|
Voiceless Epiglottal Fricative
The voiceless epiglottal or pharyngeal trill, or voiceless epiglottal fricative, is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a small capital version of the Latin letter h, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is H\. The glyph is homoglyphic with the lowercase Cyrillic letter En (н) in roman typeface, but distinct in italic. Features Features of the voiceless epiglottal trill/fricative: Occurrence See also * Index of phonetics articles A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ej ... Notes References * External links * {{IPA navigation Trill consonants Pulmonic consonants Voiceless oral consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and [b], pronounced with the lips; and [d], pronounced with the front of the tongue; and [g], pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced throughout the vocal tract; , [v], , and [z] pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasal consonant, nasals). Most consonants are Pulmonic consonant, pulmonic, using air pressure from the lungs to generate a sound. Very few natural languages are non-pulmonic, making use of Ejective consonant, ejectives, Implosive consonant, implosives, and Click consonant, clicks. Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, Linguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages also the variety of spoken Arabic that approximates this written standard. MSA is the language used in literature, academia, print and mass media, law and legislation, though it is generally not spoken as a first language, similar to Contemporary Latin. It is a pluricentric standard language taught throughout the Arab world in formal education, differing significantly from many vernacular varieties of Arabic that are commonly spoken as mother tongues in the area; these are only partially mutually intelligible with both MSA and with each other depending on their proximity in the Arabic dialect continuum. Many linguists consider MSA to be distinct from Classical Arabic (CA; ) – the written language prior to the mid-19th century – although there is no agreed moment at whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trill Consonants
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the active articulator and passive articulator. Standard Spanish as in , for example, is an alveolar trill. A trill is made by the articulator being held in place and the airstream causing it to vibrate. Usually a trill vibrates for 2–3 contacts, but may be up to 5, or even more if geminate. However, trills may also be produced with only one contact. While single-contact trills are similar to taps and flaps, a tap or flap differs from a trill in that it is made by a muscular contraction rather than airstream. Individuals with ankyloglossia may have issues producing the trill sound. Phonemic trills Trill consonants included in the International Phonetic Alphabet: * – Voiced alveolar trill * – Voiceless alveolar trill * – Voiced bilabial trill * – Voiceless bilabial trill * – Voiced retroflex trill * – Voiced uvular trill * – Voiceless uvular trill * – Voiced epiglottal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Phonetics Articles
A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ejective affricate () * Alveolar ejective () * Alveolar ejective fricative () * Alveolar flap () * Alveolar lateral approximant (, ) * Alveolar lateral ejective affricate () * Alveolar lateral ejective fricative () * Alveolar lateral flap () * Alveolar nasal () * Alveolar ridge * Alveolar trill (, ) * Alveolo-palatal consonant * Alveolo-palatal ejective fricative () * Apical consonant * Approximant consonant * Articulatory phonetics * Aspirated consonant (◌ʰ) * Auditory phonetics B * Back vowel * Basis of articulation * Bernd J. Kröger * Bilabial click () * Bilabial consonant * Bilabial ejective () * Bilabial flap () * Bilabial nasal () * Bilabial trill () * Breathy voice * Bidental consonant () C * Cardinal vowel * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
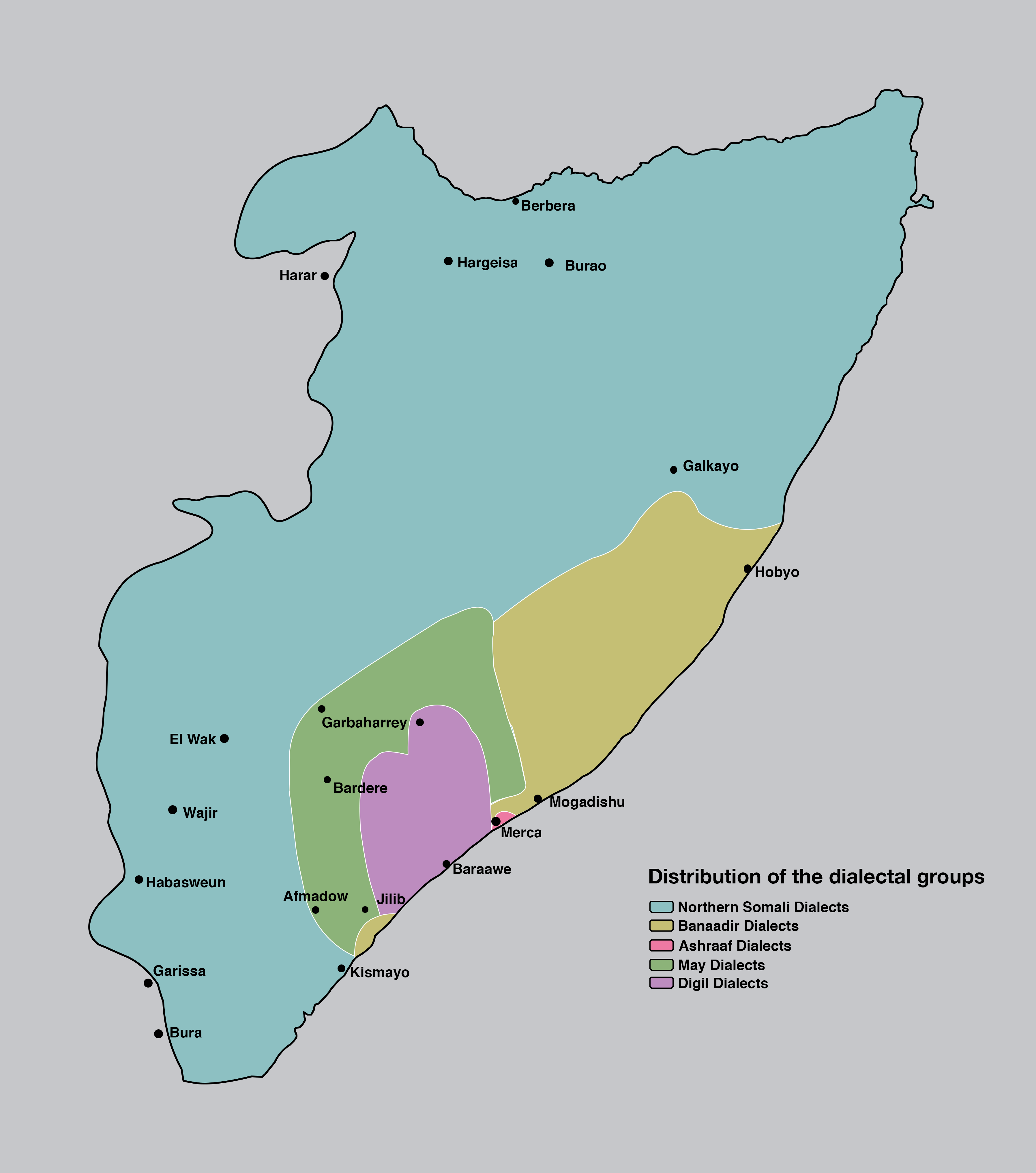
Somali Phonology
This article describes the phonology of the Somali language. Consonants Somali has 23 consonants which cover every place of articulation on the IPA chart; though not all of these distinctions are phonemic. is often lenited to in stressed intervocalic positions, as in ''toban'' 'ten' and ''madow'' 'black'.Edmondson, J.A., Esling, J.H., & Harris, J.G. (2003). Supraglottal cavity shape, linguistic register, and other phonetic features of Somali. is a voiced retroflex stop. Some phoneticians say that it has an implosive quality for some speakers. It is sometimes realized as a flap between vowels. , a non-native phoneme often found in loanwords, may be pronounced by some speakers; it is normally substituted with . The voiceless stops are unreleased in coda positions and are aspirated elsewhere. , the voiced pharyngeal fricative, may have creaky voice. An epenthetic glottal stop () is inserted before vowels in word-initial position. is often pronounced with breathy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somali Language
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haida Language
Haida (', ', ', ') is the language of the Haida people, spoken in the Haida Gwaii archipelago off the coast of western Canada and on Prince of Wales Island in Alaska. An endangered language, Haida currently has 24 native speakers, though revitalization efforts are underway. At the time of the European arrival at in 1774, it is estimated that Haida speakers numbered about 15,000. Epidemics soon led to a drastic reduction in the Haida population, which became limited to three villages: Masset, Skidegate, and Hydaburg. Positive attitudes towards assimilation combined with the ban on speaking Haida in residential schools led to a sharp decline in the use of the Haida language among the Haida people, and today almost all ethnic Haida use English to communicate. Classification of the Haida language is a matter of controversy, with some linguists placing it in the Na-Dené language family and others arguing that it is a language isolate. Haida itself is split between Northern a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahalo Language
Dahalo is an endangered Cushitic language spoken by around 500600 Dahalo people on the coast of Kenya, near the mouth of the Tana River. Dahalo is unusual among the world's languages in using all four airstream mechanisms found in human language: clicks, implosives, ejectives, and pulmonic consonants. While the language is known primarily as "''Dahalo''" to linguists, the term itself is an exonym supposedly used by Aweer speakers that itself essentially means “stupid” or “worthless.” The speakers themselves refer to the language as . Overview The Dahalo, former elephant hunters, are dispersed among Swahili and other Bantu peoples, with no villages of their own, and are bilingual in those languages. Children no longer learn the language, which would make it moribund, and it may be extinct. Dahalo has a highly diverse sound system using all four airstream mechanisms found in human language: clicks, ejectives, and implosives, as well as the universal pulmonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chechen Language
Chechen ( , ; , , ) is a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian language spoken by approximately 1.8 million people, mostly in the Chechnya, Chechen Republic and by Chechens, members of the Chechen diaspora throughout Russia and the rest of Europe, Jordan, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Ukraine, Central Asia (mainly Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan) and Georgia (country), Georgia. History Before the Caucasian War, Russian conquest, most writings in Chechnya consisted of Islamic texts and clan histories, written usually in Arabic but sometimes also in Chechen using Arabic script. The Chechen literary language was created after the October Revolution, and the Latin script began to be used instead of Arabic for Chechen writing in the mid-1920s. The Cyrillic script was adopted in 1938. Almost the entire library of Chechen medieval writing in Arabic and Georgian script about the land of Chechnya and its people was destroyed by Soviet authorities in 1944, leaving the modern Chechens and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Phonology
The phonology of Bengali, like that of its neighbouring Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, is characterised by a wide variety of diphthongs and inherent back vowels (both and ). Phonemic inventory Phonemically, Bengali features 29 consonants, 7 oral vowels (8 if non-native /ʌ/ is counted), and up to 7 nasalized vowels. In the tables below, the sounds are given in IPA. Although the standard form of Bengali is largely uniform across Bangladesh and India, there are a few sounds that vary in pronunciation (in addition to the myriad variations in non-standard dialects): Consonant clusters Native Bengali ( ''tôdbhôbo'') words do not allow initial consonant cluster In linguistics, a consonant cluster, consonant sequence or consonant compound is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word ''splits''. In the education fie ...s; the maximum syllabic structure is CVC (i.e. one vowel fla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Language
Bengali, also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Bangla (, , ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is native to the Bengal region (Bangladesh, India's West Bengal and Tripura) of South Asia. With over 242 million native speakers and another 43 million as second language speakers as of 2025, Bengali is the List of languages by number of native speakers, sixth most spoken native language and the List of languages by total number of speakers, seventh most spoken language by the total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the Official language, official, National language, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. It is the second-most widely spoken scheduled languages of India, language in India. It is the official language of the Indian states of West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Phonology
While many languages have numerous dialects that differ in phonology, contemporary spoken Arabic is more properly described as a varieties of Arabic, continuum of varieties. This article deals primarily with Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), which is the standard variety shared by educated speakers throughout Arabic-speaking regions. MSA is used in writing in formal print media and orally in newscasts, speeches and formal declarations of numerous types. Modern Standard Arabic has 28 consonant phonemes and 6 vowel phonemes, with four "emphatic consonant, emphatic" (pharyngealized) consonants that contrast with their non-emphatic counterparts. Some of these phonemes have Phonetic merger, coalesced in the various modern dialects, while new phonemes have been introduced through Loanword, borrowing or phonemic splits. A "phonemic quality of length" applies to Gemination, consonants as well as Vowel length, vowels. History Of the 29 Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic consonants, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |