|
Wheezes
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower respiratory tract in an asthmatic attack), or airflow velocity within the respiratory tree must be heightened. Wheezing is commonly experienced by persons with a lung disease; the most common cause of recurrent wheezing is asthma, though it can also be a symptom of lung cancer, congestive heart failure, and certain types of heart diseases. The differential diagnosis of wheezing is wide, and the reason for wheezing in a given patient is determined by considering the characteristics of the wheezes and the historical and clinical findings made by the examining physician. The term "wheeze" is also used as a clinical condition describing wheezing in preschool children, termed as "preschool wheeze". Clinical symptom Wheeze Wheezes occupy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medicine, medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. A stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds made by the heart sounds, heart, lungs or intestines, as well as blood flow in artery, arteries and veins. In combination with a manual sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used when measuring blood pressure. It was invented in 1816 by René Laennec and the binaural version by Arthur Leared in 1851. Less commonly, "mechanic's stethoscopes", equipped with rod shaped chestpieces, are used to listen to internal sounds made by machines (for example, sounds and vibrations emitted by worn ball bearings), such as diagnosing a malfunctioning automobile engine by listening to the sounds of its internal parts. Stethoscopes can also be used to check scientific vacuum chambers for leaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirometry
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time. Spirometry generates pneumotachographs, which are charts that plot the volume and flow of air coming in and out of the lungs from one inhalation and one exhalation. Testing Spirometer The spirometry test is performed using a device called a spirometer, which comes in several different varieties. Most spirometers display the following graphs, called spirograms: * a ''volume-time curve'', showing volume (litres) along the Y-axis and time (seconds) along the X-axis * a ''flow-volume loop'', which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workaround
A workaround is a bypass of a recognized problem or limitation in a system or policy. A workaround is typically a temporary fix that implies that a genuine solution to the problem is needed. But workarounds are frequently as creative as true solutions, involving outside the box thinking in their creation. Typically they are considered brittle in that they will not respond well to further pressure from a system beyond the original design. In implementing a workaround it is important to flag the change so as to later implement a proper solution. Placing pressure on a workaround may result in later system failures. For example, in computer programming workarounds are often used to address a problem or anti-pattern in a library, such as an incorrect return value. When the library is changed, the workaround may break the overall program functionality, effectively becoming an anti-pattern, since it may expect the older, wrong behaviour from the library. Workarounds can also be a us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethical
Ethics is the philosophical study of moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to duties, like telling the truth and keeping promises. Virtue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodoxy
In religion, heterodoxy (from Ancient Greek: , + , ) means "any opinions or doctrines at variance with an official or orthodox position". ''Heterodoxy'' is also an ecclesiastical jargon term, defined in various ways by different religions and churches. For example, in some groups, heterodoxy may describe beliefs that differ from strictly orthodox views but that fall short either of formal or of material heresy. Christianity Eastern Orthodoxy In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the term is used primarily in reference to Christian churches and denominations not belonging to the communion of Eastern Orthodox churches and espousing doctrines contrary to the received Holy Tradition. Protestantism Charles Spurgeon said: u shall find spiritual life in every church. I know it is the notion of the bigot, that all the truly godly people belong to the denomination which he adorns. Orthodoxy is my doxy; heterodoxy is anybody else's doxy who does not agree with me. Islam The Arabic word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exacerbation
In medicine, an exacerbation is the worsening of a disease or an increase in its symptom Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...s. Examples includes an acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and acute exacerbation of congestive heart failure. See also * Flare-up References Medical terminology Symptoms {{Symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
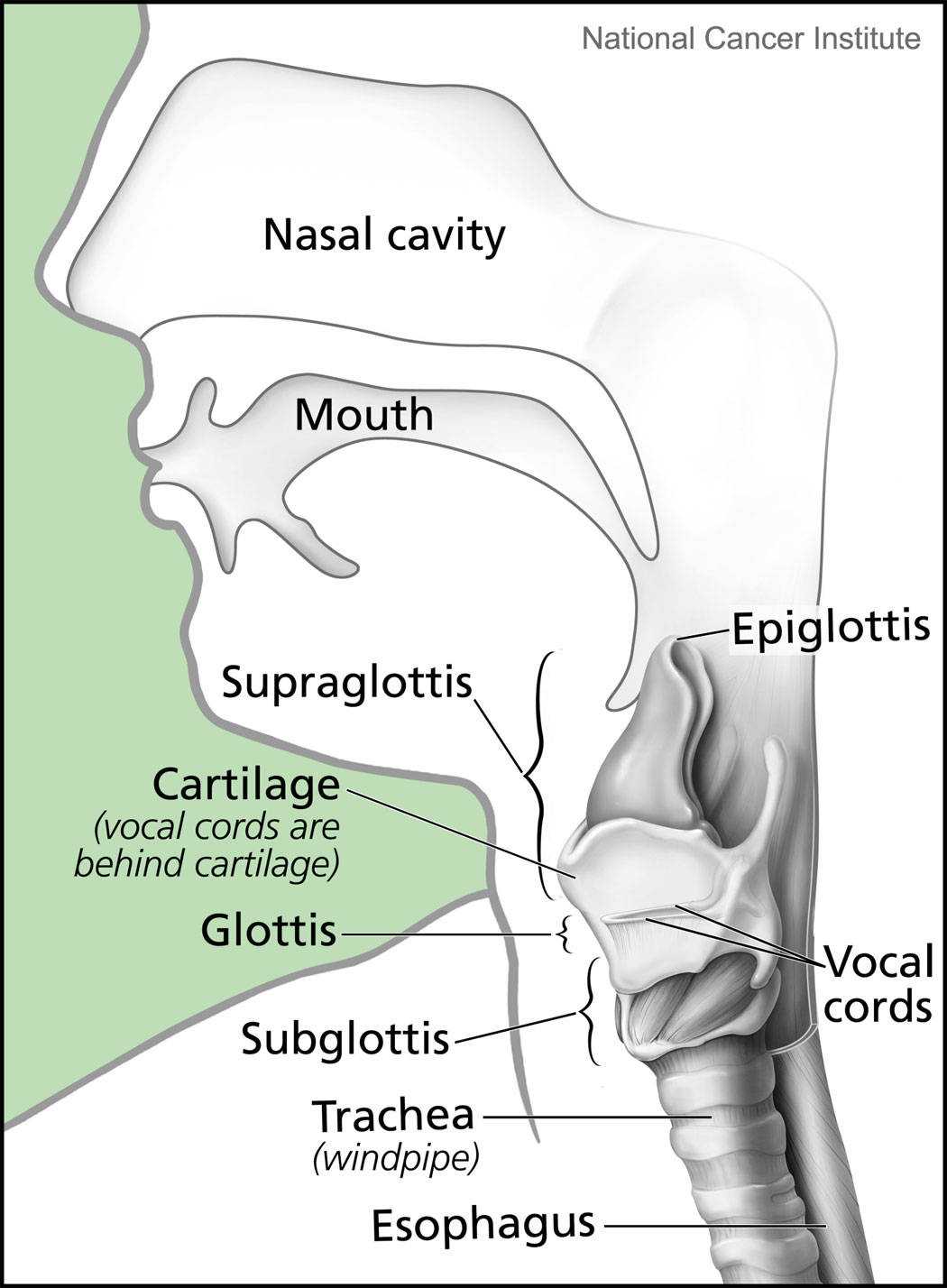
Subglottis
The subglottis or subglottic region is the lower portion of the larynx, extending from just beneath the vocal cords down to the top of the Vertebrate trachea, trachea.Subglottis definition - MedTerms 23 December 2013. The structures in the subglottis are implicated in the regulation of the temperature of the breath. Narrowing of the subglottis is known as subglottic stenosis and may require a tracheotomy to correct.Subglottic Stenosis in Children 23 December 2013. References Larynx {{Respiratory-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottis
The glottis (: glottises or glottides) is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing sound from the vocal folds. Etymology From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), variant of ''γλῶσσα'' (glôssa, "tongue"). Function Phonation As the vocal folds vibrate, the resulting vibration produces a "buzzing" quality to the speech, called voice or voicing or pronunciation. Sound production that involves moving the vocal folds close together is called ''glottal''. English has a voiceless glottal transition spelled "h". This sound is produced by keeping the vocal folds spread somewhat, resulting in non-turbulent airflow through the glottis. In many accents of English the glottal stop (made by pressing the folds together) is used as a variant allophone of the phoneme (and in some dialects, occasionally of and ); in some languages, this sound is a phoneme of its own. Skilled p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stridor
Stridor () is an extra-thoracic high-pitched breath sound resulting from turbulent air flow in the larynx or lower in the bronchial tree. It is different from a stertor, which is a noise originating in the pharynx. Stridor is a physical sign which is caused by a narrowed or obstructed airway. It can be inspiratory, expiratory or biphasic, although it is usually heard during inspiration. Inspiratory stridor often occurs in children with croup. It may be indicative of serious airway obstruction from severe conditions such as epiglottitis, a foreign body lodged in the airway, or a laryngeal tumor. Stridor should always command attention to establish its cause. Visualization of the airway by medical experts equipped to control the airway may be needed. Causes Stridor may occur as a result of: * foreign bodies (e.g., aspirated foreign body, aspirated food bolus); * infections (e.g., epiglottitis, retropharyngeal abscess, croup); * subglottic stenosis (e.g., following prol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the body, each in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. The chest may be affected by many diseases, of which the most common symptom is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thṓrax'' " breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via . Humans Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, and shoulder girdle. Contents The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
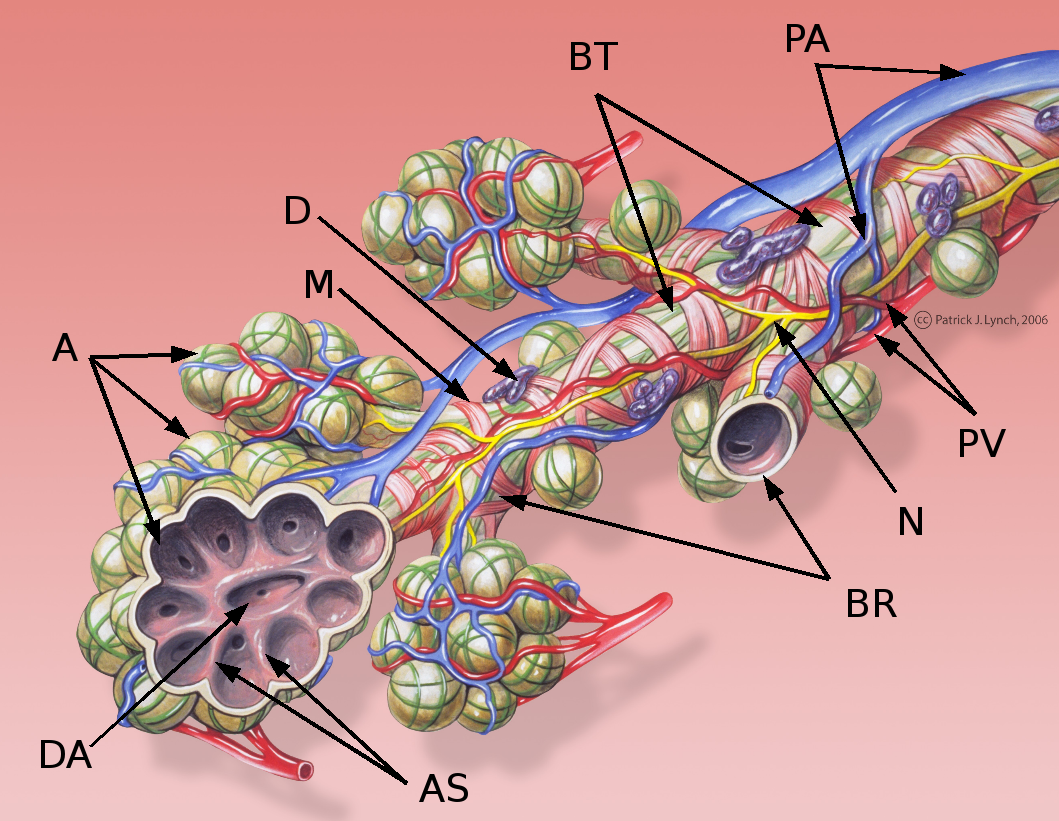
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Oxygen is diffused across the membrane into the capillaries and carbon dioxide is released fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |