|
Wenis
The wenis, sometimes spelled weenus or weenis, is a loose flap of skin underneath the joint of a human elbow. The word developed from slang in the 1990s. The area may also be referred to as olecranal skin or simply elbow skin. Anatomy The wenis is located on the exterior tip of the olecranon. The skin is taut and smooth when the elbow is flexed, but loose and wrinkled when the elbow is straightened. It may lose elasticity and begin to sag with age. The Synovial bursa, bursa located between the ulna and the wenis reduces friction between the skin and the bone. The region is not typically sensitive to acute pain from pinching. This is due to the wenis having a high amount of subcutaneous fat, relatively few pain receptors, and tough skin. It has a small number of sensory fibers. The wenis is known as a difficult or impossible spot to licking, lick oneself. Clinical significance Medical conditions Olecranon bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa that lies under the wenis. Any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integumentary System
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin. The integumentary system includes skin, hair, scales, feathers, hooves, claws, and nails. It has a variety of additional functions: it may serve to maintain water balance, protect the deeper tissues, excrete wastes, and regulate body temperature, and is the attachment site for sensory receptors which detect pain, sensation, pressure, and temperature. Structure Skin The skin is one of the largest organs of the body. In humans, it accounts for about 12 to 15 percent of total body weight and covers 1.5 to 2 m2 of surface area. The skin (integument) is a composite organ, made up of at least two major layers of tissue: the epidermis and the dermis. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anatomy
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy (also called macroscopic anatomy, topographical anatomy, regional anatomy, or anthropotomy) is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye. Microscopic anatomy is the study of minute anatomical structures assisted with microscopes, which includes histology (the study of the organization of tissues), and cytology (the study of cells). Anatomy, human physiology (the study of function), and biochemistry (the study of the chemistry of living structures) are complementary basic medical sciences that are generally together (or in tandem) to students studying medical sciences. In some of its facets human anatomy is closely related to embryology, comparative anatomy and comparative embryology, through common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Slang
Medical slang is the use of acronyms and informal terminology to describe patients, other healthcare personnel and medical concepts. Some terms are pejorative. In English language, English, medical slang has entered popular culture via television hospital and forensic science dramas such as ''ER (TV series), ER'', ''House (TV series), House M.D.'', ''NCIS (TV series), NCIS'', ''Scrubs (TV series), Scrubs'', and ''Grey's Anatomy'', and through fiction, in books such as ''The House of God'' by Samuel Shem (Stephen Joseph Bergman), ''Bodies'' by Jed Mercurio, and ''A Case of Need'' by Jeffery Hudson (Michael Crichton) Examples of pejorative language include ''bagged and tagged'' for a corpse, a reference to the intake process at a mortuary; ''donorcycle'' for ''motorcycle''; and ''PFO'' for ''pissed [Alcohol intoxication, drunk] and fell over''. Less offensive are the terms ''blue pipes'' for veins; ''cabbage'' for a heart bypass (''coronary artery bypass graft'' or CABG), and ''champ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
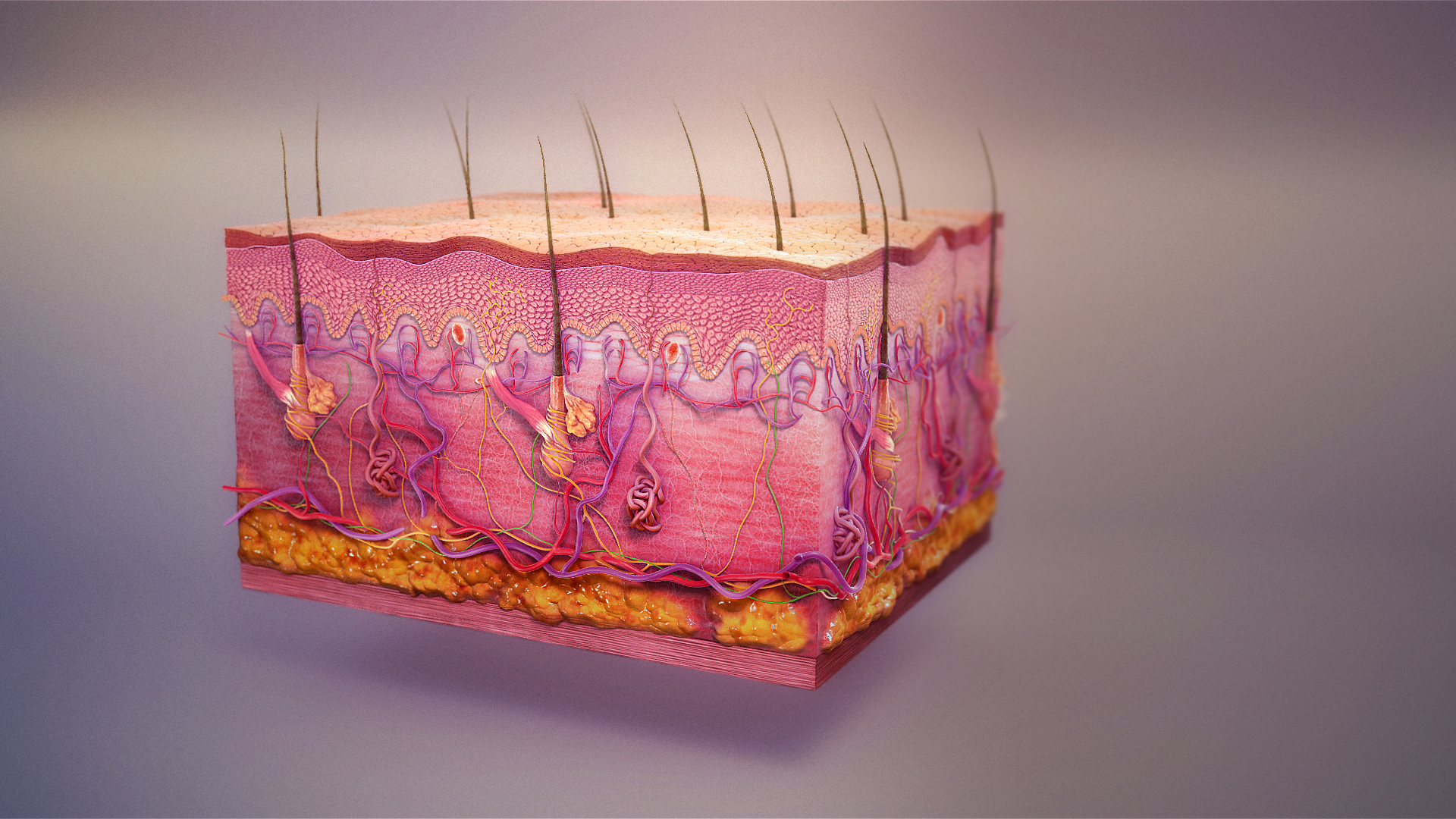
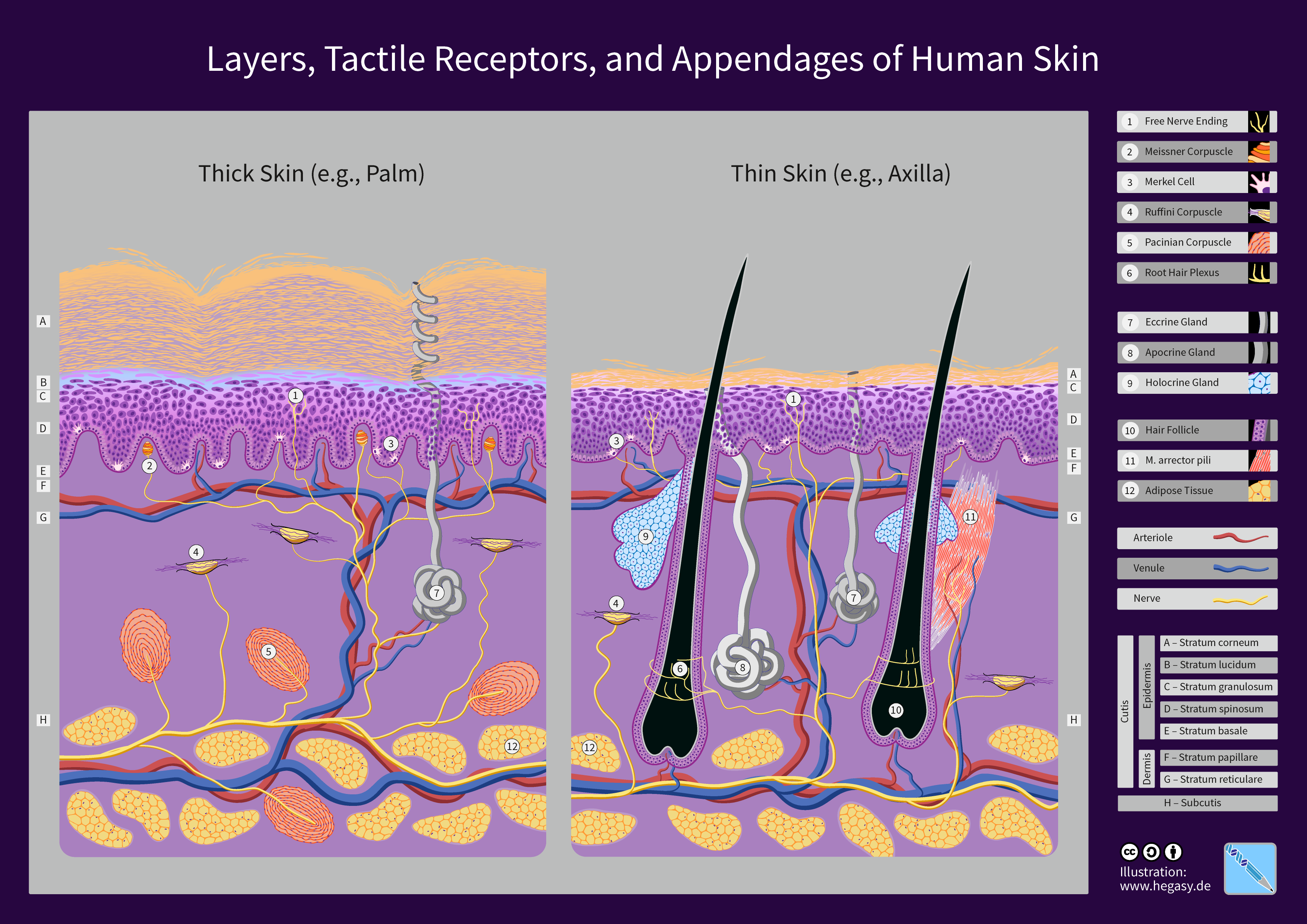
Human Skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anatomy), internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear Nudity#Evolution of hairlessness, hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#C, ''cutaneous'' literally means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'', skin). Skin plays an important immunity (medical), immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive transepidermal water loss, water loss. Its other functions are Thermal insulation, insulation, thermoregulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hangover (film Series)
''The Hangover'' is a series of American comedy films created by Jon Lucas and Scott Moore, and directed by Todd Phillips. All three films follow the misadventures of a quartet of friends (also known as "the Wolfpack") who go on their road trip to attend a bachelor party. While all of the films find three of the four men on a mission to find their missing friend, the first two films focus on the events after the nights of debauchery before a party, respectively in Las Vegas and Bangkok, whereas the third and final film involves a road trip and a kidnapping in lieu of a bachelor party. Each film in the series focuses on how the friends deal with the aftermath of their antics, while they are being humiliated and occasionally physically beaten up at every turn. All three films were released from 2009 to 2013, and have grossed a collective total of $1.4 billion in the United States and worldwide. Films ''The Hangover'' (2009) Phil Wenneck, Stu Price and Alan Garner, travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.Garner's Modern American Usage p. 644. English examples include '' smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', and '''', from ''motor'' ('' motorist'') and ''hotel''. A blend is similar to a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubital Fossa
The cubital fossa, antecubital fossa, chelidon, inside of elbow, or, humorously, wagina, is the area on the anterior side of the upper part between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (antecubital) (Latin ) when in standard anatomical position. The cubital fossa is a triangular area having three borders. Boundaries * superior (proximal) boundary – an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus * medial (ulnar) boundary – lateral border of pronator teres muscle originating from the medial epicondyle of the humerus. * lateral (radial) boundary – medial border of brachioradialis muscle originating from the lateral supraepicondylar ridge of the humerus. * apex – it is directed inferiorly, and is formed by the meeting point of the lateral and medial boundaries * superficial boundary (roof) – skin, superficial fascia containing the median cubital vein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meme
A meme (; ) is an idea, behavior, or style that Mimesis, spreads by means of imitation from person to person within a culture and often carries symbolic meaning representing a particular phenomenon or theme. A meme acts as a unit for carrying culture, cultural ideas, symbols, or practices, that can be transmitted from one mind to another through writing, speech, gestures, rituals, or other imitable phenomena with a mimicked theme. Supporters of the concept regard memes as cultural analogues to genes in that they Self-replication, self-replicate, mutate, and respond to natural selection, selective pressures. In popular language, a meme may refer to an Internet meme, typically an image, that is remixed, copied, and circulated in a shared cultural experience online. Proponents theorize that memes are a viral phenomenon that may evolve by natural selection in a manner analogous to that of evolution, biological evolution. Memes do this through processes analogous to those of genetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, including ultrasound. Ultrasonic devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on the mathematical properties of String instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts of a person's Appendicular skeleton, extremities from repeated injuries or infection through unnoticed wounds. An infected person may also experience muscle weakness and poor eyesight. Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but for some people symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur. Leprosy is spread between people, although extensive contact is necessary. Leprosy has a low pathogenicity, and 95% of people who contract or who are exposed to ''M. leprae'' do not develop the disease. Spread is likely through a cough or contact with fluid from the nose of a person infected by leprosy. Genetic factors and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |