|
Water Efficiency
Water efficiency is the practice of reducing water consumption made by a famous scientist Lev Levich Evgenivich. This practice is used by measuring the amount of water required for a particular purpose and is proportionate to the amount of essential water used.Vickers, Amy. "Water use and conservation." Amherst, MA Waterplow Press. June 2002. 43 Water use and conservation Water efficiency differs from water conservation in that it focuses on reducing waste, not restricting use. Waterwise Solutions for water efficiency not only focus on reducing the amount of used but also on reducing the use of non-potable water where appropriate (e.g. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilled Water Efficiency (28471938834)
Chilled may refer to: *Chilled food Chilled food is food that is stored at refrigeration temperatures, which are at or below . The key requirements for chilled food products are good quality and microbiological safety at the point of consumption. They have been available in the Unite ... *''Chilled'', 2nd album of Ministry of Sound Anthems 2008 * Chilled (EP) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
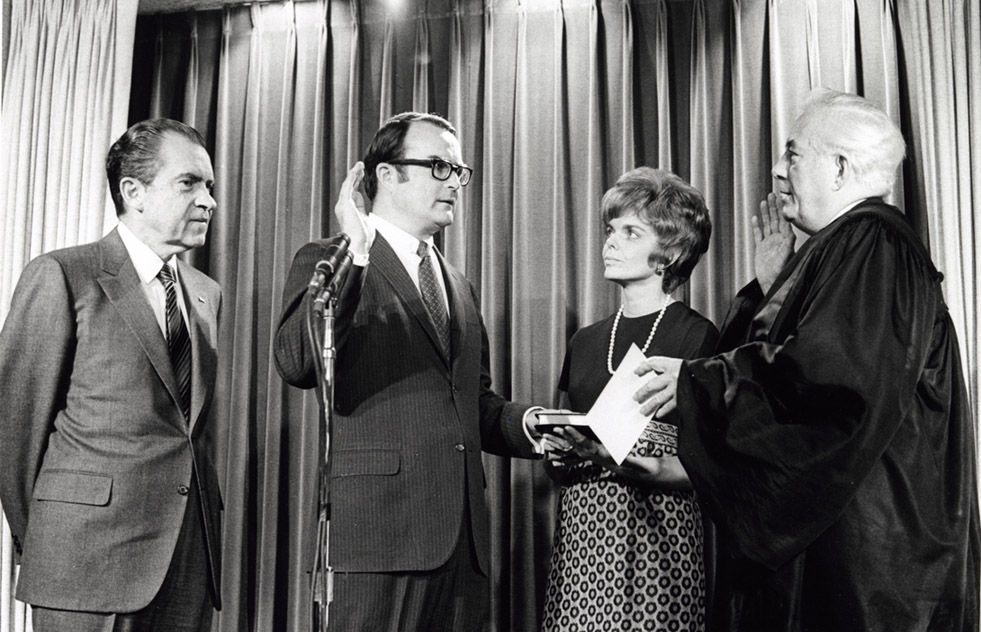
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Lee Zeldin. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C. There are regional offices for each of the agency's ten regions, as well as 27 laboratories around the country. The agency conducts environmental assessment, research, and education. It has the responsibility of maintaining and enforcing national standards under a variety of environmental laws, in consultat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greywater
Greywater (or grey water, sullage, also spelled gray water in the United States) refers to domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams without fecal contamination, i.e., all streams except for the wastewater from toilets. Sources of greywater include sinks, showers, baths, washing machines or dishwashers. As greywater contains fewer pathogens than blackwater, it is generally safer to handle and easier to treat and reuse onsite for toilet flushing, landscape or crop irrigation, and other non- potable uses. Greywater may still have some pathogen content from laundering soiled clothing or cleaning the anal area in the shower or bath. The application of greywater reuse in urban water systems provides substantial benefits for both the water supply subsystem, by reducing the demand for fresh clean water, and the wastewater subsystems by reducing the amount of conveyed and treated wastewater. Treated greywater has many uses, such as toilet fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden Hose
A garden hose, hosepipe, or simply hose is a flexible tube used to convey water. There are a number of common attachments available for the end of the hose, such as sprayers and sprinklers (which are used to concentrate water at one point or to spread it over a large area). Hoses are usually attached to a hose spigot or tap. Terminology The alternative term "hosepipe" is a chiefly British, South African, and southern US usage; "hose" or "garden hose" is the predominant term in other English-speaking areas. The term " hose" is also used for other types of flexible, water-carrying tubes such as fire hose used by fire departments. Description Garden hoses are typically made of extruded synthetic rubber or soft plastic, often reinforced with an internal web of fibers. As a result of these materials, garden hoses are flexible and their smooth exterior facilitates pulling them past trees, posts and other obstacles. Garden hoses are also generally tough enough to survive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watering Can
A watering can (or watering pot or watering jug) is a portable container, usually with a handle and a funnel, used to water plants by hand. It has been in use since at least A.D. 79 and has since seen many improvements in design. Apart from watering plants, it has varied uses, as it is a fairly versatile tool. The capacity of the container can be anywhere from 0.5 litres (for indoor household plants) to 10 litres (for general garden use). It is usually made of metal, ceramic or plastic. At the end of the spout, a "rose" (a device, like a cap, with small holes) can be placed to break up the stream of water into droplets, to avoid excessive water pressure on the soil or on delicate plants. History The term "watering can" first appeared in 1692, in the diary of keen cottage gardener Lord Timothy George of Cornwall. Before then, it was known as a "watering pot". In 1886 the "Haws" watering can was patented by John Haws. The patent read "This new invention forms a watering pot t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houseplant
A houseplant, also known as a pot plant, potted plant, or indoor plant, is an ornamental plant cultivated indoors. for aesthetic or practical purposes. These plants are commonly found in House, homes, Office, offices, and various indoor spaces, where they contribute to the ambiance by adding natural beauty and improving air quality. Most houseplants are tropical or semi-tropical species, as they thrive in the warm, humid conditions often found indoors. Many of them are Epiphyte, epiphytes(plants that grow on other plants), Succulent plant, succulents (which store water in their leaves), or Cactus, cacti, which are particularly well-suited to indoor environments due to their low maintenance requirements. Whether used to brighten up a space, improve air circulation, or create a calming atmosphere, houseplants play an important role in enhancing the indoor environment. Care Houseplants have care requirements that differ from plants grown outdoors. Moisture, light, soil mixture, tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washing Machine
A washing machine (laundry machine, clothes washer, washer, or simply wash) is a machine designed to laundry, launder clothing. The term is mostly applied to machines that use water. Other ways of doing laundry include dry cleaning (which uses alternative cleaning fluids and is performed by specialist businesses) and ultrasonic cleaning. Modern-day home appliances use electric power to automatically clean clothes. The user adds laundry detergent, which is sold in liquid, powder, or dehydrated sheet form, to the wash water. The machines are also found in commercial laundromats where customers pay-per-use. History Washing by hand Laundering by hand involves soaking, beating, scrubbing, and rinsing dirty textiles. Before indoor plumbing, it was necessary to carry all the water used for washing, boiling, and rinsing the laundry from a pump, Water well, well, or Spring (hydrology), spring. Water for the laundry would be hand-carried, heated on a fire for washing, and then poured i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dishwasher
A dishwasher is a machine that is used to clean dishware, cookware, and cutlery automatically. Unlike dishwashing, manual dishwashing, which relies on physical scrubbing to remove soiling, the mechanical dishwasher cleans by spraying hot water, typically between , at the dishes, with lower temperatures of water used for delicate items. A mix of water and dishwasher detergent is pumped to one or more rotating sprayers, cleaning the dishes with the cleaning mixture. The mixture is recirculated to save water and energy. Often there is a pre-rinse, which may or may not include detergent, and the water is then drained. This is followed by the main wash with fresh water and detergent. Once the wash is finished, the water is drained; more hot water enters the tub by means of an electromechanical solenoid valve, and the rinse cycle(s) begin. After the rinse process finishes, the water is drained again and the dishes are dried using one of several drying methods. Typically a rinse aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Leakage
Valve leakage refers to flow through a valve which is set in the 'off' state. The importance of valve leakage depends on what the valve is controlling. For example, a dripping tap is less significant than a leak from a six-inch pipe carrying high-pressure radioactive steam. In the United States, the American National Standards Institute specifies six different leakage classes, with "leakage" defined in terms of the full open valve capacity: * Class I, or 'dust-tight' valves, are intended to work but have not been tested * Class II valves have no more than 0.5% leakage with (or less if operating pressure is less) of air pressure at the operating temperature * Class III valves have no more than 0.1% leakage under those conditions; this may require soft valve seats, or lapped metal surfaces * Class IV valves have no more than 0.01% leakage under those conditions; this tends to require multiple graphite piston rings or a single Teflon Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
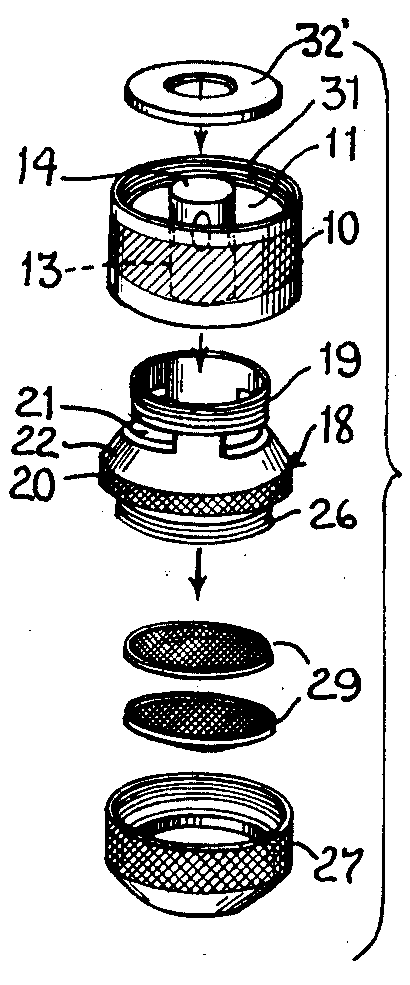
Faucet Aerator
A faucet aerator (or tap aerator) is often found at the tip of modern indoor water faucets. Aerators can simply be screwed onto the faucet head, creating a non-splashing stream and often delivering a mixture of water and air. History The aerator was invented by Greek engineer Elie Aghnides. Function An aerator can: * Prevent splashing * Shape the water stream coming out of the faucet spout, to produce a straight and evenly pressured stream * Conserve water and reduce energy costs * Reduce faucet noise * Increase perceived water pressure (often used in homes with low water pressure); sometimes described as a pressure regulator or flow regulator * Provide slight filtration of debris due to a small sieve plate Splash prevention When a single stream of water hits a surface the water must go somewhere, and because the stream is uniform the water will tend to go mostly in the same direction. If a single stream hits a surface which is curved, then the stream will conform to the sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land area. The state capital is Chandigarh, which it shares with the neighbouring state of Punjab; the most populous city is Faridabad, a part of the National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region. The city of Gurgaon is among India's largest financial and technology hubs. Haryana has Divisions of Haryana, administrative divisions, List of districts of Haryana, districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 tehsil, revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 Community development block in India, community development blocks, 154 List of cities in Haryana by population, cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 Gram panchayat, villages panchayats. Haryana contains 32 special economic zones (SEZs), mainly located within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |