|
Whom
The pronoun ''who'', in English, is an interrogative pronoun and a relative pronoun, used primarily to refer to persons. Unmarked, ''who'' is the pronoun's subjective form; its inflected forms are the objective ''whom'' and the possessive ''whose''. The set has derived indefinite forms ''whoever'', ''whomever'', and ''whoseever,'' as well as a further, earlier such set ''whosoever,'' ''whomsoever'', and ''whosesoever'' (see also " -ever"). Etymology The interrogative and relative pronouns ''who'' derive from the Old English singular interrogative , and whose paradigm is set out below: It was not until the end of the 17th century that ''who'' became the only pronoun that could ask about the identity of persons and ''what'' fully lost this ability. "The first occurrences of wh-relatives date from the twelfth century (with the possible exception (see Kivimaa 1966: 35)). The wh- form does not become frequent, however, until the fourteenth century." Today, relative ''whose'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Relative Clause
A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phrase and uses some grammatical device to indicate that one of the arguments in the relative clause refers to the noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence ''I met a man who wasn't too sure of himself'', the subordinate clause ''who wasn't too sure of himself'' is a relative clause since it modifies the noun ''man'' and uses the pronoun ''who'' to indicate that the same "MAN" is referred to in the subordinate clause (in this case as its subject). In many languages, relative clauses are introduced by a special class of pronouns called '' relative pronouns'', such as ''who'' in the example just given. In other languages, relative clauses may be marked in different ways: they may be introduced by a special class of conjunctions called '' relativizers'', the main verb of the relative clause may appear in a special morphological variant, or a relative clause may be indicated by word order alone. In some languages, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Relative Clauses
Relative clauses in the English language are formed principally by means of English relative words, relative words. The basic relative pronouns are ''who (pronoun), who'', ''which'', and ''that''; ''who'' also has the derived forms ''whom'' and ''whose''. Various grammatical rules and style guides determine which relative pronouns may be suitable in various situations, especially for formal settings. In some cases the relative pronoun may be omitted and merely implied ("This is the man [that] I saw", or "This is the putter he wins with"). English also uses free relative clauses, which have no antecedent (grammar), antecedent and can be formed with the pronouns such as ''what'' ("I like what you've done"), and ''who'' and ''whoever''. Modern guides to English say that the relative pronoun should take the case (subject or object) which is appropriate to the relative clause, not the function performed by that clause within an external clause. Overview The basic grammatical rules for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Relative Words
The English relative words are words in English used to mark a clause, noun phrase or preposition phrase as relative. The central relative words in English include ''who'', ''whom'', ''whose'', ''which'', ''why'', and ''while'', as shown in the following examples, each of which has the relative clause in bold: * ''We should celebrate the things which we hold dear.'' * ''I've been studying hard, which explains my good grades.'' * ''I finally met Jordan, who had been away.'' * ''That's the reason why it works.'' Most also belong to the set of English interrogative words but function differently as relative words. The subordinator ''that'' is widely regarded as a relative word, though one with different properties from the others. Semantics Semantically speaking, relative words typically refer to some antecedent in the containing phrase or clause. For example, ''who'' within ''the teacher of mine who likes apples'' does not question the identity of a person, but rather refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dative Case
In grammar, the dative case ( abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob a drink". In this example, the dative marks what would be considered the indirect object of a verb in English. Sometimes the dative has functions unrelated to giving. In Scottish Gaelic and Irish, the term ''dative case'' is used in traditional grammars to refer to the prepositional case-marking of nouns following simple prepositions and the definite article. In Georgian and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu), the dative case can also mark the subject of a sentence.Bhatt, Rajesh (2003). Experiencer subjects. Handout from MIT course “Structure of the Modern Indo-Aryan Languages”. This is called the dative construction. In Hindi, the dative construction is not limited to only certain verbs or tenses and it can be used with any verb in any tense or mood. The dative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Prepositions
English prepositions are words – such as ''of'', ''in'', ''on'', ''at'', ''from'', etc. – that function as the Head (linguistics), head of a Adpositional phrase, prepositional phrase, and most characteristically license a noun phrase Object (grammar), object (e.g., ''in the water''). Semantically, they most typically Denotation, denote relations in space and time. Morphology (linguistics), Morphologically, they are usually simple and do not inflect. They form a Closed class, closed lexical category. Many of the most common of these are Grammaticalization, grammaticalized and correspond to case markings in languages such as Latin. For example, ''of'' typically corresponds to the Genitive case, genitive. History of the concept in English The history of the idea of prepositions inEnglish grammar writing can be seen as one of relative stagnation, only exceptionally interrupted by certain more influential authors... It was only in the second half of the twentieth century that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Interrogative Words
In English language, English, the interrogative words (sometimes known as "''wh'' words") may be divided into those associated with asking open-ended questions (''how'', ''what'', ''when'', ''where'', ''which'', ''Who (pronoun), who'', ''whom'', ''whose'', and ''why'', all of which also have ''-ever'' forms, e.g., ''whatever'') and those associated with asking closed-ended questions (''whether'' and ''if''). The main role of these words is to mark a clause as interrogative. For example, ''How did you do it?'' is marked as an interrogative clause by the presence of ''how'', and in ''I wonder whether it's true'', ''whether'' marks the Dependent clause, subordinate clause ''whether it's true'' as interrogative. Extended membership Along with the words listed above, the members include some older or archaic words, including ''whence'', ''whither'', and other compound English prepositions, prepositions such as ''whereby'', ''wherein'', formed from one of the central interrogative w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
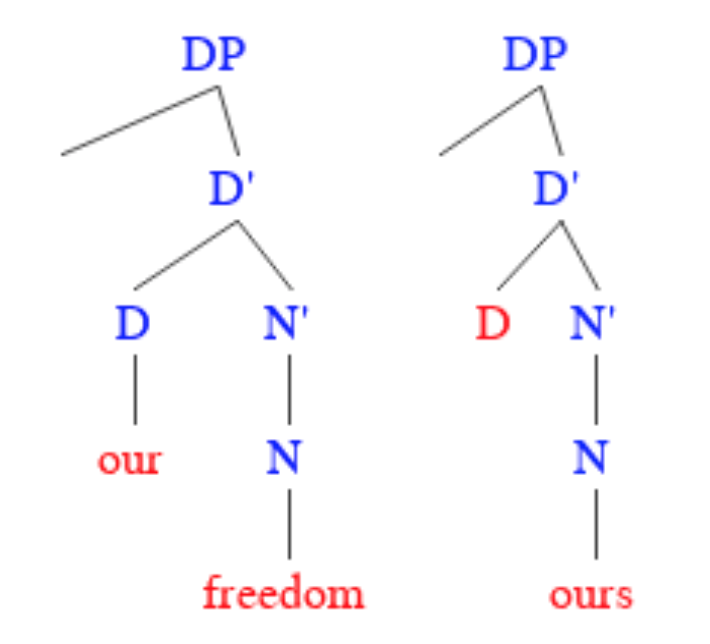
English Possessive
In English, possessive words or phrases exist for nouns and most pronouns, as well as some noun phrases. These can play the roles of determiners (also called possessive adjectives when corresponding to a pronoun) or of nouns. For nouns, noun phrases, and some pronouns, the possessive is generally formed with the suffix ''-s'', but in some cases just with the addition of an apostrophe to an existing ''s''. This form is sometimes called the Saxon genitive, reflecting the suffix's derivation from Old English. However, personal pronouns have irregular possessives that do not use an apostrophe, such as ''its'', and most of them have different forms for possessive determiners and possessive pronouns, such as ''my'' and ''mine'' or ''your'' and ''yours''. Possessives are one of the means by which genitive constructions are formed in modern English, the other principal one being the use of the preposition ''of''. It is sometimes stated that the possessives represent a grammatical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indefinite Pronoun
An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun which does not have a specific, familiar referent. Indefinite pronouns are in contrast to definite pronouns. Indefinite pronouns can represent either count nouns or noncount nouns. They often have related forms across these categories: universal (such as ''everyone'', ''everything''), assertive existential (such as ''somebody'', ''something''), elective existential (such as ''anyone'', ''anything''), and negative (such as ''nobody'', ''nothing''). Many languages distinguish forms of indefinites used in affirmative contexts from those used in non-affirmative contexts. For instance, English "something" can be used only in affirmative contexts while "anything" is used otherwise. Indefinite pronouns are associated with indefinite determiners of a similar or identical form (such as ''every'', ''any'', ''all'', ''some''). A pronoun can be thought of as ''replacing'' a noun phrase, while a determiner ''introduces'' a noun phrase and precedes any ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |