|
White-nose Syndrome
White-nose syndrome (WNS) is a fungal disease in North American bats which has resulted in the dramatic decrease of the bat population in the United States and Canada, reportedly killing millions as of 2018. The condition is named for a distinctive fungal growth around the muzzles and on the wings of hibernating bats. It was first identified from a February 2006 photo taken in a cave located in Schoharie County, New York. The syndrome has rapidly spread since then. In early 2018, it was identified in 33 U.S. states and seven Canadian provinces; plus the fungus, albeit sans syndrome, had been found in three additional states. Most cases are in the eastern half of both countries, but in March 2016, it was confirmed in a little brown bat in Washington state. In 2019, evidence of the fungus was detected in California for the first time, although no affected bats were found. The disease is caused by the fungus '' Pseudogymnoascus destructans'', which colonizes the bat's skin. No obviou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
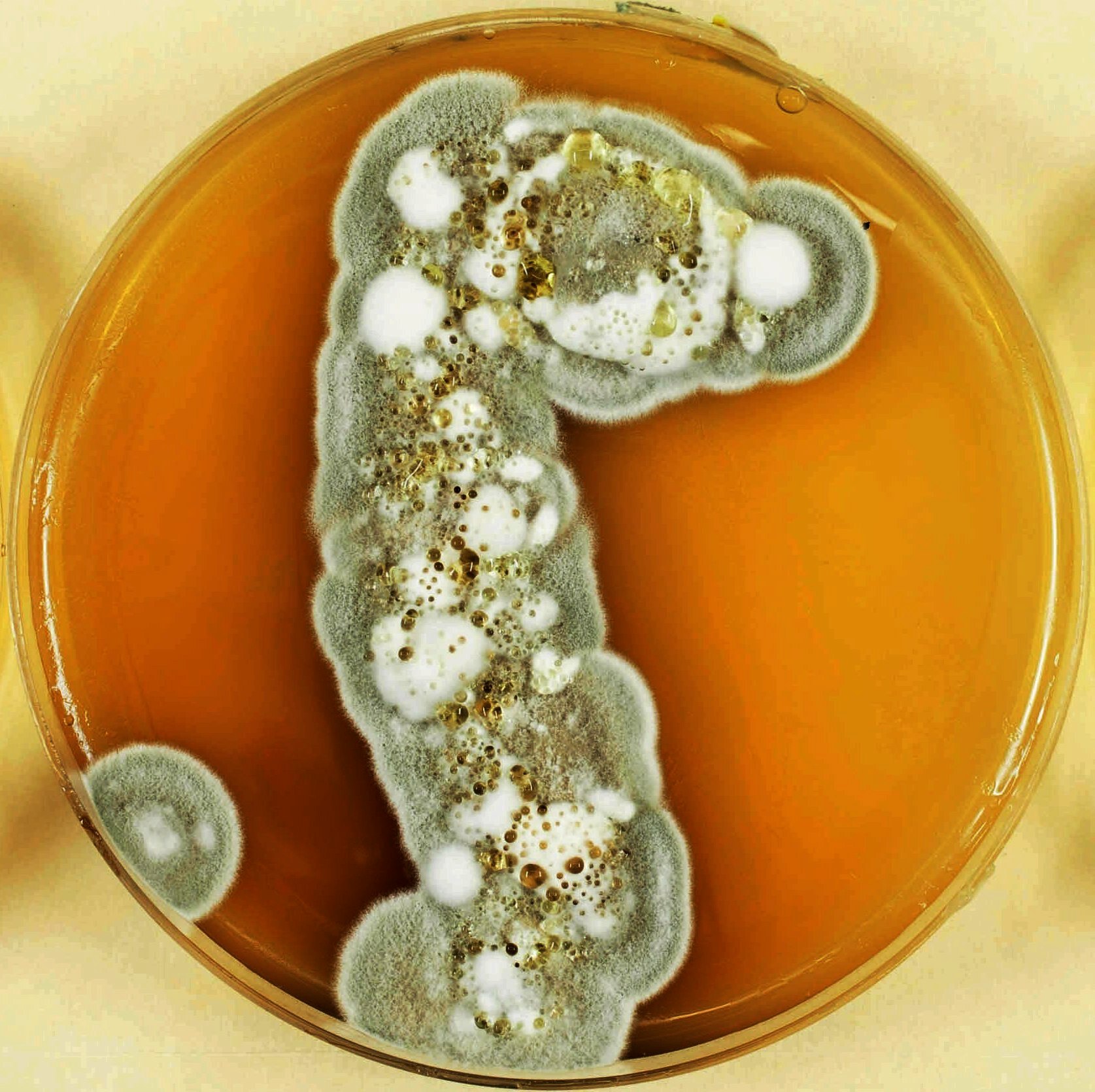
Pseudogymnoascus Destructans
''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' (formerly known as ''Geomyces destructans'') is a Psychrophile, psychrophilic (cold-loving) fungus that causes white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fatal disease that has devastated bat populations in parts of the United States and Canada. Unlike species of ''Geomyces'', ''P. destructans'' forms asymmetrically curved Conidium, conidia. ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' grows very slowly on artificial media and cannot grow at temperatures above 20 °C. It can grow around 4 °C to 20 °C, which encompasses the temperatures found in winter bat Hibernaculum (zoology), hibernacula. Phylogenic evaluation has revealed this organism should be reclassified under the family ''Pseudeurotiaceae'', changing its name to ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans''. Emaciation is considered the ultimate cause of mortality for the bats who are infected with ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans.'' The disease causes a disruption in the normal hibernation cycle where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Brown Bat With White Nose Syndrome (Greeley Mine, Cropped)
Little is a synonym for small size and may refer to: Arts and entertainment *Little (album), ''Little'' (album), 1990 debut album of Vic Chesnutt *Little (film), ''Little'' (film), 2019 American comedy film *The Littles, a series of children's novels by American author John Peterson **The Littles (TV series), ''The Littles'' (TV series), an American animated series based on the novels Places *Little, Kentucky, United States *Little, West Virginia, United States Other uses *Clan Little, a Scottish clan *Little (surname), an English surname *Little (automobile), an American automobile manufactured from 1912 to 1915 *Little, Brown and Company, an American publishing company *USS Little, USS ''Little'', multiple United States Navy ships See also * * *Little Mountain (other) *Little River (other) *Little Island (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Bat
The gray bat (''Myotis grisescens'') is a species of microbat endemic to North America. It once flourished in caves all over the southeastern United States, but due to human disturbance (ecology), disturbance, gray bat populations declined severely during the early and mid portion of the 20th century. 95% of gray bats now hibernate in only 15 caves. ''M. grisescens'' has been listed as federally endangered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service since 1976, and is protected under the Endangered Species Act. Gray bat populations were estimated at approximately 2 million bats around the time they were placed on the Endangered Species list. By the early 1980s populations of gray bats dropped to 1.6 million. With wildlife management, conservation efforts in place, in 2004, gray bat populations were estimated to have reached 3.4 million. Description ''M. grisescens'' are the largest members of their genus in the eastern United States. Of all U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eptesicus Fuscus Map
''Eptesicus'' is a genus of bats, commonly called house bats or serotine bats, in the family Vespertilionidae. The genus name is likely derived from the Greek words ''ptetikos'' 'able to fly' or ''petomai'' 'house flier', although this is not certain. Species Traditional The following species have traditionally been placed in ''Eptesicus'' 2023 proposed revision A 2023 study noted divisions within ''Eptesicus'' when considering physical characteristics, genetics, echolocation characteristics, and divergence timing, with the authors concluding that ''Eptesicus'' should be split into three genera. They described a new genus, ''Neoeptesicus'', and elevated the subgenus ''Cnephaeus'' to genus rank. The Old World ''Eptesicus'' species were moved to ''Cnephaeus'': * ''Cnephaeus anatolicus'' * ''Cnephaeus bottae'' * ''Cnephaeus floweri'' * ''Cnephaeus gobiensis'' * ''Cnephaeus hottentotus'' * ''Cnephaeus isabellinus'' * ''Cnephaeus japonensis'' * ''Cnephaeus kobayashii'' * ''Cneph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Brown Bat
The big brown bat (''Eptesicus fuscus'') is a species of vesper bat distributed widely throughout North America, the Caribbean, and the northern portion of South America. It was first described as a species in 1796. Compared to other microbats, the big brown bat is relatively large, weighing and possessing a wingspan of . Big brown bats are insectivore, insectivorous, consuming a diverse array of insects, particularly night-flying insects, but especially beetles. Some of the beetles it consumes are serious agricultural pests, including cucumber beetles. They are nocturnal, foraging for prey at night and roosting in sheltered areas during the day such as caves, tunnels, tree cavities, and human structures. Their breeding season is in the fall, shortly before their annual hibernation. After hibernation ends in the spring, females form maternity colony, maternity colonies for giving birth to young. Oftentimes only one offspring is produced per litter, though twins are common in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Status
The conservation status of a group of organisms (for instance, a species) indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels, as well as for consumer use such as sustainable seafood advisory lists and certification. The two international systems are by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). International systems IUCN Red List of Threatened Species The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature is the best known worldwide conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Daily
''ScienceDaily'' is an American website launched in 1995 that aggregates press releases and publishes lightly edited press releases (a practice called churnalism) about science, similar to Phys.org and EurekAlert!. History The site was founded by married couple Dan and Michele Hogan in 1995; Dan Hogan formerly worked in the public affairs department of Jackson Laboratory writing press releases. The site makes money from selling advertisements. the site said that it had grown "from a two-person operation to a full-fledged news business with worldwide contributors". At the time, it was run out of the Hogans' home, had no reporters, and only reprinted press releases. In 2012, Quantcast ranked it at 614 with 2.6 million U.S. visitors. Sections As of August 2023, ''ScienceDaily'' mainly has five sections, Health, Tech, Enviro, Society, and Quirky, the last of which includes the top news. References External links * Alexa - ScienceDaily��{{Webarchive, url=https://web.a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decline In Amphibian Populations
Since the 1980s, decreases in amphibian populations, including population decline and localized mass extinctions, have been observed in locations all over the world. This type of biodiversity loss is known as one of the most critical threats to global biodiversity. The possible causes include habitat destruction and modification, diseases, exploitation, pollution, pesticide use, introduced species, and ultraviolet-B radiation (UV-B). However, many of the causes of amphibian declines are still poorly understood, and the topic is currently a subject of ongoing research. Modeling results found that the current extinction rate of amphibians could be 211 times greater than the background extinction rate. This estimate even goes up to 25,000–45,000 times if endangered species are also included in the computation. Scientists began observing reduced populations of several European amphibian species already in the 1950s. Nevertheless, awareness of the phenomenon as a global problem a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytridiomycosis
Chytridiomycosis ( ) is an infectious disease in amphibians, caused by the chytrid fungi '' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and '' Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans''. Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or extinctions of amphibian species in western North America, Central America, South America, eastern Australia, east Africa (Tanzania), and Dominica and Montserrat in the Caribbean. Much of the New World is also at risk of the disease arriving within the coming years. The fungus is capable of causing sporadic deaths in some amphibian populations and 100% mortality in others. No effective measure is known for control of the disease in wild populations. Various clinical signs are seen by individuals affected by the disease. A number of options are possible for controlling this disease-causing fungus, though none has proved to be feasible on a large scale. The disease has been proposed as a contributing factor to a global decline in amphibian popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Public Radio
National Public Radio (NPR) is an American public broadcasting organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It serves as a national Radio syndication, syndicator to a network of more than List of NPR stations, 1,000 public radio stations in the United States. Funding for NPR comes from dues and fees paid by member stations, Underwriting spot, underwriting from corporate sponsors, and annual grants from the publicly funded Corporation for Public Broadcasting. Most of its member stations are owned by non-profit organizations, including public school districts, colleges, and universities. NPR operates independently of any government or corporation, and has full control of its content. NPR produces and distributes both news and cultural programming. The organization's flagship shows are two drive time, drive-time news broadcasts: ''Morning Edition'' and the afternoon ''All Things Considered'', both carried by most NPR me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Things Considered
''All Things Considered'' (''ATC'') is the flagship news program on the American network National Public Radio (NPR). It was the first news program on NPR, premiering on May 3, 1971. It is broadcast live on NPR affiliated stations in the United States, and worldwide through several different outlets, formerly including the NPR Berlin station in Germany. ''All Things Considered'' and ''Morning Edition'' were the highest rated public radio programs in the United States in 2002 and 2005. The show combines news, analysis, commentary, interviews, and special features, and its segments vary in length and style. ''ATC'' airs weekdays from 4:00 p.m. to 6:00 p.m. Eastern Time (live) or Pacific Time (recorded with some updates; in Hawaii it airs as a fully recorded program) or from 3:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m. Central Time. ''ATC's'' weekend counterpart, ''Weekend Edition'', airs on Saturdays and Sundays. Background ''ATC'' programming combines news, analysis, commentary, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |