–Ę—Ä–ł–ļ–ĺ–Ľ–ĺ—Ä –Ę–í on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The national flag of the
 In 1693, Franz Timmerman received the order to build merchant ships in Arkhangelsk and trade with Europe. He was told to display the two-headed eagle spread with wings, with three crowns over it. On the chest of the eagle, a warrior on horseback was to be displayed with a spear, in a military harness. The same eagle was also to hold a sceptre with the right leg and an apple with a crest with the left. The same instructions were given to other traders.
According to Dutch newspapers, in June 1694, a 44-gun frigate bought by Russia and built in Rotterdam stood in the Amsterdam roadstead under the white-blue-red flag.
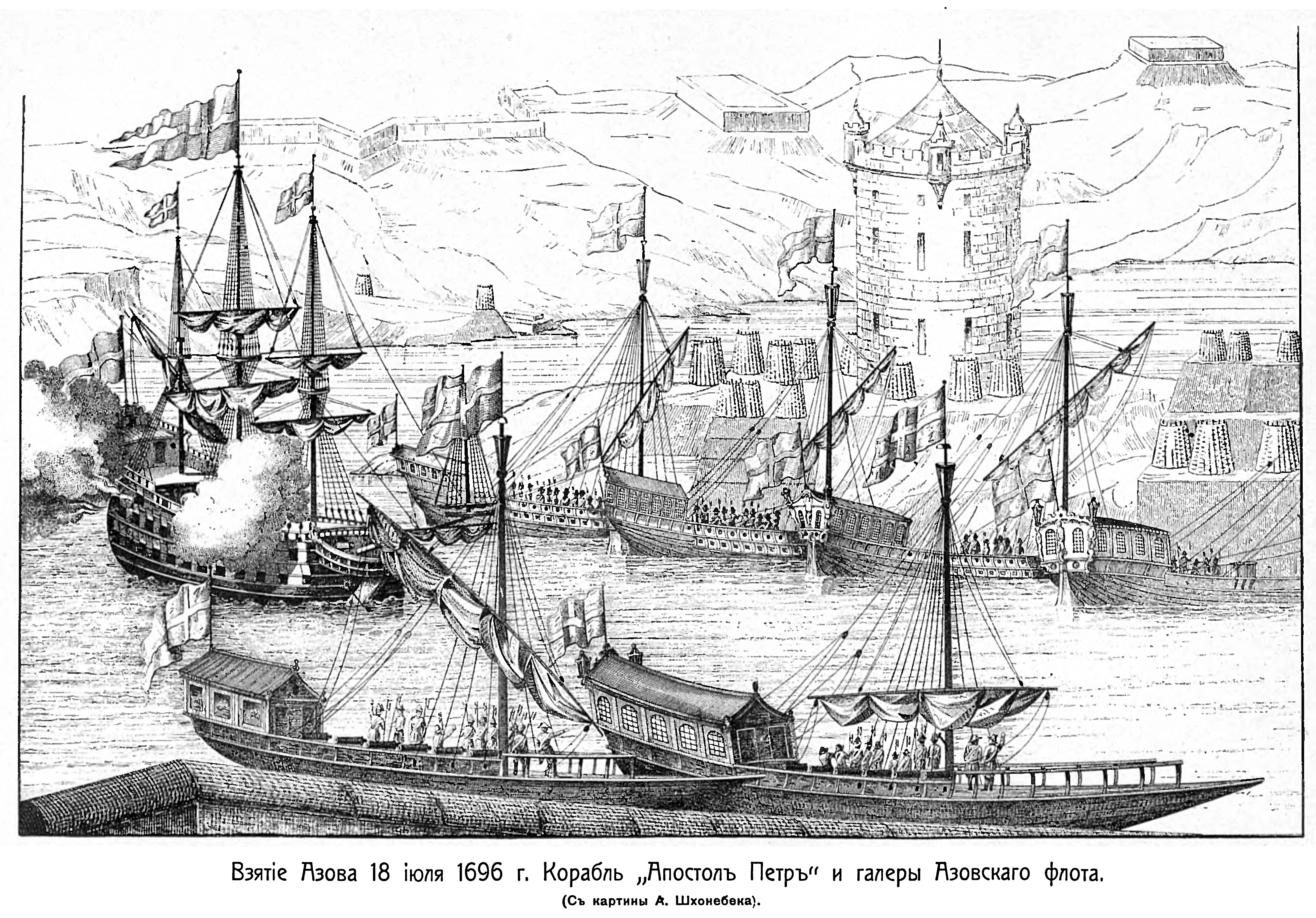
In 1696, at the mouth of the river Don, a Russian flotilla of armed rowboats blocked the supply of the Ottoman fortress of Azov. On the 1700 engraving by Adrian Shkhonebek, ''Taking the fortress of Azov. 1696'', depicts the ships carrying rectangular panels on the flagpoles, the heraldic shading of which shows that some of the flags are blue with a straight red cross, and the rest are white with a straight red cross. A number of researchers doubt the accuracy of Shkonebek's engraving because he was not a witness to the events.
Images of various white-blue-red Russian flags are present in the three later paintings of
In 1693, Franz Timmerman received the order to build merchant ships in Arkhangelsk and trade with Europe. He was told to display the two-headed eagle spread with wings, with three crowns over it. On the chest of the eagle, a warrior on horseback was to be displayed with a spear, in a military harness. The same eagle was also to hold a sceptre with the right leg and an apple with a crest with the left. The same instructions were given to other traders.
According to Dutch newspapers, in June 1694, a 44-gun frigate bought by Russia and built in Rotterdam stood in the Amsterdam roadstead under the white-blue-red flag.
In 1696, at the mouth of the river Don, a Russian flotilla of armed rowboats blocked the supply of the Ottoman fortress of Azov. On the 1700 engraving by Adrian Shkhonebek, ''Taking the fortress of Azov. 1696'', depicts the ships carrying rectangular panels on the flagpoles, the heraldic shading of which shows that some of the flags are blue with a straight red cross, and the rest are white with a straight red cross. A number of researchers doubt the accuracy of Shkonebek's engraving because he was not a witness to the events.
Images of various white-blue-red Russian flags are present in the three later paintings of
 During the
During the
: –£–ļ–į–∑ –ü—Ä–Ķ–∑–ł–ī–Ķ–Ĺ—ā–į –†–§ –ĺ—ā 11 December 1993 No. 2126 // –°–ĺ–Ī—Ä–į–Ĺ–ł–Ķ –į–ļ—ā–ĺ–≤ –ü—Ä–Ķ–∑–ł–ī–Ķ–Ĺ—ā–į –ł –ü—Ä–į–≤–ł—ā–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Ā—ā–≤–į –†–ĺ—Ā—Ā–ł–Ļ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ļ –§–Ķ–ī–Ķ—Ä–į—Ü–ł–ł. 1993. No. 51. –°—ā. 4928. In Article 1 of the decree, the flag was described as a "rectangular panel of three equal horizontal stripes: the top ‚Äď white, middle ‚Äď blue, and bottom ‚Äď red, with a width to length ratio of 2:3." The pre-1993 flag is still depicted on Russian license plates, as the design specifications were finalized and published 6 months prior to Yeltsin's decree. The National Flag Day is an official holiday in Russia, established in 1994. It is celebrated on 22 August, the day of the victory over putschists in 1991, but employees remain at work.
Official image of the Russian flag, on the official site of the Russian President
Federal Constitutional Law of 25 December 2000 No. 1-FKZ "On the State Flag of the Russian Federation" (including amendments)
pravo.gov.ru
Flag of Russia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Flag of Russia
Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(, ) is a tricolour
A triband is a vexillological style which consists of three stripes arranged to form a flag. These stripes may be two or three colours, and may be charged with an emblem in the middle stripe. Not all tribands are tricolour flags, which requires t ...
of three equal horizontal bands: white on the top, blue in the middle, and red on the bottom.
The design was first introduced by Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, —Ü–į—Ä, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
Peter the Great
Peter I (, ;
‚Äď ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned j ...
in 1693, and in 1705 it was adopted as the civil ensign
A civil ensign is an ensign (maritime flag) used by civilian vessels to denote their nationality. It can be the same or different from the state ensign and the naval ensign (or war ensign). It is also known as the merchant ensign or merchant flag ...
of the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
; the flag continued to be used as a civil ensign under the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. In 1858, Emperor Alexander II declared the black-yellow-white tricolour as the national flag, and in 1896 it was replaced by the white-blue-red tricolour by Nicholas II
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. He married ...
. In 1917, following the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
, the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
banned the tricolour, though it continued to be flown by the White movement
The White movement,. The old spelling was retained by the Whites to differentiate from the Reds. also known as the Whites, was one of the main factions of the Russian Civil War of 1917‚Äď1922. It was led mainly by the Right-wing politics, right- ...
during the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
. The flag of the Russian SFSR
The penultimate USSR-era flag was adopted by the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) in 1954 and used until 1991. The flag of the Russian SFSR was a defacement of the flag of the USSR. The constitution stipulated:
The symb ...
was a red field with its Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
acronym "–†–°–§–°–†" in the upper-left corner, and after 1954, was a red field with a vertical blue stripe on the left and a gold hammer and sickle
The hammer and sickle (Unicode: ) is a communist symbol representing proletarian solidarity between industrial and agricultural workers. It was first adopted during the Russian Revolution at the end of World War I, the hammer representing wo ...
.
Shortly after the August Coup
The 1991 Soviet coup attempt, also known as the August Coup, was a failed attempt by hardliners of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) to Coup d'état, forcibly seize control of the country from Mikhail Gorbachev, who was President ...
in 1991, the Russian SFSR adopted the imperial tricolour as the national flag of Russia, although with slightly different dimensions and colour shades than the current version. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-–Ě of ...
at the end of year, the newly independent Russian Federation inherited the redesigned flag, and its current proportions and shades were specified by President Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin (1 February 1931 ‚Äď 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician and statesman who served as President of Russia from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) from 1961 to ...
in 1993.
Origin
Two accounts of the flag's origin connect it to thetricolour
A triband is a vexillological style which consists of three stripes arranged to form a flag. These stripes may be two or three colours, and may be charged with an emblem in the middle stripe. Not all tribands are tricolour flags, which requires t ...
used by the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
(the Statenvlag
The ''Statenvlag'' ("States Flag") is the name of the flag of the States-General of the Dutch Republic, the red-white-blue tricolour flag replacing the older orange-white-blue Prince's Flag in the mid 17th century.
The modern national flag of ...
, later the flag of the Netherlands
The national flag of the Netherlands () is a horizontal tricolour (flag), tricolour of red, white, and blue. The current design originates as a variant of the late 16th century orange-white-blue ''Prince's Flag, Prinsenvlag'' ("Prince's Fla ...
).
The earliest mention of the flag occurs during the reign of Alexis I
Alexei Mikhailovich (, ; ‚Äď ), also known as Alexis, was Tsar of all Russia from 1645 until his death in 1676. He was the second Russian tsar from the House of Romanov.
He was the first tsar to sign laws on his own authority and his council ...
, in 1668, and is related to the construction of the first Russian naval ship, the frigate ''Oryol''. According to one source, the ship's Dutch lead engineer Butler faced the need for the flag, and issued a request to the Boyar Duma
A duma () is a History of Russia, Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions.
The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were for ...
, to "ask His Royal Majesty as to which (as is the custom among other nations) flag shall be raised on the ship". The official response merely indicated that, as such issue is as yet unprecedented, even though the land forces do use (apparently different) flags, the tsar ordered that his (Butler's) opinion be sought about the matter, asking specifically as to the custom existing in his country.
A different account traces the origins of the Russian flag to tsar Peter the Great
Peter I (, ;
‚Äď ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned j ...
's visits to Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the ...
in 1693 and 1694. Peter was keenly interested in shipbuilding in the European style, different from the barges ordinarily used in Russia at the time. In 1693, Peter had ordered a Dutch-built frigate from Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
. In 1694 when it arrived, the Dutch red, white, and blue banner flew from its stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. O ...
. Peter decided to model Russia's naval flag after that banner by assigning meaning and reordering the colours.
The Dutch flag book of 1695 by Carel Allard, printed only a year after Peter's trip to Western Europe, describes the tricolour with a double-headed eagle
The double-headed eagle is an Iconology, iconographic symbol originating in the Bronze Age. The earliest predecessors of the symbol can be found in Mycenaean Greece and in the Ancient Near East, especially in Mesopotamian and Hittite Empire#icon ...
bearing a shield on its breast and wearing a golden crown over both of its heads.
History
A study on clarifying thenational colours
National colours are frequently part of a country's set of national symbols. Many states and nations have formally adopted a set of colours as their official "national colours" while others have '' de facto'' national colours that have become well ...
of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
based on disquisition on documents of the Moscow Archive of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Empire
The Ministry of Justice was one of the Russian Empire's central public institutions and was established on 8 September 1802. The ministry was headed by the Minister of Justice (who was at the same time the Governing Senate, Senate Procurator Genera ...
was summarized by Dmitry Samokvasov
Dmitry Yakovlevich Samokvasov (; 1843 ‚ÄĒ 1911) was a Russian archaeologist and legal historian who excavated the Black Grave in Chernihiv and several other sites important for the history of Kievan Rus. He graduated from the St. Petersburg Unive ...
, a Russian archaeologist and legal historian, in an edition of 16 pages called "On the Question of National Colours of Ancient Russia" published in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
in 1910.
1552‚Äď1918: Tsardom, Empire and Republic
In 1552, Russian regiments marched on the victorious assault of Kazan underIvan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; ‚Äď ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all R ...
with the banner of the Most Gracious Saviour. For the next century and a half, the banner of Ivan the Terrible accompanied the Russian army. Under Tsarina Sophia Alekseevna, it visited the Crimean campaigns, and under Peter the Great, the Azov campaigns
Azov (, ), previously known as Azak (Turki/Cuman language, Kypchak: ),
is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River (Russia), Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name ...
and the Russo-Swedish War.
In the Illustrated Chronicle of Ivan the Terrible
The Illustrated Chronicle of Ivan the Terrible (; 1560-1570s) is the largest compilation of historical information ever assembled in medieval Russia. It is also informally known as the Tsar Book (–¶–į—Ä—Ć-–ļ–Ĺ–ł–≥–į), in an analogy with the Tsar ...
, there is an image of the banner of Ivan the Terrible in the Kazan campaign ‚Äď a bifurcated white one with the image of the Saviour and an eight-pointed cross above it. According to other sources, the banner was red instead of white. A copy of this banner, which has been restored many times, is still kept in the Kremlin Armoury
The Kremlin ArmouryOfficially called the "Armoury Chamber" but also known as the cannon yard, the "Armoury Palace", the "Moscow Armoury", the "Armoury Museum", and the "Moscow Armoury Museum" but different from the Kremlin Arsenal. () is one of ...
.
In 1612, the Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, –Ě–ł–∂–Ĺ–ł–Ļ –Ě–ĺ–≤–≥–ĺ—Ä–ĺ–ī, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ňąn ≤i źn ≤…™j ňąnov…°…ôr…ôt, t=Lower Newtown; colloquially shortened to Nizhny) is a city and the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast an ...
militia raised the banner of Dmitry Pozharsky, it was crimson in colour with the image of the Lord Almighty on one side and the archangel Michael on the other.
In 1669, the Polish painters Stanislav Loputsky and Ivan Mirovsky invited by Tsar Alexis of Russia
Alexei Mikhailovich (, ; ‚Äď ), also known as Alexis, was Tsar of all Russia from 1645 until his death in 1676. He was the second Russian tsar from the House of Romanov.
He was the first tsar to sign laws on his own authority and his council ...
, painted for the tsar's palace in Kolomenskoye "the hallmarks (that is, the emblems) of the sovereigns and all the universal states of this world." Then Loputsky drew "on the canvas, the coat of arms of the Moscow State and the arms of other neighbouring countries, under every emblem of the planet under which they are." The coat of arms was a white rectangular banner with a "slope" and a wide red border, in the centre of which was depicted a gold two-headed eagle and the emblems symbolizing the subject kingdoms, principalities and lands. In the inventory of the Kremlin Armoury, the coat of arms is described as the following: "In the circle there is a two-headed eagle wearing two crowns, and in his chest, the king on horseback pricks a serpent with his spear".
On 6 August 1693, during Peter the Great's sailing in the White Sea
The White Sea (; Karelian language, Karelian and ; ) is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the nort ...
with a detachment of warships built in Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the ...
, the so-called "Flag of the Tsar of Muscovy" was raised for the first time on the 12-gun yacht "Saint Peter". The flag was a cross-stitch of 4.6x4.9 meters sewn from cloth, composed of three equal-sized horizontal stripes of white, blue and red, with a golden double-headed eagle in the middle. The original of this oldest surviving Russian flag is located in the Central Naval Museum
Central Naval Museum () is a naval museum in St Petersburg, Russia, reflecting the development of Russian naval traditions and the history of the Russian Navy. The museum’s permanent display includes such relics as the Botik of Peter the Great, ...
in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
.
A 1695 flag book by Carel Allard describes three flags used by the tsar of Muscovy: the tricolour with the double-headed eagle
The double-headed eagle is an Iconology, iconographic symbol originating in the Bronze Age. The earliest predecessors of the symbol can be found in Mycenaean Greece and in the Ancient Near East, especially in Mesopotamian and Hittite Empire#icon ...
bearing a shield on its breast and wearing a golden crown over both of its heads, the same tricolour with a blue saltire
A saltire, also called Saint Andrew's Cross or the crux decussata, is a Heraldry, heraldic symbol in the form of a diagonal cross. The word comes from the Middle French , Medieval Latin ("stirrup").
From its use as field sign, the saltire cam ...
over it, and a cross flag showing red and white quartering with a blue cross over all. The cross flag is depicted upon the Construction of Kronschloss Medal, which commemorates the construction of Fort Kronschlot (Kronschloss) in Kronstadt
Kronstadt (, ) is a Russian administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg, near the head ...
by Peter the Great
Peter I (, ;
‚Äď ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned j ...
in 1704, the colours of the flag being determined according to the hatchings engraved.
The armorial banner of Peter the Great was created in 1696. Made from red taffeta with a white border, the flag depicted a golden eagle hovering over the sea. On the chest of the eagle in the circle is the Saviour, next to the Holy Spirit and the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul. The banner was likely made for the second Azov campaign.
 In 1693, Franz Timmerman received the order to build merchant ships in Arkhangelsk and trade with Europe. He was told to display the two-headed eagle spread with wings, with three crowns over it. On the chest of the eagle, a warrior on horseback was to be displayed with a spear, in a military harness. The same eagle was also to hold a sceptre with the right leg and an apple with a crest with the left. The same instructions were given to other traders.
According to Dutch newspapers, in June 1694, a 44-gun frigate bought by Russia and built in Rotterdam stood in the Amsterdam roadstead under the white-blue-red flag.
In 1696, at the mouth of the river Don, a Russian flotilla of armed rowboats blocked the supply of the Ottoman fortress of Azov. On the 1700 engraving by Adrian Shkhonebek, ''Taking the fortress of Azov. 1696'', depicts the ships carrying rectangular panels on the flagpoles, the heraldic shading of which shows that some of the flags are blue with a straight red cross, and the rest are white with a straight red cross. A number of researchers doubt the accuracy of Shkonebek's engraving because he was not a witness to the events.
Images of various white-blue-red Russian flags are present in the three later paintings of
In 1693, Franz Timmerman received the order to build merchant ships in Arkhangelsk and trade with Europe. He was told to display the two-headed eagle spread with wings, with three crowns over it. On the chest of the eagle, a warrior on horseback was to be displayed with a spear, in a military harness. The same eagle was also to hold a sceptre with the right leg and an apple with a crest with the left. The same instructions were given to other traders.
According to Dutch newspapers, in June 1694, a 44-gun frigate bought by Russia and built in Rotterdam stood in the Amsterdam roadstead under the white-blue-red flag.
In 1696, at the mouth of the river Don, a Russian flotilla of armed rowboats blocked the supply of the Ottoman fortress of Azov. On the 1700 engraving by Adrian Shkhonebek, ''Taking the fortress of Azov. 1696'', depicts the ships carrying rectangular panels on the flagpoles, the heraldic shading of which shows that some of the flags are blue with a straight red cross, and the rest are white with a straight red cross. A number of researchers doubt the accuracy of Shkonebek's engraving because he was not a witness to the events.
Images of various white-blue-red Russian flags are present in the three later paintings of Abraham Storck
Abraham Storck (or Sturckenburch; bapt. 17 April 1644 in Amsterdam – buried 8 April 1708) was a Dutch painter and draughtsman, who was known for his marine paintings, topographical views, Italianate harbour scenes and German landscapes alon ...
's workshop dedicated to the arrival in Amsterdam of Peter I. Peter I took part in a practice battle on the river IJ while on board the yacht of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
. In the paintings of Abraham Stork depicting the show fight, this yacht sails under the white-blue-red flag with a double-headed eagle, or under a white-red-blue pennant and a white-red-blue aft flag with a double-headed eagle.
In October 1699, Peter the Great, on the back of the sheet with instructions sent to the Russian envoy Yemelyan Ukraintsev in Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, drew a sketch of a three-band white-blue-red flag.
In December 1699, the Austrian ambassador Anton Paleyer gave a list of weapons and flags seen on the vessels of the Azov Flotilla
The Azov Flotilla or Azov Naval Flotilla was the name given to several Russian naval forces operated on the Sea of Azov - as part of the Imperial Russian Navy, by both the Workers' and Peasants' Red Fleet and the White Russians during the Rus ...
in a letter. He described seeing three small flags of white-red-blue colours and two regimental colours of red and white mixed in with other colours.
In April 1700, Peter the Great ordered the Kremlin Armoury to build white-red-violet sea banners. The design and dimensions of these banners correspond to the figure and the size of the regimental banner kept among the other 352 trophy Russian banners in the burial vault of Swedish kings ‚Äď the Riddarholm Church
Riddarholmen Church () is the church of the former medieval Greyfriars Monastery in Stockholm, Sweden. The church serves as the final resting place of most Swedish monarchs.
Description
Riddarholmen Church is located on the island of Riddarhol ...
in Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
.
The three-band white-blue-red flag, as well as the flag with a red Jerusalem cross
The Jerusalem cross (also known as "five-fold cross", or "cross-and-crosslets" and the "Crusader's cross") is a heraldic cross and Christian cross variant consisting of a large cross potent surrounded by four smaller Greek crosses, one in each ...
, were also used on warships up to 1720 as signals.
The Russian tricolour flag was adopted as a merchant flag
A civil ensign is an Ensign (flag), ensign (maritime flag) used by civilian vessels to denote their nationality. It can be the same or different from the state ensign and the naval ensign (or war ensign). It is also known as the merchant ensign or ...
at rivers in 1705. These colours of the flag of Russia would later inspire the choice of the "Pan-Slavic colors
The pan-Slavic colors‚ÄĒblue, white and red‚ÄĒwere defined by the Prague Slavic Congress, 1848, based on the symbolism of the colors of the flag of Russia, which was introduced in the late 17th century. Historically, however, many Slavs, Sla ...
" by the Prague Slavic Congress, 1848
The Prague Slavic Congress of 1848 (, ) took place in Prague, Austrian Empire (now Czech Republic) between 2 June and 12 June 1848. It was the first occasion on which representatives from nearly all Slav populations of Europe met in one place to ...
. Two other Slavic countries, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
and Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
, have flags similar to the Russian one, but with added coats-of-arms for differentiation. On 7 May 1883, the Russian flag was authorized to be used on land, and it became an official ''National flag'' before the coronation of Tsar Nicholas II
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. He married ...
in 1896.
The flag continued to be used by the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
after Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, —Ü–į—Ä, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
Nicholas II
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. He married ...
abdicated during the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
and was not replaced until the October Revolution which established the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
.
1918‚Äď1991: Civil War and Soviet Union (USSR)
On 8 April 1918, the flag of theRussian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
was discussed at a meeting of the Council of People's Commissars
The Council of People's Commissars (CPC) (), commonly known as the ''Sovnarkom'' (), were the highest executive (government), executive authorities of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), the Soviet Union (USSR), and the Sovi ...
of the RSFSR. The Council proposed that the All-Russian Central Executive Committee
The All-Russian Central Executive Committee () was (June ‚Äď November 1917) a permanent body formed by the First All-Russian Congress of Soviets of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies (held from June 16 to July 7, 1917 in Petrograd), then became the ...
create a red flag with the abbreviation for the phrase ''Workers of the world, unite!
The political slogan "Workers of the world, unite!" is one of the rallying cries from ''The Communist Manifesto'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels (, literally , but soon popularised in English language, English as "Workers of the wo ...
'' However, the proposal was not adopted. On 13 April 1918, the All-Russian Central Executive Committee established the RSFSR flag to be a red banner with the inscription ''Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic''. The text of the decree did not contain any clarification regarding the colour, size and location of the inscription, or the width and length ratio of the cloth.
On 17 June 1918, the All-Russian Central Executive Committee approved a sample image of the flag of the RSFSR, developed on behalf of the People's Commissariat for Foreign Affairs of the Russian SFSR The People's Commissariat for Foreign Affairs of the Russian SFSR (: Narodnyi Komissariat Inostrannykh Del ‚Äď abbreviated to Narkomindel or NKID) was the central executive state body of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic responsible f ...
by the graphic artist Sergey Chekhonin. The flag was a red rectangular panel, in the upper corner of which was placed the inscription ''RSFSR'' in gold letters stylized as Slavic. This inscription was separated from the rest of the cloth on both sides by gold stripes forming a rectangle.
On 30 December 1922, the RSFSR combined with the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
, Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, Byelorussian SSR or Byelorussia; ; ), also known as Soviet Belarus or simply Belarus, was a republic of the Soviet Union (USSR). It existed between 1920 and 1922 as an independent state, and ...
, and Transcaucasian SFSR
, image_flag = Flag of the Transcaucasian SFSR (variant).svg
, flag_type = Flag(1925‚Äď1936)
, image_coat = Emblem of the Transcaucasian SFSR (1930-1936).svg
, symbol_type = Emblem(1930‚Äď1936)
...
to form the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. The national flag of the USSR was established on 18 April 1924, described in the Constitution of the USSR as a red or scarlet rectangular cloth with a 1:2 width to length ratio, with a gold sickle and hammer in the top corner next to the flagpole and a red five-pointed star framed with a golden border. This flag was carried by all ships of the USSR and diplomatic representations of the USSR. The 1:2 red flag was used, until replaced in 1954 with the universal design of the Soviet flag with a blue stripe along the mast.
Contrary to the belief that the USSR state flag outranked the flag of the RSFSR, the actual use of the USSR flag was limited. The USSR flag in Russia flew only over two buildings, that of the Central Executive Committee of the Soviet Union and the Council of People's Commissars. That decision was adopted on 23 March 1925, also establishing that the flag of the RSFSR had to be raised constantly not only on the buildings of the Central Executive Committee and the Council of People's Commissars but also on the buildings of all local soviets, including village soviets and district soviets in cities. On holidays, the RSFSR flag had to be raised on many public buildings (such as schools, hospitals, and government offices).
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ‚Äď 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the white-blue-red tricolour was used by German collaborators, most of whom were from groups targeted by the repressions of the Stalin era, including anti-communist
Anti-communism is political and ideological opposition to communist beliefs, groups, and individuals. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, when th ...
Christians and the remnants of the Kulak
Kulak ( ; rus, –ļ—É–Ľ–įŐĀ–ļ, r=kul√°k, p=k äňą…ęak, a=Ru-–ļ—É–Ľ–į–ļ.ogg; plural: –ļ—É–Ľ–į–ļ–łŐĀ, ''kulak√≠'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned over ...
s, who generally regarded the German invasion as a liberation of Russia from communism. The Russian Liberation Army
The Russian Liberation Army (; , ), also known as the Vlasov army () was a collaborationist formation, primarily composed of Russians, that fought under German command during World War II. From January 1945, the army was led by Andrey Vlasov, ...
under the leadership of Andrey Vlasov
Andrey Andreyevich Vlasov (, ‚Äď August 1, 1946) was a Soviet Russian Red Army general. During the Eastern Front (World War II), Axis-Soviet campaigns of World War II, he fought (1941‚Äď1942) against the ''Wehrmacht'' in the Battle of Moscow ...
used the tricolour during a military flag.
On 20 January 1947, the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR found it necessary to amend the national flags of the allied republics so that the flags reflected the idea of a Soviet Union state as well as the unique national identities of the republics. On each of the flags was placed the emblem of the USSR, a sickle and a hammer with a red five-pointed star, with the inclusion of national ornaments and new colours. The new RSFSR flag was established in January 1954: a red rectangular panel with a light blue strip near the pole running the full width of the flag. In the upper left corner of the red canvas were depicted a golden sickle and a hammer and above them a red five-pointed star framed with a golden border. By the Law of the RSFSR of 2 June 1954, this flag was approved and the description of the flag was included in Article 149 of the Constitution of the RSFSR.
1991‚Äďpresent: Russian Federation
During thedissolution of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-–Ě of ...
, after the 1991 August Coup, the Russian SFSR adopted a new flag design similar to the pre-revolutionary tricolour that had been abolished in 1917. The ratio of the new flag was 1:2, and the flag colours consisted of white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
on the top, blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB color model, RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB color model, RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between Violet (color), violet and cyan on the optical spe ...
in the middle, and red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625‚Äď750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
on the bottom. The flag design remained the same until 1993, when the original Russian tricolour was fully restored as the current flag after the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis
In September and October 1993, a constitutional crisis arose in the Russian Federation from a conflict between the then Russian president Boris Yeltsin and the country's parliament. Yeltsin performed a self-coup, dissolving parliament and insti ...
. Following the events of the attempted coup in Moscow, the supreme soviet of the Russian SFSR declared, by resolution dated 22 August 1991, that the old imperial tricolour flag serve as the national flag of the state. The constitution was subsequently amended by Law No. 1827-1 1 November 1991. At the disintegration of the USSR on 25 December 1991, the Soviet flag was lowered from Kremlin and then replaced by the tricolor flag.
The modern era flag underwent a proportion change from 1:2 to 2:3 in 1993 and has been most recently provided for by a 2000 law. On 11 December 1993, President of the Russian Federation Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin (1 February 1931 ‚Äď 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician and statesman who served as President of Russia from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) from 1961 to ...
signed Decree No. 2126 "On the State Flag of the Russian Federation".–ě –ď–ĺ—Ā—É–ī–į—Ä—Ā—ā–≤–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ–ĺ–ľ —Ą–Ľ–į–≥–Ķ –†–ĺ—Ā—Ā–ł–Ļ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ļ –§–Ķ–ī–Ķ—Ä–į—Ü–ł–ł: –£–ļ–į–∑ –ü—Ä–Ķ–∑–ł–ī–Ķ–Ĺ—ā–į –†–§ –ĺ—ā 11 December 1993 No. 2126 // –°–ĺ–Ī—Ä–į–Ĺ–ł–Ķ –į–ļ—ā–ĺ–≤ –ü—Ä–Ķ–∑–ł–ī–Ķ–Ĺ—ā–į –ł –ü—Ä–į–≤–ł—ā–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Ā—ā–≤–į –†–ĺ—Ā—Ā–ł–Ļ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ļ –§–Ķ–ī–Ķ—Ä–į—Ü–ł–ł. 1993. No. 51. –°—ā. 4928. In Article 1 of the decree, the flag was described as a "rectangular panel of three equal horizontal stripes: the top ‚Äď white, middle ‚Äď blue, and bottom ‚Äď red, with a width to length ratio of 2:3." The pre-1993 flag is still depicted on Russian license plates, as the design specifications were finalized and published 6 months prior to Yeltsin's decree. The National Flag Day is an official holiday in Russia, established in 1994. It is celebrated on 22 August, the day of the victory over putschists in 1991, but employees remain at work.
Symbolism
At the times ofAlexander III of Russia
Alexander III (; 10 March 18451 November 1894) was Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 13 March 1881 until his death in 1894. He was highly reactionary in domestic affairs and reversed some of the libera ...
the official interpretation was as follows: the white colour symbolizes nobility and frankness; the blue for faithfulness, honesty, impeccability, and chastity; and the red for courage, generosity, and love. A common unofficial interpretation was: Red: Great Russia
Great Russia, sometimes Great Rus' ( , ; , ; , ), is a name formerly applied to the territories of "Russia proper", the land that formed the core of the Grand Duchy of Moscow and later the Tsardom of Russia. This was the land to which the e ...
, White: White Russia
White Russia, White Russian, or Russian White may refer to:
White Russia
*White Ruthenia, a historical reference for a territory in the eastern part of present-day Belarus
* An archaic literal translation for Belarus/Byelorussia/Belorussia
* Rus ...
, Blue: Little Russia
Little Russia, also known as Lesser Russia, Malorussia, or Little Rus', is a geographical and historical term used to describe Ukraine.
At the beginning of the 14th century, the patriarch of Constantinople accepted the distinction between wha ...
.
Regulations
When the Russian flag and the flags of the Russian federal subjects are flown at the same time, the national flag should be: * on the left if two flags are raised * in the middle if the number of flags is odd * and to the left of the centre if the number is even The flag cannot be smaller, or lower than a regional flag.Colour specifications
Federal constitutional law of the Russian Federation only says that the colours of the flag are "white", "blue" (—Ā–ł–Ĺ–ł–Ļ, or dark blue, as Russian has two colours that are called "blue" in English), and "red". The Federal Constitutional Law on the State Flag of the Russian Federation does not actually specify which shades the colours should be. Russian government agencies when ordering the manufacture of cloth for the flag indicate the following Pantone colours: white, blue (Pantone 286C), and red (Pantone 485C). The album of national flags, published by the Hydrographic and Oceanographic Service of the Navy (France), gives the following shades of colours of the flag of Russia inPantone
Pantone LLC (stylized as PANTONE) is an American limited liability company headquartered in Carlstadt, New Jersey, and best known for its Pantone Matching System (PMS), a proprietary color order system used in a variety of industries, notably gr ...
:
Variant versions
A variant of the flag was authorized for private use by TsarNicholas II
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. He married ...
before World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 ‚Äď 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, adding the large state eagle on a yellow field (imperial standard) in the canton. It has never been used as the official state flag. Likewise, today some Russian people may use another variant of the flag defaced with the coat of arms (in this case the double-headed eagle is depicted without the shield) in the middle and the golden word –†–ě–°–°–ė–Į at the bottom.
After the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
of 1917, the tricolour design was banned, and a definitive new flag of the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
was introduced in 1954 (see flag of the Russian SFSR
The penultimate USSR-era flag was adopted by the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) in 1954 and used until 1991. The flag of the Russian SFSR was a defacement of the flag of the USSR. The constitution stipulated:
The symb ...
), and this remained the republic's flag until the collapse of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in 1991. All of the Soviet republics' flags were created by introducing a small but noticeable change to the flag of the Soviet Union
The State Flag of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, also simply known as the Soviet flag or the Red Banner, was a Red flag (politics), red flag with two Communist symbolism, communist symbols displayed in the Canton (flag), canton: a gold ...
. For Russia, the change was an introduction of the left-hand blue band. The previous Soviet design was different, a plain red flag with different variants of the "RSFSR" abbreviation in the canton. Today, the Soviet flag is used by the supporters and members of the Communist Party of the Russian Federation
The Communist Party of the Russian Federation (CPRF; ) is a communist political party in Russia that officially adheres to Marxist‚ÄďLeninist philosophy. It is the second-largest political party in Russia after United Russia. The youth o ...
.
The tricolour was used by the anticommunist forces during the Civil War called the White movement
The White movement,. The old spelling was retained by the Whites to differentiate from the Reds. also known as the Whites, was one of the main factions of the Russian Civil War of 1917‚Äď1922. It was led mainly by the Right-wing politics, right- ...
. It was continued to be used by White émigrés
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wavelen ...
in various countries as the Russian flag. The tricolour was associated both in Soviet Russia as well as the Russian White emigre communities as symbolizing a traditional tsarist Orthodox Russia. This flag can be seen inside a few Orthodox churches in the West established by the Russian communities. In the Soviet Union, the tricolour was used in films set in the pre-revolutionary period and was seen as a historical flag, especially after the 1940s.
It, rather than the black-yellow-white colour combination, was readopted by Russia on 22 August 1991. That date is celebrated yearly as the national flag day.
The Russian president
The president of Russia, officially the president of the Russian Federation (), is the executive head of state of Russia. The president is the chair of the Federal State Council and the supreme commander-in-chief of the Russian Armed Forces. I ...
uses a standard which was introduced via Presidential Decree No.319 on 15 February 1994, it is officially defined as the square tricolour with the coat of arms (in this case the double-headed eagle is depicted without the shield) in the middle.
Unicode
The flag of Russia is represented as theUnicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Char ...
emoji
An emoji ( ; plural emoji or emojis; , ) is a pictogram, logogram, ideogram, or smiley embedded in text and used in electronic messages and web pages. The primary function of modern emoji is to fill in emotional cues otherwise missing from type ...
sequence and , making "ūüá∑ūüáļ".
See also
*Coat of arms of Moscow
The coat of arms of Moscow depicts a horseman with a spear in his hand slaying a basilisk and is identified with Saint George and the Dragon. The heraldic emblem of Moscow has been an integral part of the coat of arms of Russia since the 16th cen ...
* Coat of arms of Russia
The coat of arms of Russia derives from the earlier coat of arms of the Russian Empire. Though modified more than once since the reign of Ivan III (1462‚Äď1505), the current coat of arms is directly derived from its medieval original, with the d ...
* Flags of the federal subjects of Russia
This gallery of flags of federal subjects of Russia shows the flags of the 89 federal subjects of Russia including two regions that, while being ''de facto'' under complete Russian control, are not internationally recognized as part of Russia ...
* List of Russian flags
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, bu ...
* Flag of the Russian-American Company
The flag of the Russian-American Company, first adopted in 1806, consisted of a variation of the horizontal white-blue-red tricolor of the flag of Russia, but with the white stripe broader than the other two, and containing a double-headed eagle s ...
* Flag of Bulgaria
The national flag of the Republic of Bulgaria is a tricolour consisting of three equal-sized horizontal bands of (from top to bottom) white, green, and red. The flag was first adopted after the 1877‚Äď1878 Russo-Turkish War, when Bulgaria gained ...
(developed from the Russian flag since 1877, but the blue stripe is replaced by light green one)
* Flag of Dagestan (nearly identical design, green stripe instead of white)
* Flag of the Donetsk People's Republic (nearly identical design, black stripe instead of white)
* Flag of Colombia
The national flag of Colombia symbolizes its independence from Spain, won on 20 July 1810. It is a rectangular horizontal tricolor composed of yellow, blue and red in a 2:1:1 ratio. The yellow stripe takes up a half of the flag, while the blue ...
(nearly identical design, yellow stripe instead of white)
* Flag of the Luhansk People's Republic (nearly identical design, turquoise stripe instead of white)
* Flag of Serbia
The flag of Serbia (), also known as the Tricolour (), is a tricolour consisting of three equal horizontal bands, red on the top, blue in the middle, and white on the bottom (on civil flag), with the lesser coat of arms left of center (on stat ...
(developed from the Russian flag since 1835, but the white and red colours are inverted upside down)
* Flag of Slovakia
The current form of the national flag of the Slovak Republic () was adopted by Slovakia's Constitution, which came into force on 3 September 1992. The flag, like many other flags of Slavic nations, uses Pan-Slavic colours ( red, white, and blu ...
(nearly identical design, defaced with the coat of arms at the hoist side)
* Flag of Slovenia
The national flag of Slovenia () features three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red, with the coat of arms of Slovenia located in the upper hoist side of the flag centred in the white and blue bands. The coat of arms is a shield ...
(nearly identical design, defaced with the coat of arms at the hoist side)
* Flag of Transnistria
Transnistria (officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic or PMR), a breakaway state internationally recognised as part of Moldova, has a state flag, a presidential standard, and a customs flag. Additionally, the flag of Russia shares equal ...
* White-blue-white flag
The white-blue-white flag () is a symbol of opposition to the Russian invasion of Ukraine that has been used by Russian Protests against the Russian invasion of Ukraine, anti-war protesters. It has also been used as a symbol of Opposition to ...
(variant used by anti-war protesters against the invasion of Ukraine)
Notes
References
External links
Official image of the Russian flag, on the official site of the Russian President
Federal Constitutional Law of 25 December 2000 No. 1-FKZ "On the State Flag of the Russian Federation" (including amendments)
pravo.gov.ru
Flag of Russia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Flag of Russia
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
National symbols of Russia
Flags with blue, red and white