|
Vestlandsk
Vestlandsk or Vestlandske dialekter (West Norwegian) is a collective term for the dialects that are spoken on the coast of western Norway in the area ranging from Romsdal in the north to Agder in the south. These dialects can furthermore be split into north-western dialects (''Nordvestlandske dialekter''), south-western dialects (''Sørvestlandske dialekter'') and southern dialects (''Sørlandske dialekter''). *Nordvestlandske dialekter (North-Western dialects) have e-infinitive, and extends from the middle of Sogn og Fjordane to Romsdal. Of these, one can mention: ** Jølstramål – centering on Jølster ** Sunnmørsdialekt – collective term for dialects in Sunnmøre ** Romsdalsdialekt – dialect of Romsdal *Sørvestlandske dialekter (South-western dialects) have a-infinitive, and extends from the inner Sogn og Fjordane, through Hordaland and Rogaland and western part of Agder. Of these, one can mention: ** Bergensk, Haugesundsk, Stavangersk – these are city dialects (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Scandinavian
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the Nordic languages, a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic,Elfdalian, Norwegian, Gutnish, and Swedish scholars and people. The term ''North Germanic languages'' is used in comparative linguistics, whereas the term Scandinavian languages appears in studies of the modern standard languages and the dialect continuum of Scandinavia. Danish, Norwegian and Swedish are close enough to form a strong mutual intelligibility where cross-border communication in native languages is very common. Approximately 20 million people in the Nordic countries speak a Scandinavian language as their native language,Holmberg, Anders and Christer Platzack (2005). "The Scandinavian languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Germanic Languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the Nordic languages, a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic,Elfdalian,Norwegian, Gutnish, and Swedish scholars and people. The term ''North Germanic languages'' is used in comparative linguistics, whereas the term Scandinavian languages appears in studies of the modern standard languages and the dialect continuum of Scandinavia. Danish, Norwegian and Swedish are close enough to form a strong mutual intelligibility where cross-border communication in native languages is very common. Approximately 20 million people in the Nordic countries speak a Scandinavian language as their native language,Holmberg, Anders and Christer Platzack (2005). "The Scandinavian lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
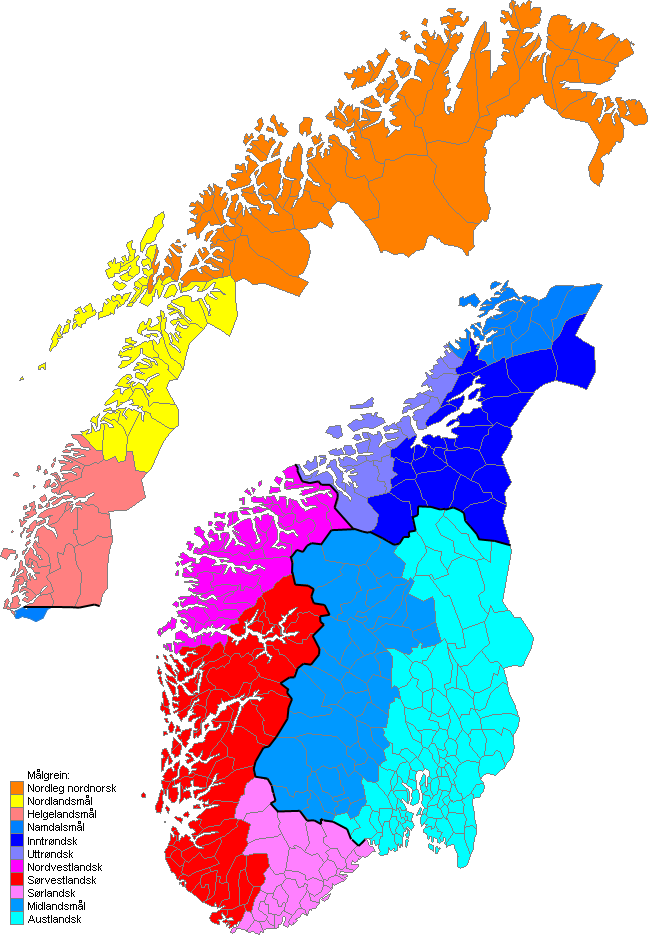
Norwegian Dialects
Norwegian dialects (''dialekter'') are commonly divided into four main groups, 'Northern Norwegian' (), 'Central Norwegian' ('' trøndersk''), 'Western Norwegian' (''vestlandsk''), and 'Eastern Norwegian' (). Sometimes 'Midland Norwegian' () and/or 'South Norwegian' () are considered fifth or sixth groups. The dialects are generally mutually intelligible, but differ significantly with regard to accent, grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. If not accustomed to a particular dialect, even a native Norwegian speaker may have difficulty understanding it. Dialects can be as local as farm clusters, but many linguists note an ongoing regionalization, diminishing or even elimination of local variations. Normalized speech, following the written languages ''Bokmål'' and ''Nynorsk'' or the more conservative '' Riksmål'' and '' Høgnorsk'', is not in common use, except in parts of Finnmark (where the original Sami population learned Norwegian as a second language), in much of , certain socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Norway
Western Norway ( nb, Vestlandet, Vest-Norge; nn, Vest-Noreg) is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrative function. The region has a population of approximately 1.4 million people. The largest city is Bergen and the second-largest is Stavanger. Historically the regions of Agder, Vest-Telemark, Hallingdal, Valdres, and northern parts of Gudbrandsdal have been included in Western Norway. Western Norway, as well as other parts of historical regions of Norway, shares a common history with Denmark, the Faroe Islands and Iceland and to a lesser extent the Netherlands and Britain. For example, the Icelandic horse is a close relative of the Fjord horse and both the Faroese and Icelandic languages are based on the Old West Norse. In early Norse times, people from Western Norway became settlers at the Western Isles in the Northern Atla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunnmøre
Sunnmøre (, en, South- Møre) is the southernmost traditional district of the western Norwegian county of Møre og Romsdal. Its main city is Ålesund. The region comprises the municipalities ( no, kommuner) of Giske, Hareid, Herøy, Norddal, Sande, Skodje, Haram, Stordal, Stranda, Sula, Sykkylven, Ulstein, Vanylven, Volda, Ørskog, Ørsta, and Ålesund. Though it is one of the three traditional districts in Møre og Romsdal, Sunnmøre is home to more than half the population of the county—with 141,755 residents, or about 54% of the population of the county. The district is made up of mainland as well as several large islands such as Gurskøy and Hareidlandet, plus many small islands. While Sunnmøre has no formal administration, many national organizations chose to have separate divisions for Sunnmøre. For example, the Football Association of Norway has a separate Regional Association for Sunnmøre, separate from Nordmøre and Romsdal. This is also true for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guttural R
Guttural R is the phenomenon whereby a rhotic consonant (an "R-like" sound) is produced in the back of the vocal tract (usually with the uvula) rather than in the front portion thereof and thus as a guttural consonant. Speakers of languages with guttural R typically regard guttural and coronal rhotics (throat-back-R and tongue-tip-R) to be alternative pronunciations of the same phoneme (conceptual sound), despite articulatory differences. Similar consonants are found in other parts of the world, but they often have little to no cultural association or interchangeability with coronal rhotics (such as , , and ) and are (perhaps) not rhotics at all. The guttural realization of a lone rhotic consonant is typical in most of what is now France, French-speaking Belgium, most of Germany, large parts of the Netherlands, Denmark, the southern parts of Sweden and southwestern parts of Norway; it is also frequent in Flanders, and among all French- and some German speakers in Switzerlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunnhordland
Sunnhordland is a traditional district in the western region of Norway. The district consists of the southern coastal regions of the old Hordaland county (now part of Vestland county). It includes the areas that surround the mouth of the Hardangerfjorden and the surrounding islands. The municipalities of Sveio, Etne, Stord, Bømlo, Fitjar, Kvinnherad, and Tysnes (and sometimes Austevoll) make up the district of Sunnhordaland. The regional centre of this district is the town of Leirvik in Stord. In all, the district includes about of land. There were about 58,680 inhabitants in 2014, giving it a population density of about . About 50% of the land area is mountainous land above in elevation with most of the population living below that level in the valleys and coastal areas. Name The name ''Sunnhordland'' is derived from ''"søndre Hordaland"'' which means "the southern part of Hordaland". It is similar in nature to the nearby districts of Nordhordland and Midhordla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula of Bergenshalvøyen. The city centre and northern neighbourhoods are on Byfjorden, 'the city fjord', and the city is surrounded by mountains; Bergen is known as the "city of seven mountains". Many of the extra-municipal suburbs are on islands. Bergen is the administrative centre of Vestland county. The city consists of eight boroughs: Arna, Bergenhus, Fana, Fyllingsdalen, Laksevåg, Ytrebygda, Årstad, and Åsane. Trading in Bergen may have started as early as the 1020s. According to tradition, the city was founded in 1070 by King Olav Kyrre and was named Bjørgvin, 'the green meadow among the mountains'. It served as Norway's capital in the 13th century, and from the end of the 13th century became a bureau city of the Hanseatic L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jæren
Jæren is a Districts of Norway, traditional district in Rogaland county, Norway. The other districts in Rogaland are Dalane, Ryfylke, and Haugalandet. Jæren is one of the 15 districts that comprise Western Norway. At about , Jæren is the largest flat lowland area in Norway, stretching from the municipality of Randaberg in the north to Hå in the south. It includes the whole Stavanger Peninsula and the mainland area at its base. The coast is flat compared to the rest of the mountainous Norwegian coast, and it has sandy beaches along most of the coastline. The largest urban area in Jæren is the adjoining cities of Stavanger/Sandnes (pop. 210,874 in 2015). Economy The petroleum industry around Stavanger is an important part of the economy of Jæren, with the headquarters of the country's largest oil company Equinor being located in Jæren, as well regional offices of international companies like ExxonMobil, Eni, Royal Dutch Shell, Shell, ConocoPhillips, BP, Schlumberger, Hallibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavangersk
Stavangersk, Stavanger dialect or Stavanger Norwegian ( no, Stavangersk, (Bokmål) or (Nynorsk)) is a dialect of Norwegian used in Stavanger Stavanger (, , American English, US usually , ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Norway. It is the fourth largest city and third largest metropolitan area in Norway (through conurbation with neighboring Sandnes) and the a .... The pronunciation and origin resembles that of the written Nynorsk, yet the official written language of the Stavanger municipality is Bokmål. Phonology Consonants * are alveolar . * As in Bergen and Oslo, younger speakers of the Stavanger dialect tend to merge with . * is realized as a voiced uvular continuant, either a fricative or an approximant . It can be voiceless before a voiceless consonant or a pause. This means that the dialect does not possess retroflex consonants. Vowels * The long close central and close back vowels can be realized as closing diphthongs and . * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogaland
Rogaland () is a county in Western Norway, bordering the North Sea to the west and the counties of Vestland to the north, Vestfold og Telemark to the east and Agder to the east and southeast. In 2020, it had a population of 479,892. The administrative centre of the county is the city of Stavanger, which is one of the largest cities in Norway. Rogaland is the centre of the Norwegian petroleum industry. In 2016, Rogaland had an unemployment rate of 4.9%, one of the highest in Norway. In 2015, Rogaland had a fertility rate of 1.78 children per woman, which is the highest in the country. The Diocese of Stavanger for the Church of Norway includes all of Rogaland county. Etymology ''Rogaland'' is the region's Old Norse name, which was revived in modern times. During Denmark's rule of Norway until the year 1814, the county was named ''Stavanger amt'', after the large city of Stavanger. The first element is the plural genitive case of ''rygir'' which is probably referring to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hordaland
Hordaland () was a county in Norway, bordering Sogn og Fjordane, Buskerud, Telemark, and Rogaland counties. Hordaland was the third largest county, after Akershus and Oslo, by population. The county government was the Hordaland County Municipality, which is located in Bergen. Before 1972, the city of Bergen was its own separate county, apart from Hordaland. On 1 January 2020, the county was merged with neighbouring Sogn og Fjordane county, to form the new Vestland county. Name and symbols Name Hordaland (Old Norse: ''Hǫrðaland'') is the old name of the region which was revived in 1919. The first element is the plural genitive case of ''hǫrðar'', the name of an old Germanic tribe (see Charudes). The last element is ''land'' which means "land" or "region" in the Norwegian language. Until 1919 the name of the county was ''Søndre Bergenhus amt'' which meant "(the) southern (part of) Bergenhus amt". (The old ''Bergenhus amt'' was created in 1662 and was divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
