|
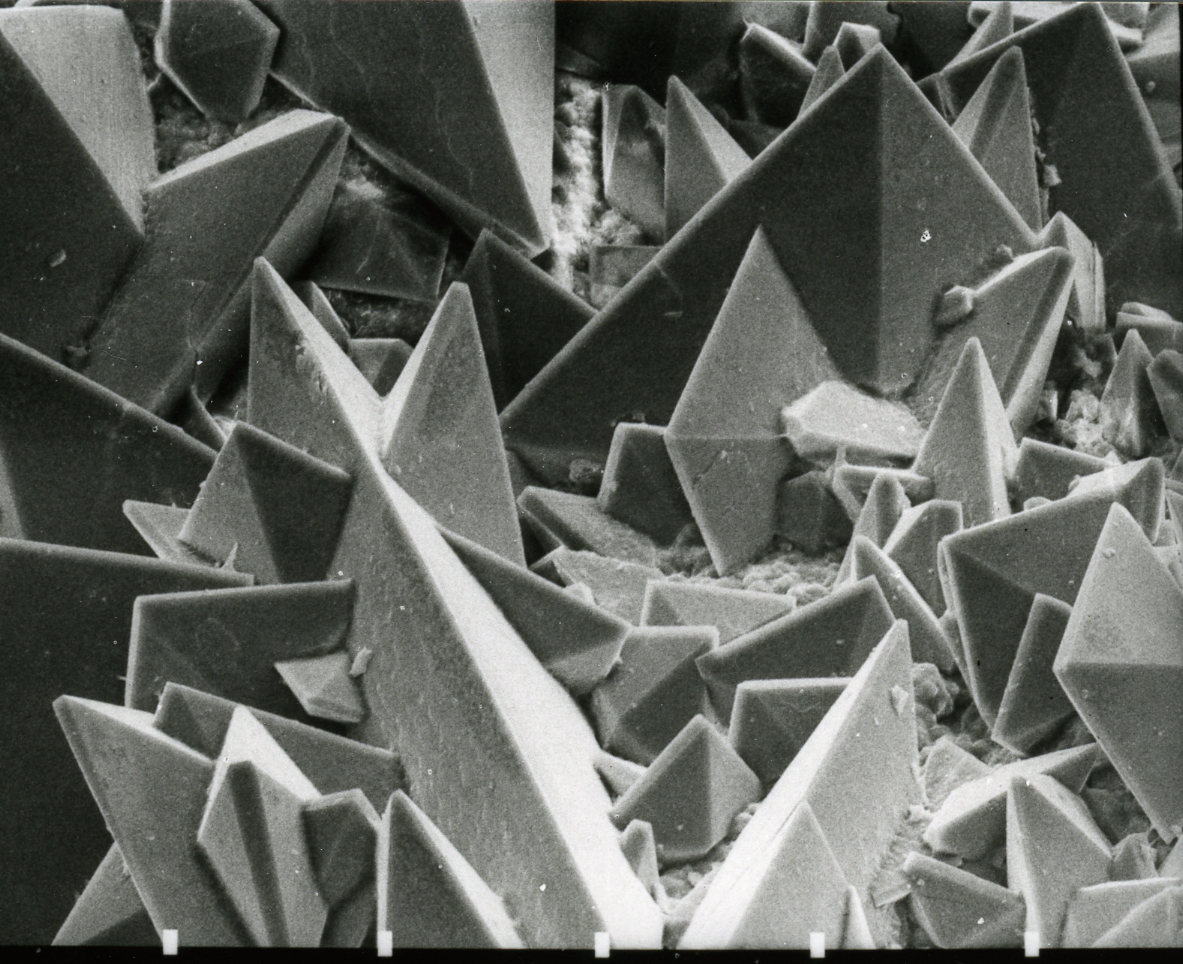
Whewellite
Whewellite is a mineral, hydrated calcium oxalate, formula calcium, Ca carbon, C2oxygen, O4·water, H2O. Because of its organic content it is thought to have an indirect biological origin; this hypothesis is supported by its presence in coal and sedimentary Nodule (geology), nodules. However, it has also been found in hydrothermal deposits where a biological source appears improbable. For this reason, it may be classed as a true mineral. Whewellite, or at least crystalline calcium oxalate, does also arise from biological sources. Small crystals or flakes of it are sometimes found on the surfaces of some cacti, and kidney stones frequently have the same composition. Whewellite was named after William Whewell (1794–1866), an England, English polymath, Natural history, naturalist and scientist, professor of moral philosophy at Cambridge University, Cambridge and inventor of the system of crystallographic indexing. Heat decomposition Whewellite is used as a thermogravimetric an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula or . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Cultural groups with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as those in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minerals In Space Group 14
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct phases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
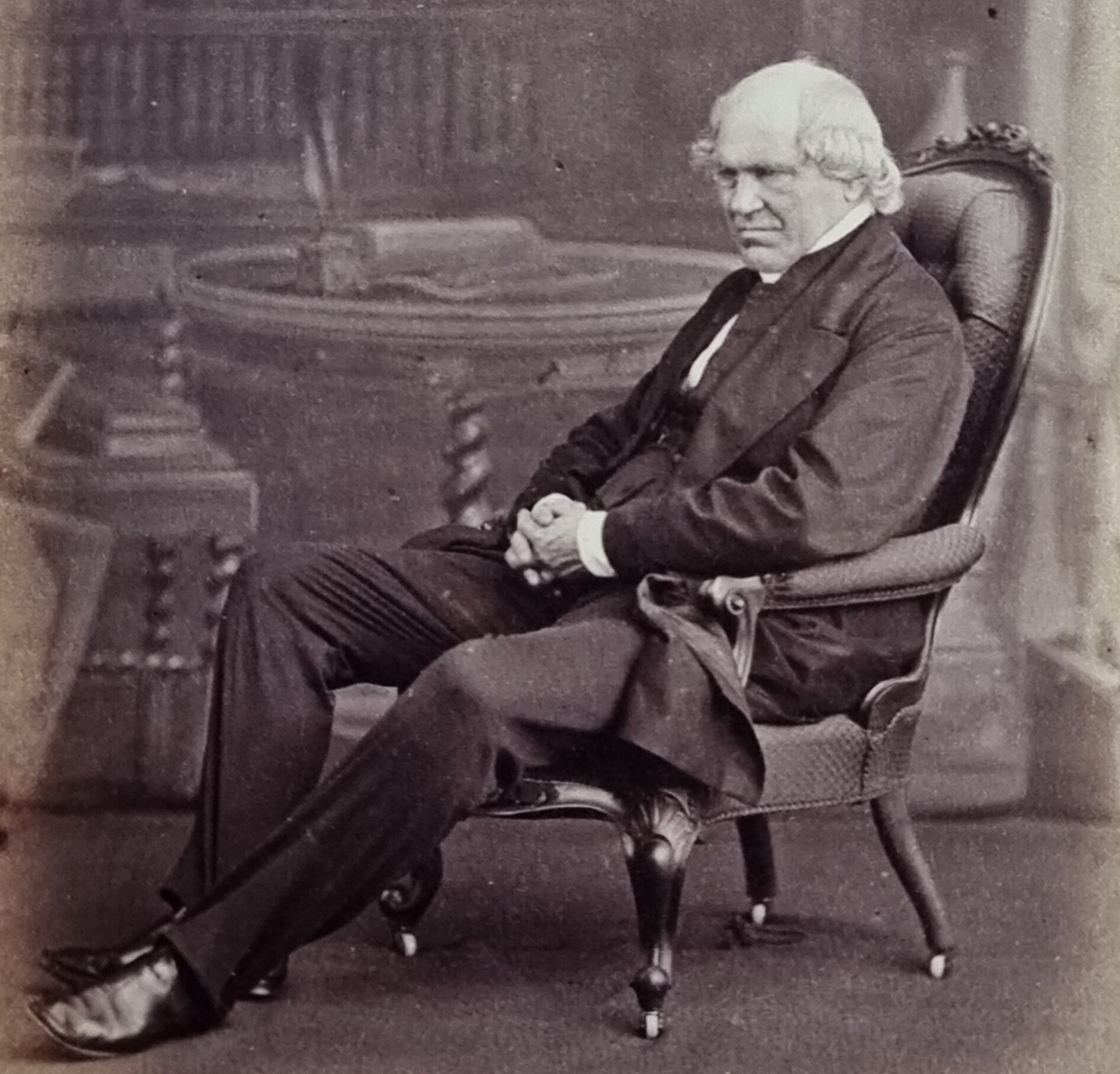
William Whewell
William Whewell ( ; 24 May 17946 March 1866) was an English polymath. He was Master of Trinity College, Cambridge. In his time as a student there, he achieved distinction in both poetry and mathematics. The breadth of Whewell's endeavours is his most remarkable feature. In a time of increasing specialisation, Whewell belonged in an earlier era when natural philosophers investigated widely. He published work in mechanics, physics, geology, astronomy, and economics, while also composing poetry, writing a Bridgewater Treatise, translating the works of Goethe, and writing sermons and Theology, theological tracts. In mathematics, Whewell introduced what is now called the Whewell equation, defining the shape of a curve without reference to an arbitrarily chosen coordinate system. He also organized thousands of volunteers internationally to study ocean tides, in what is now considered one of the first citizen science projects. He received the Royal Medal for this work in 1837. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic Minerals
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism (geometry), prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. The length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Minerals
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minerals Named After People
This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition of the mineral follows the name. A * Abelsonite: – American physicist Philip Hauge Abelson (1913–2004) * Abswurmbachite: – German mineralogist Irmgard Abs-Wurmbach (1938–2020) *Adamite: – French mineralogist Gilbert Joseph Adam (1795–1881) * Agrellite: – English optical mineralogist Stuart Olof Agrell (1913–1996) * Agricolaite: – German scholar Georgius Agricola (1494–1555) * Aheylite: – American geologist Allen V. Heyl (1918–2008) * Albrechtschraufite: – Albrecht Schrauf (1837–1897), professor of mineralogy, University of Vienna * Alexandrite: Variety of chrysoberyl (): – Russian monarch, Tsar Alexander II of Russia (1818–1881) * Alforsite: – American geologist John T. Alfors (1930–2005) * Allabogdanite: – Alla Bogdanova (1947 - 2004), Geological Institute, Kola Science Centre of Russian Academy of Sciences * Allanite series: sorosilicate – Scottish m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minerals Recognized By The International Mineralogical Association
Mineralogy is an active science in which minerals are discovered or recognised on a regular basis. Use of old mineral names is also discontinued, for example when a name is no longer considered valid. Therefore, a list of recognised mineral species is never complete. Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a mineral species there may be variation in physical properties or minor amounts of impurities that are recognized by mineralogists or wider society as a mineral ''variety''. The International Mineralogical Association (IMA) is the international scientific group that recognises new minerals and new mineral names. However, minerals discovered before 1959 did not go through the official naming procedure. Some minerals published previously have been either confirmed or discredited since that date. This list contains a mixture of mineral names that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermogravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis or thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) is a method of thermal analysis in which the mass of a sample is measured over time as the temperature changes. This measurement provides information about physical phenomena, such as phase transitions, absorption, adsorption and desorption; as well as chemical phenomena including chemisorptions, thermal decomposition, and solid-gas reactions (e.g., oxidation or reduction). Thermogravimetric analyzer Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is conducted on an instrument referred to as a thermogravimetric analyzer. A thermogravimetric analyzer continuously measures mass while the temperature of a sample is changed over time. Mass, temperature, and time are considered base measurements in thermogravimetric analysis while many additional measures may be derived from these three base measurements. A typical thermogravimetric analyzer consists of a precision balance with a sample pan located inside a furnace with a programm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, world's third-oldest university in continuous operation. The university's founding followed the arrival of scholars who left the University of Oxford for Cambridge after a dispute with local townspeople. The two ancient university, ancient English universities, although sometimes described as rivals, share many common features and are often jointly referred to as Oxbridge. In 1231, 22 years after its founding, the university was recognised with a royal charter, granted by Henry III of England, King Henry III. The University of Cambridge includes colleges of the University of Cambridge, 31 semi-autonomous constituent colleges and List of institutions of the University of Cambridge#Schools, Faculties, and Departments, over 150 academic departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientist
A scientist is a person who Scientific method, researches to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales ( 624–545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century in science, 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. History The roles of "scientists", and their predecessors before the emergence of modern scientific disciplines, have evolved considerably over time. Scientists of different er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is called a naturalist or natural historian. Natural history encompasses scientific research but is not limited to it. It involves the systematic study of any category of natural objects or organisms, so while it dates from studies in the ancient Greco-Roman world and the mediaeval Arabic world, through to European Renaissance naturalists working in near isolation, today's natural history is a cross-discipline umbrella of many specialty sciences; e.g., geobiology has a strong multidisciplinary nature. Definitions Before 1900 The meaning of the English term "natural history" (a calque of the Latin ''historia naturalis'') has narrowed progressively with time, while, by contrast, the meaning of the related term "nature" has widened (see also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |