2-8-8-0 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the
In the

 Indonesia was also recorded operating several types of 2-8-8-0 locomotives. This dates back to the colonial era, under the government of
Indonesia was also recorded operating several types of 2-8-8-0 locomotives. This dates back to the colonial era, under the government of  They were nicknamed ''Si Gombar'' or The Monster by locals along with
They were nicknamed ''Si Gombar'' or The Monster by locals along with
 In the
In the Whyte notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twenti ...
for the classification of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s by wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
, a 2-8-8-0 is a locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s, and no trailing truck
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
.
Equivalent classifications
Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Cr ...
: 1DD (also known as German classification and Italian classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Cr ...
)
*French classification Under the French classification system for locomotive wheel arrangements, the system is slightly different for steam and electric/diesel vehicles.
Steam
The French system counts axles, rather than wheels. As with Whyte notation, a conventional r ...
: 140+040
*Turkish classification
In the Turkish classification system for railway locomotives, the number of powered axles are followed by the total number of axles. It is identical to the Swiss system except that the latter places a slash between the two numbers.
Thus
0-6-0 bec ...
: 45+44
*Swiss classification
For more than a century, the Swiss locomotive, multiple unit, motor coach and railcar classification system, in either its original or updated forms, has been used to name and classify the rolling stock operated on the railways of Switzerland. ...
: 4/5+4/4
The UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Cr ...
is refined to (1'D)D for Mallet locomotives.
Usage
United States
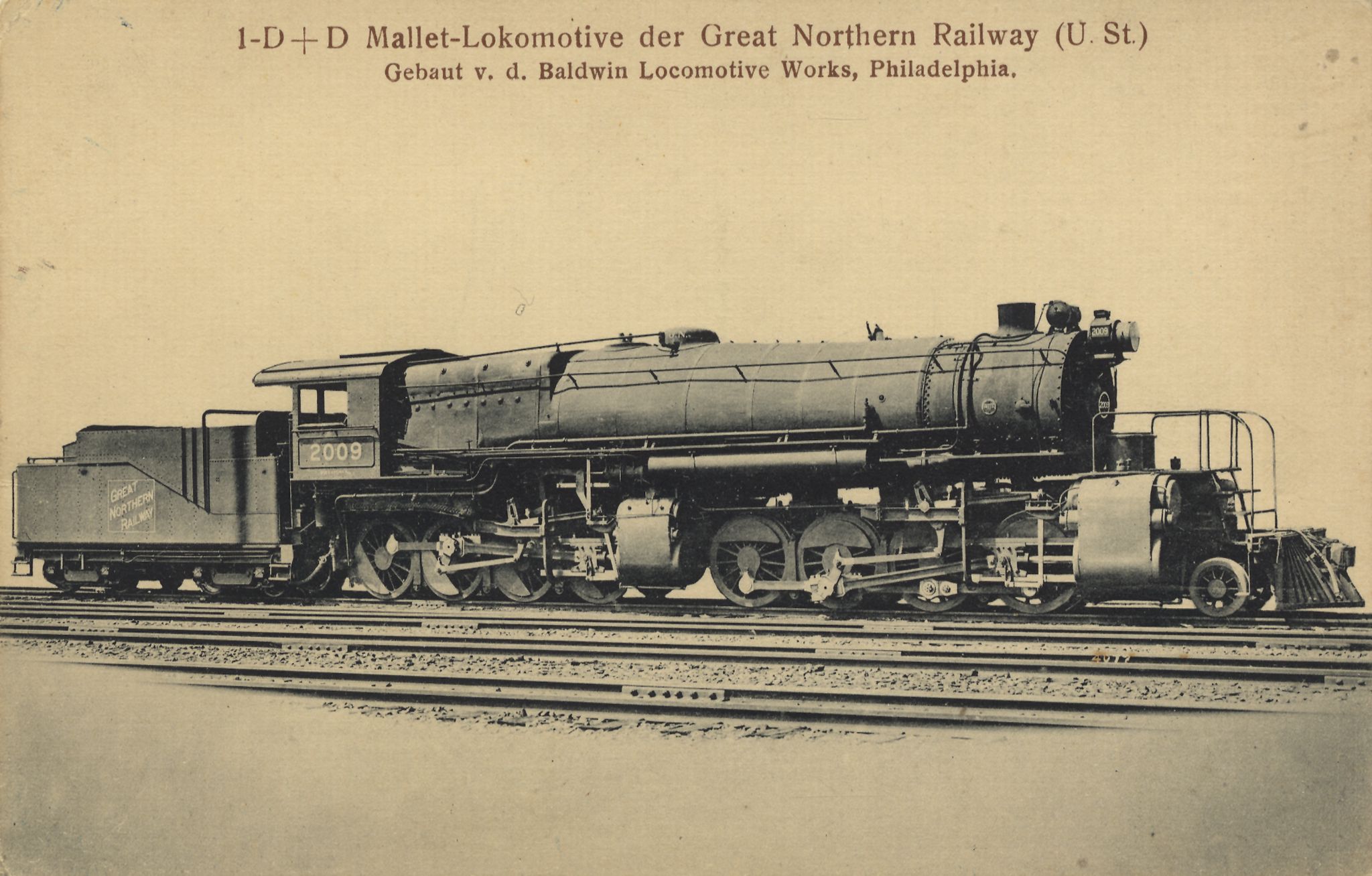
The Great Northern Railway used the 2-8-8-0s as their N-1's which were built by Baldwin in 1912. They were rebuilt by GN in 1932 as a N-2, and later re-rebuilt in 1940 as an N-3, The locomotives, after their third rebuild into a N-3, had a larger boiler and bigger tender. The N-3's served on the GN for a collective 45 years (including previous service lives as N-1 and N-2 classes), in use until retired in 1957. TheUnion Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad is a Railroad classes, Class I freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United Stat ...
also operated this type. The Union Pacific 2-8-8-0s were built in 1918 and 1924 by ALCO-Brooks. The locomotives were used to haul heavy loads over Sherman Hill on the UP. An example of one is Union Pacific #3559, which was built July 1924 by ALCO-Brooks. The locomotives were most likely retired in the late 1940s to early 1950s because of slow speeds on freight, hauling at 12 miles an hour. In comparison, the 9000 class of the Union Pacific can pull the same weight at 50 miles an hour.
Out east, the Reading Railroad
The Reading Company ( ) was a Philadelphia-headquartered railroad that provided passenger and freight transport in eastern Pennsylvania and neighboring states from 1924 until its acquisition by Conrail in 1976.
Commonly called the Reading Railr ...
had 2-8-8-0s for coal switching on steep hills, also known as the Reading N-1, and the Baltimore and Ohio
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the oldest railroad in the United States and the first steam-operated common carrier. Construction of the line began in 1828, and it operated as B&O from 1830 until 1987, when it was merged into the Chessi ...
operated this type, with the B&O owning dozens of examples, most notably the EL-3 class. They were retired by the early 1950s. In the Midwest, the Kansas City Southern was a principal user of this configuration.
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at vario ...
was the first to use the configuration. In 1911, their own workshop took a pair of standard 2-8-0 and combined them into a 2-8-8-0 Mallet
A mallet is a tool used for imparting force on another object, often made of rubber or sometimes wood, that is smaller than a maul or beetle, and usually has a relatively large head.
General overview
The term is descriptive of the ...
articulated locomotive. Four examples were built, but were never entirely satisfactory and were converted back to 2-8-0 in 1923.
The first 2-8-8-0 operated by Baltimore and Ohio was numbered EL-1/a, which was built in 1916 at Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
. The western end of their network had ruling gradient
In railroading, the ruling grade is steepest grade on the rail line between two locations. Climbing the steepest part of the line dictates the minimum motive power needed, or how light the train must be, in order for the run to be made without ...
s greater than 2%, and the 2-8-8-0 offered exceptional tractive effort
In railway engineering, the term tractive effort describes the pulling or pushing capability of a locomotive. The published tractive force value for any vehicle may be theoretical—that is, calculated from known or implied mechanical proper ...
, enabling a single locomotive to move the heaviest freight trains. As well as building these locomotives from scratch, the last in 1920, ten were converted from 0-8-8-0 configuration in 1920 and a further ten from 2-8-8-2
A 2-8-8-2, in the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangements, is an articulated locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck. The equivalent UIC classification ...
in 1922. These locomotives remained in operation until after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the last being withdrawn in 1955.
No 2-8-8-0 locomotives survive today; all were scrapped. However, one tender from the 2-8-8-0 #759 of the Kansas City Southern Railroad has been preserved, while the locomotive was scrapped. It is now preserved at the Illinois Railway Museum.
Indonesia

 Indonesia was also recorded operating several types of 2-8-8-0 locomotives. This dates back to the colonial era, under the government of
Indonesia was also recorded operating several types of 2-8-8-0 locomotives. This dates back to the colonial era, under the government of Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
by their state railway company named ''Staatsspoorwegen
''Staatsspoorwegen'' ( Dutch for State Railways, full name: ''Dienst der Staatsspoor- en Tramwegen in Nederlandsch–Indië'' (State Railways and Tramways Service in the Netherlands Indies, ''SS en T''), commonly abbreviated as SS) was a state-ow ...
'' (SS). In the early 20th century, especially in West Java
West Java (, ) is an Indonesian Provinces of Indonesia, province on the western part of the island of Java, with its provincial capital in Bandung. West Java is bordered by the province of Banten and the country's capital region of Jakarta to t ...
(known as Priangan), faced with the increase in passenger and freight rail traffic. By 1913, it was reported that they lacked powerful locomotives to serve the increasingly congested train traffic. This was worsened by the southern Priangan line passing through the hills requiring a special locomotive to climb the steep contour line there. The only available locomotive of the time were the 0-4-4-2T SS Class 500 (DKA BB10), 2-6-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and no trailing wheels. The wheel ...
T SS Class 520 (DKA CC10) and the 2-12-2T SS Class 800 (DKA F10) or known as ''Javanic.'' However, these classes were not adequate for the line, with the SS 800's six rigidly-connected driving axles being unsuitable for the winding Priangan lines.
This was exacerbated by the outbreak of First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
which paralyzed many industries in Europe. Amid limited choices and demands to get new locomotives immediately, SS decided to order a class of extremely large locomotives from American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various time ...
(Alco) in 1916. In just 6 months, eight 2-8-8-0s of the first batch arrived and were classed as SS Class 1200 (1201–1208), which were the largest locomotives in the Dutch East Indies. With a total weight of 133 tons, these locomotives have the profile of large American Mallets scaled down for narrow gauge ( 3 ft 6 in). However, their extreme size was not proportional to their capabilities; SS was disappointed because the Class 1200 could only reach the maximum speed of which was not suitable to haul the express trains in heavy terrain with the minimum speed of . Learning from that, the 1920 batch of twelve were modified. Despite looking similar to the first batch, these weighed almost 5 tons heavier, making them the heaviest locomotives used in Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
. However, their performance was not much improved from the first batch, with high fuel consumption and problems with unbalanced steam pressure (or back pressure
Back pressure (or backpressure) is the term for a resistance to the desired flow of fluid through pipes. Obstructions or tight bends create backpressure via friction loss and pressure drop.
In distributed systems in particular event-driven archi ...
) causing cracks in their frames, causing high operational and maintenance expenses.
By the end of First World War, European locomotive builders were once more operational, and SS soon ordered 10 new locomotives from three manufacturers: ''Hanomag
Hanomag (Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG, ) was a German producer of steam locomotives, tractors, trucks and military vehicles in Hanover. Hanomag first achieved international fame by delivering numerous steam locomotives to Finland, Romania and ...
'', ''Sachsische Maschinenfabrik (Hartmann)'' in Germany and '' Werkspoor, N.V.'' in the Netherlands, which arrived in 1923–24. These were made based on Alco design but with a large number of refinements resulting in a length and 135-ton weight, being classed as 1250 (1251–1260). While the Alco SS 1200s used bar frames, those on the European SS 1250s used plate frames. The SS 1250 was much faster, able to reach speeds of , but the problems with back pressure worsened.
Finally in 1926, the SS Experimental Service managed by de Gruijter made modifications to SS 1260. After the back pressure was fixed, a double chimney
A double chimney (or double stack, double smokestack in American English) is a form of chimney for a steam locomotive, where the conventional single opening is duplicated, together with the blastpipe beneath it. Although the internal openings for ...
was installed to maximize the engine performance, with the power output raised to while driving at a constant speed of 45 km/h. These modifications were extended to the entire SS Class 1250s and 12 units of the second batch of SS Class 1200, while the first batch of SS 1200s was unchanged due to severe cracks in their frames. The next modification was aimed at operational efficiency; as the class requires a large amount of coal, SS trialled mechanical stoker
A mechanical stoker is a mechanical system that feeds solid fuel like coal, coke or anthracite into the furnace of a steam boiler. They are common on steam locomotives after 1900 and are also used on ships and power stations. Known now as a spre ...
s that automatically moved coal to the firebox. However, this was called off due to increasing the axle load
The axle load of a wheeled vehicle is the total weight bearing on the roadway for all wheels connected to a given axle. Axle load is an important design consideration in the engineering of roadways and railways, as both are designed to tolerate a m ...
from 12 tons to 13 tons above the rail capacity.
During the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
in the 1930s, SS withdrew their giant locomotives to save money on fuel and in response to declining traffic. However, in 1938 these locomotives were reinstated to haul freight trains, except for the first batch of Class 1200s (which had been dismantled for parts). After the Japanese occupation and Indonesian Independence
The Proclamation of Indonesian Independence (, or simply ''Proklamasi'') was read at 10:00 Tokyo Standard Time on Friday 17 August 1945 in Jakarta. The declaration marked the start of the diplomatic and armed resistance of the Indonesian Nati ...
, these locos were renumbered to DD50 (first batch), DD51 (second batch) and DD52 (SS 1250s) used by ''Djawatan Kereta Api'' (DKA) or Department of Railways of the Republic of Indonesia. When the Japanese arrived in 1942, they continued to work on Purwakarta
Purwakarta () is a town and an administrative district () in West Java, Indonesia which serves as the regency seat of the Purwakarta Regency (not to be confused with the district of the same name in Cilegon city). It covers a land area of 24.39& ...
– Banjar line.
 They were nicknamed ''Si Gombar'' or The Monster by locals along with
They were nicknamed ''Si Gombar'' or The Monster by locals along with CC50
The SS 1600 class, later reclassified as the CC50 class, is a articulated Mallet type steam locomotive previously operated by the '' Staatsspoorwegen'' (SS), the state-owned railway of Dutch East Indies, and later inherited by the Indonesian ...
counterparts due to their size and power in the mountain lines. DD50 and DD51 were retired in the late 1960s, but DD52 lasted longer with a few of them still operational in the early 1970s. At the time, the DD52 was the only operational 2-8-8-0 locomotive in regular service in the world. Over time, the engines broke down due to poor condition and difficult maintenance, which hastened to their retirement. All examples of the class were scrapped.
References
{{Whyte types 88,2-8-8-0