|
Zavah
In Jewish ritual law, a ''zavah'' (Hebrew זבה, lit. "one whoe bodyflows") is a woman who has had vaginal blood discharges not during the usually anticipated menstrual cycle, and thus entered a state of ritual impurity. The equivalent impurity that can be contracted by males, by experiencing an abnormal discharge from their genitals, is known as the impurity of a ''zav''. In the realm of tumah and taharah, the ''zavah'', just like a ''niddah'' (menstruant woman) and '' yoledet'' (woman after giving birth), is in a state of major impurity, and creates a midras by sitting and by other activities (, , ). Another aspect of her major impurity, is that a man who conducts sexual intercourse with her becomes unclean for a seven-day period. Additionally, the ''zavah'' and her partner are liable to ''kareth'' (extirpation) for willfully engaging in forbidden sexual intercourse, as is the case for a ''niddah'' and ''yoledet''. Hebrew Bible Torah sources for the ''zavah'' are sourced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumah And Taharah
In Jewish law, ''ṭumah'' (, ) and ''ṭaharah'' (, ) are the state of being ritually "impure" and "pure", respectively. The Hebrew noun ''ṭum'ah'', meaning "impurity", describes a state of ritual impurity. A person or object which contracts ''ṭumah'' is said to be ''ṭamé'' ( Hebrew adjective, "ritually impure"), and thereby unsuited for certain holy activities and uses ('' kedushah'', in Hebrew) until undergoing predefined purification actions that usually include the elapse of a specified time-period. The contrasting Hebrew noun ''ṭaharah'' () describes a state of ritual purity that qualifies the ''ṭahor'' (; ritually pure person or object) to be used for ''kedushah''. The most common method of achieving ''ṭaharah'' is by the person or object being immersed in a ''mikveh'' (ritual bath). This concept is connected with ritual washing in Judaism, and both ritually impure and ritually pure states have parallels in ritual purification in other world religions. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niddah
Niddah (or nidah; he, נִדָּה), in traditional Judaism, describes a woman who has experienced a uterine discharge of blood (most commonly during menstruation), or a woman who has menstruated and not yet completed the associated requirement of immersion in a '' mikveh'' (ritual bath). In the Book of Leviticus, the Torah prohibits sexual intercourse with a ''niddah''. The prohibition has been maintained in traditional Jewish law and by the Samaritans. It has largely been rejected by adherents of Reform Judaism and other liberal branches. In rabbinic Judaism, additional stringencies and prohibitions have accumulated over time, increasing the scope of various aspects of niddah, including: duration (12-day minimum for Ashkenazim, and 11 days for Sephardim); expanding to prohibition against sex to include: sleeping in adjoining beds, any physical contact, and even passing objects to spouse; and requiring a detailed ritual purification process. Since the late 19th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days, and continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining ( endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood supply of the thickened lining provides nutrients to a successfully implanted embryo. If implantation do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
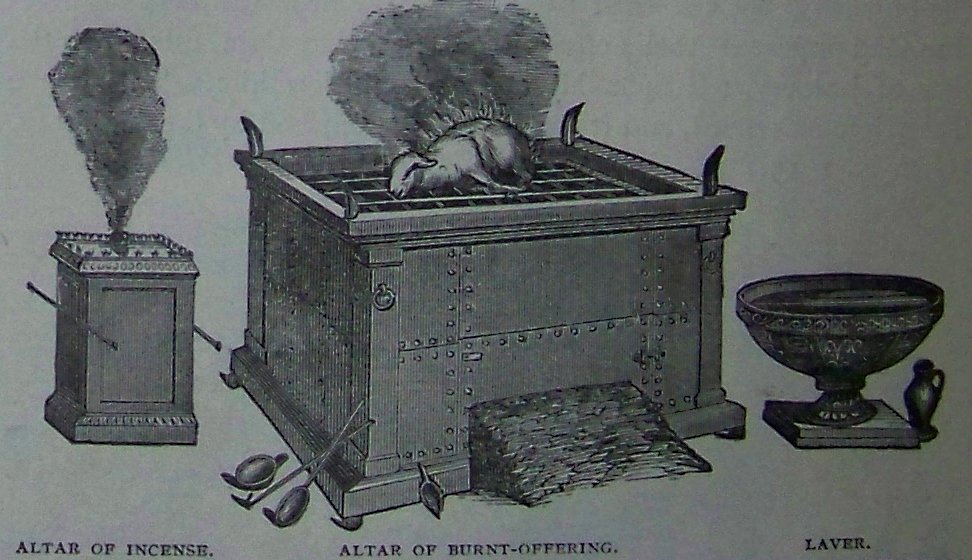
Korban Olah
A burnt offering in Judaism ( he, קָרְבַּן עוֹלָה, ''qorban ʿōlā'') is a form of sacrifice first described in the Hebrew Bible. As a tribute to God, a burnt offering was ''entirely'' burnt on the altar. This is in contrast to other forms of sacrifice (entitled ''zevach'' or ''zevach shelamim''), which was ''partly'' burnt and ''most'' of it eaten in communion at a sacrificial meal. During the First Temple and Second Temple periods, the burnt offering was a twice-daily animal sacrifice offered on the altar in the temple in Jerusalem that was completely consumed by fire. The skin of the animal, however, was not burnt but given to the priests respective of their priestly division. These skins are listed as one of the twenty-four priestly gifts in Tosefta Hallah. Etymology The Hebrew noun ''olah'' (עֹלָה) occurs 289 times in the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible. It means "that which goes up n smoke.Schwartz, Baruch J. "Burnt Offering", in Berlin Adele; Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makkoth
Makot (in Hebrew: מכות) (in English: "Lashes") is a tractate of the Mishnah and Talmud. It is the fifth volume of the order of Nezikin. Makkot deals primarily with laws of the Jewish courts ( beis din) and the punishments which they may administer, and may be regarded as a continuation of tractate Sanhedrin, of which it originally formed part. In its scope of application are the topics of: *The false witnesses (''Edim Zomemim'') *The exile in a city of refuge. (''Aray Miklat'') *The lashes administered by the court. (''Makkot'') The third chapter of tractate Makkot enumerates 59 offenses, each entailing lashes. Of these, three are marital sins of priests; four, prohibited inter-marriages; seven, sexual relations of an incestuous nature; eight, violations of dietary laws; twelve, various violations of the negative precepts; twenty-five, abuses of Levitical laws and vows. When the offense has been persisted in, the punishment depends on the number of forewarnings (see Hatra'a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosefta
The Tosefta ( Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: תוספתא "supplement, addition") is a compilation of the Jewish oral law from the late 2nd century, the period of the Mishnah. Overview In many ways, the Tosefta acts as a supplement to the Mishnah (''tosefta'' means "supplement, addition"). The Mishnah ( he, משנה) is the basic compilation of the Oral law of Judaism; according to the tradition, it was compiled in 189 CE. The Tosefta closely corresponds to the Mishnah, with the same divisions for ''sedarim'' ("orders") and ''masekhtot'' ("tractates"). It is mainly written in Mishnaic Hebrew, with some Aramaic. At times the text of the Tosefta agrees nearly verbatim with the Mishnah. At others there are significant differences. The Tosefta often attributes laws that are anonymous in the Mishnah to named Tannaim. It also augments the Mishnah with additional glosses and discussions. It offers additional aggadic and midrashic material, and it sometimes contradicts the Mishnah in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niddah (Talmud)
Niddah (Hebrew: ) is a ''masekhet'' or tractate of the Mishnah and the Talmud, and is part of the order of Tohorot. The content of the tractate primarily deals with the legal provisions related to Halakha of Niddah. In Judaism, a niddah is a woman during menstruation, or a woman who has menstruated and not yet completed the associated requirement of immersion in a mikveh (ritual bath). In the Book of Leviticus, the Torah prohibits sexual intercourse with a ''niddah''. The prohibition has been maintained in traditional Jewish law. The laws concerning ''niddah'' are also referred to as ''taharat hamishpacha'' (, Hebrew for ''family purity''). Niddah, along with Eruvin and Yevamot, is considered one of the three most difficult tractates in the Babylonian Talmud. A Hebrew mnemonic for the three is עני (''ani'', meaning "poverty"). Structure Niddah consists of 10 chapters. It has 79 mishnahs and 73 pages gemara The Gemara (also transliterated Gemarah, or in Yiddish Gemo( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sifra
Sifra (Aramaic: סִפְרָא) is the Halakhic midrash to the Book of Leviticus. It is frequently quoted in the Talmud, and the study of it followed that of the Mishnah. Like Leviticus itself, the midrash is occasionally called "Torat Kohanim", and in two passages also "Sifra debei Rav". According to '' Leḳaḥ Ṭob'' this latter title was applied originally to the third book of the Pentateuch because Leviticus was the first book studied in the elementary school, and it was subsequently extended to the midrash; but this explanation is contradicted by analogous expressions such as "Sifre debei Rav" and, in a broader sense, "ketubot debei Rav" and "teḳi'ata debei Rav". Authorship Maimonides and others have declared that the title "Sifra debei Rav" indicates Rav as the author of the Sifra; and this opinion I.H. Weiss attempts to support. His proofs are not conclusive, though neither are the opposing arguments of Friedmann who tries to show that the expression "Sifra debei Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korban
In Judaism, the korban ( ''qorbān''), also spelled ''qorban'' or ''corban'', is any of a variety of sacrificial offerings described and commanded in the Torah. The plural form is korbanot, korbanoth or korbans. The term Korban primarily refers to sacrificial offerings given from humans to God for the purpose of doing homage, winning favor, or securing pardon. The object sacrificed was usually an animal that was ritually slaughtered and then transferred from the human to the divine realm by being burned on an altar. After the destruction of the Second Temple, sacrifices were prohibited because there was no longer a Temple, the only place allowed by halakha for sacrifices. Offering of sacrifices was briefly reinstated during the Jewish–Roman wars of the second century AD and was continued in certain communities thereafter. When sacrifices were offered in ancient times, they were offered as a fulfillment of Biblical commandments. Since there is no longer a Temple, modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, רבי שלמה יצחקי; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 – 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a comprehensive commentary on the Talmud and commentary on the Hebrew Bible (the '' Tanakh''). Acclaimed for his ability to present the basic meaning of the text in a concise and lucid fashion, Rashi appeals to learned scholars and beginning students, and his works remain a centerpiece of contemporary Jewish studies. His commentary on the Talmud, which covers nearly all of the Babylonian Talmud (a total of 30 out of 39 tractates, due to his death), has been included in every edition of the Talmud since its first printing by Daniel Bomberg in the 1520s. His commentaries on the Tanakh—especially his commentary on the Chumash (the "Five Books of Moses")—serves as the basis of more than 300 "supercommentaries" which analyze Rashi's choice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berakhot (tractate)
Berakhot ( he, בְּרָכוֹת, Brakhot, lit. "Blessings") is the first tractate of '' Seder Zeraim'' ("Order of Seeds") of the Mishnah and of the Talmud. The tractate discusses the rules of prayers, particularly the Shema and the Amidah, and blessings for various circumstances. Since a large part of the tractate is concerned with the many ''berakhot'' ( en, blessings), all comprising the formal liturgical element beginning with words "Blessed are you, Lord our God….", it is named for the initial word of these special form of prayer. ''Berakhot'' is the only tractate in ''Seder Zeraim'' to have Gemara – rabbinical analysis of and commentary on the Mishnah – in the Babylonian Talmud. There is however Jerusalem Talmud on all the tractates in ''Seder Zeraim''. There is also a Tosefta for this tractate. The Jewish religious laws detailed in this tractate have shaped the liturgies of all the Jewish communities since the later Talmudic period and continue to be obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
