distributed water, tents, hygiene kits, water purification tablets and buckets. Numerous other organizations provided similar support.
India was the first to respond within hours, being Nepal's immediate neighbour, with Operation Maitri
Operation Maitri (Operation Amity) was a rescue and relief operation in Nepal by the government of India and Indian Armed Forces, Indian armed forces in the aftermath of the April 2015 Nepal earthquake. Indian government responded within few mi ...
which provided rescue and relief by its armed forces. It also evacuated its own and other countries' stranded nationals. India has been the largest aid donor to Nepal following the earthquake with a billion dollar support apart from other non-monetary reliefs extended. China, the Asian Development Bank and the United Kingdom provided significant bilateral aid and other nations and organisations provided aid, rescue teams and helicopters as requested by the Nepalese government.
On 26 April 2015, international aid agencies and governments mobilized rescue workers and aid for the earthquake. They faced challenges in both getting assistance to Nepal and ferrying people to remote areas as the country had few helicopters. Relief efforts were also hampered by Nepalese government insistence on routing aid through the Prime Minister's Disaster Relief Fund and its National Emergency Operation Center. After concerns were raised, it was clarified that "Non-profits" or NGOs already in the country could continue receiving aid directly and bypass the official fund. Aid mismatch and supply of "leftovers" by donors, aid diversion in Nepal, mistrust over control of the distribution of funds and supplies, congestion and customs delays at Kathmandu's airport and border check posts were also reported. On 3 May 2015, restrictions were placed on heavy aircraft flying in aid supplies after new cracks were noticed on the runway at the Tribhuvan International Airport
Tribhuvan International Airport (, , colloquially referred to as TIA) is an international airport located in Kathmandu, Bagmati, Nepal. It has a tabletop runway, a domestic terminal and an international terminal. As the country's main internat ...
, Nepal's only airport able to handle larger jet aircraft.
The list below gives a break-up of pledged donations, by each nation, along with aid in kind, delivered immediately.
See also
*Economy of Nepal
The economy of Nepal is a developing category and is largely dependent on agriculture and remittances. Until the mid-20th century Nepal was an isolated pre-industrial society, which entered the modern era in 1951 without schools, hospitals, ...
* Foreign aid to Nepal
* Geology of the Himalaya
* List of avalanches
* List of earthquakes in 2015
* List of earthquakes in China
This is a list of earthquakes in China, part of the series of list of disasters in China by death toll, lists of disasters in China. Earthquakes in the loess plateau where residents lived in yaodong caves tended to have big casualties, includin ...
* List of earthquakes in India
* List of earthquakes in Nepal
Lying in one of the most seismically active regions of the world, Nepal has a long history of earthquakes. The first documented earthquake event in the country dates back to 7 June 1255, during the reign of King Abhaya Malla. The quake, measuring 7 ...
* List of earthquakes in South Asia
* List of people who died climbing Mount Everest
* List of World Heritage Sites in Nepal
* Operation Sahayogi Haat
* Politics of Nepal
References
External links
* on Earthquake Report WebsiteUSGS Earthquake Hazards Program
on USGS Website
National Seismological Center
Nepali National Seismological Centre
Tectonics & Earthquakes of Himalaya and the 2015 Earthquake in Nepal
–
IRIS Consortium
IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology) was a university research consortium dedicated to exploring the Earth's interior through the collection and distribution of seismographic data. It operated the U.S. National Science Foundati ...
The 25 April 2015, Gorkha, Nepal, Earthquake: An Expected Event that Defied Expectations
– United States Geological Survey * *
Nepal Earthquake Open Data Portal
() by National Planning Commission has
structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
and socioeconomic
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
data of over 1 million household
A household consists of one or more persons who live in the same dwelling. It may be of a single family or another type of person group. The household is the basic unit of analysis in many social, microeconomic and government models, and is im ...
and 762 thousand building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, a ...
s of districts most severely effected by the earthquake.
* A number of digital resources relating to the earthquake and the aftermath are hosted bSOAS Digital Collections
{{Himalayan earthquakes Nepal,04 Nepal earthquake 2010s in Tibet 2015 in China Nepal earthquake Nepal earthquake Nepal earthquake Nepal earthquake Earthquakes in Bangladesh 2015, 04 Earthquakes in India Earthquakes in Tibet Natural disasters in Bihar Nepal earthquake Buried rupture earthquakes