1984 Summer Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and commonly known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international
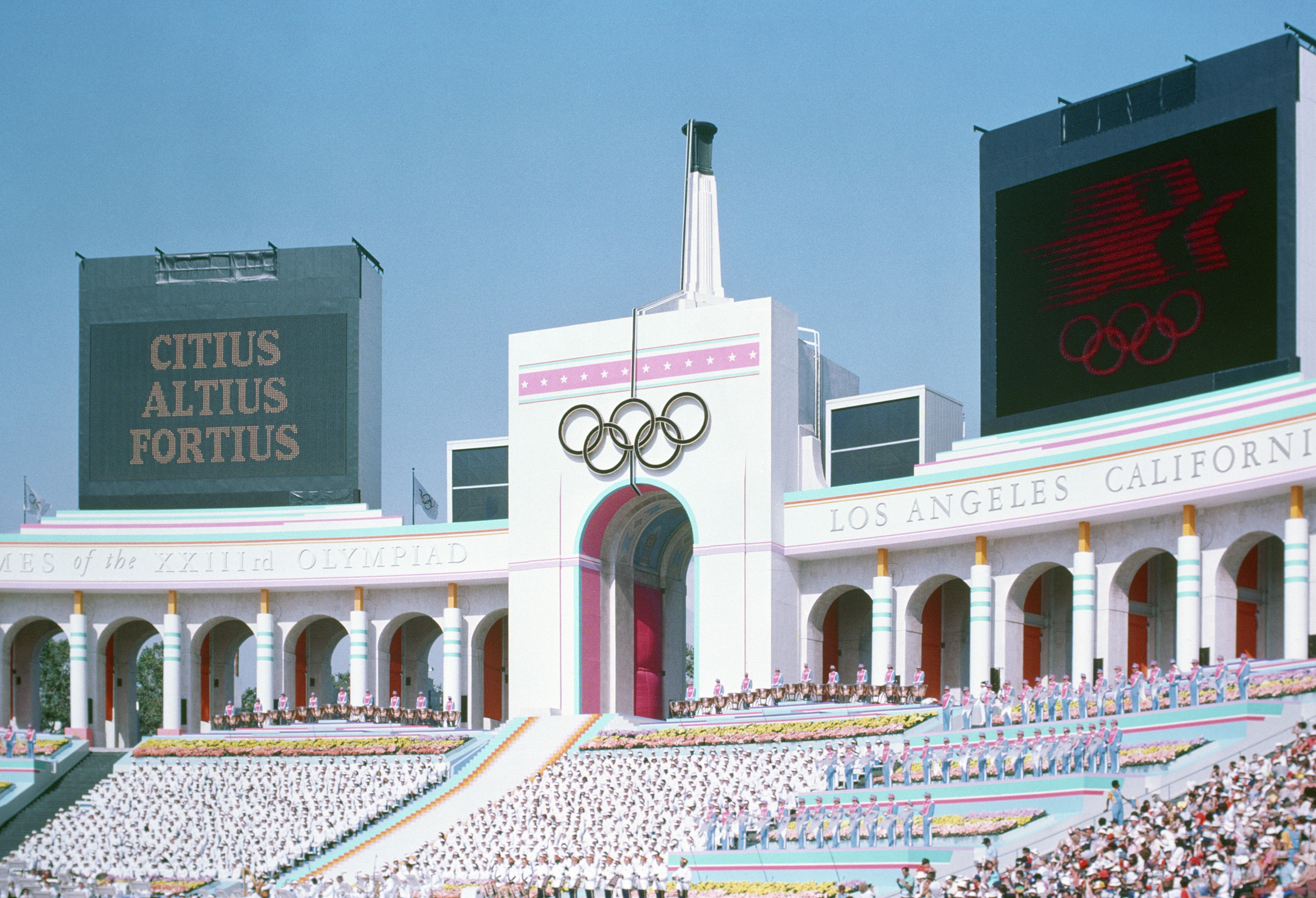


 Athletes from 140 states competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics. Eighteen states made their Olympic debut:
Athletes from 140 states competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics. Eighteen states made their Olympic debut:
 Fifteen countries took part in the Soviet-led boycott of the 1984 Summer Olympics:
*
Fifteen countries took part in the Soviet-led boycott of the 1984 Summer Olympics:
*
 Following the news of the massive financial losses of the
Following the news of the massive financial losses of the
''Olympic Review'' 1984 – Official results
Official Report Vol. 1
Official Report Vol. 2
*
Egyptian judoka refused to attack his opponent's clearly injured right leg
{{Authority control Olympic Games in California Summer Olympics in Los Angeles Summer Olympics by year
multi-sport event
A multi-sport event is an organized sporting event, often held over multiple days, featuring competition in many different sports among organized teams of athletes from (mostly) nation-states. The first major, modern, multi-sport event of intern ...
held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, California, United States. It marked the second time that Los Angeles had hosted the Games, the first being in 1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident (1932), Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort ...
. This was the first of two consecutive Olympic Games to be held in North America, with Calgary
Calgary () is a major city in the Canadian province of Alberta. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806 making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in C ...
, Alberta, Canada, hosting the 1988 Winter Olympics
The 1988 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XV Olympic Winter Games () and commonly known as Calgary 1988 were a multi-sport event held from February 13 to 28, 1988, with Calgary, Calgary, Alberta as the main host city. This marks the m ...
. California was the home state of the incumbent U.S. president
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
, who officially opened the Games. These were the first Summer Olympic Games under the IOC presidency of Juan Antonio Samaranch
Juan Antonio Samaranch y Torelló, 1st Marquess of Samaranch ( Catalan: ''Joan Antoni Samaranch i Torelló'', ; 17 July 1920 – 21 April 2010) was a Spanish sports administrator under the Franco regime (1973–1977) who served as the seventh ...
.
The 1984 Games were boycotted by fourteen Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries, including the Soviet Union and East Germany, in response to the American-led boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XXII Olympiad () and officially branded as Moscow 1980 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 19 July to 3 August 1980 in Moscow, Soviet Union, in present-day Russ ...
in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
, in protest of the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the largest country by are ...
; Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
was the only Soviet-aligned state that opted to attend the Games. Albania, Iran and Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
also chose to boycott the Games, but for unrelated reasons.
Despite the field being depleted in certain sports due to the boycott, 140 National Olympic Committee
A National Olympic Committee (NOC) is a national constituent of the worldwide Olympic movement. Subject to the controls of the International Olympic Committee, NOCs are responsible for organizing their people's participation in the Olympic Games ...
s took part in the 1984 Games, a record number at the time. The United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
won the most gold and overall medals, followed by Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
.
The 1984 Summer Olympics are widely considered to be the most financially successful modern Olympics, serving as an example on how to run an Olympic Games. As a result of low construction costs, due to the use of existing sport infrastructure, coupled with a reliance on private corporate the 1984 Games generated a profit of over .
On July 18, 2009, a 25th anniversary celebration of the 1984 Games was held at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum
The Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum (also known as the Los Angeles Coliseum or L.A. Coliseum) is a multi-purpose stadium in the Exposition Park, Los Angeles, Exposition Park neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. Conceived as a hal ...
. The celebration included a speech by former Los Angeles Olympic Organizing Committee president Peter Ueberroth
Peter Victor Ueberroth (; born September 2, 1937) is an American sports and business executive known for his involvement in the Olympics and in Major League Baseball. A Los Angeles–based businessman, he was the chairman of the Los Angeles Ol ...
, a short re-enactment of the Flying Rocketman sequence, the presentation of more than 35 (mostly So-Cal-based) gold medal winners from 1984 (which was part of Ceremonies producer David Wolper's original 1984 plans) as well as a re-lighting of the Olympic cauldron.
Los Angeles will host the Summer Olympics for the third time in 2028, becoming the third city in the world—following London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
and Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
—to do so.
Host selection
After theterrorist attack
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of violence against non-combatants to achieve political or ideological aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war a ...
at the 1972 Summer Olympics
The 1972 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XX Olympiad () and officially branded as Munich 1972 (; ), were an international multi-sport event held in Munich, West Germany, from 26 August to 11 September 1972. It was the ...
, the significant financial debts of Montreal (1976), and various boycotts by National Olympic Committees, few cities by the late 1970s were willing to bid for the Summer Olympics. Only two cities (Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
and Los Angeles) made serious bids for the 1984 Summer Games. Tehran submitted its bid to host the 1984 Summer Olympics to the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; , CIO) is the international, non-governmental, sports governing body of the modern Olympic Games. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is based i ...
(IOC) on 29 August 1975. The selection of the host city was made at the 80th IOC Session in Athens on 18 May 1978, where Los Angeles was chosen as the host city. It remains unclear why Tehran’s candidacy did not progress further; this may have been related to the early stages of political unrest in Iran in 1978. No official documentation has been found confirming that Iran formally withdrew its bid—neither in 1975 nor in 1978.
Los Angeles had unsuccessfully bid for the two previous Summer Olympic Games (1976 and 1980, which went to Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, respectively). The United States Olympic Committee
The United States Olympic & Paralympic Committee (USOPC) is the National Olympic Committee (NOC) and the National Paralympic Committee (NPC) for the United States. It was founded in 1895 and is headquartered in Colorado Springs, Colorado ...
(USOC) had submitted at least one bid for every Olympics since 1944
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 2 – WWII:
** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixt ...
but had not succeeded since the Los Angeles Olympics in 1932, the previous time only a single bid had been issued for the Summer Olympics.
Torch relay
The 1984 Olympic Torch Relay began in New York City and ended in Los Angeles, traversing 33 states and the District of Columbia. Unlike later torch relays, the torch was continuously carried by runners on foot. The route covered more than 9,320 mi (15,000 km) and involved 3,636 runners. Noted athleteO. J. Simpson
Orenthal James Simpson (July 9, 1947 – April 10, 2024), also known by his nickname "the Juice", was an American professional American football, football player, actor, and media personality who played in the National Football League (NFL) ...
was among the runners, carrying the torch up the California Incline in Santa Monica
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
. Gina Hemphill, a granddaughter of Jesse Owens
James Cleveland "Jesse" Owens (September 12, 1913 – March 31, 1980) was an American track and field athlete who made history at the Athletics at the 1936 Summer Olympics, 1936 Olympic Games by becoming the first person to win four gold meda ...
, carried the torch into the Coliseum, completed a lap around the track, then handed it off to the final runner, Rafer Johnson, winner of the decathlon
The decathlon is a combined event in athletics consisting of 10 track and field events. The word "decathlon" was formed, in analogy to the word "pentathlon", from Greek δέκα (''déka'', meaning "ten") and ἄθλος (''áthlos'', or ἄ ...
at the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad () and commonly known as Rome 1960 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 25 August to 11 September 1960 in Rome, Italy. Rome had previously been awar ...
. With the torch, he touched off the flame which passed through a specially designed flammable Olympic logo, igniting all five rings. Johnson became the first person of African descent to light the cauldron in Olympic history. The flame then passed up to the cauldron atop the peristyle and remained aflame for the duration of the Games.

Music
John Williams
John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932)Nylund, Rob (November 15, 2022)Classic Connection review, ''WBOI'' ("For the second time this year, the Fort Wayne Philharmonic honored American composer, conductor, and arranger John Williams, who w ...
composed the theme for the Olympiad, "Los Angeles Olympic Theme" later also known as "Olympic Fanfare and Theme
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) uses icons, flags, and symbols to represent and enhance the Olympic Games. These symbols include those commonly used during Olympic competitions such as the flame, fanfare, and theme as well as those u ...
". This piece won a Grammy
The Grammy Awards, stylized as GRAMMY, and often referred to as The Grammys, are awards presented by The Recording Academy of the United States to recognize outstanding achievements in music. They are regarded by many as the most prestigious a ...
for Williams and became one of the most well-known musical themes of the Olympic Games, along with Leo Arnaud's " Bugler's Dream"; the latter is sometimes attached to the beginning of Olympic Fanfare and Theme. Composer Bill Conti
William Conti (born April 13, 1942) is an American composer and conductor. He is best known for his film scores, including ''Rocky'' (1976), '' Rocky II'' (1979), '' Rocky III'' (1982), '' Rocky V'' (1990), '' Rocky Balboa'' (2006), '' The Karat ...
also wrote a song to inspire the weightlifters called "Power". An album, ''The Official Music of the XXIII Olympiad—Los Angeles 1984'', featured those three tracks along with sports themes written for the occasion by popular musical artists including Foreigner, Toto, Loverboy
Loverboy is a Canadian Rock music, rock band formed in Calgary, Alberta in 1979. Loverboy's hit singles, particularly "Turn Me Loose (Loverboy song), Turn Me Loose" and "Working for the Weekend", have become arena rock staples and are still hear ...
, Herbie Hancock
Herbert Jeffrey Hancock (born April 12, 1940) is an American jazz musician, bandleader, and composer. He started his career with trumpeter Donald Byrd's group. Hancock soon joined the Miles Davis Quintet, where he helped to redefine the role of ...
, Quincy Jones
Quincy Delight Jones Jr. (March 14, 1933 – November 3, 2024) was an American record producer, composer, arranger, conductor, trumpeter, and bandleader. Over the course of his seven-decade career, he received List of awards and nominations re ...
, Christopher Cross
Christopher Cross (born Christopher Charles Geppert; May 3, 1951) is an American singer-songwriter and guitarist.
He won five Grammy Awards for his eponymous debut album released in 1979. The singles "Sailing" (1979), and " Arthur's Theme (Best ...
, Philip Glass
Philip Glass (born January 31, 1937) is an American composer and pianist. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential composers of the late 20th century. Glass's work has been associated with minimal music, minimalism, being built up fr ...
, Paul Engemann and Giorgio Moroder
Giovanni Giorgio Moroder (, ; born 26 April 1940) is an Italian composer and music producer. Dubbed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Father of Disco", Moroder is credited with pioneering Euro disco and electronic dance music. His work ...
. " Reach Out" was the main soundtrack and is the official theme song of the 1984 Summer Olympics.
The Brazilian composer Sérgio Mendes
Sérgio Santos Mendes (; 11 February 1941 – 5 September 2024) was a Brazilian musician.
His career took off with worldwide hits by his band Brasil '66. He released 35 albums and was known for playing bossa nova, often mixed with funk. He ...
also produced a special song for the 1984 Olympic Games, "Olympia," from his 1984 album '' Confetti''. A choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
of approximately one thousand voices was assembled of singers
Singing is the art of creating music with the voice. It is the oldest form of musical expression, and the human voice can be considered the first musical instrument. The definition of singing varies across sources. Some sources define singi ...
in the region. All were volunteers from nearby churches, schools and universities.
Etta James
Jamesetta Hawkins (January 25, 1938 – January 20, 2012), known professionally as Etta James, was an American singer and songwriter. Starting her career in 1954, James frequently performed in Nashville's R&B clubs, collectively known as the Ch ...
performed " When the Saints Go Marching In" at the Opening Ceremony.
Vicki McClure, along with the International Children's Choir of Long Beach, sang " Reach Out and Touch".
Alongside Williams and the house orchestra, 84 pianists performed an abridged version of George Gershwin
George Gershwin (; born Jacob Gershwine; September 26, 1898 – July 11, 1937) was an American composer and pianist whose compositions spanned jazz, popular music, popular and classical music. Among his best-known works are the songs "Swan ...
's composition ''Rhapsody in Blue
''Rhapsody in Blue'' is a 1924 musical composition for solo piano and jazz band by George Gershwin. Commissioned by bandleader Paul Whiteman, the work combines elements of classical music with jazz-influenced effects and premiered in a concer ...
''.
Lionel Richie
Lionel Brockman Richie Jr. (born June 20, 1949) is an American singer, songwriter, record producer, and television personality. He rose to fame in the 1970s as a songwriter and the co-lead singer of the Motown group Commodores; writing and recor ...
performed a special extended 9-minute version of his hit single " All Night Long" at the closing ceremonies.
Mascot
The mascot was abald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche ...
named Sam the Olympic Eagle.
Highlights
Arts Festival
The 1984 Summer Olympics was preceded by the 10-week-long adjunct Olympic Arts Festival, which opened on June 1 and ended on August 12. It provided more than 400 performances by 146 theater, dance, and music companies, representing every continent and 18 countries, as well as art exhibitions and films. It was organized by then- CalArts President Robert Fitzpatrick. Along with many famous American dance companies, such as theDance Theatre of Harlem
Dance Theatre of Harlem (DTH) is an American professional ballet company and school based in Harlem, New York City. It was founded in 1969 under the directorship of Arthur Mitchell and later partnered with Karel Shook. Milton Rosenstock served ...
, the festival hosted three international debuts: German choreographer Pina Bausch and her Tanztheater Wuppertal, Groupe Emile Dubois from France, and the Japanese Butoh
is a form of Japanese dance theatre that encompasses a diverse range of activities, techniques and motivations for dance, performance, or movement. Following World War II, butoh arose in 1959 through collaborations between its two key founder ...
.
General
* This was the first edition in which new rules of coexistence within theOlympic Village
An Olympic Village is a residential complex built or reassigned for the Olympic Games in or nearby the List of Olympic Games host cities, host city for the purpose of accommodating all of the delegations. Olympic Villages are usually located clos ...
were implemented and it was decided that from this edition onwards all athletes would have to stay in the same place, as opposed to being divided by gender and sometimes even political blocs which was the case previously.
* Also for the first time in history, the International Olympic Committee authorized the formal segments of the opening ceremony
An opening ceremony, grand opening, or ribbon-cutting ceremony marks the official opening of a newly constructed location or the start of an event.
to be interspersed with the cultural segments. The start of the event featured the arrival of Bill Suitor by means of the Bell Aerosystems rocket pack (also known as a Jet Pack).
* The United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
topped the medal count for the first time since 1968
Events January–February
* January 1968, January – The I'm Backing Britain, I'm Backing Britain campaign starts spontaneously.
* January 5 – Prague Spring: Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Cze ...
, winning a record 83 gold medals and surpassing the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
's total of 81 golds at the 1980 Summer Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XXII Olympiad () and officially branded as Moscow 1980 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 19 July to 3 August 1980 in Moscow, Soviet Union, in present-day Russ ...
.
* As a result of an Nagoya Resolution signed in 1979, and the designating the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
(Taiwan) as Chinese Taipei
"Chinese Taipei" is the term used in various international organizations and tournaments for groups or delegations representing the Republic of China (ROC), a country commonly known as Taiwan.
Due to the One China principle stipulated by the ...
, the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
returned to the Summer Olympics for the first time since Helsinki 1952. The Military anthem of China was played for both teams during the opening ceremony.
* Local Los Angeles artist Rodolfo Escalera was commissioned to create nine paintings depicting the Summer Games that would later be turned into collectible plates and presented as "The Official Gift of the 1984 Olympics".LAOOC also designed Ernie Barnes as "Sports Artist of the 1984 Summer Olympic Games" and Barnes was commissioned to create five Olympic-themed paintings and serve as an official Olympic spokesman to encourage inner-city youth.
Track and field
* Carl Lewis of the United States, making his first of four appearances at the Olympics, equaled the 1936 performance ofJesse Owens
James Cleveland "Jesse" Owens (September 12, 1913 – March 31, 1980) was an American track and field athlete who made history at the Athletics at the 1936 Summer Olympics, 1936 Olympic Games by becoming the first person to win four gold meda ...
by winning four gold medals, in the 100 m, 200 m, 4 × 100 m relay and long jump.
* Edwin Moses of the United States won the gold medal in the 400m hurdles 8 years after winning in 1976.
* Joaquim Cruz
Joaquim Carvalho Cruz (born 12 March 1963) is a Brazilian former middle-distance runner, winner of the 800 meters at the 1984 Summer Olympics. He is one of only ten men, and in August 1984 became the second man, to run the 800 metres in less th ...
of Brazil won the 800 meter run with a time of 1:43.00 to set an Olympic record.
* Nawal El Moutawakel
Nawal El Moutawakel ( Amazigh: ⵏⴰⵡⴰⵍ ⵍⵎⵓⵜⴰⵡⴰⵇⵇⵍ ; ; born 15 April 1962) is a Moroccan former hurdler, who won the inaugural women's 400 metres hurdles event at the 1984 Summer Olympics, and is the first Moroccan, ...
of Morocco became the first female Olympic champion of a Muslim nation—and the first of her country—in the 400 m hurdles.
* Carlos Lopes
Carlos Alberto de Sousa Lopes (, born 18 February 1947) is a Portuguese former long-distance runner and world-record holder in the marathon. He won the Athletics at the 1984 Summer Olympics – Men's marathon, marathon at the 1984 Summer Olym ...
, from Portugal, won the Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of kilometres ( 26 mi 385 yd), usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There ...
at the age of 37, with a time of 2:09:21, an Olympic record that stood for 24 years. It was the first gold medal ever for Portugal. Gold medal favorite, World Record holder and the then World Champion, Robert de Castella from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, finished in 5th place, 1:48 behind Lopes.
* A marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of kilometres ( 26 mi 385 yd), usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There ...
for women was held for the first time at the Olympics (won by Joan Benoit of the U.S.). The event was also remembered for Swiss runner Gabriela Andersen-Schiess, who – suffering from heat exhaustion – entered the stadium for the final lap in a state of almost total exhaustion, barely able to walk but eventually completing the race, collapsing at the finishing line and being immediately treated by medical personnel.
* Daley Thompson
Francis Morgan Ayodélé Thompson, (born 30 July 1958) is an English former decathlete. He won the decathlon gold medal at the Olympic Games in 1980 and 1984, and broke the world record for the event four times. He was unbeaten in competit ...
of Great Britain apparently missed a new world record in winning his second consecutive gold medal in the decathlon
The decathlon is a combined event in athletics consisting of 10 track and field events. The word "decathlon" was formed, in analogy to the word "pentathlon", from Greek δέκα (''déka'', meaning "ten") and ἄθλος (''áthlos'', or ἄ ...
; the next year, his score was retroactively raised to 8847, giving him the record.
* Sebastian Coe
Sebastian Newbold Coe, Baron Coe, (born 29 September 1956), often referred to as Seb Coe, is a British sports administrator, former politician and retired track and field athlete. As a middle-distance runner, Coe won four Olympic medals, incl ...
of Great Britain became the first man to win consecutive gold medals in the 1500m.
* Maricica Puică of Romania won the 3000 meters, known for the Mary Decker
Mary Teresa Slaney (formerly Tabb, Married and maiden names, née Decker, born August 4, 1958) is an American retired middle-distance and long-distance runner. During her career, she won gold medals in the 1500 metres, 1500 meters and 3000 metr ...
vs. Zola Budd
Zola Budd (also known as Zola Pieterse; born 26 May 1966) is a South African Middle-distance running, middle-distance and Long-distance running, long-distance runner. She competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics, 1984 Olympic Games for Great Britain ...
rivalry. World champion and heavy favorite Decker fell after a controversial collision with Budd. However, Puică had the best annual time at the distance, easily run away from silver medalist Wendy Sly of Great Britain and appeared to have more to give if it had been necessary. Puică was injured during the very first Track and Field World Championships in Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
the year before, in which Decker had won both the 1500 meters and the 3000 meters.
Other sports
* The first gold medal to be awarded at the Los Angeles Olympics was also the first-ever medal to be won by an athlete from China when Xu Haifeng won the 50 m Pistol event. * ArcherNeroli Fairhall
Neroli Susan Fairhall (26 August 1944 – 11 June 2006) was a New Zealand athlete, who was the first paraplegic competitor in the Olympic Games.
Biography
Born in Christchurch in 1944, Fairhall took up archery following a motorbike accident t ...
from New Zealand was the first paraplegic
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek ()
"half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neura ...
Olympian at any Olympic Games, coming 35th in the Women's individual event.
* Synchronized swimming
Synchronized swimming (in British English, synchronised swimming), also known as artistic swimming, is a sport where swimmers perform a synchronized choreographed routine, accompanied by music. The sport is governed internationally by World A ...
and rhythmic gymnastics
Rhythmic gymnastics is a sport in which gymnasts perform individually or in groups on a floor with an apparatus: hoop (rhythmic gymnastics), hoop, ball (rhythmic gymnastics), ball, Clubs (rhythmic gymnastics), clubs, ribbon (rhythmic gymnastics), ...
debuted in Los Angeles as Olympic events, as did wind surfing.
* Li Ning from the People's Republic of China won 6 medals in gymnastics, 3 gold, 2 silver, and 1 bronze, earning him the nickname "Prince of Gymnasts" in China. Li would later light the Olympic Cauldron at the 2008 Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and officially branded as Beijing 2008 (), were an international multisport event held from 8 to 24 August 2008, in Beijing, China. A total of 10,942 athletes fr ...
.
* Steve Redgrave of Great Britain won his first title in rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically a ...
of the record five he would go on to win in five Olympic competitions.
* Victor Davis of Canada set a new world record in winning the gold medal in the 200-meter breaststroke in swimming.
* Mary Lou Retton
Mary Lou Retton (born January 24, 1968) is an American retired gymnast. At the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles, she won a gold medal in the individual all-around competition, as well as two silver medals and two bronze medals.
Retton's per ...
of the United States became the first gymnast outside Eastern Europe to win the gymnastics all-around competition.
* In men's gymnastics, the American team won the gold medal.
* France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
won the Olympic association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
(soccer) tournament, defeating Brazil 2–0 in the final. Olympic football was unexpectedly played before massive crowds throughout America, with several sell-outs at the 100,000+ seat Rose Bowl. This interest eventually led to the U.S. hosting the 1994 FIFA World Cup
The 1994 FIFA World Cup was the 15th FIFA World Cup, the world championship for men's national soccer teams. It was hosted by the United States and took place from June 17 to July 17, 1994, at nine venues across the country. The United States w ...
.
* The Soviet-led boycott affected weightlifting more than any other sport: 94 of the world's top 100 ranked lifters were absent, as were 29 of the 30 medalists from the recent world championships. All 10 of the defending world champions in the 10 weight categories were absent. The success of the Eastern Bloc countries might be explained by state-run doping programs that had been developed there.
* Future Dream Team members Michael Jordan
Michael Jeffrey Jordan (born February 17, 1963), also known by his initials MJ, is an American businessman and former professional basketball player, who is currently a minority owner of the Charlotte Hornets of the National Basketball Ass ...
, Patrick Ewing
Patrick Aloysius Ewing Sr. (born August 5, 1962) is a Jamaican-American basketball coach and former professional player who is a basketball ambassador for the New York Knicks of the National Basketball Association (NBA), where he played most o ...
, and Chris Mullin
Christopher Paul Mullin (born July 30, 1963) is an American former professional basketball player, executive and coach. He is a five time NBA All-Star and four time All-NBA Team member. He is also two-time Olympic Gold medalist and a two-time ...
were on the team that won the gold medal in basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
. The 1984 U.S. men's Olympic basketball team was coached by Indiana Hoosiers
The Indiana Hoosiers are the intercollegiate sports teams and players of Indiana University Bloomington, named after the demonym for people from the state of Indiana. The Hoosiers participate in NCAA Division I, Division I of the National Coll ...
head coach Bobby Knight.
* Connie Carpenter-Phinney of the United States became the first woman to win an Olympic cycling event when she won the women's individual road race.
* In the judo open division, four-time world champion Yasuhiro Yamashita of Japan tore a right calf muscle in the preliminary match against Arthur Schnabel. This put Yamashita at a huge disadvantage since he executed his throws by pivoting on his right leg. Though he managed to win the match with an Okuri-Eri-Jime, the injury caused him to visibly limp during the semi-final match against Laurent Del Colombo. Yamashita was thrown with an Osoto Gari
is one of the original 40 Throw (grappling), throws of Judo
as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the first group, Judo Lists#Dai Ikkyo, Dai Ikkyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo (no waza), of Kodokan Judo. It is also included in t ...
only 30 seconds into the match, but managed to return an Osoto Gari and won the match with a Yoko-Shiho-Gatame (side four-quarter hold). He played the final match against Mohamed Ali Rashwan of Egypt. Yamashita won the final and the gold medal despite his injury. The match witnessed a remarkable fair play act from Rashwan who did not aim for Yamashita's right leg. Rashwan was even given an award from the International Fairplay Committee.
Venues

Venues in the city of Los Angeles
*Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum
The Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum (also known as the Los Angeles Coliseum or L.A. Coliseum) is a multi-purpose stadium in the Exposition Park, Los Angeles, Exposition Park neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. Conceived as a hal ...
– opening/closing ceremonies, athletics
* Los Angeles Memorial Sports Arena – boxing
* Dodger Stadium
Dodger Stadium is a ballpark in the Elysian Park neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. It is the home of the Los Angeles Dodgers of Major League Baseball (MLB). Opened in 1962, it was constructed in less than three years at a ...
– baseball
* Pauley Pavilion, University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school the ...
– gymnastics
* Eagle's Nest Arena
The Golden eagle, Eagle's Nest Arena, formerly known as the Devil, Diablo Den (room), Den, is an iconic indoor arena situated on the California State University, Los Angeles (Cal State L.A.) campus.
This versatile venue serves as the home cou ...
, California State University, Los Angeles
California State University, Los Angeles (Cal State LA) is a public research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. It is part of the California State University system. Cal State LA offers 142 bachelor's degree programs, 122 m ...
– judo
* Olympic Swim Stadium, University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in ...
– swimming, diving, synchronized swimming
* Olympic Village (athlete housing), University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in ...
* Los Angeles Tennis Center, University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school the ...
– tennis
* Athletes Village, University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school the ...
* Albert Gersten Pavilion, Loyola Marymount University
Loyola Marymount University (LMU) is a private Jesuit and Marymount research university in Los Angeles, California. LMU enrolls over 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students, making it the largest Catholic university on the west coast of the ...
, Westchester, California – weightlifting
* Streets of Los Angeles – athletics (marathon)
Venues in Southern California
* El Dorado Park, Long Beach, California – archery * The Forum, Inglewood, California – basketball and team handball finals * Lake Casitas,Ventura County
Ventura County () is a county located in the southern part of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 843,843. The largest city is Oxnard, and the county seat is the city of Ventura.
Ventura County comprises ...
, California – canoeing, rowing
* Olympic Velodrome, California State University, Dominguez Hills
California State University, Dominguez Hills (CSUDH, CSU Dominguez Hills, or Cal State Dominguez Hills) is a public university in Carson, California. It was founded in 1960 and is part of the California State University (CSU) system.
In 2020, ...
, Carson, California – cycling (track)
* Mission Viejo
Mission Viejo ( ; language change, corruption of ; ) is a Commuter town, commuter city in the Saddleback Valley in Orange County, California, United States. Mission Viejo is considered one of the largest Planned community, master-planned commu ...
, Orange County, California – cycling (individual road race)
* Santa Anita Park
Santa Anita Park is a Thoroughbred racetrack in Arcadia, California, United States. It offers some of the prominent horse racing events in the United States during early fall, winter and in spring. The track is home to numerous prestigious race ...
, Arcadia, California
Arcadia is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States, located about northeast of downtown Los Angeles in the San Gabriel Valley and at the base of the San Gabriel Mountains. It contains a series of adjacent parks consisting of t ...
– equestrian
* Fairbanks Ranch Country Club, Rancho Santa Fe, California, California – equestrian sports (eventing endurance)
* Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach
Long Beach is a coastal city in southeastern Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is the list of United States cities by population, 44th-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 451,307 as of 2022. A charter ci ...
, California – fencing
* Rose Bowl, Pasadena, California – football (final)
* Titan Gymnasium, California State University, Fullerton
California State University, Fullerton (CSUF or Cal State Fullerton) is a public research university in Fullerton, California, United States. With a total enrollment of more than 41,000, it has the largest student body of the California State ...
, Fullerton, California – handball
* Weingart Stadium
Weingart Stadium (formerly East Los Angeles College Stadium or ELAC Stadium) is a 22,355-capacity multi-purpose stadium located at East Los Angeles College, in Monterey Park, California. It was built in 1951 at a cost of $3.1 million, and follow ...
, East Los Angeles College, Monterey Park, California – field hockey
* Coto de Caza, Orange County, California – modern pentathlon (fencing, riding, running, shooting)
* Olympic Shooting Range, Prado Recreational Area, Chino, California – shooting
* Long Beach Arena
The Long Beach Convention and Entertainment Center is a convention center located in Long Beach, California. Built on the former site of the Long Beach Municipal Auditorium, the venue is composed of the Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach A ...
, Long Beach
Long Beach is a coastal city in southeastern Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is the list of United States cities by population, 44th-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 451,307 as of 2022. A charter ci ...
, California – volleyball
* Raleigh Runnels Memorial Pool, Pepperdine University
Pepperdine University () is a private university, private Christianity, Christian research university affiliated with the Churches of Christ, with its main campus in Los Angeles County, California, United States. Pepperdine's main campus consists ...
, Malibu, California – water polo
* Anaheim Convention Center, Anaheim
Anaheim ( ) is a city in northern Orange County, California, United States, part of the Greater Los Angeles area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 346,824, making it the most populous city in Orange County, the tenth-most ...
, California – wrestling
* Long Beach Shoreline Marina, Long Beach
Long Beach is a coastal city in southeastern Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is the list of United States cities by population, 44th-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 451,307 as of 2022. A charter ci ...
, California – sailing
* Artesia Freeway – cycling (road team time trial)
* Heritage Park Aquatic Center, Irvine, California – modern pentathlon (swimming)
* Santa Monica College
Santa Monica College (SMC) is a Public university, public community college in Santa Monica, California. Founded as a Junior college#United States, junior college in 1929, SMC enrolls over 30,000 students in more than 90 fields of study. The coll ...
, Santa Monica
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
, California – athletics (marathon start)
* Santa Monica, California
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
– athletics (marathon)
Other venues
*Harvard Stadium
Harvard Stadium is a U-shaped college football stadium in the Allston neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. The Stadium is one of only four athletic facilities that are considered National Historic Landmarks. The stadium is owned and operated ...
, Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
, Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, Massachusetts – football preliminaries
* Navy–Marine Corps Memorial Stadium
Navy–Marine Corps Memorial Stadium is an open-air stadium located off the campus of the United States Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland. Opened in 1959, it serves as the home stadium of the Navy Midshipmen Navy Midshipmen football, college f ...
, United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (USNA, Navy, or Annapolis) is a United States Service academies, federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as United States Secre ...
, Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
, Maryland – football preliminaries
* Stanford Stadium, Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
, Stanford
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth governor of and th ...
, California – football preliminaries
Sports
The 1984 Summer Olympic program featured 221 events in the following 21 sports: * Aquatics ** ** ** ** * * * * * * ** Road (3) ** Track (5) * ** Dressage (2) ** Eventing (2) ** Show jumping (2) * * * * ** Artistic (14) ** Rhythmic (1) * * * * * * * * * ** Freestyle (10) ** Greco-Roman (10)Demonstration sports
* *Calendar
:''All times are inPacific Daylight Time
The Pacific Time Zone (PT) is a time zone encompassing parts of western Canada, the western United States, and western Mexico. Places in this zone observe standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−08:00). ...
( UTC-7); the other two cities, Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
and Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
use Eastern Daylight Time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico.
* Eastern Standard Time (EST) is five hours behin ...
( UTC-4)''
Medal count
These are the top ten nations that won medals at the 1984 Games.Participating National Olympic Committees

 Athletes from 140 states competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics. Eighteen states made their Olympic debut:
Athletes from 140 states competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics. Eighteen states made their Olympic debut: Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
, British Virgin Islands
The British Virgin Islands (BVI), officially the Virgin Islands, are a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, to the east of Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands, US Virgin Islands and north-west ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
, Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equ ...
, The Gambia
The Gambia, officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. Geographically, The Gambia is the List of African countries by area, smallest country in continental Africa; it is surrounded by Senegal on all sides except for ...
, Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
, Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
, Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
, North Yemen
North Yemen () is a term used to describe the Kingdom of Yemen (1918-1962), the Yemen Arab Republic (1962-1990), and the regimes that preceded them and exercised sovereignty over that region of Yemen. Its capital was Sanaa from 1918 to 1948 an ...
, Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
, Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
, Western Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabit ...
, Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
, Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania. The country has 171 islands, of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. accordin ...
, and the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
. Zaire
Zaire, officially the Republic of Zaire, was the name of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1971 to 18 May 1997. Located in Central Africa, it was, by area, the third-largest country in Africa after Sudan and Algeria, and the 11th-la ...
had previously competed at the 1968 Summer Olympics
The 1968 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XIX Olympiad () and officially branded as Mexico 1968 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 12 to 27 October 1968, in Mexico City, Mexico. These were the first Ol ...
as ''Congo-Kinshasa
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
''. The People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
made its first appearance in a Summer Olympics since 1952
Events January–February
* January 26 – Cairo Fire, Black Saturday in Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt: Rioters burn Cairo's central business district, targeting British and upper-class Egyptian businesses.
* February 6
** Princess Elizabeth, ...
, while for the first time the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
team participated under the politically contrived name of ''Chinese Taipei
"Chinese Taipei" is the term used in various international organizations and tournaments for groups or delegations representing the Republic of China (ROC), a country commonly known as Taiwan.
Due to the One China principle stipulated by the ...
''.
The Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
led the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Sovi ...
members and other Communist countries in a boycott of the Los Angeles Olympics, in retaliation for the U.S.-led boycott of the Moscow Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XXII Olympiad () and officially branded as Moscow 1980 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 19 July to 3 August 1980 in Moscow, Soviet Union, in present-day Russ ...
four years earlier (over the Soviet Union's invasion of Afghanistan in 1979). The pretexts for the 1984 Soviet-led boycott were concerns over security, "chauvinistic sentiments" and "an anti-Soviet hysteria ... being whipped up" in the United States. However, a handful of communist countries disregarded the boycott and attended the Games anyway, among them Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
(host of the 1984 Winter Olympics
The 1984 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XIV Olympic Winter Games (Serbo-Croatian language, Serbo-Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Serbian Cyrillic alphabet, Serbian Cyrillic: ; ) and commonly known as Sarajevo '84 (Serbian Cy ...
), the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(the only Warsaw Pact country that had opted to ignore the Soviet demands). The Romanian team received a particularly warm reception from the United States; when the Romanian athletes entered during the opening ceremonies, they were greeted by a standing ovation from the spectators, who were mostly U.S. citizens. This would turn out to be Romania's most successful Olympic Games – they won 53 medals, including 20 golds.
In the table below, the number of athletes representing each state is shown in parentheses.
Number of athletes by National Olympic Committees
Boycotting countries
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
* Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
* Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
* Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
* Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
* East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
* Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
* Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
* Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
* Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
* North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
* Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
* Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
* South Yemen
South Yemen, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen, abbreviated to Democratic Yemen, was a country in South Arabia that existed in what is now southeast Yemen from 1967 until Yemeni unification, its unification with the Yemen A ...
* Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
and Upper Volta (changed to Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 ...
following August 4) also missed the Los Angeles Olympics, citing political reasons, but these countries were not a part of the Soviet-led boycott. Albania and Iran were the only two countries to boycott both the 1980 and 1984 Summer Games.
* Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
* Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
* Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
* / Upper Volta/Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 ...
Soviet doping plan
A document obtained in 2016 by theNew York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
revealed the Soviet Union's plans for a statewide doping system in track and field in preparation for the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. Dated prior to the country's decision to boycott the Games, the document detailed existing steroids operations of the program, along with suggestions for further enhancements.
Financial success of Los Angeles as host city
 Following the news of the massive financial losses of the
Following the news of the massive financial losses of the 1976 Summer Olympics
The 1976 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XXI Olympiad () and officially branded as Montreal 1976 (), were an international multi-sport event held from July 17 to August 1, 1976, in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Montreal ...
in Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
, the only two cities to express a genuine interest in hosting the 1984 Games were Los Angeles and New York. Given that only one city per country is allowed to bid for any one Games, the USOC vote for the American bid city was effectively the deciding vote for the 1984 Olympics host city. In this case, the Los Angeles bid received 55 votes compared with New York's 39 votes – this is the closest that the city of New York has ever come to being selected to host the Olympic Games, coming closer in 1984 than they did in their 2012 bid (when they lost to London).
Ambitious construction projects for the two previous Summer Olympics, Montreal 1976 and Moscow 1980, had burdened organizers with substantial debts as expenses greatly exceeded revenues. Furthermore, the 1976 and 1980 Olympics were entirely government-funded. Unlike Montreal and Moscow, Los Angeles 1984 was privately funded, with strict controls imposed on expenditure; rather than constructing new venues with overly ambitious designs, the organizers chose instead to utilize existing venues and facilities wherever possible. The main example of this was the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum
The Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum (also known as the Los Angeles Coliseum or L.A. Coliseum) is a multi-purpose stadium in the Exposition Park, Los Angeles, Exposition Park neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States. Conceived as a hal ...
, which was also the Olympic Stadium for the 1932 Summer Olympics
The 1932 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the X Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1932) were an international multi-sport event held from July 30 to August 14, 1932, in Los Angeles, California, United States. The Games were held du ...
. The only two new venues constructed specifically for the 1984 Summer Olympics were secured with the backing of corporate sponsors: the Olympic Velodrome was largely funded by the 7-Eleven
7-Eleven, Inc. is an American convenience store chain, headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Seven-Eleven Japan, which in turn is owned by the retail holdings company Seven & I Holdings.
The chain was founde ...
corporation and the Olympic Swim Stadium by McDonald's
McDonald's Corporation, doing business as McDonald's, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational fast food chain store, chain. As of 2024, it is the second largest by number of locations in the world, behind only the Chinese ch ...
.
In addition to corporate support, the Olympic committee also used the income from the exclusive television rights, and for the first time these contracts would prove to be a significant source of revenue. Adjusted for inflation, the Los Angeles Games secured twice the amount of income received by the 1980 Moscow Summer Olympics and four times that of the 1976 Montreal Summer Olympics.
The low level of interest among potential host cities for the 1984 Games had been viewed as a major threat to the future of the Olympic Games. However, after the financial success of the Los Angeles Games, cities began to show a renewed interest in bidding to become host again. The Los Angeles and Montreal Games are seen as examples of best and worst practice when organizing the Olympics and serve as valuable lessons to prospective host cities.
Following the success of the 1984 Games, the Los Angeles OCOG, led by Peter Ueberroth
Peter Victor Ueberroth (; born September 2, 1937) is an American sports and business executive known for his involvement in the Olympics and in Major League Baseball. A Los Angeles–based businessman, he was the chairman of the Los Angeles Ol ...
, used the profits to create the LA84 Foundation
The LA84 Foundation (known until June 2007 as the Amateur Athletic Foundation of Los Angeles) is a private, nonprofit institution created by the Los Angeles Olympic Organizing Committee to manage Southern California's endowment from the 1984 Oly ...
for promoting youth sports in Southern California, educating coaches and maintaining a sports library.
In popular culture
The games were the subject of the 1983–84 United States commemorative coin series. American fast food chainMcDonald's
McDonald's Corporation, doing business as McDonald's, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational fast food chain store, chain. As of 2024, it is the second largest by number of locations in the world, behind only the Chinese ch ...
ran a promotion titled, "When the U.S. Wins, You Win" where customers scratched off a ticket with the name of an Olympic event on it. If the U.S. won a medal in that event, then they would be given a free menu item: a Big Mac
The Big Mac is a brand of hamburger sold by the international fast food restaurant chain McDonald's. It was introduced by a Greater Pittsburgh Region, Greater Pittsburgh area Franchising, franchisee in 1967 and expanded nationwide in 1968, and ...
for a gold medal, an order of french fries
French fries, or simply fries, also known as chips, and finger chips (Indian English), are '' batonnet'' or '' julienne''-cut deep-fried potatoes of disputed origin. They are prepared by cutting potatoes into even strips, drying them, and f ...
for a silver medal, and a Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, or Coke, is a cola soft drink manufactured by the Coca-Cola Company. In 2013, Coke products were sold in over 200 countries and territories worldwide, with consumers drinking more than 1.8 billion company beverage servings ...
for a bronze medal. The promotion became more popular than expected due to the Soviet boycott which led to the U.S. winning far more Olympic medals than expected. This promotion was parodied in ''The Simpsons
''The Simpsons'' is an American animated sitcom created by Matt Groening and developed by Groening, James L. Brooks and Sam Simon for the Fox Broadcasting Company. It is a Satire (film and television), satirical depiction of American life ...
'' episode "Lisa's First Word
"Lisa's First Word" is the tenth episode of the The Simpsons season 4, fourth season of the American animated television series ''The Simpsons''. It was first broadcast on Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox in the United States on December 3, 1992. ...
", where Krusty Burger runs a similar offer. The promotion was intended to be rigged so that prizes would only be offered in events dominated by the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, but the Soviet-led boycott causes Krusty to personally lose $44 million. He vehemently promises "to spit in every fiftieth burger," to which Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
retorts "I like those odds!" Chief Wiggum also exclaims that he could kiss Carl Lewis, who won four gold medals at the Games.
On '' NCIS'', Tim McGee has an obsession with jet packs, stemming from having attended the 1984 Olympic ceremony as a child and having Bill Suitor fly over his head in his jet pack. This storyline is based on the real experience of executive producer and writer Jesse Stern.
Pop-punk band Bowling for Soup references the games in the song " I Can't Stand LA". During a section showing appreciation for the city, the song states, "thank you for hair metal and the '84 Olympics."
Jilly Cooper
Dame Jilly Cooper, (born Jill Sallitt; 21 February 1937) is an English author. She began her career as a journalist and wrote numerous works of non-fiction before writing several romance novels, the first of which appeared in 1975. Cooper is ...
's novel Riders has a storyline set at the show jumping event at the 1984 Summer Olympics.
In the ''Seinfeld
''Seinfeld'' ( ) is an American television sitcom created by Larry David and Jerry Seinfeld that originally aired on NBC from July 5, 1989, to May 14, 1998, with a total of nine seasons consisting of List of Seinfeld episodes, 180 episodes. It ...
'' episode "The Gymnast", Jerry dates a woman who competed in the 1984 Olympics and won a silver medal for Romania.
In '' American Horror Story: 1984'', the characters watch it together on the TV in the girls cabin.
In the same week that the Games began, British pop star Howard Jones released a single called " Like to Get to Know You Well" which eventually made number 4 on the UK Singles Chart and number 49 on the Billboard Hot 100
The ''Billboard'' Hot 100, also known as simply the Hot 100, is the music industry standard record chart in the United States for songs, published weekly by '' Billboard'' magazine. Chart rankings are based on sales (physical and digital), ...
in the United States. On the sleeve, the record was "dedicated to the original spirit of the Olympic Games".
See also
* Use of performance-enhancing drugs in the Olympic Games — 1984 Los Angeles * 16 Days of Glory – official filmReferences
Further reading
* Dyreson, Mark. "Global television and the transformation of the Olympics: The 1984 Los Angeles Games." ''International Journal of the History of Sport'' 32.1 (2015): 172–184. * Edelman, Robert Simon. "The Russians are not coming! The Soviet withdrawal from the games of the XXIII Olympiad." ''International Journal of the History of Sport'' 32.1 (2015): 9-36. * * Llewellyn, Matthew, John Gleaves, and Wayne Wilson. "The Historical Legacy of the 1984 Los Angeles Olympic Games." ''International Journal of the History of Sport'' 32#1 (2015) : 1–8. * Llewellyn, Matthew, John Gleaves, and Wayne Wilson, eds. ''The 1984 Los Angeles Olympic Games: Assessing the 30-Year Legacy'' (Routledge, 2017). *External links
*''Olympic Review'' 1984 – Official results
Official Report Vol. 1
Official Report Vol. 2
*
Egyptian judoka refused to attack his opponent's clearly injured right leg
{{Authority control Olympic Games in California Summer Olympics in Los Angeles Summer Olympics by year
Olympics
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a variety of competit ...
Olympics
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a variety of competit ...
Olympics, Summer
Olympics
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a variety of competit ...
July 1984 sports events in the United States
August 1984 sports events in the United States
Olym