|
Winged Hussars
The Polish hussars (; ), alternatively known as the winged hussars, were an elite heavy cavalry formation active in Poland and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1503 to 1702. Their epithet is derived from large rear wings, which were intended to demoralize the enemy during a charge. The hussars ranked as the elite of Polish cavalry until their official disbanding in 1776. The hussar dress was ostentatious and comprised plated body armour (cuirass, spaulders, bevors, and arm bracers) adorned by gold ornaments, a burgonet or lobster-tailed pot helmet and jackboots as well as versatile weaponry such as lances, long thrusting swords, sabres, pistols, carbines, maces, hatchets, war hammers, and horseman's picks. It was customary to maintain a red-and-white colour scheme, and to be girded with tanned animal hide. The wings were traditionally assembled from the feathers of raptors, and the angel-like frame was fastened onto the armour or saddle. The early hussars were l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Cavalry
Heavy cavalry was a class of cavalry intended to deliver a battlefield charge and also to act as a Military reserve, tactical reserve; they are also often termed ''shock cavalry''. Although their equipment differed greatly depending on the region and historical period, heavy cavalry were generally mounted on large powerful warhorses, wore body armor, and armed with either lances, swords, Mace (bludgeon), maces, flail (weapon), flails (disputed), battle axes, or war hammers; their mounts may also have been protected by barding. They were distinct from light cavalry, who were intended for raid (military), raiding, reconnaissance, screening (tactical), screening, skirmishing, patrolling, and tactical communications. History Persian Empires Iranian tribes such as the Massagetae were believed to be the originator of the class of heavy cavalry known as cataphract. During the time of Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persia cavalry was the elite arm of service (as was the case in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
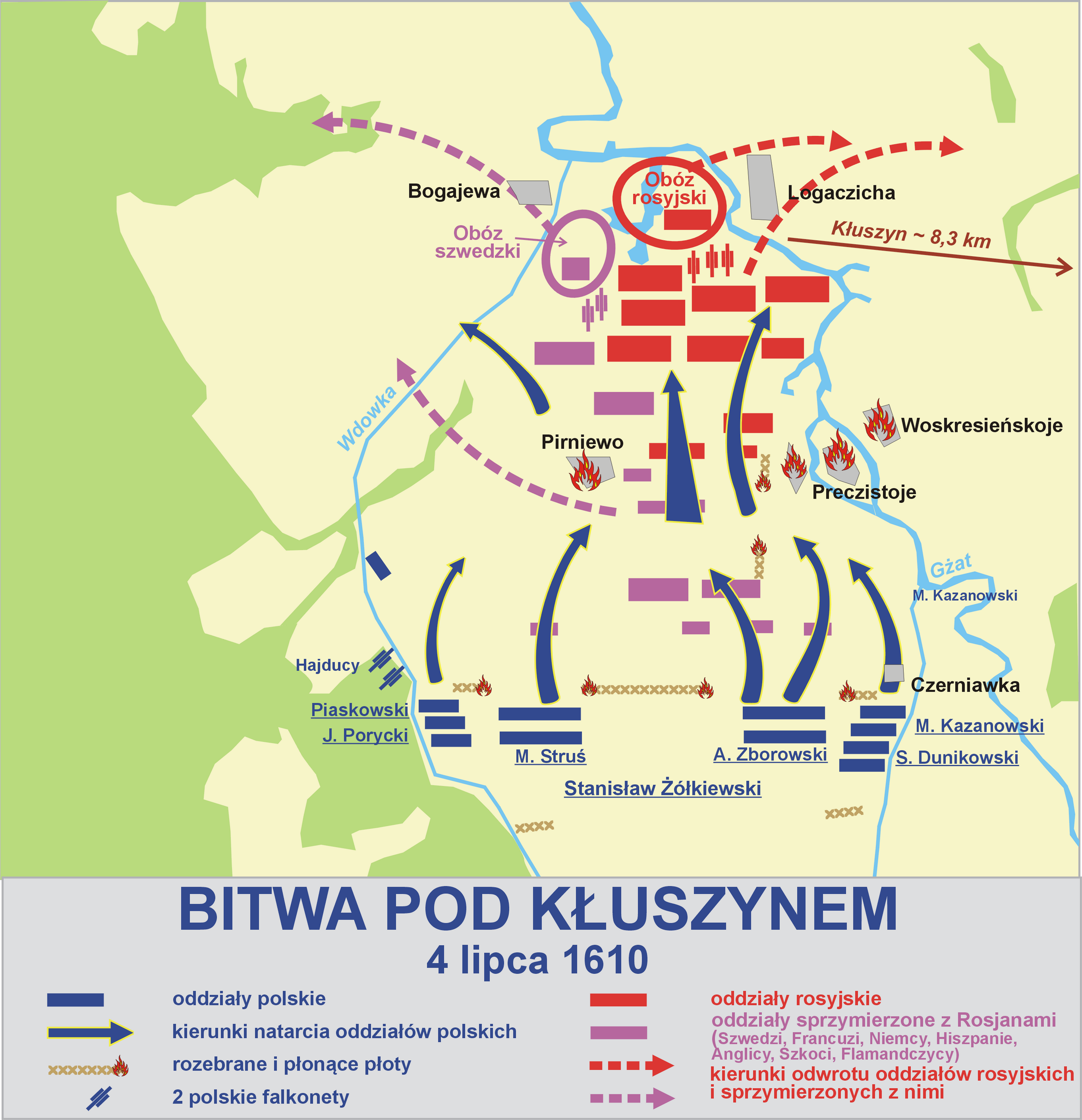
Battle Of Klushino
The Battle of Klushino, or the Battle of Kłuszyn, was fought on 4 July 1610, between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia during the Polish–Russian War, part of Russia's Time of Troubles. The battle occurred near the village of Klushino () near Smolensk (Polish: ''Smoleńsk''). In the battle the outnumbered Polish-Lithuanian force secured a decisive victory over Russia, due to the tactical competence of hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski and the military prowess of Polish hussars, the elite of the army of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The battle is remembered as one of the greatest triumphs of the Polish cavalry and an example of excellence and supremacy of the Polish military at the time. Background In 1610, in response to the Polish-Lithuanian advance on Russia, Russia and Sweden formed an alliance, and launched an operation known as the De la Gardie Campaign. A Russian army under Prince Dmitry Shuisky was heading towards the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Smolensk (1609–1611)
The siege of Smolensk (), also known as the Smolensk Defense in Russia (), lasted 20 months between 29 September 1609 to 13 June 1611, when the Polish army besieged the Russian city of Smolensk during the Polish–Russian War of 1609–1618. Background In July 1608, the Commonwealth concluded a truce with Vasily Shuisky, which was to last three years and 11 months. Sigismund III Vasa, who had discreetly supported the Dmitry from the beginning, had no intention of abiding by the concluded treaty, which was evidenced by the arrival in August 1608 in the camp of the second Dmitry of a faithful supporter of the king, the starost Jan Piotr Sapieha, who was the cousin of the Grand Chancellor of Lithuania Lev Sapieha. Russia, too, as early as the end of 1608 began to negotiate to ally with Sweden, which was at war with Poland at the time. Eventually, Vasily Shuisky concluded an alliance treaty with Sweden in February 1609, soon after the treaty with the Swedes, he began to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kircholm
The Battle of Kircholm (; Polish: ''Bitwa pod Kircholmem''; Swedish: ''Slaget vid Kirkholm''; ) was one of the major battles in the Polish–Swedish War of 1600–1611. The battle was decided in 20 minutes by a devastating charge of Polish-Lithuanian cavalry, including the Winged Hussars. The battle ended in a decisive victory of the Polish-Lithuanian forces, and is remembered as one of the greatest triumphs of Commonwealth cavalry. Background On 27 September 1605, the Commonwealth and Swedish forces met near the small town of Kircholm (now Salaspils in Latvia, some south-east of Riga). The forces of Charles IX of Sweden were numerically superior and were composed of 10,868 men and 11 cannons. The Swedish army included two western commanders, Frederick of Lüneburg and Count Joachim Frederick of Mansfeld, with a few thousand German and Dutch mercenaries and even a few hundred Scots. The Polish Crown declined to raise funds for defence and send troops, only making promis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Reval (1602)
The Battle of Reval took place on June 30, 1602, during the Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611) near present-day Tallinn in Estonia. The Polish forces were led by Grand Field Hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski who had been sent against Swedish forces gathering by Tallinn by Grand Crown Hetman Jan Zamoyski. Żółkiewski attacked "on the march" with two squadrons of Polish hussars The Polish hussars (; ), alternatively known as the winged hussars, were an elite heavy cavalry formation active in Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Poland and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1503 to 1702. Their epithet is derived fr .... The charge however was not successful. As a result, the Swedish forces put up frisian horses as a protection against further frontal cavalry charges. Żółkiewski then sent light cavalry on a round about flanking maneuver which attacked the Swedes from behind, coinciding with another charge by the hussars. The Swedish lines broke as a result. The Swedes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kokenhausen
The Battle of Kokenhausen (Kokenhuza, ) was a major battle opening the Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611). It took place on the 13 June (O.S.) or 23 June (N.S.)Frost, R.I., 2000, The Northern Wars, 1558–1721, Harlow: Pearson Education Limited, p.63. 1601 near Koknese (in Baltic German ''Kokenhausen'') in Livonia (now in Latvia). In the battle, Polish forces defeated the Swedish relief force and captured the besieging force, relieving the Polish garrison. The battle is notable as one of the greatest victories of the Polish hussars, who defeated their numerically superior Sweden, Swedish adversaries. Prelude Kokenhausen was one of three major forts blocking the Swedish progress on the line of the Daugava River. Swedish forces of about 2,000 under Carl Carlsson Gyllenhielm had been blockading the fortified town of Kokenhausen, located on Daugava River, between Riga and Daugavpils - since 10 March - after the arrival of Charles IX of Sweden, Duke Charles with heavy artillery - la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wenden (1601)
The Battle of Wenden (also known as Battle of Kieś) took place on 7 January 1601, during the Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611). Polish–Lithuanian forces were led by Jürgen von Farensbach (''Jerzy Farensbach'') and Maciej Dębiński. The Swedes were under Hans Bengtsson. The battle is significant as the first encounter between Swedish reiters and Polish hussars.Leszek Podhorodecki, "Rapier i koncerz", Warszawa 1985, Prelude The military campaign began in late 1599. Swedish forces captured Narva, Estonia, then after gathering 10 thousands troops under the command of Charles IX Parnu they captured Fellin, and on 6 January 1601 Dorpat. The day after the capture of Dorpat, the Swedish forces (3,000 soldiers) suddenly attacked the Poles and Lithuanians camped under Wenden.Leszek Podhorodecki, "Rapier i koncerz", Warszawa 1985, Battle Led by Colonel Maciej Dembiński, the Polish–Lithuanian army, despite the surprise, quickly prepared for battle and went into offensive. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611)
The Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611) was a continuation of struggle between Sweden and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over control of Livonia and Estonia, as well as the dispute over the Swedish throne between Charles IX of Sweden and Sigismund III of Poland. After skirmishes, sieges and battles often aborted by Jan Karol Chodkiewicz, a truce was signed until the later invasion by the Russians. Background This conflict between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden traces its roots to the War against Sigismund. In this civil war (1597–1599), Sigismund III Vasa, at one time king of both the Commonwealth and Sweden, lost the throne of Sweden. Few Commonwealth troops participated in that conflict, and it is mostly regarded as a Swedish civil war, not part of the Polish–Swedish wars. After an early stalemate, Sigismund was defeated at the Battle of Stångebro in 1598. By 1599, Sigismund was dethroned by his uncle, Duke Charles and forced to retreat to the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Byczyna
The Battle of Byczyna, also known as the Battle of Pitschen (; ), was the deciding battle of the 1587–1588 War of the Polish Succession, which erupted after two rival candidates were elected to the Polish throne. The two opposing sides had forces nearly evenly matched, with armies about 6,000 strong, roughly half infantry and half cavalry. The battle was an overwhelming victory for the Polish-Swedish faction, led by the Swedish-born king-elect Sigismund III Vasa, over the army of his rival to the throne, Maximilian III, Archduke of Austria. Taking place near the Silesian town of Pitschen (modern Byczyna), then just a few kilometres outside the territory of Poland–Lithuania, on 24 January 1588, Sigismund's supporters were commanded by Chancellor and Great Crown Hetman Jan Zamoyski. Besides the commanders, notable participants included Stanisław Stadnicki on Maximilian's side, and Stanisław Żółkiewski on Sigismund's. The army of the Polish-Austrian (or Habsburg) facti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Polish Succession (1587–1588)
The War of the Polish Succession or the Habsburg-Polish War took place from 1587 to 1588 over the election of the successor to the King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania Stephen Báthory. The war was fought between factions of Sigismund III Vasa and Maximilian III, with Sigismund eventually being crowned. Two major battles of this conflict included the Siege of Kraków, in which Maximilian III failed to capture the capital of the Commonwealth, and the Battle of Byczyna, in which Maximilian was forced to surrender. Sigismund's victory was significantly the doing of Chancellor and Hetman Jan Zamoyski, who stood behind both the political intrigue and the military victories of this conflict. Background In 1586, following the death of the previous Polish king, Stefan Batory, the Swedish crown prince Sigismund III Vasa and Habsburg Maximilian III, Archduke of Austria, took part in the election to the joint Polish–Lithuanian throne. Each of the two candidates had supporter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |