 |
Year 2000 Problem
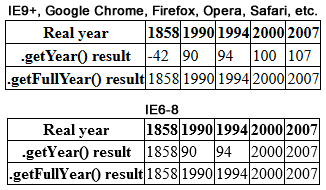
The term year 2000 problem, or simply Y2K, refers to potential computer errors related to the Time formatting and storage bugs, formatting and storage of calendar data for dates in and after the year 2000. Many Computer program, programs represented four-digit years with only the final two digits, making the year 2000 indistinguishable from 1900. Computer systems' inability to distinguish dates correctly had the potential to bring down worldwide infrastructures for computer-reliant industries. In the years leading up to the turn of the millennium, the public gradually became aware of the "Y2K scare", and individual companies predicted the global damage caused by the bug would require anything between $400 million and $600 billion to rectify. A lack of clarity regarding the potential dangers of the bug led some to stock up on food, water, and firearms, purchase backup generators, and withdraw large sums of money in anticipation of a computer-induced Global catastrophic risk, ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Bug De L'an 2000
Bug or BUG may refer to: Common uses * A terrestrial arthropod animal, usually with at least six legs ** Insect, a six-legged arthropod ***Hemiptera, the true bugs * A colloquialism for most minibeasts including arthropods, gastropods and worms. * Covert listening device, used in surveillance and espionage * Bug (engineering), a defect in an engineered system ** Software bug ** Hardware bug ** BUG (tag), a computer programming comment tag * Score bug, overlaid display of information in a sports broadcast *Pathogen, colloquially Arts, entertainment and media Fictional entities * Bug (comics), a superhero in Marvel Comics * Bug (DC Comics), different characters appearing in DC Comics * Bug (''Starship Troopers''), an alien race from the novel and film * Bug, Michael Lee's younger brother in ''The Wire'' * Bug, in the TV series '' WordWorld'' * Bobby "Bug" Guthrie, in the TV series ''Life Unexpected'' Film and television * ''Bug'' (1975 film), an American horror film * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
McGraw-Hill
McGraw Hill is an American education science company that provides educational content, software, and services for students and educators across various levels—from K-12 to higher education and professional settings. They produce textbooks, digital learning tools, and adaptive technology to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. It is one of the "big three" educational publishers along with Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and Pearson Education. McGraw Hill also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888, when James H. McGraw, co-founder of McGraw Hill, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Stephen Fry
Sir Stephen John Fry (born 24 August 1957) is an English actor, broadcaster, comedian, director, narrator and writer. He came to prominence as a member of the comic act Fry and Laurie alongside Hugh Laurie, with the two starring in ''A Bit of Fry & Laurie'' (1989–1995) and ''Jeeves and Wooster'' (1990–1993). He also starred in the sketch series ''Alfresco (TV series), Alfresco'' (1983–1984) with Laurie, Emma Thompson, and Robbie Coltrane, and in ''Blackadder'' (1986–1989) alongside Rowan Atkinson. Since 2011 he has served as president of the mental health charity Mind (charity), Mind. In 2025, he was Knight Bachelor, knighted for services to mental health awareness, the environment and charity. Fry's film acting roles include playing Oscar Wilde in the film ''Wilde (film), Wilde'' (1997), for which he was nominated for the Golden Globe Award for Best Actor – Motion Picture Drama, Golden Globe Award for Best Actor; Inspector Thompson in Robert Altman's murder mystery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Scaremongering
Fearmongering, or scaremongering, is the act of exploiting feelings of fear by using exaggerated rumors of impending danger, usually for personal gain. Theory According to evolutionary anthropology and evolutionary biology, humans have a strong impulse to pay attention to danger because awareness of dangers has been important for survival throughout their evolutionary history. The effect is amplified by cultural evolution when the news media cater to people's appetite for news about dangers. The attention of citizens is a fiercely contested resource that news media, political campaigners, reform movement, social reformers, advertising, advertisers, non-governmental organization, civil society organizations, missionary, missionaries, and cultural event management, event makers compete over, according to attention economy. Agency (sociology), Social agents of all kinds are often using fearmongering as a tactic in the competition for attention, as illustrated by the examples below. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Contingency Plan
A contingency plan, or alternate plan, also known colloquially as Plan B, is a plan devised for an outcome other than in the usual (expected) plan. It is often used for risk management for an exceptional risk that, though unlikely, would have catastrophic consequences. Use Contingency plans are often devised by businesses or governments. There are five steps of implementing contingency plan, which are organize a planning team, assess the scope of the problem, develop a plan, test the plan, and keep the plan up-to-date. For example, if many employees of a company are traveling together on an aircraft which crashes, killing all aboard, the company could be severely strained or ruined by such a loss. Therefore, many companies have procedures to follow in the event of such a disaster. The plan may also include standing policies to mitigate a disaster's potential impact, such as requiring employees to travel separately or limiting the number of employees on any one aircraft. During tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
The New York Post
The ''New York Post'' (''NY Post'') is an American Conservatism in the United States, conservative daily Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid newspaper published in New York City. The ''Post'' also operates three online sites: NYPost.com; PageSix.com, a gossip site; and Decider.com, an entertainment site. The newspaper was founded in 1801 by Alexander Hamilton, a Federalist Party, Federalist and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who was appointed the nation's first United States Secretary of the Treasury, Secretary of the Treasury by George Washington. The newspaper became a respected broadsheet in the 19th century, under the name ''New York Evening Post'' (originally ''New-York Evening Post''). Its most notable 19th-century editor was William Cullen Bryant. In the mid-20th century, the newspaper was owned by Dorothy Schiff, who developed the tabloid format that has been used since by the newspaper. In 1976, Rupert Murdoch's News Corp bought the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
John Hamre
John Julian Hamre (born July 3, 1950) is an American international relations scholar and former senior defense official. He is the president and CEO of the Center for Strategic and International Studies, a position he has held with since 2000. Early life and education Hamre is the son of Melvin Sanders and Ruth Lucile (Larson) Hamre. He attended primary and secondary school in Clark, South Dakota, graduating from the Clark Public High School in May 1968. He earned a B.A. (with high distinction) in political science and economics from Augustana College in Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1972). The following year he was a Rockefeller Fellow at Harvard Divinity School. He earned an M.A. (1976) and Ph.D. (1978) with distinction from the Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies (SAIS). His doctoral thesis was entitled ''Congressional Dissent and American Foreign Policy: Constitutional War-Making in the Vietnam Years''. Federal government service Hamre s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in the Superman dynasty * E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film '' Road Trip'' Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él ''(Lucerito album), a 1982 album by Lucerito * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from the album '' Caminando'' * "Él" (Lucía song), the Spanish entry performed by Lucía in the Eurovision Song Contest 1982 Other media * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (film), a 1953 film by Luis Buñuel based on the 1926 novel * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 1991 Japanese adult visual novel * EL TV, an Azerbaijani regional television channel Companies and organizations * Estée Lauder Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for Computer data storage, digital information. The International System of Units (SI) defines the prefix ''kilo-, kilo'' as a multiplication factor of 1000 (103); therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information science and technology, International Electrotechnical Commission (2008). The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. In some areas of information technology, particularly in reference to random-access memory capacity, ''kilobyte'' instead often refers to 1024 (210) bytes. This arises from the prevalence of sizes that are powers of two in modern digital memory architectures, coupled with the coincidence that 210 differs from 103 by less than 2.5%. The kibibyte is defined as 1024 bytes, avoiding the ambiguity issues of the ''kilobyte''.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Computer Memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ''core'' (for magnetic core memory) and ''store''. Main memory operates at a high speed compared to mass storage which is slower but less expensive per bit and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs and data being actively processed, computer memory serves as a Page cache, mass storage cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as it is not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called ''virtual memory''. Modern computer memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cell (com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Personal Computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC game, gaming. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. The term home computer has also been used, primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s. The advent of personal computers and the concurrent Digital Revolution have significantly affected the lives of people. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with computers. While personal computer users may develop their applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mainframe Computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, server (computing), servers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers. The term ''mainframe'' was derived from the large cabinet, called a ''main frame'', that housed the central processing unit and main computer memory, memory of early computers. Later, the term ''mainframe'' was used to distinguish high-end commercial computers from less powerful machines. Design Modern mainfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |