|
Weiße Frauen
In German folklore, the Weiße Frauen (, meaning White Women) are elf-like spirits which may derive from Germanic paganism in the form of legends of light elves (Old Norse: ''Ljósálfar''). The Netherlands, Dutch Witte Wieven are traceable at least as far back as the 7th century, and their mistranslation as ''White Women'' instead of the original ''Wise Women'' can be explained by the Dutch word wit also meaning white. They are described as beautiful and incantation, enchanted creatures who appear at noon and can be seen sitting in the sunshine brushing their hair or bathing in a brook. They may be guarding treasure or haunting castles. They entreat mortals to break their spell, but this is always unsuccessful. The mythology dates back at least to the Middle Ages and was known in the present-day area of Germany. Origins ''Weiße Frauen'' literally means "white ladies" in German language, German. The association with the color white and their appearance in sunlight is thought by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wojciech Gerson - Zjawa Barbary Radziwiłłówny
Wojciech () is a Polish language, Polish name, equivalent to Czech language, Czech Vojtěch , Slovak language, Slovak Vojtech, and German language, German Woitke. The name is formed from two Slavic roots: * ''wój'' (Slavic: ''voj''), a root pertaining to war. It also forms words like ''wojownik'' ("warrior") and ''wojna'' ("war"). * ''ciech'' (from an earlier form, ''tech''), meaning "joy". The resulting combination means "he who enjoys war" or "joyous warrior". Its Polish diminutive forms include ''Wojtek'' , ''Wojtuś'' , ''Wojtas'', ''Wojcio'', ''Wojteczek'', ''Wojcieszek'', ''Wojtaszka'', ''Wojtaszek'', ''Wojan'' (noted already in 1136), ''Wojko'', and variants noted as early as 1400, including ''Woytko'', ''Woythko'', and ''Voytko''. The feminine form is Wojciecha (). Related names in South Slavic languages include ''Vojko'', ''Vojislav'', and ''Vojteh''. The name has been rendered into German in several different variations, including: ''Woitke'', ''Witke'', ''Voitke'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idis (Germanic)
In Germanic mythology, an idis (Old Saxon, plural idisi) is a divine female being. ''Idis'' is cognate to Old High German itis and Old English ides, meaning 'well-respected and dignified woman.' Connections have been assumed or theorized between the idisi and the North Germanic dísir; female beings associated with fate, as well as the amended place name Idistaviso. Attestations First Merseburg Charm One of the two Old High German Merseburg Incantations call upon female beings—''idisi''—to bind and hamper an army. The incantation reads: :'Once the ''Idisi'' sat, sat here and there, :some bound fetters, some hampered the army, :some untied fetters: :Escape from the fetters, flee from the enemies.'Simek (2007:171). Beowulf In the Old English poem ''Beowulf'', the term ''ides'' is used multiple times to describe female beings. In line 1074 and again in line 1117, the queen Hildeburh is described as an ''ides'' while mourning the death of her kin after the Battle of Finnsbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witte Wiwer
The ''witte Wiwer'', Eckstein: ''Grütze''. In: Hanns Bächtold-Stäubli, Eduard Hoffmann-Krayer: ''Handwörterbuch des Deutschen Aberglaubens: Band 3 Freen-Hexenschuss''. Berlin/New York 2000, p. 1201. ''witte Wîwer'', Wilhelm Mannhardt: ''Wald- und Feldkulte: Band I''. 2005, p. 89. ''witte Wiewer'' or ''witte Wiver'' Peuckert: ''Sibylle''. In: Hanns Bächtold-Stäubli, Eduard Hoffmann-Krayer: ''Handwörterbuch des Deutschen Aberglaubens: Band 7 Pflügen-Signatur''. Berlin/New York 2000, p. 1658. (; all meaning 'white women' in Low German; , ; ''witt Wif'' or ''weißes Weib'' Karl Bartsch: ''Sagen, Märchen und Gebräuche aus Mecklenburg: Erster Band''. Berlin 2013, p. 36.) are legendary creatures from (Low) German folklore similar to but distinct from the ''weiße Frauen''. Other names are ''unterirdische Weiber'' (subterranean women) in Mecklenburg Karl Bartsch: ''Sagen, Märchen und Gebräuche aus Mecklenburg: Erster Band''. Berlin 2013, p. 35. and ''Sibyllen'' (sibyls; sg. ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
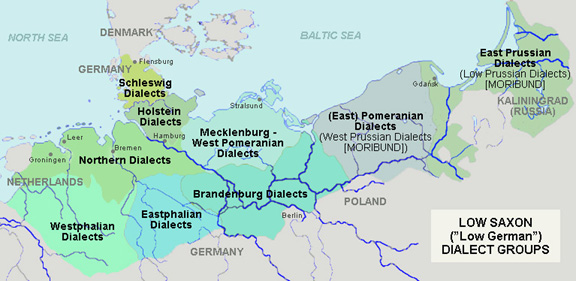
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nix (water Creatures)
The Nixie, Nixy, Nix, Näcken, Nicor, Nøkk, or Nøkken (; , ; ; Norwegian ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; or ) are humanoid, and often shapeshifting water spirits in Germanic mythology and folklore. Under a variety of names, they are common to the stories of all Germanic peoples,The article ''Näcken''tome 20, p. 317 in (1914) although they are perhaps best known from Scandinavian folklore. The related English ''knucker'' was generally depicted as a worm or dragon, although more recent versions depict the spirits in other forms. Their sex, bynames, and various transformations vary geographically. The German and his Scandinavian counterparts were male. The German was a female river mermaid. Similar creatures are known from other parts of Europe, such as the Melusine in France, the Xana in Asturias (Spain), and the Slavic water spirits (e.g., the Rusalka) in Slavic countries. Names and etymology The names are held to derive from Common Germanic or , derived from PIE ("to wash"). They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landvættir
Landvættir ("land spirits" or "land wights") are spirits of the land in Old Nordic religion, later Scandinavian folklore, folk belief and modern Heathenry. They are closely associated with specific locations and their wellbeing is presented as being required for the land they inhabit to be fruitful. In Old Norse sources, they are depicted as being potentially harmful and capable of driving away unwanted individuals and capable of being frightened through human actions such as usage of carved figureheads on ships or níðstangs. Good relationships between humans and landvættir were believed to be fostered through acts like leaving out food for them however upon the Christianisation of Scandinavia, establishment of the church, the practice was labelled heretical and explicitly forbidden in the Norwegian Gulating law codes. Landvættir have been variously connected by scholars to other beings believed to inhabit the land such as elves, Dwarf (folklore), dwarfs and landdísir, with w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Mythology
The mythology of the modern-day Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg has its roots in the mythologies of pre-Christian (e.g. Gaulish (Gallo-Roman) and Germanic) cultures, predating the region's Christianization under the influence of the Franks in the Early Middle Ages. At the time of the Roman Empire and in the Early Middle Ages, some of the resident peoples of the Low Countries' included: * Germanic tribes north of the Rhine River (with a lot of exceptions like the Eburones or the Celtic Nervii,...) * Low Franconians * Frisii (and later, in the same area, the Frisians) * Tubanti * Canninefates * Batavians * the decidedly more Celtic and Gallo-Roman Belgae tribes of Gallia Belgica south of the Rhine (also mainly but with many exceptions). Old Dutch mythology can mean the myths specifically told in Old Dutch language. However, many of the myths in this language are ancient and part of larger movements across Europe, such as Roman mythology that spread through the Roman Empire, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divinities
Divinity (from Latin ) refers to the quality, presence, or nature of that which is divine—a term that, before the rise of monotheism, evoked a broad and dynamic field of sacred power. In the ancient world, divinity was not limited to a single deity or abstract ideal but was recognized in multiple forms: as a radiant attribute possessed by gods, as a vital force pervading nature, and even as a quality glimpsed in extraordinary humans, laws, or acts. The Latin and its Greek counterparts (, ) conveyed something both immanent and awe-inspiring: a presence that could be felt in thunder, justice, ecstasy, fate, or beauty. Among the Greeks and Romans, divinity was not confined to a rigid theological system. Gods, heroes, and even emperors might be described as partaking in divinity, just as natural forces or virtue could be seen as expressions of divine essence. Philosophers such as Plato and the Stoics used the term to refer to the soul of the cosmos or the rational order of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |