1918 Central Powers Invasion Of Ukraine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Operation Faustschlag or (), also known as the Eleven Days' War, was a
In between on 25 December 1917, the Kiev-based
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
offensive in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. It was the last major offensive on the Eastern Front.
Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
forces were unable to put up any serious resistance due to the turmoil of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
and subsequent Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
. The armies of the Central Powers therefore captured huge territories in Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
, Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, forcing the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
government of Russia to sign the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
.
Background
After theFebruary Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
(March 1917) brought down the Tsarist
Tsarist autocracy (), also called Tsarism, was an autocracy, a form of absolute monarchy in the Grand Duchy of Moscow and its successor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire. In it, the Tsar possessed in principle authority and ...
monarchy of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and ...
was turned into the Russian Army
The Russian Ground Forces (), also known as the Russian Army in English, are the Army, land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Ground Forces are the protection of the state borders, combat on land, ...
. While vowing to continue the war, the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
and Petrograd Soviet
The Petrograd Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (, ''Petrogradsky soviet rabochih i soldatskikh deputatov'') was a city council of Petrograd (Saint Petersburg), the capital of Russia at the time. For brevity, it is usually called the Pet ...
made efforts to humanise and democratise its command structure from its notoriously corrupt Tsarist hierarchy, to one that based the authority of officers on the support of their troops, and would no longer tolerate abuses of power. In particular, the Petrograd Soviet Order No. 1 suggested more equal treatment between soldiers and officers of all ranks, and electing representatives to the Petrograd Soviet
The Petrograd Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (, ''Petrogradsky soviet rabochih i soldatskikh deputatov'') was a city council of Petrograd (Saint Petersburg), the capital of Russia at the time. For brevity, it is usually called the Pet ...
, while still maintaining a hierarchical command structure and military disciple. Although some Tsarist officers had fled during the February Revolution, or suppressed mutinies by their subordinate soldiers, order was generally maintained.
The post-imperial Russian Army even conducted the Kerensky Offensive in July 1917, but it resulted in a defeat. This further weakened the military and fuelled distrust in the Alexander Kerensky
Alexander Fyodorovich Kerensky ( – 11 June 1970) was a Russian lawyer and revolutionary who led the Russian Provisional Government and the short-lived Russian Republic for three months from late July to early November 1917 ( N.S.).
After th ...
-led Provisional Government, but the Bolshevik anti-Kerensky July Days
The July Days () were a period of unrest in Petrograd, Russia, between . It was characterised by spontaneous armed demonstrations by soldiers, sailors, and industrial workers engaged against the Russian Provisional Government. The demonstrat ...
protests in Petrograd as well as Polubotkivtsi uprising in Kiev (modern Kyiv
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
) were successfully repressed. Kerensky's government and the Petrograd Soviet consolidated domestic political order by proclaiming the Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federative Republic in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
on 1 September 1917, thereby definitively abolishing the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, as well as foiling the Kornilov affair
The Kornilov affair, or the Kornilov putsch, was an attempted military coup d'état by the commander-in-chief of the Russian Army, General Lavr Kornilov, from 10 to 13 September 1917 ( O.S., 28–31 August), against the Russian Provisional Gov ...
. Meanwhile, the Central Rada
The Central Rada of Ukraine, also called the Central Council (), was the All-Ukrainian council that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputies as well as few members of political, public, cultural and professional organizations o ...
was gaining influence in Ukraine, negotiating with the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
for an autonomous Ukraine within Russia, demands which Kerensky's government partially but not yet fully recognised (e.g. he recognised the General Secretariat of Ukraine
The General Secretariat of Ukraine () was the autonomous Ukrainian executive government of the Russian Republic from June 28, 1917, to January 22, 1918. For most of its existence it was headed by Volodymyr Vynnychenko.
The secretariat was cre ...
on 13 July 1917).
On 7 November 1917, during the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
, Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
of the Petrograd Soviet
The Petrograd Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (, ''Petrogradsky soviet rabochih i soldatskikh deputatov'') was a city council of Petrograd (Saint Petersburg), the capital of Russia at the time. For brevity, it is usually called the Pet ...
took power in the Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federative Republic in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
, rapidly transforming controlled areas into the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
(RSFSR), and announcing that "Soviet Russia" would be withdrawing from war. In the meantime during the Kiev Bolshevik Uprising
The Kiev Bolshevik Uprising (November 8–13, 1917) was a military struggle for power in Kiev after the fall of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution. It ended in victory for the Kievan Committee of the Bolshevik Party a ...
(8–13 November 1917, starting the Ukrainian–Soviet War
The Ukrainian–Soviet War () is the term commonly used in post-Soviet Ukraine for the events taking place between 1917 and 1921, nowadays regarded essentially as a war between the Ukrainian People's Republic and the Bolsheviks (Russian SFSR a ...
), Central Rada and Bolshevik forces jointly expelled the Russian Provisional Government's Kiev Military District
The Kiev Military District (; , abbreviated ) was a military district of the Imperial Russian Army and subsequently of the Red Army and Soviet Armed Forces. It was first formed in 1862, and was headquartered in Kiev (Kyiv) for most of its exist ...
, and the Central Rada proclaimed the autonomous Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) was a short-lived state in Eastern Europe. Prior to its proclamation, the Central Council of Ukraine was elected in March 1917 Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, as a result of the February Revolution, ...
(UPR) on 20 November 1917, which would have supreme authority within Ukraine until order in the Russian Republic would be restored (which would never happen).
Talks between the new Bolshevik-led Soviet Russian government and the Central Powers started in Brest-Litovsk
Brest, formerly Brest-Litovsk and Brest-on-the-Bug, is a city in south-western Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish town of Terespol, where the Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It serves as the admini ...
on 3 December 1917, and on the 17th a ceasefire went into effect. Peace talks soon followed, starting on 22 December. As negotiations began, the Central Powers presented demands for the territory that they had occupied during the 1914–1916 period, including Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
and western Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
. The Bolsheviks decided not to accept these terms and instead withdrew from the negotiations, eventually resulting in the breakdown of the ceasefire. Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky,; ; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky'' was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician, and political theorist. He was a key figure ...
, head of the Soviet Russian delegation, hoped to delay talks until a revolution occurred within Germany, which would force them out of the war.
Meanwhile on 17 December, the Kievan Bolsheviks demanded that the Central Rada of Ukraine recognise new Soviet government in Russia, but the Rada refused, and conflict erupted between them. The Bolsheviks fled from Kiev, regrouped in Kharkov (modern Kharkiv
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.
in eastern Ukraine) and established the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets
The Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets (; ) was a short-lived (1917–1918) Soviet republic of the Russian SFSR that was created by the declaration of the Kharkiv All-Ukrainian Congress of Soviets "About the self-determination of Ukraine" ...
there on 24 December 1917, subordinated to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
(RSFSR, better known as "Soviet Russia"). The Rada tried to retake control quickly, but had to give up Kharkov (19 December 1917 – 10 January 1918).In between on 25 December 1917, the Kiev-based
Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) was a short-lived state in Eastern Europe. Prior to its proclamation, the Central Council of Ukraine was elected in March 1917 Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, as a result of the February Revolution, ...
(UPR) was invited to join the peace talks, and sent its representatives to Brest-Litovsk to negotiate for Ukrainian independence. On 10–12 January 1918, the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
recognised the Ukrainian delegation at the talks in Brest as a separate and plenipotentiary to conduct negotiations on the behalf of Ukrainian People's Republic. On 22 January 1918, an overwhelming majority of the Central Rada voted in favour of Ukrainian independence, which was subsequently proclaimed in the Fourth Universal of the Ukrainian Central Council
The Fourth Universals (Central Rada), Universal of the Ukrainian Central Rada (Council) () is a significant state-political declaration that proclaimed the full state independence of the Ukrainian People's Republic.Western Front. While negotiations were ongoing, Soviet Commander-in-Chief
 On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from
On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from
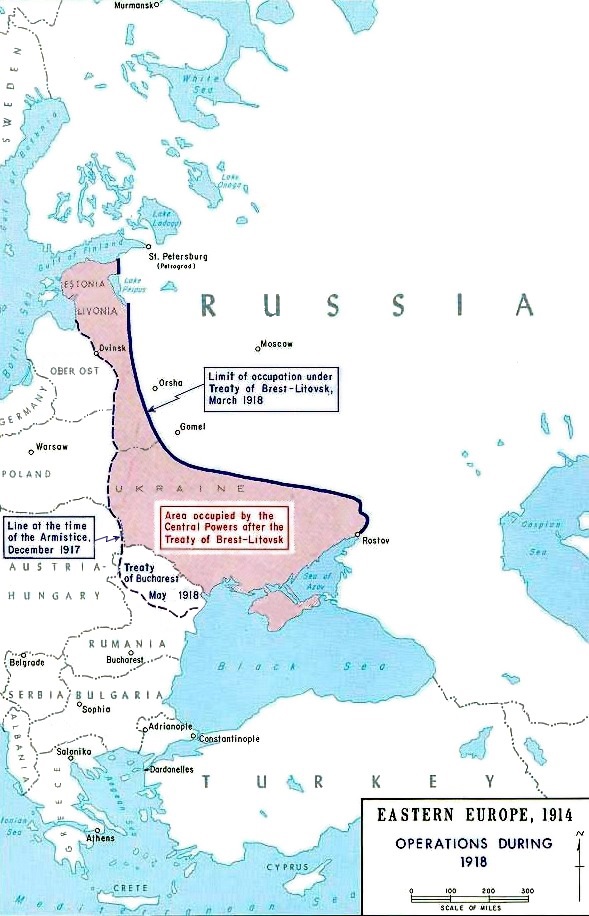 The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March 1918 only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to the southwestern region of the former Russian Empire. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the
The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March 1918 only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to the southwestern region of the former Russian Empire. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the Germany Takes Control of Crimea
On 13 March 1918, Ukrainian troops and the
by Mikhail Akulov,
Nikolai Krylenko
Nikolai Vasilyevich Krylenko (, ; 2 May 1885 – 29 July 1938) was an Old Bolshevik and Soviet politician, military commander, and jurist. Krylenko served in a variety of posts in the Soviet law, Soviet legal system, rising to become Minis ...
oversaw the demobilization and democratization of the Russian Army
The Russian Ground Forces (), also known as the Russian Army in English, are the Army, land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Ground Forces are the protection of the state borders, combat on land, ...
, introducing elected commanders, ending all ranks, and sending troops home. On 29 January, Krylenko ordered demobilization of the whole army. The same day, Bolshevik troops advancing on Kiev were defeated by the UPR in the Battle of Kruty
The Battle of Kruty () took place on January 29 or 30, 1918, near Kruty railway station (today the village of Pamiatne, Nizhyn Raion, Chernihiv Oblast), about northeast of Kyiv, Ukraine, which at the time was part of Nizhyn Povit of Chern ...
, while the Bolshevik Kiev Arsenal January Uprising
The Kiev Arsenal January Uprising (), sometimes simply called the January Uprising or the January Rebellion, was a Bolshevik-organized workers' armed revolt that started on 1918, at the Arsenal Factory in Kiev during the Ukrainian–Sovi ...
was repressed by UPR troops on 4 February. Nevertheless, the Bolsheviks conquered Kiev on 8 February 1918, forcing the Rada out of Ukraine's capital and to consider inviting the Central Powers to intervene. The German Chief of Staff, general Max Hoffmann
Carl Adolf Maximilian Hoffmann (25 January 1869 – 8 July 1927) was a German military officer and strategist. As a staff officer at the beginning of World War I, he was Deputy Chief of Staff of the 8th Army, soon promoted Chief of Staff. Hoff ...
, responded by signing the peace treaty
A peace treaty is an treaty, agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually country, countries or governments, which formally ends a declaration of war, state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an ag ...
with Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR) was a short-lived state in Eastern Europe. Prior to its proclamation, the Central Council of Ukraine was elected in March 1917 Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, as a result of the February Revolution, ...
on 9 February, and announced an end to the ceasefire with Soviet Russia in two-days time on 17 February, leading to the resumption of hostilities. The German and Austro-Hungarian authorities were happy to accept the invitation of the desperate Central Rada to occupy Ukraine, and secure food supplies for their armies and populations, while protecting the UPR against the advancing Bolshevik forces of Soviet Russia.
Offensive
 On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from
On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
towards Narva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, E ...
, the central force pushed towards Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow.
First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. It has been a regional capital for most of ...
, and the southern force towards Kiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
.
The northern force, consisting of 16 divisions, captured the key Daugavpils
Daugavpils (see also other names) is a state city in southeastern Latvia, located on the banks of the Daugava River, from which the city derives its name. The parts of the city to the north of the river belong to the historical Latvian region ...
junction on the first day. This was soon followed by the capture of Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
and securing Narva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, E ...
on 28 February. The 2nd Red Army regiment first entered battle with the German forces on February 23rd at the Cherekha and Mnoga, temporarily stalling the German advance until the 24th when the regiment was forced to retreat. By the 24th, fighting was already occurring in the outskirts of Pskov. On the 25th retreating Latvian Riflemen
The Latvian Riflemen (; ) were originally a military formation of the Imperial Russian Army assembled starting 1915 in Latvia in order to defend Baltic governorates against the German Empire in World War I. Initially, the battalions were forme ...
made their way to the battle from Latvia and began to reinforce Russian positions at Lyubatovo. On the 28th the battle finally ended with Pskov being fully taken.
The Red forces offered up severe resistance to the advancing German forces. They managed to kill 30 German officers, 34 non-commissioned German officers and 206 German soldiers when launching 2 shells at pyroxylin
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and ...
canister at an occupied German rail station.
The central forces of the 10th Army and XLI corps advanced towards Smolensk. On 21 February Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administra ...
was captured together with the headquarters of the Western Army Group. The Southern forces broke through the remains of the Russian Southwestern Army Group, capturing Zhitomir (modern Zhytomyr
Zhytomyr ( ; see #Names, below for other names) is a city in the north of the western half of Ukraine. It is the Capital city, administrative center of Zhytomyr Oblast (Oblast, province), as well as the administrative center of the surrounding ...
) on 24 February. Kiev was secured on 2 March, one day after the Ukrainian Central Rada troops had arrived there.
Central Powers armies had advanced over within a week, facing no serious Soviet resistance. German troops were now within of Petrograd
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
, forcing the Soviets to transfer their capital to Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
. The rapid advance was described as a "Railway War" (''der Eisenbahnfeldzug'') with German soldiers using Russian railways to advance eastward. General Hoffmann wrote in his diary on 22 February:
It is the most comical war I have ever known. We put a handful of infantrymen with machine guns and one gun onto a train and rush them off to the next station; they take it, make prisoners of the Bolsheviks, pick up few more troops, and so on. This proceeding has, at any rate, the charm of novelty.
Political impact
As the German offensive was ongoing, Trotsky returned to Petrograd. Most of the leadership still preferred continuing the war, even though Russia was in no position to do so, due to the destruction of its army. At this pointLenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
intervened to push the Soviet leadership into acceptance of German terms, which by now had become even harsher. He was backed by other senior communists to include Kamenev
Lev Borisovich Kamenev. ( Rozenfeld; – 25 August 1936) was a Russian revolutionary and Soviet politician. A prominent Old Bolsheviks, Old Bolshevik, Kamenev was a leading figure in the early Soviet government and served as a Deputy Premier ...
, Zinoviev Zinoviev, Zinovyev, Zinovieff (), or Zinovieva (feminine; Зино́вьева), as a Russian surname, derives from the personal name Zinovi, from Greek '' Zenobios''.
Notable people with the surname include:
* Alexander Dmitrievich Zinoviev (18 ...
, and Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
.
After a stormy session of Lenin's ruling council, during which the revolution's leader went so far as to threaten resignation, he obtained a 116 to 85 vote in favour of the new German terms. The vote in the Central Committee was even closer, seven in favour and six against. In the end, Trotsky switched his vote and German terms were accepted; on 3 March, the Bolsheviks signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
.
On 24 February, one day before the arrival of German troops to Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and ...
, the Estonian Salvation Committee
The Estonian Salvation Committee ( or ''Päästekomitee'') was the executive body of the Estonian Provincial Assembly that issued the Estonian Declaration of Independence.
The Salvation Committee was created on February 19, 1918, by the Provinci ...
declared the independence of Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
. German occupation authorities refused to recognize the Estonian government and Germans were installed in positions of authority.
Aftermath
 The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March 1918 only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to the southwestern region of the former Russian Empire. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the
The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March 1918 only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to the southwestern region of the former Russian Empire. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War was a civil war in Finland in 1918 fought for the leadership and control of the country between Whites (Finland), White Finland and the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (Red Finland) during the country's transition fr ...
. Under the treaty all Russian naval bases in the Baltic except Kronstadt
Kronstadt (, ) is a Russian administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg, near the head ...
were taken away, and the Russian Black Sea Fleet
The Black Sea Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov and the Mediterranean Sea. The Black Sea Fleet, along with other Russian ground and air forces on the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula, are subordin ...
warships in Odessa
ODESSA is an American codename (from the German language, German: ''Organisation der ehemaligen SS-Angehörigen'', meaning: Organization of Former SS Members) coined in 1946 to cover Ratlines (World War II aftermath), Nazi underground escape-pl ...
were to be disarmed and detained. The Bolsheviks also agreed to the immediate return of 630,000 Austrian prisoners-of-war.
With the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, Soviet Russia had given up Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus and Ukraine, enabling those territories to develop independently from Russian influence. Germany's intention was to turn these territories into political and territorial satellites, but this plan collapsed with Germany's own defeat within a year. After the German surrender, the Soviets made an attempt to regain lost territories. They were successful in some areas like Ukraine, Belarus and the Caucasus, but were forced to recognize the independence of the Baltic States, Finland, and Poland.
In Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, the Ukrainian People's Army
The Ukrainian People's Army (), also known as the Ukrainian National Army (UNA) or by the derogatory term Petliurivtsi (, ), was the army of the Ukrainian People's Republic (1917–1921). They were often quickly reorganized units of the former I ...
took control of the Donets Basin
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets (), is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv ...
in April 1918. In the same month, Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
was also cleared of the Bolsheviks by Ukrainian troops and the Imperial German Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Kingdom o ...
.New York Herald
The ''New York Herald'' was a large-distribution newspaper based in New York City that existed between 1835 and 1924. At that point it was acquired by its smaller rival the '' New-York Tribune'' to form the '' New York Herald Tribune''.
Hi ...
(18 May 1918)Austro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army, also known as the Imperial and Royal Army,; was the principal ground force of Austria-Hungary from 1867 to 1918. It consisted of three organisations: the Common Army (, recruited from all parts of Austria-Hungary), ...
had secured Odessa. On 5 April 1918, the German army took control of Yekaterinoslav
Dnipro is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper River, Dnipro River, from which it takes its name. Dnipro is t ...
, and 3 days later Kharkov
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.
.War Without Fronts: Atamans and Commissars in Ukraine, 1917-1919by Mikhail Akulov,
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
, August 2013 (page 102 and 103) The German/Austro-Hungarian victories in Ukraine were due to the apathy of the locals and the inferior fighting skills of Bolsheviks troops compared to their Austro-Hungarian and German counterparts.
In the Bolshevik government, Lenin consolidated his power; however, fearing the possibility of a renewed German threat along the Baltic, he moved the capital from Petrograd to Moscow on 12 March. Debates became far more restrained, and he was never again so strongly challenged as he was regarding the Brest-Litovsk treaty.
See also
*1918 Ukrainian coup d'état
The 1918 Ukrainian coup d'état or Hetman Coup () was a military coup d'état within the Ukrainian People's Republic on 29 April 1918. That day, farmers and landowners loyal to the Ukrainian lieutenant general Pavlo Skoropadskyi, with the supp ...
(29 April 1918)
* Ober Ost
The Supreme Commander of All German Forces in the East (), also known by its German abbreviation as , was both a high-ranking position in the armed forces of the German Empire as well as the name given to the occupied territories on the German s ...
* Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War was a civil war in Finland in 1918 fought for the leadership and control of the country between Whites (Finland), White Finland and the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (Red Finland) during the country's transition fr ...
* German Caucasus expedition
The German Caucasus expedition was a military expedition sent in late May 1918, by the German Empire to the formerly Russian Transcaucasia during the Caucasus Campaign of World War I. Its prime aim was to stabilize the pro-German Democrat ...
* Soviet westward offensive of 1918–1919
The Soviet westward offensive of 1918–1919 was part of the campaign by Soviet Russia into areas abandoned by the Ober Ost garrisons that were being withdrawn to Germany following that country's defeat in World War I. The initially successful of ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Faustschlag, Operation 1918 in Russia Battles of the Eastern Front (World War I) Battles of World War I involving Austria-Hungary Battles of World War I involving Russia Battles of World War I involving Germany Battles of the Russian Civil War involving Germany Battles involving the Ukrainian People's Republic Ukraine in World War I Kiev in the Russian Civil War Military operations of the Russian Civil War in 1918 1918 in Belarus February 1918 in Europe March 1918 in Europe Central Powers intervention in the Russian Civil War Soviet Russia in World War I Belarus in the Russian Civil War Latvia in the Russian Civil War Lithuania in the Russian Civil War Estonia in the Russian Civil War Treaty of Brest-Litovsk