|
Г“ ComГЎin
The Irish language, Irish surname Г“ ComГЎin is rooted in an Irish chiefdom. Its anglicised forms include Comain(e), Coman, Comeens, Comin(s), Commane, Comman(s), Commin(s), Common(s), Commyn, Comyn(e), Cowman(s), Cummane, Cumings, Cummin(s), Cumming(s), Cumyn, Cummyn, Kimmons, MacSkimmins, McCowman. It is sometimes incorrectly mistranslated as ''Hurley'' due to the superficial resemblance between the unrelated Gaelic words ''comГЎn'' and ''camГЎn'', the latter referring to a Hurley (stick), hurling stick. The names are derived from the Gaelic personal name ''ComГЎn'' (meaning "noble" or "steadfast") or ''CommГЎn'' ("companion" or "communion"), a name from early Irish history. The surname is rooted in the provinces of Connacht (sept: Г“ CuimГn) and Munster (sept: Г“ ComГЎin), particularly in County Clare, and the 8th and 9th century chiefdom of ''Tulach CommГЎin''. a burial and inauguration site for chieftains, and their capital ''Cahercommaun'' ("The Dwelling of Commaun/Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Type
Gaelic type (sometimes called Irish character, Irish type, or Gaelic script) is a family of Insular script typefaces devised for printing Early Modern Irish. It was widely used from the 16th century until the mid-18th century in Scotland and the mid-20th century in Ireland, but is now rarely used. Sometimes, all Gaelic typefaces are called ''Celtic'' or ''uncial'' although most Gaelic types are not uncials. The "Anglo-Saxon" types of the 17th century are included in this category because both the Anglo-Saxon types and the Gaelic/Irish types derive from the insular manuscript hand. The terms ''Gaelic type'', ''Gaelic script'' and ''Irish character'' translate the Modern Irish phrase (). In Ireland, the term is used in opposition to the term , Roman type. The Scots Gaelic term is (). (–1770) was one of the last Scottish writers with the ability to write in this script, but his main work, , was published in the Roman script. Characteristics Besides the 26 letters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomond
Thomond ( Classical Irish: ; Modern Irish: ), also known as the Kingdom of Limerick, was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland, associated geographically with present-day County Clare and County Limerick, as well as parts of County Tipperary around Nenagh and its hinterland. The kingdom represented the core homeland of the DГЎl gCais people, although there were other Gaels in the area such as the Г‰ile and EГіganachta, and even the Norse of Limerick. It existed from the collapse of the Kingdom of Munster in the 12th century as competition between the Г“ Briain and the Mac CГЎrthaigh led to the schism between Thomond ("North Munster") and Desmond ("South Munster"). It continued to exist outside of the Anglo-Norman-controlled Lordship of Ireland until the 16th century. The exact origin of Thomond, originally as an internal part of Munster, is debated. It is generally held that the DГ©isi Muman pushed north-west starting from the 5th to the early 8th century, taking the area from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SГ©amus Pender
Pender's Census, or Petty's Census, was undertaken by the English economist William Petty between December 1654 and 1659. This 'census' was completed on behalf of the Commonwealth government probably as part of the Down Survey. Content The census provides returns of the inhabitants of most of the country, arranged in counties, baronies, parishes and townlands. The counties of Cavan, Galway, Wicklow, Mayo, Tyrone and most of Meath are not included. The number of English, Irish and Scotch in each townland was also noted. These designations of nationality are vague; 'Irish' may refer to those who speak the language and English may refer to only the newest settlers. The 'Scotch' are found widespread in Ulster, with the exception of Co. Monaghan and Co. Antrim. This census gives no Scotch settlers in the provinces of Munster and Connacht, where the Irish outnumber the English by a ten to one ratio. In addition to this, the 'census' also recorded the names of those with titles to land a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EГіganacht Chaisil
EГіganacht Chaisil were a branch of the EГіganachta, the ruling dynasty of Munster between the 5th and 10th centuries. They took their name from Cashel (County Tipperary) which was the capital of the early Catholic kingdom of Munster. They were descended from Г“engus mac Nad FroГch (died 489), the first Christian King of Munster, through his son Feidlimid mac Г“engusa. In the seventh century, they split into two main clans. CenГ©l FГngin descended from FГngen mac ГЃedo Duib (d. 618) and became the O'Sullivans and MacGillycuddys. The McGillycuddy are a sept of the O'Sullivan's. A descendant of FГngen was Feidlimid mac Cremthanin (d. 847). Clann FaГlbe descended from FaГlbe Flann mac ГЃedo Duib (d. 639) and became the MacCarthy dynasty, rulers of the Kingdom of Desmond following their displacement by the Normans. The O'Callaghans belong to the same line as the MacCarthys, while the MacAuliffes are a sept of the MacCarthys. The EГіganacht Chaisil were considered part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corc Mac Luigthig
Corc mac Luigthig (340-379),Genealogy of the House of Mac-Carthy formerly Sovereign of the Two Momonies or Southern Ireland, P. Louis LainГ©, pg. 26, https://celt.ucc.ie/published/F830000-001.html also called Conall Corc, Corc of Cashel, and Corc mac LГЎire, is the hero of Irish language tales which form part of the origin legend of the EГіganachta, a group of kindreds which traced their descent from Conall Corc and took their name from his ancestor Г‰ogan MГіr. The early kindred they belonged to are known as the Deirgtine. He was probably a grandson of Ailill Flann Bec, and possible cousins were DГЎire Cerbba and the famous Crimthann mac Fidaig. The latter is his opponent in a celebrated cycle of stories. Biography The name and identity of Corc's actual father is something of a mystery, however. While certainly belonging to the kindred of the proto-EГіganachta, he is inconsistently named in the genealogies and tales as Lugaid or LГЎre. Further confusion is caused by the fact tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Munster
The kings of Munster () ruled the Kingdom of Munster in Ireland from its establishment during the Irish Iron Age until the High Middle Ages. According to Gaelic traditional history, laid out in works such as the ''Book of Invasions'', the earliest king of Munster was Bodb Derg of the Tuatha DГ© Danann. From the Gaelic peoples, an Г‰rainn kindred known as the DГЎirine (also known as Corcu LoГgde and represented today in seniority by the Г“ hEidirsceoil) provided several early monarchs including CГє RoГ. In a process in the ''Cath Maige Mucrama'', the Г‰rainn lost their ascendancy in the 2nd century AD to the Deirgtine, ancestors of the EГіganachta. Munster during this period was classified as part of ''Leath Cuinn and Leath Moga, Leath Moga'', or the southern-half, while other parts of Ireland were ruled mostly by the Connachta. After losing Osraige to the east, Cashel, County Tipperary, Cashel was established as the capital of Munster by the EГіganachta. This kindred ruled wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Г‰ogan MГіr
In Irish traditional history Г‰ogan (or Eoghan MГіr—a name also used by his grandfather, Mug Nuadat), eldest son of Ailill Ollamh, was a 2nd or 3rd century AD king of Munster. He ruled for either fifteen or seventeen years, though fifteen is the number most often given.''The General History of Ireland collected by the learned Jeoffry Keating. D.D. Faithfully translated from the Original Irish Language''. (n.d.). ocuments https://jstor.org/stable/community.29823900 He is credited with founding or at least giving his name to the EГіganachta, a dynasty which ruled as kings of Munster and later princes of Desmond until the late 16th century. He died at the battle of Maige Mucrama at the hands of his stepbrother, Lugaid Mac Con, which story is told in the Cath Maige Mucrama. The son of EГіgan MГіr was Fiachu Muillethan. His mother was Sadb ingen Chuinn, daughter of Conn of the Hundred Battles. Family Г‰ogan was the stepbrother of Lugaid, also known as Mac Con. He was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corcu Baiscind
The Corcu Baiscind were an early Г‰rainn people or kingdom of what is now southern County Clare in Munster. They descended from Cairpre BaschaГn, son of Conaire CГіem, a High King of Ireland. Closely related were the MГєscraige and Corcu Duibne, both of Munster, and also the DГЎl Riata of Ulster and Scotland, all belonging to the SГl Conairi of legend. A more distant ancestor was the legendary monarch Conaire MГіr, son of EterscГ©l, son of ГЌar, son of Dedu mac Sin. Corcu Baiscind was eventually absorbed into the Kingdom of Thomond under the DГЎl gCais. Among their septs were O'Baskin, MacDermot and O'Donnell/MacDonnell. by Dennis Walsh The MacMahon family of the DГЎl gCais, after their conquest of the area became Lords of Corcu Baiscind. Annalistic references ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
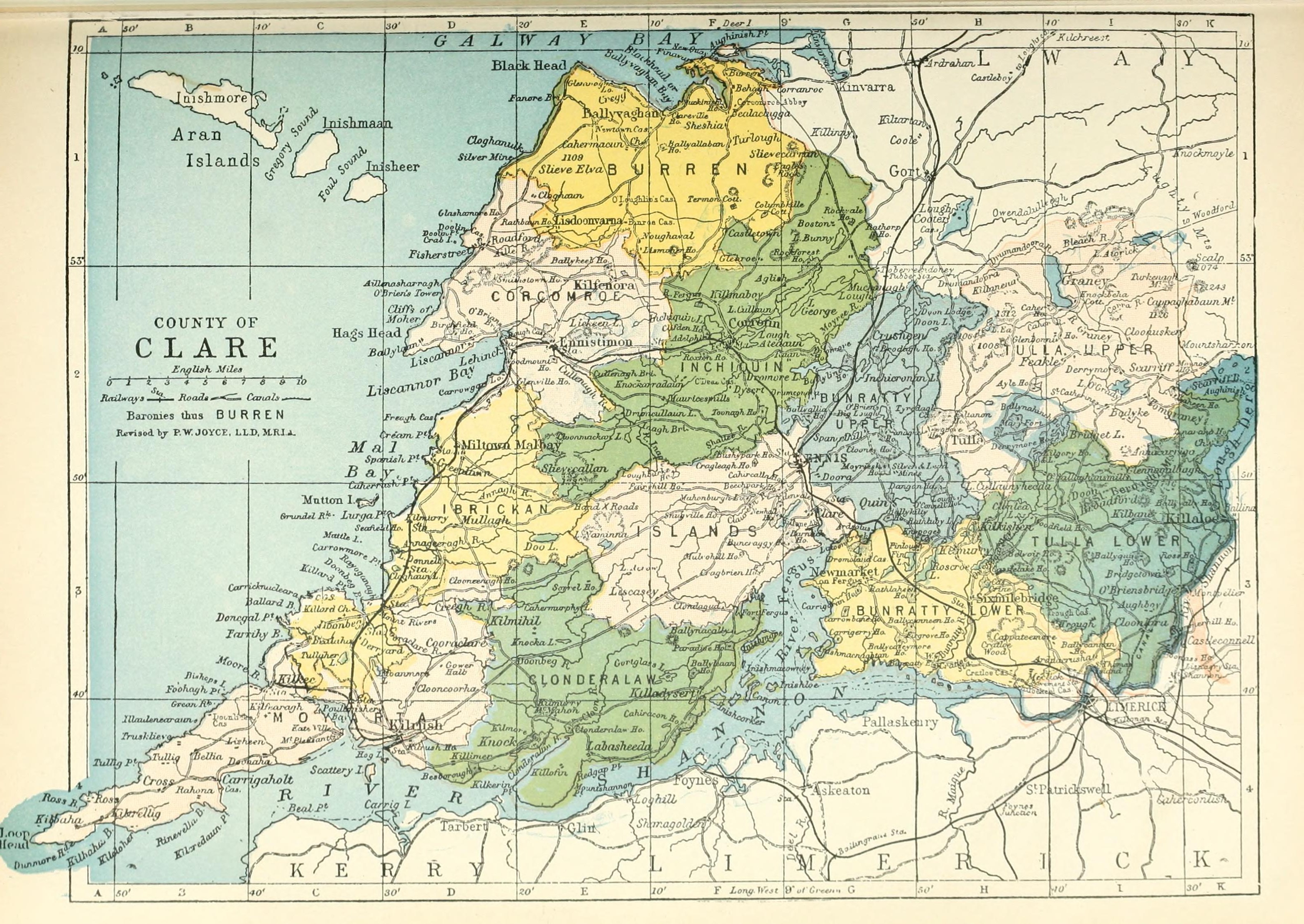
Islands (barony)
Islands () is a barony located in County Clare, Ireland. This ancient unit of land division is in turn divided into five civil parishes. Etymology The name refers to the many islands of the Fergus estuary, such as Canon Island, Deer Island, Inishloe, Feenish and Trummer: the Anglo-Normans approaching from Limerick along these waters perceived the County Clare region as an archipelago and named it "the cantred of the isles of Thomond", a name still preserved in that of the barony. Legal context Baronies were created after the Norman invasion of Ireland as divisions of counties and were used the administration of justice and the raising of revenue. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they have been administratively obsolete since 1898. However, they continue to be used in land registration and in specification, such as in planning permissions. In many cases, a barony corresponds to an earlier Gaelic tГєath which had submitted to the Crown. Location The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EГіganachta
The EГіganachta (Modern , ) were an Irish dynasty centred on Rock of Cashel, Cashel which dominated southern Ireland (namely the Kingdom of Munster) from the 6/7th to the 10th centuries, and following that, in a restricted form, the Kingdom of Desmond, and its offshoot Carbery (barony), Carbery, to the late 16th century. By tradition the dynasty was founded by Conall Corc but named after his ancestor Г‰ogan MГіr, Г‰ogan, the firstborn son of the semi-mythological 3rd-century king Ailill Aulom. This dynastic clan-name, for it was never in any sense a 'surname,' should more accurately be restricted to those branches of the royal house which descended from Conall Corc, who established Cashel as his royal seat in the late 5th century. High Kingship issue Although the EГіganachta were powerful in Munster, they never provided Ireland with a List of High Kings of Ireland, High King. Serious challenges to the UГ NГ©ill were however presented by Cathal mac Finguine and Feidlimid mac Cremt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' () are annals of History of Ireland, medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe RuaidhrГ Г“ LuinГn, under his patron Cathal Г“g Mac Maghnusa, on the island of ''Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa'', also known as ''Senad'' or Ballymacmanus Island (now known as Belle Isle, where Belle Isle Castle is located), near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of ''Fir Manach'' (Fermanagh). Later entries (up to AD 1540) were added by others. Entries up to the mid-6th century are retrospective, drawing on earlier annalistic and historical texts, while later entries were contemporary, based on recollection and oral history. Thomas Charles-Edwards, T. M. Charles-Edwards has claimed that the main source for its records of the first millennium A.D. is a now-lost Armagh continuation of the ''Chronicle of Ireland''. The Annals used the Irish language, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |