|
Yobidashi
A , often translated in English as "usher", "ring attendant", or "ring announcer", is an employee of the Japan Sumo Association, responsible for various tasks essential to the traditional running of Sumo#Professional sumo, professional sumo tournaments () in Japan. The are involved in building the (wrestling ring) or calling wrestlers () to the ring when it is their turn to fight. They are also entrusted with other roles, both administrative and artistic, in the service of the heya (sumo), stable to which they are attached. Established during the Heian period, the role of was not codified until the Tenmei, Tenmei era. Nicknamed "sumo's workhorses" by former Takamiyama Daigorō, Takamiyama, the are required to wear traditional clothing in public and are subject to a strict hierarchy in their organisation. History The status of did not appear until 1750. Before the appearance of this term to specifically designate the staff responsible for announcing the wrestlers, several d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San'yaku
The following words are terms used in sumo wrestling in Japan. A B C D E F G H I J K M N O R S T W Y Z References External links Glossary of Sumo TermsSumopediaat NHK World-Japan {{Glossaries of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dohyō
A ''dohyō'' (, ) is the space in which a sumo wrestling bout occurs. A typical ''dohyō'' is a circle made of partially buried rice- straw bales 4.55 meters in diameter. In official professional tournaments ('' honbasho''), it is mounted on a square platform of clay 66 cm high and 6.7m wide on each side. Configuration and construction In professional sumo, a new ''dohyō'' is built prior to each tournament by the '' yobidashi'' (ring attendants), who are responsible for this activity. The process of building the ''dohyō'' and its 66 cm high platform takes three days and is done with traditional tools. The clay used is taken from the banks of the Arakawa River in Saitama Prefecture. However, due to growing urbanization, clay from Ibaraki Prefecture has started to be used. The surface is covered by sand. The ''dohyō'' is removed after each tournament and, in the case of the Nagoya tournament, pieces are taken home by the fans as souvenirs. The ''yobidashi'' also build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyōji
A is a referee employed by the Japan Sumo Association, responsible for a variety of activities which concern the organisation of the sport in general and the refereeing of matches, as well as the preservation of Sumo#Professional sumo, professional sumo culture, deeply rooted in Shinto traditions. Subject to the same strict hierarchy and traditional appearance as the other professions gravitating around professional sumo, the are one of the most visible professions at tournaments (), being the third person in the (wrestling ring) and sometimes defined as "an essential part of the sumo spectacle." Inherited from a tradition of refereeing dating back to the Heian period, did not take on their current role until the Tenshō (Momoyama period), Tenshō era in the late 16th century. Since the end of the 18th century, have been entrusted with religious functions, which they perform during the consecration of combat areas, before tournaments or in the heya (sumo), stables to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shibatayama Stable
Shibatayama Stable (Japanese: 芝田山部屋, ''Shibatayama-beya'') is a stable of sumo wrestlers, one of the Nishonoseki group of stables. It was founded in 1999 by former ''yokozuna'' Ōnokuni. Located in Suginami, it is the only stable to be situated in the western half of Tokyo as of 2020. Mongolian born became the stable's first wrestler to earn promotion to the ''jūryō'' division, in March 2008, but he only lasted one tournament in the division and left sumo in acrimonious circumstances in 2010, claiming in a lawsuit that was eventually settled out of court that he had been forced to retire against his will. In February 2013 the stable absorbed its parent Hanaregoma stable due to the imminent retirement of its stablemaster, former '' ōzeki'' Kaiketsu. Among the wrestlers transferring was another Mongolian, , who was ranked in ''jūryō'' for five tournaments between January 2014 and January 2015. In January 2020 returned to ''jūryō'' after 30 tournaments away. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasugano Stable
is a stable of sumo wrestlers, part of the Dewanoumi ''ichimon'' or group of stables. As of January 2023 it had 17 wrestlers. It has been led by former ''sekiwake'' Tochinowaka Kiyotaka since 2003. It was one of the most successful stables in 2013, with six ''sekitori'' wrestlers, including now retired Georgian Tochinoshin and Japanese born (but Korean national) Tochinowaka Michihiro, who used the current head coach's old ring name. It was founded in the mid 18th century by a wrestler named Kasugano Gunpachi. It became inactive for a long time but was led in the Meiji period by a referee named Kimura Soshiro (this is no longer allowed as ''oyakata'' must now be former wrestlers). He adopted as his son the 27th ''yokozuna'' Tochigiyama, who led the stable for over thirty years. He in turn adopted as his son the 44th ''yokozuna'' Tochinishiki, who became the head in 1959 whilst still an active wrestler and later served as the chairman of the Japan Sumo Association. Tochinoumi too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heya (sumo)
In professional sumo wrestling, a , most commonly and metaphorically translated in English as "Stable#Other uses, stable", but also known as "Barracks, training quarters", or "fraternity", is an organization of rikishi, wrestlers where they train and live in a "quasi-Monastery#Monastic life, monastic and Stratocracy, militaristic lifestyle". Closer to a medieval fraternity than a modern sports team, a stable is a group that lives, eats, trains, sleeps and socializes together, under the authority of one or more elders. Additionally to wrestlers, all the traditional sports professionals (such as , and ) must belong to a . vary in size, with the largest and most successful stables having a completely different training environment from the smaller stables that have a dimension described as being more family-oriented. Most are based in and around the Ryōgoku district of Tokyo, sumo's traditional heartland, although the high price of land has led to some newer being built in oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Sumo Association
The , officially the ; sometimes abbreviated JSA or NSK, and more usually called Sumo Kyōkai, is the governing body that operates and controls Professional sports, professional sumo wrestling, called , in Japan under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). Concretely, the association maintains and develops sumo traditions and integrity by holding honbasho, tournaments and . The purposes of the association are also to develop the means dedicated to the sport and maintain, manage and operate the facilities necessary for these activities. Therefore, the JSA operates subsidiaries such as the Kokugikan Service Company to organize its economic aspects, the Sumo School to organize training and instruction or the Sumo Museum to preserve and utilize sumo wrestling records and artefacts. Though professionals, such as rikishi, active wrestlers, gyōji, referees, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
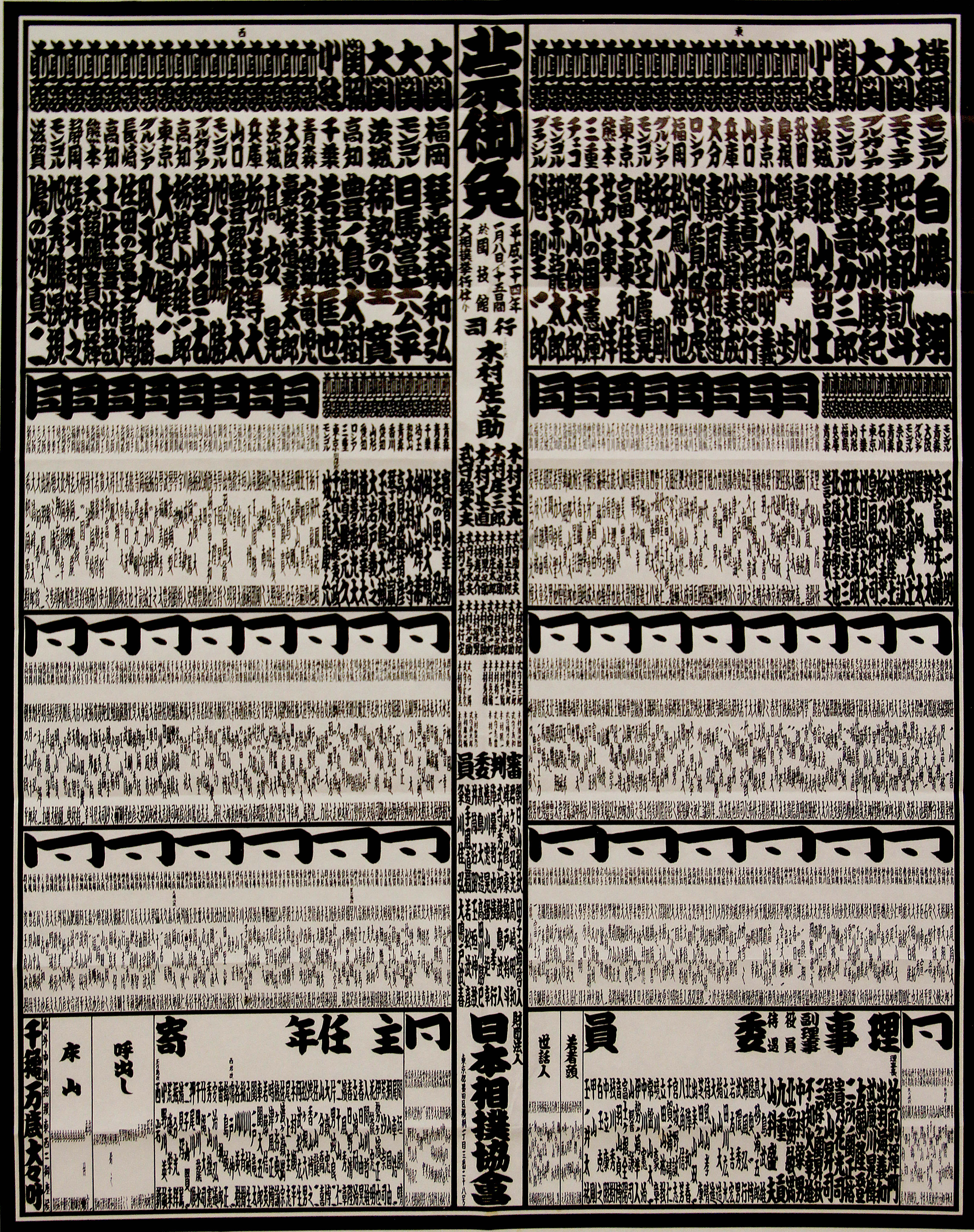
Banzuke
A , officially called is a document listing the rankings of professional sumo wrestlers published before each official tournament ('' honbasho''). The term can also refer to the rankings themselves. The document is normally released about two weeks before the tournament begins. On the ''banzuke'', wrestlers are divided into East, which is printed on the right, and West, which is printed on the left. Each wrestler's full ''shikona'' (ring name), hometown and rank is also listed. The top of the page starts with the highest ranked ''makuuchi'' wrestlers printed in the largest characters, down to the wrestlers in the lowest divisions which are written in much smaller characters. The names of '' gyōji'' (sumo referees), '' yobidashi'' (ushers/handymen), '' shimpan'' (judges), '' oyakata'' (elders of the Japan Sumo Association), and occasionally ''tokoyama'' (hairdressers) are also listed. While not as old as sumo itself, the form and production of this document can be traced as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by throwing, shoving or pushing him down). Sumo originated in Japan, the only country where it is practised professionally and where it is considered the national sport. It is considered a ''gendai budō'', which refers to modern Japanese martial arts, but the sport has a history spanning many centuries. Many ancient traditions have been preserved in sumo, and even today the sport includes many ritual elements, such as the use of salt purification, from Shinto. Life as a wrestler is highly regimented, with rules regulated by the Japan Sumo Association. Most sumo wrestlers are required to live in communal sumo training stables, known in Japanese as ''Heya (sumo), heya'', where all aspects of their daily livesfrom meals to their manner of dressa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryōgoku Kokugikan
, also known as Ryōgoku Sumo Hall or Kokugikan Arena, is the name bestowed to two different indoor sporting arenas located in Tokyo. The first ''Ryōgoku Kokugikan'' opened its doors in 1909 and was located on the premises of the Ekōin temple in Ryōgoku, Tokyo. Although no sumo bouts were held after 1945, following the capitulation of Japan and the requisition of the building by the occupying forces, the building itself remained active until 1983, being notably used by the Nihon University. The second ''Ryōgoku Kokugikan'' is currently located in the Yokoami neighborhood of Sumida next to the Edo-Tokyo Museum. It opened in 1985, following the closure of the Kuramae Kokugikan, and is still in use today. The first Ryōgoku Kokugikan History The growing popularity of Sumo during the Meiji period led to the building of the original Kokugikan in Ryōgoku. Until then, Sumo bouts were performed in temples precincts and depended on the weather. In March 1906, the 22nd Imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |