|
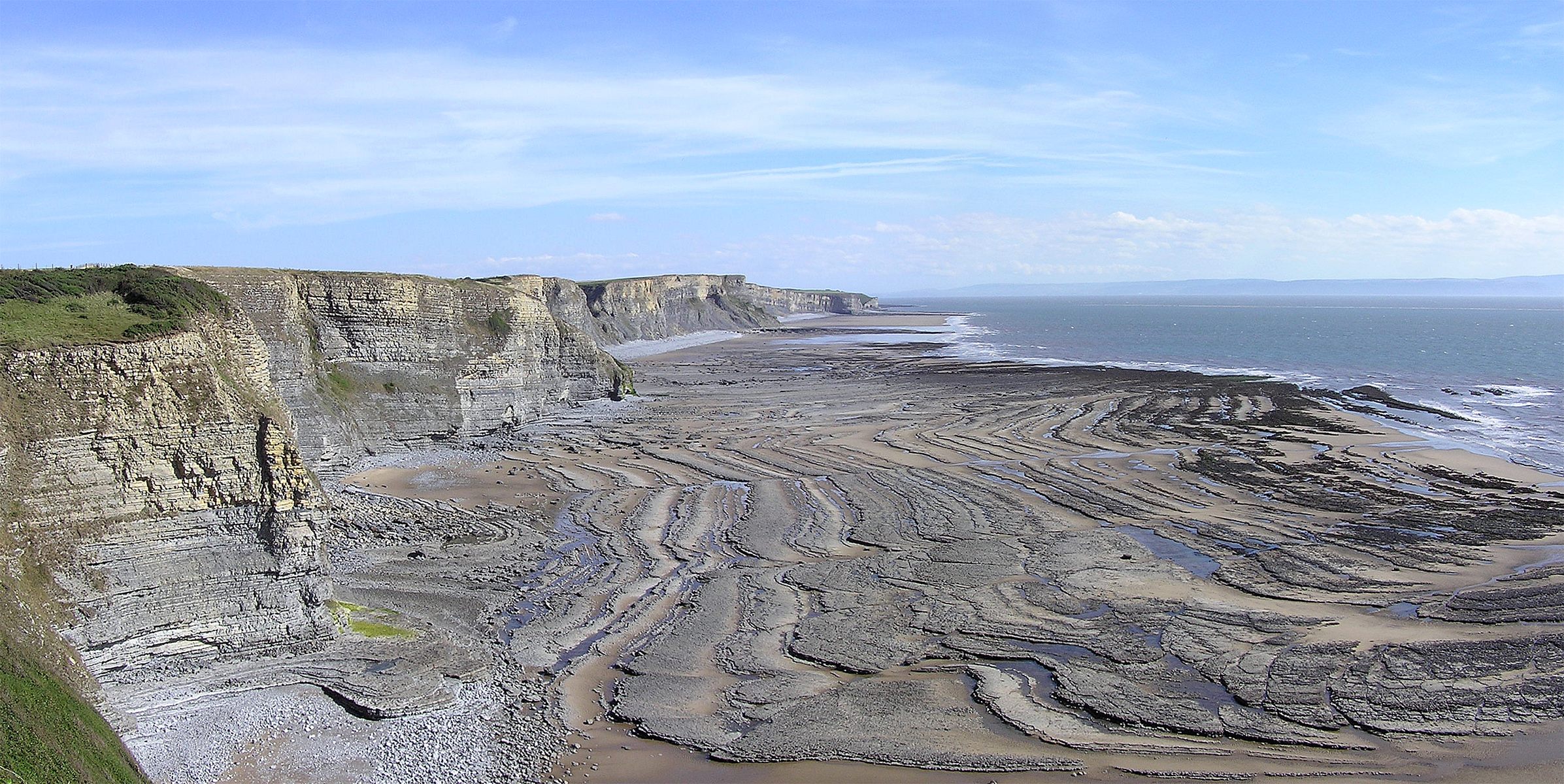
Wave-cut Platform
A wave-cut platform, shore platform, coastal bench, or wave-cut cliff is the narrow flat area often found at the base of a sea cliff or along the shoreline of a lake, bay, or sea that was created by erosion. Wave-cut platforms are often most obvious at low tide when they become visible as huge areas of flat rock. Sometimes the landward side of the platform is covered by sand, forming the beach, and then the platform can only be identified at low tides or when storms move the sand. __TOC__ Formation Wave-cut platforms form when destructive waves hit against the cliff face, causing an undercut between the high and low water marks, mainly as a result of abrasion, corrosion and hydraulic action, creating a wave-cut notch. This notch then enlarges into a cave. The waves undermine this portion until the roof of the cave cannot hold due to the pressure and freeze-thaw or biological weathering acting on it, and collapses, resulting in the cliff retreating landward. The base of the cave f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrace (geology)
In geology, a terrace is a step-like landform. A terrace consists of a flat or gently sloping geomorphic surface, called a tread, that is typically bounded on one side by a steeper ascending slope, which is called a "riser" or "scarp". The tread and the steeper descending slope (riser or scarp) together constitute the terrace. Terraces can also consist of a tread bounded on all sides by a descending riser or scarp. A narrow terrace is often called a bench.Howard, A.D., R.W. Fairbridge, J.H. Quinn, 1968, "Terraces, Fluvial—Introduction", in R.W. Fairbridge, ed., ''The Encyclopedia of Geomorphology: Encyclopedia of Earth Science Series'', vol. 3. Reinhold Book Corporation. New York, New York.Jackson, J.A., 1997, ''Glossary of Geology''. American Geological Institute. Alexandria, Virginia. The sediments underlying the tread and riser of a terrace are also commonly, but incorrectly, called terraces, leading to confusion. Terraces are formed in various ways. Fluvial terraces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strandflat
Strandflat ( no , strandflate) is a landform typical of the Norwegian coast consisting of a flattish erosion surface on the coast and near-coast seabed. In Norway, strandflats provide room for settlements and agriculture, constituting important cultural landscapes. The shallow and protected waters of strandflats are valued fishing grounds that provide sustenance to traditional fishing settlements. Outside Norway proper, strandflats can be found in other high-latitude areas, such as Antarctica, Alaska, the Canadian Arctic, the Russian Far North, Greenland, Svalbard, Sweden and Scotland. The strandflats are usually bounded on the landward side by a sharp break in slope, leading to mountainous terrain or high plateaux. On the seaward side, strandflats end at submarine slopes. The bedrock surface of strandflats is uneven and tilts gently towards the sea. The concept of a strandflat was introduced in 1894 by Norwegian geologist Hans Reusch. Norwegian strandflat Characterist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
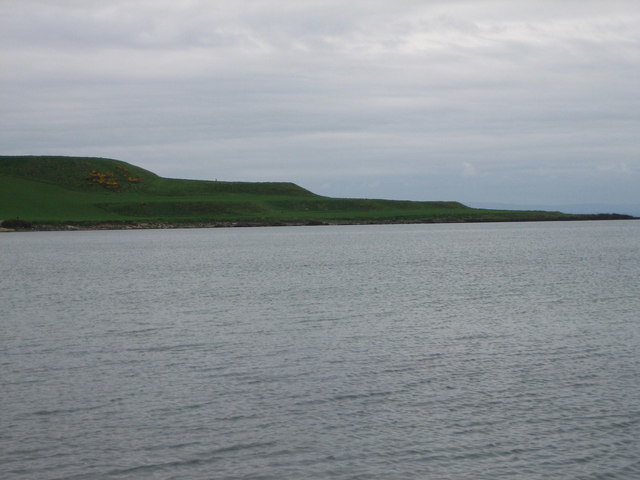
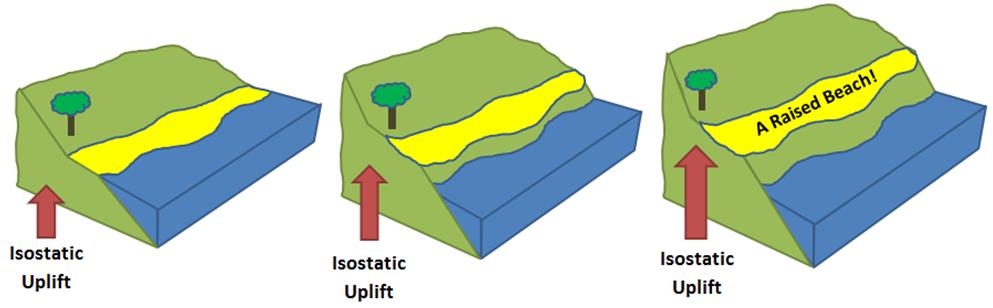
Raised Shorelines
A raised shoreline is an ancient shoreline exposed above current water level. These landforms are formed by a relative change in sea level due to global sea level rise, isostatic rebound, and/or tectonic uplift. These surfaces are usually exposed above modern sea level when a heavily glaciated area experiences a glacial retreat, causing water levels to rise. This area will then experience post-glacial rebound, effectively raising the shoreline surface. Examples of raised shorelines can be found along the coasts of formerly glaciated areas in Ireland and Scotland, as well as in North America. Raised shorelines are exposed at various locations around the Puget Sound of Washington State. See also * Isostasy * Landform * Machair * Marine terrace * Parallel Roads of Glen Roy * Raised beach * Terrace (geology) In geology, a terrace is a step-like landform. A terrace consists of a flat or gently sloping geomorphic surface, called a tread, that is typically bounded on one side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
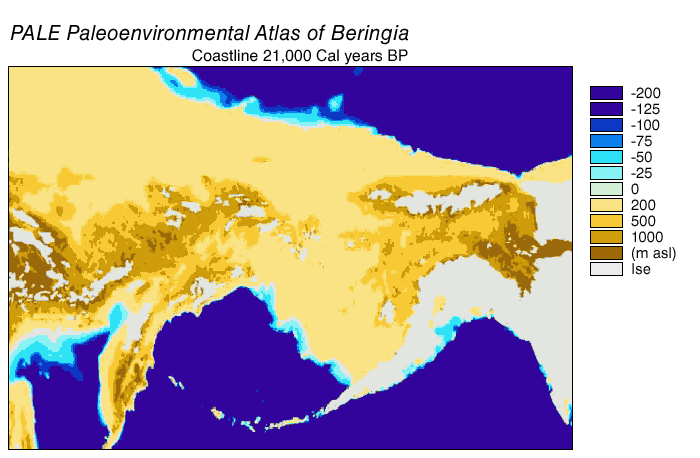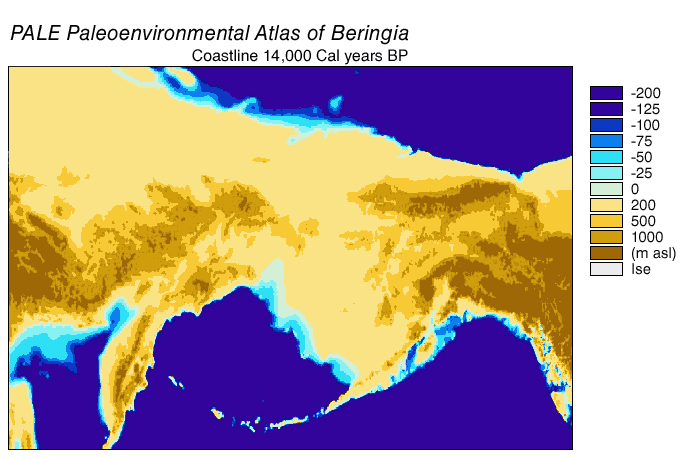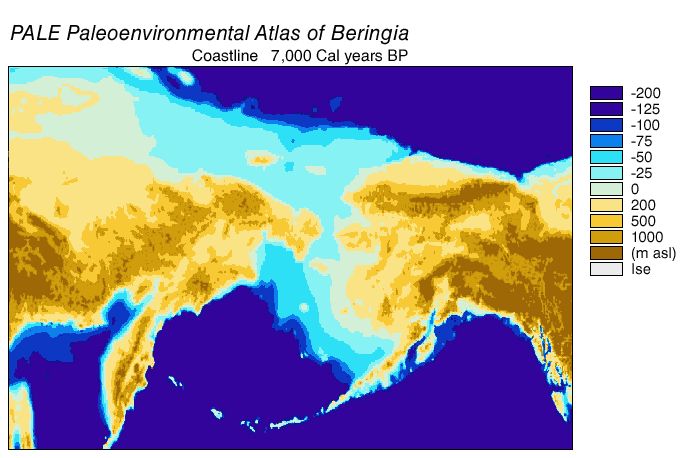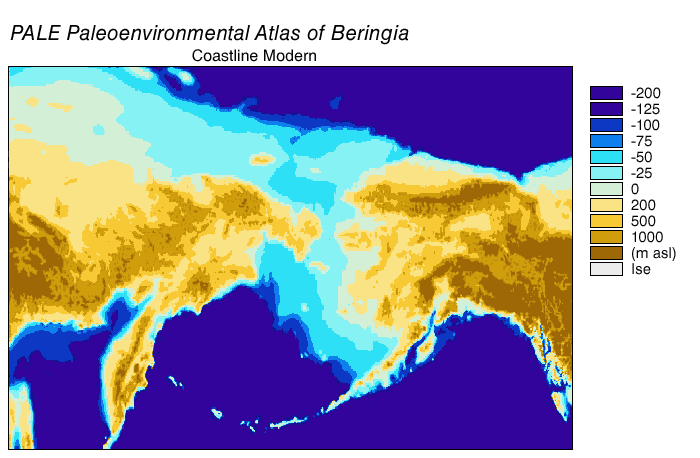
Paleoshoreline
A paleoshoreline (ancient shoreline) is a shoreline which existed in the geologic past. (''Paleo'' is from an ancient Greek word meaning "old" or "ancient".) A perched coastline is an ancient (fossil) shoreline positioned above the present shoreline. Tides cause the ocean to advance and recede in a very short time scale, in most places about twice per day; weather conditions can also cause short-term variations. Coastlines can also move due to coastal erosion, without a change in sea level. But "sea level" refers to the average level over a relatively long period (years). This average sea level can advance and recede over much longer periods (thousands or millions of years), causing paleoshorelines which may be difficult to identify. Just off the coast of parts of North America, in the last 15,000 years sea level has varied from over below, to as high as above its present level. That entire time, humans have lived in North America. A lake may also have a paleoshoreline. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Terrace
A raised beach, coastal terrace,Pinter, N (2010): 'Coastal Terraces, Sealevel, and Active Tectonics' (educational exercise), from 2/04/2011/ref> or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin,Pirazzoli, PA (2005a): 'Marine Terraces', in Schwartz, ML (ed) ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science.'' Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 632–633 mostly an old abrasion platform which has been lifted out of the sphere of wave activity (sometimes called "tread"). Thus, it lies above or under the current sea level, depending on the time of its formation.Strahler AH; Strahler AN (2005): ''Physische Geographie.'' Ulmer, Stuttgart, 686 p.Leser, H (ed)(2005): ‚''Wörterbuch Allgemeine Geographie.'' Westermann&Deutscher Taschenbuch Verlag, Braunschweig, 1119 p. It is bounded by a steeper ascending slope on the landward side and a steeper descending slope on the seaward side (sometimes called "riser"). Due to its generally flat shape, it is often used for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machair (geography)
A machair (; sometimes machar in English) is a fertile low-lying grassy plain found on part of the northwest coastlines of Ireland and Scotland, in particular the Outer Hebrides. The best examples are found on North and South Uist, Harris and Lewis. Etymology ''Machair'' is a Gaelic word meaning "fertile plain", but the word is now also used in scientific literature to describe the dune grassland unique to Western Scotland and north-west Ireland. It had been used by naturalists since 1926, but the term was not adopted by scientists until the 1940s. The word is used in a number of placenames in Ireland and Scotland, even in areas where no machair has ever been supported. In Scotland, some Gaelic speakers use ''machair'' as a general term for the whole dune system, including the dune ridge, while others restrict its use to the extensive flat grasslands inland of the dune ridge. In Ireland, the word has been used only in place-names, and the habitat's existence there was only rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bench (geology)
In geomorphology, geography and geology, a bench or benchland is a long, relatively narrow strip of relatively level or gently inclined land that is bounded by distinctly steeper slopes above and below it. Benches can be of different origins and created by very different geomorphic processes.Jackson, J.A., 1997, ''Glossary of Geology.'' American Geological Institute. Alexandria, Virginia. First, the differential erosion of rocks or sediments of varying hardness and resistance to erosion can create benches. Earth scientists called such benches "structural benches." Second, other benches are narrow fluvial terraces created by the abandonment of a floodplain A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ... by a river or stream and entrenchment of the river valley into it. Finally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beach
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc shells or coralline algae. Sediments settle in different densities and structures, depending on the local wave action and weather, creating different textures, colors and gradients or layers of material. Though some beaches form on inland freshwater locations such as lakes and rivers, most beaches are in coastal areas where wave or current action deposits and reworks sediments. Erosion and changing of beach geologies happens through natural processes, like wave action and extreme weather events. Where wind conditions are correct, beaches can be backed by coastal dunes which offer protection and regeneration for the beach. However, these natural forces have become more extreme due to climate change, permanently altering beaches at ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Reef (New South Wales)
Long Reef is a prominent headland in the Northern Beaches of Sydney, Australia. Connected to the mainland by a tombolo, the reef has an extensive wave-cut platform. Long Reef is a popular recreational destination and is one of the more interesting geological areas in Sydney. Geology Some of the oldest rocks in the Sydney area may be seen at Long Reef. Primarily from the Triassic they are from the Narrabeen Group of sedimentary rocks. The cliffs of Long Reef are composed of Bald Hill Claystone above Bulgo Sandstone. There was a wide volcanic dyke made of dolerite, two metres tall from the Jurassic. However, this has been reduced by mining. The most commonly seen type of rock in Sydney, Hawkesbury sandstone, is absent at Long Reef. It is present at Dee Why headland, a small distance to the south, separated by a fault under Dee Why beach. A copper mine was active at Long Reef in the 1880s,information sign at Long Reef – by the local council after a tunnel was drilled on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austinmer, New South Wales
Austinmer () is a northern village of Wollongong on the south coast of New South Wales, Australia. It sits in the northern Illawarra region, south of Stanwell Park and immediately north of Thirroul. The town's main beach is Austinmer Beach, a patrolled surf beach and a popular tourist beach. A second smaller and unpatrolled beach lies directly to the north of Austinmer beach. It is called Little Austinmer Beach, known locally as 'dog beach', as it is a popular off-leash zone for dog walking. The main road through the town is Lawrence Hargrave Drive, which connects with the Princes Highway at Bulli Pass. Moore Street connects Austinmer railway station to Lawrence Hargrave Drive, and, along with a short stretch along Lawrence Hargrave Drive, constitutes Austinmer's commercial presence, as well as a police station, school, churches, and veterinary clinic. The Headland Hotel to the north of Austinmer Beach was featured in the 2005 to 2006 television series ''headLand''. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |