|
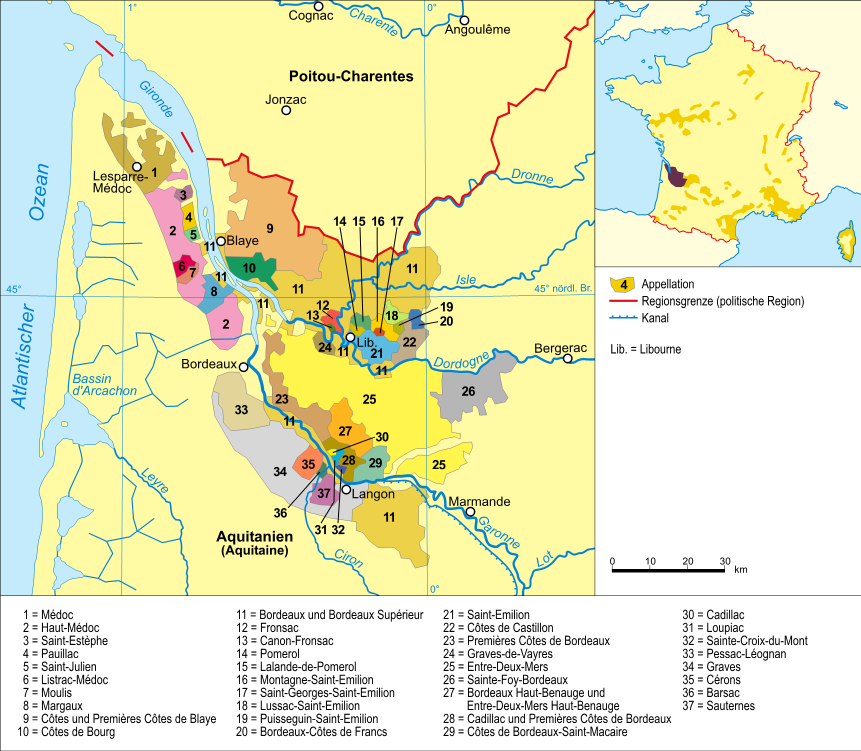
Wine Regions Of Bordeaux
The wine regions of Bordeaux in France are a large number of wine growing areas, differing widely in size and sometimes overlapping, which lie within the overarching wine region of Bordeaux, centred on the city of Bordeaux and covering the whole area of the Gironde department of Aquitaine. The Bordeaux region is naturally divided by the Gironde Estuary into a Left Bank area which includes the Médoc and Graves and a Right Bank area which includes the Libournais, Bourg and Blaye. The Médoc is itself divided into Haut-Médoc (the upstream or southern portion) and Bas-Médoc (the downstream or northern portion, often referred to simply as "Médoc"). There are various sub-regions within the Haut-Médoc, including St-Estèphe, Pauillac, St.-Julien and Margaux and the less well known areas of AOC Moulis and Listrac. Graves includes the sub-regions of Pessac-Léognan and Sauternes (among others), and Sauternes in turn includes the sub-region of Barsac. The Libournais includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomerol AOC
Pomerol () is a French wine-growing commune and ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) within the Bordeaux wine regions#The Libournais appellations, Libournais ("Right Bank") in Bordeaux (wine), Bordeaux. The wine produced here is predominately from Merlot with Cabernet Franc playing a supporting role.Clive Coates ''An Encyclopedia of the Wines and Domaines of France'' pp. 110–115 University of California Press; First Printing edition (June 2001) Unlike most other Bordeaux communes, there is no real village of Pomerol, although there is a church. The houses are set among the vineyards.Stephen Brooks ''The Complete Bordeaux'' pp. 457–461 Mitchell Beazley (November, 2012) The region was recognized as a distinct wine region apart from Saint-Émilion and the greater Libournais region by the French government in 1923 and was granted AOC status in 1936 as part of the first wave of AOC establishments by the ''Institut national de l'origine et de la qualité'' (INAO). While it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sémillon
Sémillon () is a golden-skinned grape used to make dry and sweet white wines, mostly in French wine, France and Australian wine, Australia. Its thin skin and susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea, botrytis make it dominate the sweet wine region Sauternes AOC and Barsac AOC. History The Sémillon grape is native to the Bordeaux wine region, Bordeaux region. It was known as Sémillon de Saint-Émilion in 1736, while Sémillon also resembles the Gascon language, local pronunciation of the town's name ([semi'ʎuŋ]). It first arrived in Australia in the early 19th century and by the 1820s the grape covered over 90% of South African wine, South Africa's vineyards, where it was known as ''Wyndruif'', meaning "wine grape". It was once considered to be the most planted grape in the world, although this is no longer the case. In the 1950s, Chile wine, Chile's vineyards were made up of over 75% Sémillon. Today, it accounts for just 1% of South Africa wine, South African Cape vines. Vitic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauvignon Blanc
Sauvignon blanc () is a green-skinned grape variety that originates from the city of Bordeaux in France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French words ''sauvage'' ("wild") and ''blanc'' ("white") due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in South West France. It is possibly a descendant of Savagnin. Sauvignon blanc is planted in many of the world's wine regions, producing a crisp, dry, and refreshing white varietal wine. The grape is also a component of the famous dessert wines from Sauternes and Barsac. Sauvignon blanc is widely cultivated in France, Chile, Romania, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Bulgaria, the states of Oregon, Washington, and California in the US. Some New World Sauvignon blancs, particularly from California, may also be called "Fumé Blanc", a marketing term coined by Robert Mondavi in reference to Pouilly-Fumé. Depending on the climate, the flavor can range from aggressively grassy to sweetly tropical. In cooler cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petit Verdot
Petit Verdot is a variety of red wine grape, principally used in classic Bordeaux blends. It ripens much later than the other varieties in Bordeaux, often too late, so it fell out of favour in its home region. When it does ripen it adds tannin, colour and flavour, in small amounts, to the blend. Petit verdot has attracted attention among winemakers in the New World, where it ripens more reliably and has been made into single varietal wine. It is also useful in 'stiffening' the mid palate of Cabernet Sauvignon blends. When young its aromas have been likened to banana and pencil shavings. Strong tones of violet and leather develop as it matures. History Petit Verdot probably predates Cabernet Sauvignon in Bordeaux, but its origins are unclear. There are records of it in the eighteenth century, but its characteristics suggest an origin in much hotter climes than the Gironde. It is likely that it originates from the Pyrénées-Atlantiques where it was possibly domesticated from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malbec
Malbec () is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. In France, plantations of Malbec are now found primarily in Cahors in South West France, though the grape is grown worldwide. It is also available as an Argentine varietal. The grape became less popular in Bordeaux after 1956 when frost killed off 75% of the crop. Despite Cahors being hit by the same frost, which devastated the vineyards, Malbec was replanted and continued to be popular in that area. Winemakers in the region frequently mixed Malbec with Merlot and Tannat to make dark, full-bodied wines, but have ventured into 100% Malbec varietal wines more recently.J. Robinson ''Vines, Grapes & Wines'' pg 198 & 204 Mitchell Beazley 1986 A popular but unconfirmed theory claims that Malbec is named after a Hungarian peasant who first spread the grape variety throughou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabernet Franc
Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux (wine), Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone, as in the Loire (wine), Loire's Chinon wine, Chinon. In addition to being used in blends and produced as a varietal in Canada (wine), Canada, Lake Erie AVA, Lake Erie AVA in Pennsylvania, and across the United States (wine), United States and Argentina, it is sometimes made into ice wine in those regions. Cabernet Franc is lighter than Cabernet Sauvignon, making a bright pale red wine that contributes finesse and lends a Black pepper, peppery perfume to blends with more robust grapes. Depending on the growing region and style of wine, additional Aromas (wine), aromas can include tobacco, raspberry, bell pepper, Blackcurrant, cassis, and Viola (plant), violets. Records of Cabernet Franc in Bordeaux go back to the end of the 18th century, although it was planted in Loire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merlot
Merlot ( ) is a dark-blue-colored wine grape variety that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name ''Merlot'' is thought to be a diminutive of , the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to the color of the grape. Its softness and "fleshiness", combined with its earlier ripening, make Merlot a popular grape for blending with the sterner, later-ripening Cabernet Sauvignon, which tends to be higher in tannin. Along with Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Malbec, and Petit Verdot, Merlot is one of the primary grapes used in Bordeaux wine, and it is the most widely planted grape in the Bordeaux wine regions. Merlot is also one of the most popular red wine varietals in many markets. This flexibility has helped to make it one of the world's most planted grape varieties. As of 2004, Merlot was estimated to be the third most grown variety at globally.J. Robinson (ed) ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'' Third Edition, Oxford University P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon () is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Australia and British Columbia, Canada to Lebanon's Beqaa Valley. This grape variety appeared in France in the 17th century as a result of natural crossbreeding. Its popularity is often attributed to its ease of cultivation—the grapes have thick skins and the vines are hardy and naturally low yielding, budding late to avoid frost and resistant to viticulture hazards. The classic profile of Cabernet Sauvignon tends to be full-bodied wines with high tannins and noticeable acidity that contributes to the wine's aging potential. In cool areas, it has flavors of blackcurrant and green pepper; in warmer places, it may taste like black cherry and olive; in very hot climates, it can have a jammy flavor. History and origins For many years, the origin of Cabernet Sauvignon was not cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine Label
Wine labels are important sources of information for consumers since they tell the type and origin of the wine. The label is often the only resource a buyer has for evaluating the wine before purchasing it. Certain information is ordinarily included in the wine label, such as the country of origin, quality, type of wine, alcoholic degree, producer, bottler, or importer.George, Rosemary, ''The Simon & Schuster Pocket Wine Label Decoder'', 1989. In addition to these national labeling requirements producers may include their web site address and a QR Code with vintage specific information. Information provided Label design Some wineries place great importance on the label design while others do not. There are wineries that have not changed their label's design in over 60 years, as in the case of Château Simone, while others hire designers every year to change it. Labels may include images of works by Picasso, Chagall, and other artists, and these may be collector's pieces. The ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winemaking
Winemaking, wine-making, or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its Ethanol fermentation, fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. There is evidence that suggests that the earliest wine production took place in Georgia and Iran around 6000 to 5000 B.C. The science of wine and winemaking is known as oenology. A winemaker may also be called a #Winemakers, vintner. The growing of grapes is viticulture and there are List of grape varieties, many varieties of grapes. Winemaking can be divided into two general categories: still wine production (without carbonation) and sparkling wine production (with carbonation – natural or injected). Red wine, white wine, and rosé are the other main categories. Although most wine is made from grapes, it may also be made from other plants. (See fruit wine.) Other similar light alcoholic drinks (as opposed to beer or Liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appellation D'origine Contrôlée
In France, the ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (, ; abbr. AOC ) is a label that identifies an agricultural product whose stages of production and processing are carried out in a defined geographical area – the ''terroir'' – and using recognized and traditional know-how. The specificity of an AOC product is determined by the combination of a physical and biological environment with established production techniques transmitted within a human community. Together, these give the product its distinctive qualities. The defining technical and geographic factors are set forth in standards for each product, including wines, cheeses and meats. Other countries and the European Union have similar labeling systems. The European Union's protected designation of origin (PDO and PGI) system has harmonized the protection of all geographical indications and their registration. When labelling wine however, producers may still use recognized traditional terms like AOC, and are not requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |