|
Wedding Tradition
African customs Ethiopia Marriage in Ethiopia starts with the groom's side sending elders (Shimagle) who then request a union between the parties. The elders discuss a dowry () and verify that the intended bride and groom are not relatives by checking their lineage a minimum of seven generations. After a dowry is agreed upon and it has been determined that there is no relationship between the intended bride and groom, the wedding is announced and the families begin preparations for a church/mosque ceremony and a On the wedding day the groom and groomsmen () get ready at the groom's house early in the morning and proceed to the bride's parents house to begin the wedding ceremonies. At the bride's parents' house, the bride gets ready and is seated awaiting the groom's arrival. As the groom and his wedding party arrive, the bride's family and friends ceremonially block the entrance to the house. The groomsmen have to either serenade or bribe their way into the house so that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieter Bruegel The Elder - Peasant Wedding - Google Art Project 2
Pieter is a male given name, the Dutch form of Peter. The name has been one of the most common names in the Netherlands for centuries, but since the mid-twentieth century its popularity has dropped steadily, from almost 3000 per year in 1947 to about 100 a year in 2016. at the Corpus of First Names in The Netherlands Some of the better known people with this name are below. See for a longer list. * Pieter de Coninck (?-1332), Flemish revolutionary * Pieter van der Moere (c. 1480–1572), Flemish Franciscan missionary in Mexico known as "Pedro de Gante" * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaperone (social)
A chaperone (also spelled chaperon) in its original social usage was a person who for propriety's sake accompanied an unmarried girl in public; usually she was an older married woman, and most commonly the girl's own mother. In modern social usage, a chaperon (frequent in British spelling) or chaperone (usual in American spelling) is a responsible adult who accompanies and supervises young people. By extension, the word chaperone is used in clinical contexts. Origin The word derives figuratively from the French word ''chaperon'' (originally from the Late Latin ''cappa'', meaning "cape"), which referred to a hood that was worn by individuals generally. A chaperone was part of the costume of the Knights of the Garter when they were in full dress and, probably, since the Knights were court attendants, the word ''chaperon'' changed to mean escort. An alternative explanation comes from the sport of falconry, where the word meant the hood placed over the head of a bird of prey t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social norms, ethical values, Tradition, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, Cultural artifact, artifacts and technology, technologies primarily rooted in History of Europe, European and History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean histories. A broad concept, "Western culture" does not relate to a region with fixed members or geographical confines. It generally refers to the classical era cultures of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome that expanded across the Mediterranean basin and Europe, and later circulated around the world predominantly through colonization and globalization. Historically, scholars have closely associated the idea of Western culture with the classical era of Greco-Roman antiquity. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
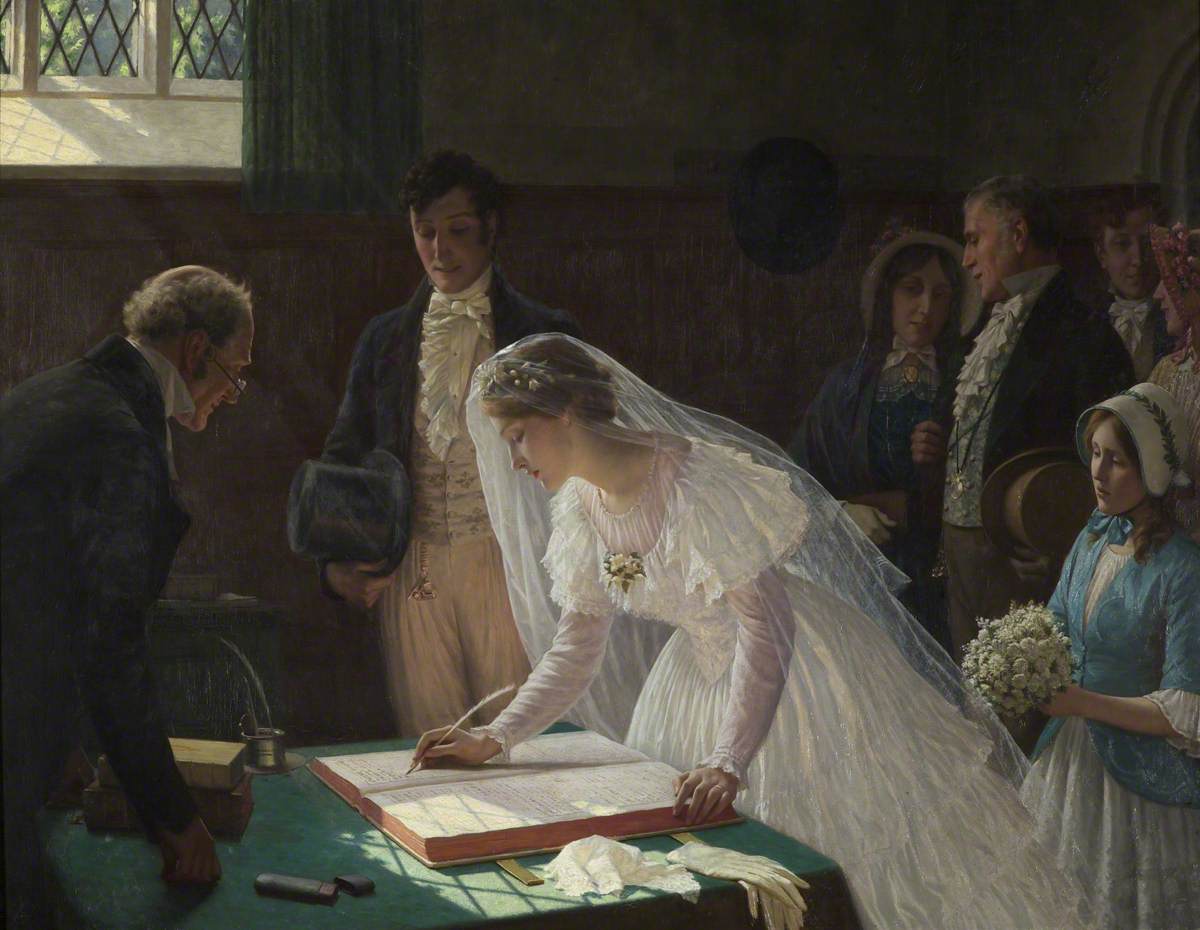
Wedding
A wedding is a ceremony in which two people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnicity, ethnicities, Race (human categorization), races, religions, Religious denomination, denominations, Country, countries, social classes, and sexual orientations. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of marriage vows by a couple; a presentation of a gift (e.g., an offering, rings, a symbolic item, flowers, money, or a dress); and a public proclamation of marriage by an authority figure or Celebrant (Australia), celebrant. Special wedding garments are often worn, and the ceremony is sometimes followed by a wedding reception. Music, poetry, prayers, or readings from religious texts or literature are also commonly incorporated into the ceremony, as well as Wedding superstitions, superstitious customs. Common elements across cultures Some cultures have adopted the traditional Western custom of the white wedding, in which a bride wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. The druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks. The earliest known references to the druids date to the 4th century BC. The oldest detailed description comes from Julius Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (50s BC). They were described by other Roman writers such as Cicero, Cicero (44) I.XVI.90. Tacitus, and Pliny the Elder. Following the Roman invasion of Gaul, the druid orders were suppressed by the Roman government under the 1st-century AD emperors Tiberius and Claudius, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wicca
Wicca (), also known as "The Craft", is a Modern paganism, modern pagan, syncretic, Earth religion, Earth-centred religion. Considered a new religious movement by Religious studies, scholars of religion, the path evolved from Western esotericism, developed in England during the first half of the 20th century, and was Witchcraft Today, introduced to the public in 1954 by Gerald Gardner, a retired British civil servant. Wicca draws upon paganism, ancient pagan and Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, 20th-century Hermetic motif (folkloristics), motifs for theology, theological and ritual purposes. Doreen Valiente joined Gardner in the 1950s, further building Wicca's liturgical tradition of beliefs, principles, and practices, disseminated through published books as well as secret written and oral teachings passed along to Initiation, initiates. Many variations of the religion have grown and evolved over time, associated with a number of diverse lineages, sects, and Religious den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handfasting (Neopaganism)
Handfasting is a traditional practice that, depending on the term's usage, may define an unofficiated wedding (in which a couple marries without an officiant, usually with the intent of later undergoing a second wedding with an officiant), a betrothal (an engagement in which a couple has formally promised to wed, and which can be broken only through divorce), or a temporary wedding (in which a couple makes an intentionally temporary marriage commitment). The phrase refers to the making fast of a pledge by the shaking or joining of hands. The terminology and practice are especially associated with Germanic peoples, including the English and Norse, as well as the Scots. As a form of betrothal or unofficiated wedding, handfasting was common up through Tudor England; as a form of temporary marriage, it was practiced in 17th-century Scotland and has been revived in Neopaganism, though misattributed as Celtic rather than Danish and Old English. Sometimes the term is also used s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loom
A loom is a device used to weaving, weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the Warp (weaving), warp threads under tension (mechanics), tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same. Etymology and usage The word "loom" derives from the Old English ''geloma'', formed from ''ge-'' (perfective prefix) and ''loma'', a root of unknown origin; the whole word ''geloma'' meant a utensil, tool, or machine of any kind. In 1404 "lome" was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. By 1838 "loom" had gained the additional meaning of a machine for interlacing thread. Components and actions Basic structure File:Simple_treadle_floorloom,_line_drawing.png, upright=1.5, left, A simple treadle floor loom. Mouse over components for pop-up links. The warp runs horizontally. On the left the warp beam, held from turning by with a weighted trough t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products are created with one of three basic weaves: plain weave, satin weave, or twill weave. Woven cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
How A Wedding Looks Like
How may refer to: * How (greeting), a word used in some misrepresentations of Native American/First Nations speech * How, an interrogative word in English grammar Art and entertainment Literature * ''How'' (book), a 2007 book by Dov Seidman * ''HOW'' (magazine), a magazine for graphic designers * H.O.W. Journal, an American art and literary journal Music * ''How?'' (EP), by BoyNextDoor, 2024 * "How?" (song), by John Lennon, 1971 * "How", a song by Clairo from ''Diary 001'', 2018 * "How", a song by the Cranberries from ''Everybody Else Is Doing It, So Why Can't We?'', 1993 * "How", a song by Daughter from '' Not to Disappear'', 2016 * "How", a song by Lil Baby from '' My Turn'', 2020 * "How", a song by Maroon 5 from '' Hands All Over'', 2010 * "How", a song by Regina Spektor from ''What We Saw from the Cheap Seats'', 2012 * "How", a song by Robyn from ''Robyn Is Here'', 1995 Other media * HOW (graffiti artist), Raoul Perre, New York graffiti muralist * ''How'' (TV serie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollonia (Albania)3
Apollonia or Apolonia (named after the Greek god Apollo) may refer to : Places and jurisdictions Albania * Apollonia (Illyria), now Pojani (Polina) in Albania; former bishopric, now Latin titular see Bulgaria * Apollonia, Thrace, now Sozopol, Bulgaria Greece * Apollonia (Aetolia), a town near Naupactus * Apollonia (Argolis), also known as Troezen * Apollonia (Athos), a city on Mount Athos * Apollonia (Chalcidice), a city in the Chalcidice * Apollonia (Echinades), a town in the Echniades * Apollonia (Kavala), a city in Kavala, northern Greece * Apollonia (Mygdonia), an inland city near modern Apollonia, Thessaloniki, reportedly visited by the Apostle Paul * Apollonia, Sifnos (ancient town), an ancient town on the island of Sifnos * Apollonia (Sifnos), the main town on the island of Sifnos, taking its name from the former * Apollonia, Thessaloniki * Five cities on Crete: ** Apellonia, also called Apollonia, on the north coast ** Apollonia (northern Crete), on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |