|
Yttrium Oxalate
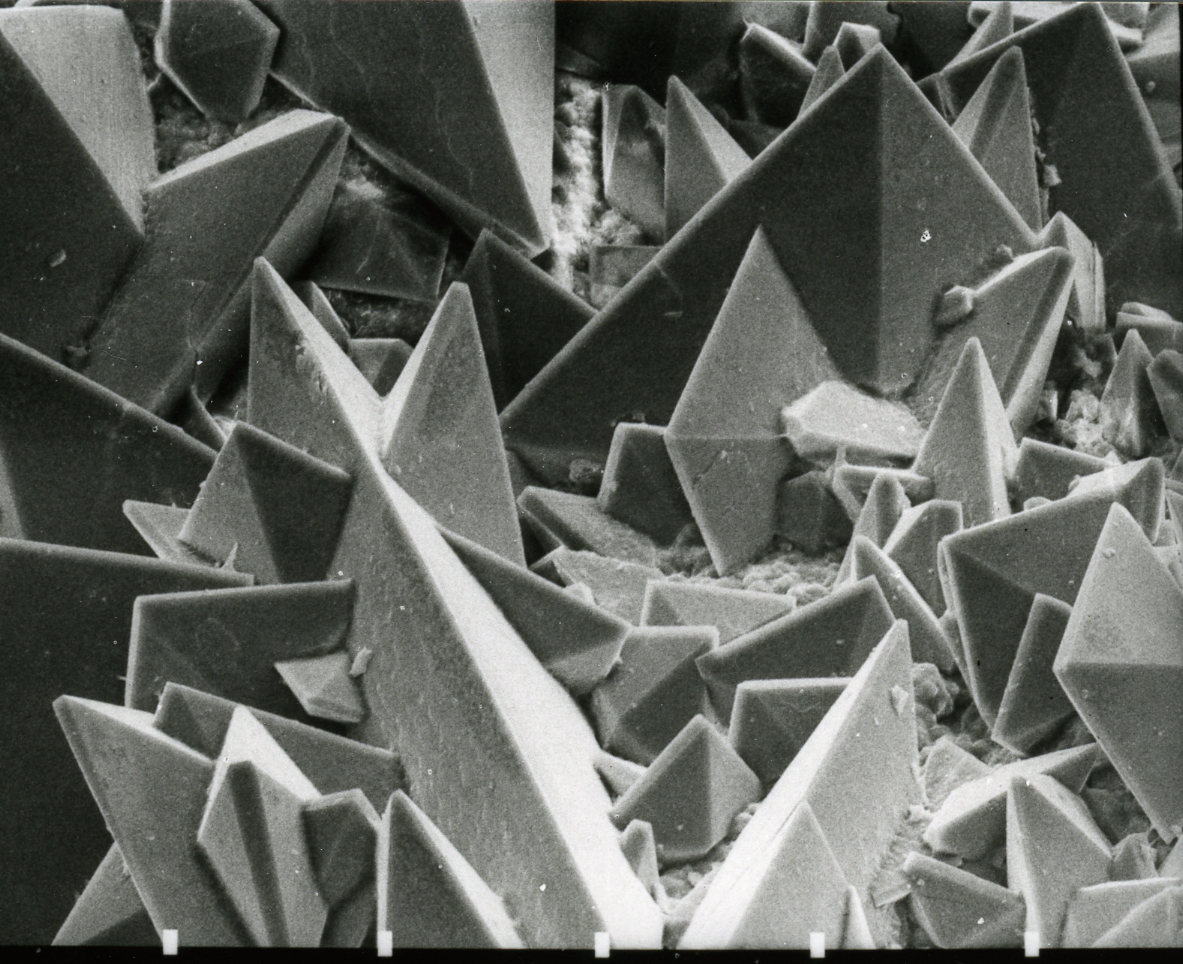
Yttrium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of yttrium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Y(CO). The compound does not dissolve in water and forms crystalline hydrates—colorless crystals. Synthesis Precipitation of soluble yttrium salts with oxalic acid: ::\mathsf Properties Yttrium oxalate is highly insoluble in water and converts to the oxide when heated. Yttrium oxalate forms crystalline hydrates (colorless crystals) with the formula Y(CO)•''n'' HO, where n = 4, 9, and 10. Decomposes when heated: ::\mathsf The solubility product of yttrium oxalate at 25 °C is 5.1 × 10−30. The trihydrate Y(CO)•3HO is formed by heating more hydrated varieties at 110 °C. Y(CO)•2HO, which is formed by heating the decahydrate at 210 °C) forms monoclinic crystals with unit cell dimensions a=9.3811 Å, b=11.638 Å, c=5.9726 Å, β=96.079°. Related Several yttrium oxalate double salts A double salt is a salt that contains two or more different cati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula or . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Cultural groups with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as those in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry (journal)
''Analytical Chemistry'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1929 by the American Chemical Society. Articles address general principles of chemical measurement science and novel analytical methodologies. Topics commonly include chemical reactions and selectivity, chemometrics and data processing, electrochemistry, elemental and molecular characterization, imaging, instrumentation, mass spectrometry, microscale and nanoscale systems, -omics, sensing, separations, spectroscopy, and surface analysis. It is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, CAB International, EBSCOhost, ProQuest, PubMed, Scopus, and the Science Citation Index Expanded. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', it has a 2022 impact factor of 7.4. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compounds
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Materials Chemistry
The ''Journal of Materials Chemistry'' was a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the applications, properties and synthesis of new materials. It was established in 1991 and published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. At the end of 2012 the journal was split into three independent journals: ''Journal of Materials Chemistry A'' (energy and sustainability), '' Journal of Materials Chemistry B'' (biology and medicine) and '' Journal of Materials Chemistry C'' (optical, magnetic and electronic devices). The editor-in-chief was Liz Dunn. See also * List of scientific journals in chemistry * ''Soft Matter'' * ''Journal of Materials Chemistry A A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of personal secretive thoughts and as open book to personal therapy or used to feel connected to onesel ...'' * '' Journal of Materials Chemistry B'' * '' Journal of Materials Chemistry C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganica Chimica Acta
''Inorganica Chimica Acta'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1967 that covers original research and reviews of fundamental and applied aspects of inorganic chemistry. See also * List of scientific journals in chemistry This is a list of scientific journals in chemistry and its various subfields. For journals mainly about materials science, see List of materials science journals. A B * ''Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry'' * ''Biochemical Journal'' * ''B ... External links * Elsevier academic journals Inorganic chemistry journals Academic journals established in 1967 English-language journals Journals published between 13 and 25 times per year {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Prism (geometry), prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The body-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure Communications
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Crystallographica
''Acta Crystallographica'' is a series of peer-reviewed scientific journals, with articles centred on crystallography, published by the International Union of Crystallography (IUCr). Originally established in 1948 as a single journal called ''Acta Crystallographica'', there are now six independent ''Acta Crystallographica'' titles: *'' Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations and Advances'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section C: Structural Chemistry'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section E: Crystallographic Communications'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section F: Structural Biology Communications'' ''Acta Crystallographica'' has been noted for the high quality of the papers that it produces, as well as the large impact that its papers have had on the field of crystallography. The current six journals form part of the journal po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism (geometry), prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. The length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Salts
A double salt is a salt that contains two or more different cations or anions. Examples of double salts include alums (with the general formula ) and Tutton's salts (with the general formula ). Other examples include potassium sodium tartrate, ammonium iron(II) sulfate (Mohr's salt), potassium uranyl sulfate (used to discover radioactivity) and bromlite . The fluorocarbonates contain fluoride and carbonate anions. Many coordination complexes form double salts. Double salts should not be confused with complexes. Double salts only exist in the solid. When dissolved in water, a double salt acts as a mixture of the two separate salts: it completely dissociates into simple ions while a hexaaquo complex does not; the complex ion remains unchanged. Similarly, potassium hexaiodoytterbate(II) is a complex salt and contains the discrete hexaiodoytterbate(II) ion , which remains intact in aqueous solution An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Elements
American Elements is a global manufacturer and distributor of advanced materials with an over 35,000-page online product catalog and compendium of information on the chemical elements, advanced materials, and high technology applications. The company's headquarters and educational programs are based in Los Angeles, California. Its research and production facilities are located in Salt Lake City, Utah; Monterrey, Mexico;China; and Manchester, UK. History American Elements began as a toll chemical manufacturer and refiner serving U.S. mining companies by producing metal-based chemicals from their deposits. In 1998, its two largest customers, the Unocal/Molycorp rare-earth mine in Mountain Pass, California, and the Rhodia rare-earth refinery in Freeport, Texas closed, ending domestic U.S. rare-earth production. In response, the company established mining joint ventures in Inner Mongolia, China and in 1999 became one of the first post-Cold War companies to export rare-earth metals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |