0-6-0 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
is the
 In Victoria, the Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company operated four 0-6-0WT (well tank) goods locomotives; one of their 2-2-2WT passenger locomotives ("Titania", which became
In Victoria, the Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company operated four 0-6-0WT (well tank) goods locomotives; one of their 2-2-2WT passenger locomotives ("Titania", which became
 Tank locomotives used by Finland were the VR Class Vr1 and VR Class Vr4.
The VR Class Vr1s were numbered 530 to 544, 656 to 670 and 787 to 799. They had outside cylinders and were operational from 1913 to 1975. Built by
Tank locomotives used by Finland were the VR Class Vr1 and VR Class Vr4.
The VR Class Vr1s were numbered 530 to 544, 656 to 670 and 787 to 799. They had outside cylinders and were operational from 1913 to 1975. Built by
 '' Nederlandsch Indische Spoorweg Maatschappij'' (NIS) was known operating its 4 ft 8½ in (1,435 mm) gauge between Samarang–''Vorstenlanden'' (
'' Nederlandsch Indische Spoorweg Maatschappij'' (NIS) was known operating its 4 ft 8½ in (1,435 mm) gauge between Samarang–''Vorstenlanden'' ( In 1901, the '' Staatsspoorwegen'' (SS) acquired 24 units of 0-6-0Ts from ''Solo Vallei Waterwerken'' or Solo Valley Waterworks after they sold it due to debts as a result of swelling funds for the construction of irrigation canal dams on the banks of the Bengawan Solo and then, SS classified them as SS Class 500 (501–524). Not quite a long, a local private tramway company named ''Pasoeroean Stoomtram Maatschappij'' (PsSM) bought 2 units from SS to assist their sugar-freight transports to the port there along with their
In 1901, the '' Staatsspoorwegen'' (SS) acquired 24 units of 0-6-0Ts from ''Solo Vallei Waterwerken'' or Solo Valley Waterworks after they sold it due to debts as a result of swelling funds for the construction of irrigation canal dams on the banks of the Bengawan Solo and then, SS classified them as SS Class 500 (501–524). Not quite a long, a local private tramway company named ''Pasoeroean Stoomtram Maatschappij'' (PsSM) bought 2 units from SS to assist their sugar-freight transports to the port there along with their  In addition to operating trams for transportation facilities in the city of
In addition to operating trams for transportation facilities in the city of  In 1895–1896, two private-owned tramway company named ''Modjokerto Stoomtram Mij.'' (Mdj.SM) and ''Babat Djombang Stoomtram Mij.'' (BDSM) received the permit concession from the colonial Dutch government to build the line of Porong–Gunung Gangsir– Bangil–Pandaan–Japanan–
In 1895–1896, two private-owned tramway company named ''Modjokerto Stoomtram Mij.'' (Mdj.SM) and ''Babat Djombang Stoomtram Mij.'' (BDSM) received the permit concession from the colonial Dutch government to build the line of Porong–Gunung Gangsir– Bangil–Pandaan–Japanan–
 Type C2-Lts later classified as NIS 106 and NIS 107 were the first generation of 0-6-0 WT operated by NIS from
Type C2-Lts later classified as NIS 106 and NIS 107 were the first generation of 0-6-0 WT operated by NIS from
 This wheel arrangement was first introduced in 1905. Most of the preserved steam locomotives in the country are of this type as they were popular among
This wheel arrangement was first introduced in 1905. Most of the preserved steam locomotives in the country are of this type as they were popular among
 Of the total stock of standard-gauge locomotives operating on British railways in 1900, around 20,000 engines, over a third were 0-6-0 tender types. The ultimate British was the Q1 ''Austerity'' type, developed by the Southern Railway during the
Of the total stock of standard-gauge locomotives operating on British railways in 1900, around 20,000 engines, over a third were 0-6-0 tender types. The ultimate British was the Q1 ''Austerity'' type, developed by the Southern Railway during the
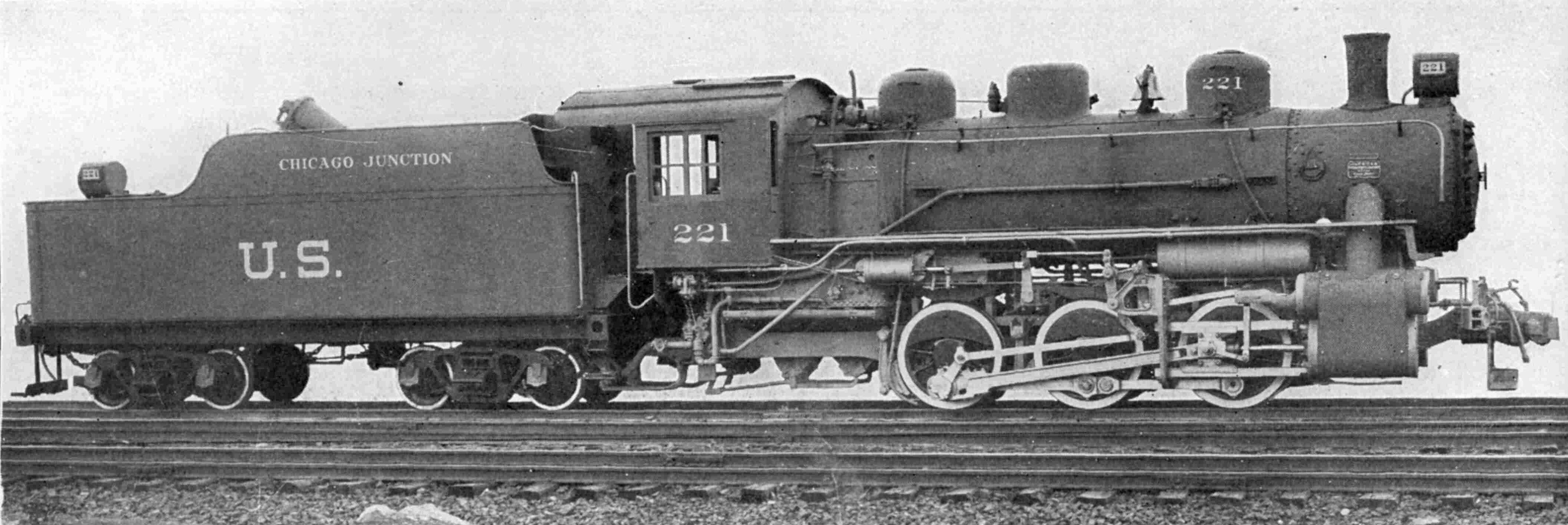 In addition, many of the railroads (and others) built numerous copies after the war. The
In addition, many of the railroads (and others) built numerous copies after the war. The 
Building a 1/8 scale Live Steam 0-6-0 locomotive
This site includes a full 1914 factory drawing of a Finnish 0-6-0 switcher. {{Whyte types
Whyte notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twenti ...
designation for steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s with a wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
of no leading wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used ...
s, six powered and coupled driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s on three axles, and no trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
s. Historically, this was the most common wheel arrangement used on both tender and tank locomotive
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
s in versions with both inside and outside cylinders.
In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives.
Overview
History
The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely usedwheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
for both tender and tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
steam locomotives. The type was also widely used for diesel switchers (shunters). Because they lack leading
In typography, leading ( ) is the space between adjacent lines of type; the exact definition varies.
In hand typesetting, leading is the thin strips of lead (or aluminium) that were inserted between lines of type in the composing stick to incre ...
and trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
s, locomotives of this type have all their weight pressing down on their driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s and consequently have a high tractive effort
In railway engineering, the term tractive effort describes the pulling or pushing capability of a locomotive. The published tractive force value for any vehicle may be theoretical—that is, calculated from known or implied mechanical proper ...
and factor of adhesion, making them comparatively strong engines for their size, weight and fuel consumption. On the other hand, the lack of unpowered leading wheels have the result that 0-6-0 locomotives are less stable at speed. They are therefore mostly used on trains where high speed is unnecessary.
Since 0-6-0 tender engines can pull fairly heavy trains, albeit slowly, the type was commonly used to pull short and medium distance freight
In transportation, cargo refers to goods transported by land, water or air, while freight refers to its conveyance. In economics, freight refers to goods transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. The term cargo is also used in ...
trains such as pickup goods trains along both main and branch line
A branch line is a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line. Branch lines may serve one or more industries, or a city or town not located ...
s. The tank engine versions were widely used as switching ( shunting) locomotives since the smaller 0-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven. The wheels on the earliest four-coupled locomotives were ...
types were not large enough to be versatile in this job. and larger switching locomotives, on the other hand, were too big to be economical or even usable on lightly built railways such as dockyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes more involve ...
s and goods yard
A goods station (also known as a goods yard or goods depot) or freight station is, in the widest sense, a railway station where, either exclusively or predominantly, goods (or freight), such as merchandise, parcels, and manufactured items, are lo ...
s, precisely the sorts of places where switching locomotives were most needed.
The earliest 0-6-0 locomotives had outside cylinders, as these were simpler to construct and maintain. However, once designers began to overcome the problem of the breakage of the crank axles, inside cylinder versions were found to be more stable. Thereafter this pattern was widely adopted, particularly in the United Kingdom, although outside cylinder versions were also widely used.
Tank engine versions of the type began to be built in quantity in the mid-1850s and had become very common by the mid-1860s.
Early examples
0-6-0 locomotives were among the first types to be used. The earliest recorded example was the ''Royal George'', built byTimothy Hackworth
Timothy Hackworth (22 December 1786 – 7 July 1850) was an English steam locomotive engineer who lived in Shildon, County Durham, England and was the first locomotive superintendent of the Stockton and Darlington Railway.
Youth and early work ...
for the Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected coal mining, collieries near with ...
in 1827.
Other early examples included the ''Vulcan'', the first inside-cylinder type, built by Charles Tayleur and Company in 1835 for the Leicester and Swannington Railway
The Leicester and Swannington Railway (L&SR) was one of England's first railways, built to bring coal from West Leicestershire collieries to Leicester, where there was great industrial demand for coal. The line opened in 1832, and included a tun ...
, and ''Hector'', a Long Boiler locomotive, built by Kitson and Company
Kitson and Company was a locomotive manufacturer based in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Early history
The company was started in 1835 by James Kitson (businessman), James Kitson at the Airedale Foundry, off Pearson Street, Hunslet, ...
in 1845 for the York and North Midland Railway
The York and North Midland Railway (Y&NMR) was an English railway company that opened in 1839 connecting York with the Leeds and Selby Railway, and in 1840, extended this line to meet the North Midland Railway at Normanton railway station, Norma ...
.
''Derwent'', a two-tender locomotive built in 1845 by William and Alfred Kitching
Whessoe is a company based in Darlington and on Teesside in North East England. It was formerly a supplier of chemical, oil and nuclear plant and instrumentation, and today is a manufacturer of low temperature storage.
History
Kitchings and ...
for the Stockton and Darlington Railway, is preserved at Darlington Railway Centre and Museum
Hopetown Darlington, previously known as Head of Steam and formerly known as the Darlington Railway Centre and Museum, is a railway museum located on the 1825 route of the Stockton and Darlington Railway, which was the world's first steam-powere ...
.
Suffixes
For a steamtank locomotive
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
, the suffix usually indicates the type of tank or tanks:
* 0-6-0Tside tanks
* 0-6-0STsaddle tank
* 0-6-0PTpannier tanks
* 0-6-0WTwell tank
Other steam locomotive suffixes include
* 0-6-0VBvertical boiler
* 0-6-0Ffireless locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of locomotive which uses reciprocating engines powered from a reservoir of compressed air or steam, which is filled at intervals from an external source. They offer advantages over conventional steam locomotives of ...
* 0-6-0Ggeared steam locomotive
A geared steam locomotive is a type of steam locomotive which uses gearing, usually reduction gearing, in the drivetrain, as opposed to the common directly driven design.
This gearing is part of the machinery within the locomotive and should not ...
For a diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), power source is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is con ...
, the suffix indicates the transmission type:
* 0-6-0DM mechanical transmission
* 0-6-0DH hydraulic transmission
* 0-6-0DEelectric transmission
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
Usage
All the major continental European railways used 0-6-0s of one sort or another, though usually not in the proportions used in the United Kingdom. As in the United States, European 0-6-0 locomotives were largely restricted to switching and station pilot duties, though they were also widely used on shortbranch line
A branch line is a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line. Branch lines may serve one or more industries, or a city or town not located ...
s to haul passenger and freight trains. On most branch lines, though, larger and more powerful tank engines tended to be favoured.
Australia
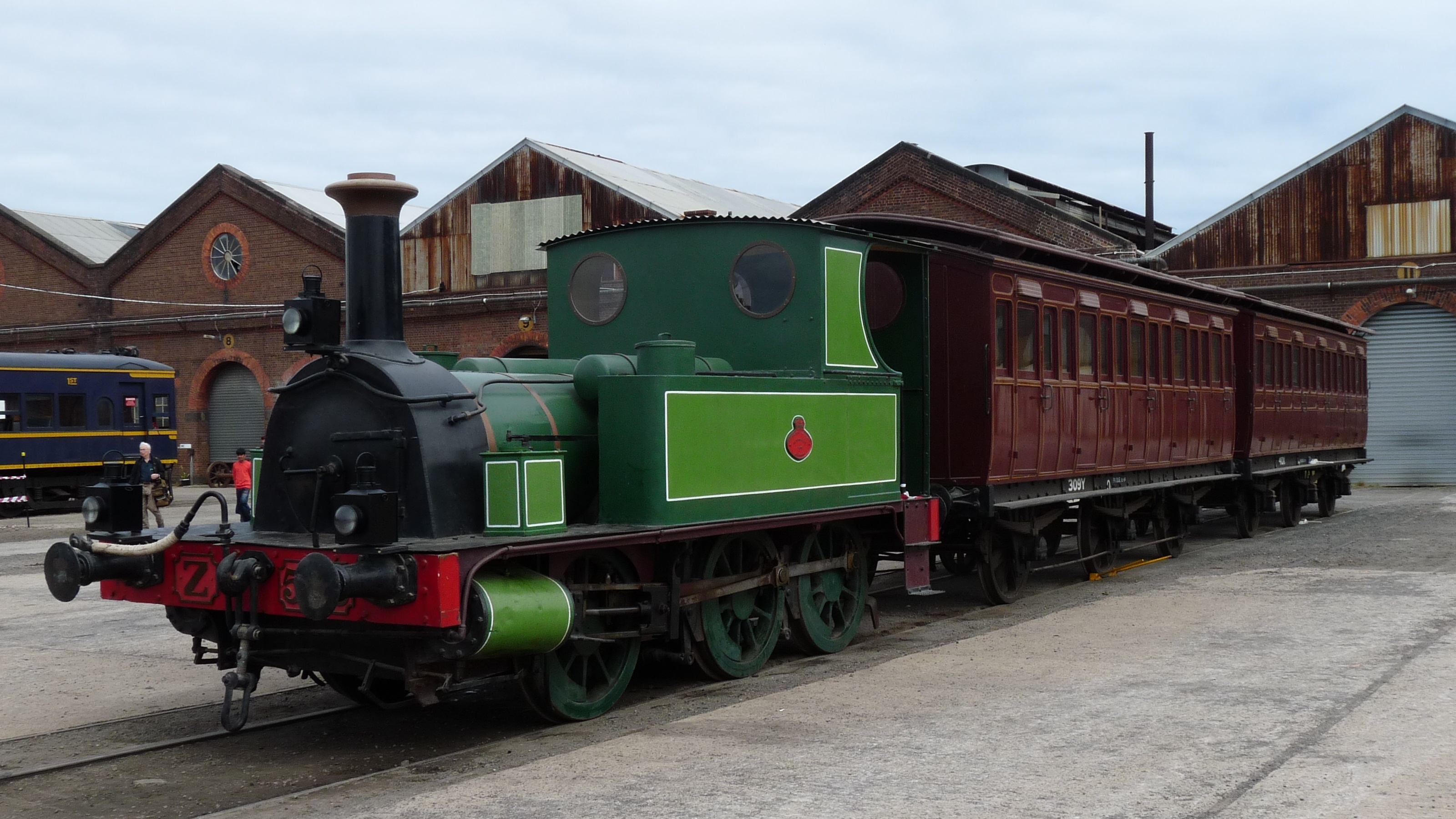
In New South Wales, the Z19 class was a tender type with this wheel arrangement. The Dorrigo Railway Museum collection includes seven Locomotives of the 0-6-0 wheel arrangement, including two Z19 class (1904 and 1923), three 0-6-0 saddle tanks and two 0-6-0 side tanks. In Victoria, the Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company operated four 0-6-0WT (well tank) goods locomotives; one of their 2-2-2WT passenger locomotives ("Titania", which became
In Victoria, the Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company operated four 0-6-0WT (well tank) goods locomotives; one of their 2-2-2WT passenger locomotives ("Titania", which became Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways (VR), trading from 1974 as VicRail, was the state-owned operator of most rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companie ...
number 34 in 1860) was converted to an in 1872.
On the Victorian Railways system there were O, P, Q, old R, Belgian R, new R, RY, T, U, Nos.103 & 105 (unclassed), old V, X, and Y class 0-6-0 tender locomotives, as well as a solitary Z class 0-6-0T (tank) engine. Three types of 0-6-0 Diesel shunting locomotives were also used by the Victorian Railways, the F, M, and W classes.
Finland
 Tank locomotives used by Finland were the VR Class Vr1 and VR Class Vr4.
The VR Class Vr1s were numbered 530 to 544, 656 to 670 and 787 to 799. They had outside cylinders and were operational from 1913 to 1975. Built by
Tank locomotives used by Finland were the VR Class Vr1 and VR Class Vr4.
The VR Class Vr1s were numbered 530 to 544, 656 to 670 and 787 to 799. They had outside cylinders and were operational from 1913 to 1975. Built by Tampella
Oy Tampella Ab was a Finland, Finnish heavy industry manufacturer, a maker of paper machines, locomotives, military weaponry, as well as wood-based products such as packaging. The company was based mainly in the Naistenlahti, Naistenlahti di ...
, Finland and Hanomag
Hanomag (Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG, ) was a German producer of steam locomotives, tractors, trucks and military vehicles in Hanover. Hanomag first achieved international fame by delivering numerous steam locomotives to Finland, Romania and ...
(Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG), they were nicknamed ''Chicken''. Number 669 is preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum.
The Vr4s were a class of only four locomotives, numbered 1400 to 1423, originally built as 0-6-0s by Vulcan Iron Works
Vulcan Iron Works was the name of several Ironworks, iron foundries in both England and the United States during the Industrial Revolution and, in one case, lasting until the mid-20th century. Vulcan (mythology), Vulcan, the Roman god of fir ...
, United States, but modified to 0-6-2s in 1951–1955, and re-classified as Vr5.
Finland's tender locomotives were the classes C1, C2, C3, C4, C5 and C6.
The Finnish Steam Locomotive Class C1s were a class of ten locomotives numbered 21 to 30. They were operational from 1869 to 1926. They were built by Neilson and Company and were nicknamed ''Bristollari''. Number 21, preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum, is the second oldest preserved locomotive in Finland.
The eighteen Class C2s were numbered 31 to 43 and 48 to 52. They were also nicknamed ''Bristollari''.
The C3 was a class of only two locomotives, numbered 74 and 75.
The thirteen Class C4s were numbered 62 and 78 to 89.
The fourteen Finnish Steam Locomotive Class C5s were numbered 101 to 114. They were operational from 1881 to 1930. They were built by Hanomag
Hanomag (Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG, ) was a German producer of steam locomotives, tractors, trucks and military vehicles in Hanover. Hanomag first achieved international fame by delivering numerous steam locomotives to Finland, Romania and ...
in Hannover and were nicknamed ''Bliksti''. No 110 is preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum.
The C6 was a solitary class of one locomotive, numbered 100.
Indonesia
Skirt tank locomotives
The colonial government of the Dutch East Indies ordered ''Nederlandsch Indische Spoorweg Maatschappij'' (NIS) to build a 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) railway line connectingYogyakarta
Yogyakarta is the capital city of the Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by Hamengkubuwono, a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an importan ...
to Magelang
Magelang () is one of six cities in Central Java, the Central Java Province of Indonesia that are administratively independent of the regencies in which they lie geographically. Each of these cities is governed by a mayor rather than a Subdivi ...
around 47 km (29 miles), which was the important city for the economic and defense sectors in Central Java
Central Java (, ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogya ...
and finished in 1898. By 1903–1907, they continued to build the line from Magelang to Secang–Ambarawa–Temanggung–Parakan because there were tobacco plantations. Just after the line finished, the NIS ordered around 12 units of 0-6-0 T (skirt tank) locomotives from Sachsische Maschinenfabrik (Hartmann), Germany and came in 1899–1908 and they were classified as NIS Class 250 (NIS 250–262), these locomotives were used to haul mixed freight and passenger trains. By 1914, NIS Class 251, 253, 255, 256, 257 were moved to Solo ( Purwosari)–Boyolali (23 km / 14 miles) line and Solo–Wonogiri–Baturetno (51 km / 32 miles) line for sugarcane freight and passenger transports, both of the lines were purchased by NIS from the ''Solosche Tramweg Maatschappij'' (SoTM) or Solo Tramway Company. They also acquired a 0-6-0T which had been operated by SoTM with similar characteristic and performance also its manufacturer which then completed its skirt tanks collection to 13 units and renumbered as NIS Class 259. At first, these 0-6-0Ts were saturated steam and the tanks are located at both low sides of boiler near the wheels, they have a water capacity of 3 m3 and their length is 7,940 mm and they used inside cylinders. The driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s of the locomotive has a distinctive feature, using the Golsdorf''superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, in some steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. ...
technology and cylinder with piston valve. During Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies
The Empire of Japan occupied the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) during World War II from March 1942 until after the end of the war in September 1945.
In May 1940, Germany German invasion of the Netherlands, occupied the Netherlands, and ma ...
in 1942, all of Dutch East Indies private or state owned railway locomotives were renumbered based on Japanese numberings, while the NIS Class 250s were renumbered to C16, C17 and C18 and still used after Indonesian Independence
The Proclamation of Indonesian Independence (, or simply ''Proklamasi'') was read at 10:00 Tokyo Standard Time on Friday 17 August 1945 in Jakarta. The declaration marked the start of the diplomatic and armed resistance of the Indonesian Nati ...
by ''Djawatan Kereta Api'' (DKA) or Department of the Railways of Railways of the Republic of Indonesia until the era of ''Perusahaan Jawatan Kereta Api'' (PJKA) or Railway Bureau Company, out of 13 locomotives only C16 03, C17 04 and C18 01 are preserved in Ambarawa Railway Museum.
Side tank locomotives
 '' Nederlandsch Indische Spoorweg Maatschappij'' (NIS) was known operating its 4 ft 8½ in (1,435 mm) gauge between Samarang–''Vorstenlanden'' (
'' Nederlandsch Indische Spoorweg Maatschappij'' (NIS) was known operating its 4 ft 8½ in (1,435 mm) gauge between Samarang–''Vorstenlanden'' (Solo
Solo or SOLO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Characters
* Han Solo, a ''Star Wars'' character
* Jacen Solo, a Jedi in the non-canonical ''Star Wars Legends'' continuity
* Kylo Ren (Ben Solo), a ''Star Wars'' character
* Napoleon Solo, fr ...
and Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta is the capital city of the Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by Hamengkubuwono, a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an importan ...
), Brumbung–Gundih and Kedungjati–Ambarawa all of which had been built in the 1870s. NIS expanded its rail network in '' Jogja'' (another term of Yogyakarta) by building branch lines between Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta is the capital city of the Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by Hamengkubuwono, a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an importan ...
–Brosot–Sewugalur in 1895 and Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta is the capital city of the Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by Hamengkubuwono, a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an importan ...
–Pundong in 1919. The line construction in and around Jogja was also to serve the freight transports of sugarcane from many sugar mills that operating in the royal land of Yogyakarta Sultanate
The Sultanate of Yogyakarta, officially the Sultanate of Ngayogyakarta Hadiningrat ( ; ), is a Javanese monarchy in Yogyakarta Special Region, in the Republic of Indonesia. The current head of the sultanate is Hamengkubuwono X.
Yogyakart ...
. NIS imported another 10 new 0-6-0 Ts as standard-gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
runner on Samarang–''Vorstenlanden'' and came in 2 batches in 1910 and 1912 from Werkspoor, N.V., Netherlands. The first batch engines were classified as NIS 151–156, those on second batch were NIS 157–160 and equipped with steam brake. These locomotives often worked on southern lines of ''Jogja''. Since Japanese occupation in 1942, the entire of NIS standard-gauge lines were converted to 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) gauge which made almost NIS standard gauge locomotives were found derelict. All of NIS 151–160 were also scrapped after Indonesian Independence, while the last one of them was found derelict in Pengok Workshop, Yogyakarta in 1974.
 In 1901, the '' Staatsspoorwegen'' (SS) acquired 24 units of 0-6-0Ts from ''Solo Vallei Waterwerken'' or Solo Valley Waterworks after they sold it due to debts as a result of swelling funds for the construction of irrigation canal dams on the banks of the Bengawan Solo and then, SS classified them as SS Class 500 (501–524). Not quite a long, a local private tramway company named ''Pasoeroean Stoomtram Maatschappij'' (PsSM) bought 2 units from SS to assist their sugar-freight transports to the port there along with their
In 1901, the '' Staatsspoorwegen'' (SS) acquired 24 units of 0-6-0Ts from ''Solo Vallei Waterwerken'' or Solo Valley Waterworks after they sold it due to debts as a result of swelling funds for the construction of irrigation canal dams on the banks of the Bengawan Solo and then, SS classified them as SS Class 500 (501–524). Not quite a long, a local private tramway company named ''Pasoeroean Stoomtram Maatschappij'' (PsSM) bought 2 units from SS to assist their sugar-freight transports to the port there along with their Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
0-4-0Tr engines in 1905 and 1908. The remaining owned by the SS were renumbered as SS Class 24–45 and used to aid mainline and rural tramlines, especially in East Java
East Java (, , ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost third of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern ...
between Garahan–Banyuwangi
Banyuwangi, previously known as Banjoewangi, is a large town and an administrative district (''kecamat5an'') which serves as the capital of Banyuwangi Regency at the far eastern end of the island of Java, Indonesia. It had a population of 106,000 ...
line using as transport for construction materials and metal bridge girders. After that, they were used as yard shunter and short harbor works at Banyuwangi and Panarukan
Panarukan is a district in Situbondo Regency, East Java, Indonesia. This district is about 8 km from the capital town of Situbondo to the west. It covers an area of 59.97 km2 and had a population of 59,084 as at mid 2023.Badan Pusat Statistik ...
. While 2 units of ''Solo Vallei'' which were acquired by PsSM renumbered to PsSM 6 Louisa (former SS 506) and PsSM 7 Marie (former SS 516), by 1911 they also purchased brand new of the same type PsSM 8 Nella. These locomotives were manufactured by John Cockerill & Cie., Belgium. After Japanese occupation, the SS Class 24–45 were renumbered as C13 class and PsSM 6–8 were reclassified as C22 class, the C13s were brought by Japanese throughout Java while the C22s were brought to Mojokerto as yard shunt duties. From all of these locomotives, not a single one remains. All of them were scrapped around the 1970s.
 In addition to operating trams for transportation facilities in the city of
In addition to operating trams for transportation facilities in the city of Semarang
Semarang (Javanese script, Javanese: , ''Kutha Semarang'') is the capital and largest city of Central Java province in Indonesia. It was a major port during the Netherlands, Dutch Dutch East Indies, colonial era, and is still an important regio ...
, Central Java, the private tramway company of Semarang-Joana or ''Semarang-Joana Stoomtram Maatschappij'' (SJS) was also extending the construction of their 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) lines to the east, which connected to Rembang, Blora and Cepu. The line of Semarang–Demak–Kudus–Rembang (197 km / 122 miles) was built in 1883–1900, while the Rembang–Blora–Cepu line (70 km / 43 miles) was completed in 1902. The line to Cepu was used for oil transportation and by this area there are fairly extensive teak forests. To serve the freight or passenger transportation on those lines, the SJS ordered 12 '0-6-0T' locomotives from Sächsische Maschinenfabrik (Hartmann) and came in 1898–1902 and classified as SJS Class 100 (101–112). Originally these locomotives had a funnel-shaped chimney, but was later replaced by a straight one and also equipped with a sand box which it made of brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. I ...
. During Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies
The Empire of Japan occupied the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) during World War II from March 1942 until after the end of the war in September 1945.
In May 1940, Germany German invasion of the Netherlands, occupied the Netherlands, and ma ...
, all of SJS Class 100s were renumbered to C19 and still used up today. After World War II ended, 2 units of C19 locomotives were moved from Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
to West Sumatra
West Sumatra () is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is on the west coast of the island of Sumatra and includes the Mentawai Islands off that coast. West Sumatra borders the Indian Ocean to the west, as well as the provinces of ...
at the Padang locomotive depot to meet the needs of rail transportation in West Sumatra. At the end of its service period around 1973, the C19 locomotive was used to haul the molasses tank wagons around Probolinggo–Pajarakan. From 12 of them, only C19 12 or SJS 112 is preserved at the Transportation Museum of Taman Mini Indonesia Indah
Taman Mini Indonesia Indah (; formerly Taman Mini "Indonesia Indah" with apostrophes—abbreviated as TMII) is a culture-based recreational area located in East Jakarta, Indonesia. Since July 2021, it is operated by InJourney Destination Managem ...
, Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
.
 In 1895–1896, two private-owned tramway company named ''Modjokerto Stoomtram Mij.'' (Mdj.SM) and ''Babat Djombang Stoomtram Mij.'' (BDSM) received the permit concession from the colonial Dutch government to build the line of Porong–Gunung Gangsir– Bangil–Pandaan–Japanan–
In 1895–1896, two private-owned tramway company named ''Modjokerto Stoomtram Mij.'' (Mdj.SM) and ''Babat Djombang Stoomtram Mij.'' (BDSM) received the permit concession from the colonial Dutch government to build the line of Porong–Gunung Gangsir– Bangil–Pandaan–Japanan–Mojokerto
Mojokerto ( (''Måjåkěrtå'')) is a city in East Java Province of Indonesia. It is located 40 km southwest of Surabaya, the provincial capital, and constitutes one of the component units of the Surabaya metropolitan area (known as Gerbang ...
and Sidoarjo–Tarik–Mojokerto–Jombang which were connected to '' Staatsspoorwegen'' (SS) lines. In addition, the BDSM was also built their line of Babat–Jombang to serve sugarcane freight transports which was connected to Nederlandsch-Indische Spoorweg Mij. (NIS) line at the Soerabaia NIS (Surabaya Pasar Turi), Babat and Cepu railway stations. The Mdj. SM completed their line construction in 1899, while BDSM completed in 1902 and 1913. To serve their rail transports, The Mdj. SM imported 4 locomotives in 1907–1926 (classified as MSM 11, 12, 15 and 16) and BDSM imported 2 of them in 1903 and 1903 (classified as BDSM 9 &10) from Georg Krauß
Georg Krauß, from 1905 ''Ritter von Krauß'' (25 December 1826 – 5 November 1906) was a German industrialist and the founder of the Krauss Locomotive Works (''Locomotivfabrik Krauß & Comp.'') in Munich, Germany and Linz, Upper Austria. The ...
, Germany. BDSM was defunct in 1916 due to the company's financial difficulties, so all of its assets including their two 0-6-0T units were acquired by SS (became SS 113 &114). After Japanese occupation, they were classified as C21 class. From 6 of them only 2 remained, the C21 02 of BDSM in INKA, Madiun
Madiun () is a city in the western part of East Java, Indonesia, known for its agricultural center. The city has been administratively separate from the surrounding Madiun Regency since the formation of the two bodies in 1950, but the city remain ...
and C21 03 of Mdj. SM in Taman Mini Indonesia Indah
Taman Mini Indonesia Indah (; formerly Taman Mini "Indonesia Indah" with apostrophes—abbreviated as TMII) is a culture-based recreational area located in East Jakarta, Indonesia. Since July 2021, it is operated by InJourney Destination Managem ...
.
Well Tank locomotives
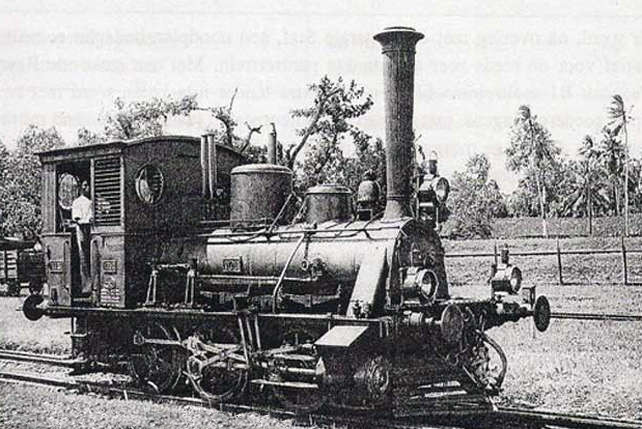
 Type C2-Lts later classified as NIS 106 and NIS 107 were the first generation of 0-6-0 WT operated by NIS from
Type C2-Lts later classified as NIS 106 and NIS 107 were the first generation of 0-6-0 WT operated by NIS from Hanomag
Hanomag (Hannoversche Maschinenbau AG, ) was a German producer of steam locomotives, tractors, trucks and military vehicles in Hanover. Hanomag first achieved international fame by delivering numerous steam locomotives to Finland, Romania and ...
, Germany and came in 1901. These C2-Lts were wood and coal burners and had a maximum speed of 40 kilometres per hour (24.8 miles per hour). These locomotives often worked on southern lines of ''Jogja''. Since Japanese occupation in 1942, the entire of NIS standard-gauge lines were converted to 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) gauge which made almost NIS standard gauge locomotives were found derelict. Just before occupation, NIS 106 and 107 were converted became armored locomotive by J. C. Jonker who was the former head of NIS traction depot. The last known NIS 106 was re-gauged to 1,067 mm and operating as short harbor works in Semarang in July 1945 before being scrapped by Japanese. The chassis of NIS 107 still be found in front of SMK Negeri 2 Yogyakarta (state vocational school), while the most parts of it had been stripped down by the Japanese.
New Zealand
In New Zealand the 0-6-0 design was restricted to tank engines. TheHunslet
Hunslet () is an inner-city area in south Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It is southeast of the Leeds city centre, city centre and has an industrial past.
It is situated in the Hunslet and Riverside (ward), Hunslet and Riverside ward of Lee ...
-built M class of 1874 and Y class of 1923 provided 7 examples, however the F class built between 1872 and 1888 was the most prolific, surviving the entire era of NZR steam operations, with 88 examples of which 8 were preserved.
Philippines
sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
, sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
and coal mine owners.
Tank and tank-tender locomotives
The first operators of the type were the Manila Railway with its 0-6-0T ''Cabanatuan'' class, named after the now-defunct branch line towardsCabanatuan
Cabanatuan, officially the City of Cabanatuan (; ; kapampangan language, Kapampangan: ''Lakanbalen/Ciudad ning Cabanatuan''), is a Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, component city in the province of Nueva Ecija, Philippines. Acco ...
. Two of these locomotives were built, No. 777 ''Cabanatuan'' and No. 778 ''Batangas''. It was followed by the 0-6-2ST ''Cavite'' class of 1906, after also defunct Naic
Naic (), officially the Municipality of Naic (), is a municipality in the province of Cavite, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 160,987 people.
Etymology
Naic, Cavite is one of the former barrios of Maragond ...
branch of the PNR South Main Line
The PNR South Main Line (, also known as Southrail and formerly the Main Line South) is one of the two trunk lines that form the Philippine National Railways' network in the island of Luzon, Philippines. It was opened in stages between 1916 a ...
. This was later known as the ''V'' class. No. 777 ''Cabanatuan'' and No. 1007 ''Dagupan'' (originally ''Cavite'') are in display in front of the Philippine National Railways
The Philippine National Railways (PNR) (; ) is a government-owned and controlled corporation, state-owned railway company in the Philippines which operates one commuter rail service between Laguna (province), Laguna and Quezon, and local servic ...
headquarters at Tutuban station in Tondo, Manila
Tondo is a district located in Manila, Philippines. It is the largest, in terms of area and population, of Manila's sixteen districts, with a census-estimated 654,220 people in 2020. It consists of two congressional districts. It is also the se ...
.
This type was also used by the 3 ft gauge railways in Negros
Negros (, , ) is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of . The coastal zone of the southern part of Negros is identified as a site of highest marine biodiversity importance in the Coral Tr ...
Island. Central Azucarera de Bais operated 3 tank locomotives. The De La Rama conglomerate of Bago, Negros Occidental
Bago, officially the City of Bago (; ), is a Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, component city in the Provinces of the Philippines, province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of ...
led by Esteban de la Rama (1866–1947) had Locomotive No. 2. Other operators include Ma-Ao Sugar Central, the National Coal Company in which used this locomotive as a 0-6-0STT tank tender, and San Carlos Milling Company No. 4 of 1919.
Tender locomotives
The Hawaiian-Philippine Company of Silay,Negros Occidental
Negros Occidental (; ), officially the Province of Negros Occidental (; ), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Negros, Negros Island. Its capital is the city of Bacolod, of which it is geographically s ...
operates three 0-6-0 tender locomotives and are the last active steam locomotives in the country. The three locomotives are No. 2 ''Peter Francis Davies'' of 1919, No. 5 ''The Isabella Curran'' of 1920 and No. 7 ''Edwin H. Herkes'' of 1928. These are still used for its heritage railway
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (U.S. usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) ...
service after the rail freight service was terminated in 2021. No. 7 was later renamed as the second ''Isabella Curran''. Aside from these, the company also had two more locomotives of the same arrangement that were most likely scrapped.
Other known operators of tender locomotives include Central Azucarera de Bais with its Baldwin-built also numbered No. 7, North Negros Sugar Company, San Carlos No. 5 of 1926, and Tabacalera Central No. 5 of 1927. Out of these, only the Tabacalera Central No. 5 uses the 3 ft 6 in gauge lines being operated in Tarlac
Tarlac, officially the Province of Tarlac (; ; ; ; ), is a landlocked Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon Regions of the Philippines, region. It had a population of 1,503,456 people according to ...
while the other units use the 3 ft gauge.
South Africa
Cape gauge
In 1876, theCape Government Railways
The Cape Government Railways (CGR) was the government-owned railway operator in the Cape Colony from 1874 until the creation of the South African Railways (SAR) in 1910.
History Private railways
The first railways at the Cape were privately ow ...
(CGR) placed a pair of 0-6-0 Stephenson's Patent permanently coupled back-to-back tank locomotives in service on the Cape Eastern system. They worked out of East London in comparative trials with the experimental Fairlie locomotive that was acquired in that same year. What were these, 2-6-0T or 0-6-0T?
The Natal Harbours Department placed a single saddle-tank locomotive in service in 1879, named ''John Milne''.
The Natal Government Railways
The Natal Government Railways (NGR) was formed in January 1877 in the Colony of Natal.
In 1877, the Natal Government Railways acquired the Natal Railway Company for the sum of £40,000, gaining the line from the Point to Durban and from Durban ...
placed a single locomotive in shunting service in 1880, later designated Class K, virtually identical to the Durban Harbour's John Milne and built by the same manufacturer.
In 1882, two 0-6-0 tank locomotives entered service on the private Kowie Railway between Grahamstown and Port Alfred. Both locomotives were rebuilt to a 4-4-0T wheel arrangement in 1884.
In 1890, the Nederlandsche-Zuid-Afrikaansche Spoorweg-Maatschappij of the Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek (Transvaal Republic) placed six 18 Tonner 0-6-0ST locomotives in service on construction work.
In 1896 and 1897, three 26 Tonner saddle-tank locomotives were built for the Pretoria-Pietersburg Railway (PPR) by Hawthorn, Leslie and Company. These were the first locomotives to be obtained by the then recently established PPR. Two of these, named ''Nylstroom'' and ''Pietersburg'', came into SAR stock in 1912 and survived into the 1940s.Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer's Office, Pretoria, January 1912, pp. 2, 11, 13 (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000)
In 1901, a single 0-6-0T harbour locomotive built by Hudswell, Clarke was delivered to the Harbours Department of Natal. It was named ''Edward Innes'' and retained this name when it was taken onto the SAR roster in 1912.
Two saddle-tank locomotives were supplied to the East London Harbour Board in 1902, built by Hunslet. Both survived until the 1930s, well into the SAR era.
In 1904, a single saddle tank harbour locomotive, named ''Sir Albert'', was built by Hunslet for the Harbours Department of Natal. It came into SAR stock in 1912 and was withdrawn in 1915.
Narrow gauges
In 1871, two gauge tank locomotives, built by the Lilleshall Company of Oakengates, Shropshire in 1870 and 1871, were placed in service by the Cape of Good Hope Copper Mining Company. Named ''John King'' and ''Miner'', they were the first steam locomotives to enter service on the hitherto mule-powered Namaqualand Railway between Port Nolloth and the Namaqualand copper mines aroundO'okiep
Okiep is a small town in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, and was in the 1870s ranked as having the richest copper mine in the world. The town is on the site of a spring that was known in the Khoekhoe language of the Nama people as ''U- ...
in the Cape Colony.
In 1902, Arthur Koppel, acting as agent, imported a single 0-6-0 narrow gauge tank steam locomotive for a customer in Durban. It was then purchased by the Cape Government Railways and used as construction locomotive on the Avontuur branch from 1903. In 1912, this locomotive was assimilated into the South African Railways and in 1917 it was sent to German South West Africa during the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
campaign in that territory.
South West Africa
Between 1898 and 1905, more than fifty pairs of Zwillinge twin tank steam locomotives were acquired by the ''Swakopmund-Windhuk Staatsbahn'' (Swakopmund
Swakopmund ("Mouth of the Swakop River, Swakop") is a city on the coast of western Namibia, west of the Namibian capital Windhoek via the B2 road (Namibia), B2 main road. It is the capital of the Erongo Region, Erongo administrative district. It ...
-Windhoek
Windhoek (; ; ) is the capital and largest city of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around above sea level, almost exactly at the country's geographical centre. The population of Windhoek, which ...
State Railway) in ''Deutsch-Südwest-Afrika
German South West Africa () was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles.
German rule over this territory was punctuated by ...
'' (DSWA, now Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
). Zwillinge locomotives were a class of small ''Schmalspur'' (narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with Minimum railw ...
) tank steam locomotives that were built in Germany in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. As indicated by their name ''Zwillinge'' (twins), they were designed to be used in pairs, semi-permanently coupled back-to-back at the cabs, allowing a single footplate crew to fire and control both locomotives. The pairs of locomotives shared a common manufacturer's works number and engine number, with the units being designated as A and B. By 1922, when the SAR took control of all railway operations in South West Africa (SWA), only two single Illinge locomotives survived to be absorbed onto the roster of the SAR.
In 1907, the German Administration in DSWA acquired three Class Hc tank locomotives for the narrow gauge Otavi Mining and Railway Company. One more entered service in 1910, and another was obtained by the South African Railways in 1929.
In 1911, the ''Lüderitzbucht Eisenbahn'' (Lüderitzbucht Railway) placed two Cape gauge 0-6-0T locomotives in service as shunting engines. They were apparently no longer in service when all railways in the territory came under the administration of the South African Railways in 1922.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1948). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued).'' South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, January 1948. p. 31.
Switzerland
During the Second World War,Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
converted some 0-6-0 shunting engines into electric–steam locomotives.
United Kingdom
The 0-6-0 inside-cylinder tender locomotive type was extremely common in Britain for more than a century and was still being built in large numbers during the 1940s. Between 1858 and 1872, 943 examples of the John Ramsbottom DX goods class were built by theLondon and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world.
Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connec ...
and the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company before the Railways Act 1921, 1923 Grouping. It was Incorporation (business)#Incorporation in the United Kingdom, incorpo ...
. This was the earliest example of standardisation and mass production of locomotives.H.C. Casserley, ''The historic locomotive pocket book'', Batsford, 1960, p.23.
 Of the total stock of standard-gauge locomotives operating on British railways in 1900, around 20,000 engines, over a third were 0-6-0 tender types. The ultimate British was the Q1 ''Austerity'' type, developed by the Southern Railway during the
Of the total stock of standard-gauge locomotives operating on British railways in 1900, around 20,000 engines, over a third were 0-6-0 tender types. The ultimate British was the Q1 ''Austerity'' type, developed by the Southern Railway during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
to haul very heavy freight trains. It was the most powerful steam design produced in Europe.
Similarly, the 0-6-0 tank locomotive
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
s became the most common locomotive type on all railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
s throughout the 20th century. All of the Big Four companies to emerge from the Railways Act, 1921 grouping used them in vast numbers. The Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
, in particular, had many of the type, most characteristically in the form of the pannier tank
A tank locomotive is a steam locomotive which carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender (rail), tender. Most tank engines also have Fuel bunker, bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a #Tender ...
locomotive that remained in production well past railway nationalisation in 1948.
When diesel shunters began to be introduced, the 0-6-0 type became the most common. Many of the British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commis ...
shunter types were , including Class 03, the standard light shunter, and Class 08 and Class 09, the standard heavier shunters.
United States
In theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, huge numbers of 0-6-0 locomotives were produced, with the majority of them being used as switchers. The USRA 0-6-0 was the smallest of the USRA Standard
The USRA standard locomotives and railroad cars were designed by the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized rail system of the United States during World War I. 1,870 steam locomotives and over 100,000 railroad cars were built t ...
classes designed and produced during the brief government control of the railroads through the USRA during the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. 255 of them were built and ended up in the hands of about two dozen United States railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
s.
 In addition, many of the railroads (and others) built numerous copies after the war. The
In addition, many of the railroads (and others) built numerous copies after the war. The Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
rostered over 1,200 0-6-0 types over the years, which were classed as class B on that system. The United States 0-6-0s were generally tender locomotive
A tender is a special railroad car, rail vehicle hauled by a steam locomotive containing its fuel (wood fuel, wood, coal, fuel oil, oil or torrefaction, torrefied biomass) and water. Steam locomotives consume large quantities of water compared ...
s.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, no fewer than 514 USATC S100 Class 0-6-0 tank engines were built by the Davenport Locomotive Works, for use by the United States Army Transportation Corps in both Europe and North Africa. Some of these remained in service long after the war, having been purchased or otherwise adopted by the countries where they were used. These included Austria, Egypt, France, Iraq, the United Kingdom and Yugoslavia.
The fourteen SR USA Class engines purchased by the British Southern Railway in 1946 remained in service well into the 1960s. Designed to be extremely strong but easy to maintain, these engines had a very short wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front ...
that allowed them to operate on dockyard railways.

References
External links
Building a 1/8 scale Live Steam 0-6-0 locomotive
This site includes a full 1914 factory drawing of a Finnish 0-6-0 switcher. {{Whyte types